- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Assay of the Carboxylase Activity of Rubisco from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
Published: Vol 5, Iss 23, Dec 5, 2015 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1672 Views: 10395
Reviewed by: Maria SinetovaAgnieszka ZienkiewiczAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols
A Semi-throughput Procedure for Assaying Plant NADP-malate Dehydrogenase Activity Using a Plate Reader
Kevin Baudry and Emmanuelle Issakidis-Bourguet
Aug 20, 2023 1463 Views
An in vitro Assay to Probe the Formation of Biomolecular Condensates
Yu Zhang and Shen Lisha
Sep 5, 2023 3190 Views
Immunofluorescence for Detection of TOR Kinase Activity In Situ in Photosynthetic Organisms
Ana P. Lando [...] Giselle M. A. Martínez-Noël
Dec 20, 2024 1806 Views
Abstract
The performance of the carbon-fixing enzyme, ribulose 1, 5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (EC 4.1.1.39, Rubisco), controls biomass accumulation in green plants, algae and most autotrophic bacteria. In particular, the carboxylase activity of Rubisco incorporates carbon from CO2 to ribulose 1, 5-bisphosphate (RuBP) producing two molecules of 3-phosphoglycerate. Here a detailed protocol is given for the assay of the carboxylase activity of Rubisco from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, a model organism for chloroplast studies and a fitting host for biotechnologically oriented genetic manipulation of the enzyme. Rubisco has to be pre-incubated with Mg2+ ions and bicarbonate to induce the catalytically competent active center (Laing and Christeller, 1976). Once Rubisco is activated, the assay of its carboxylase activity described here is based on the fixation of 14C-carbon dioxide/bicarbonate into acid-resistant radioactivity (Lorimer et al., 1977). Although a spectrophotometric assay is also available (Lilley and Walker, 1974), the method based on fixation of a radioactive substrate is irreplaceable when processing a large number of samples, and it is still the technique most often used for the determination of Rubisco activity.
Keywords: Ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenaseMaterials and Reagents
- Sephadex G-25 columns (PD-10) (GE Healthcare, catalog number: 17-0851-01 )
- Snap cap plastic tubes of 4 ml (Bio-Vials) (Beckman Coulter, catalog number: 566353 ) and tube racks
- Laboratory film (Parafilm M) (Thomas Scientific, Pechiney Plastic Packaging, catalog number: PM-996 )
- Chlamydomonas reinhardtii cell extract containing Rubisco
- Tris [2-amino, 2-hydroxymethyl, 1, 3-propanediol] (Trizma base) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T-1503 )
- Magnesium chloride hexahydrate (MgCl2.6H2O) (Merck Millipore Corporation, catalog number: 1.05833 )
- Sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) (Merck Millipore Corporation, catalog number: 1.06329 )
- D-Ribulose 1, 5-bisphosphate sodium salt hydrate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: R-0878 )
Note: this is presented as a sodium salt hydrate, containing 4 Na+ and 3 H2O per molecule, with a global weight of 452.1 g/mol. - Sodium 14C-bicarbonate (52 mCi/mmol) (PerkinElmer, catalog number: NEC086H )
- 2, 5-diphenyl oxazol (PPO) (Sigma-Aldrich, Fluka, catalog number: 43140 )
- 1, 4-bis-(5-phenyl-2-oxazolyl) benzene (POPOP) (Sigma-Aldrich, Fluka, catalog number: 15150 )
Note: Product 15150 has been discontinued. - 2-Phenylethylamine (Merck Millipore Corporation, catalog number: 8.07334 )
- Toluene (Panreac, catalog number: 131745-1611 )
- Methanol (Scharlau S.L., catalog number: ME-0301 )
- Scintillation cocktail (Cocktail 22 Normascint) (Scharlau S.L., catalog number: CO-0135 )
- dH2O (deionized water) (processed by the Milli-Q system from Merck Millipore Corporation)
- Activation buffer (AB) (see Recipes)
- Reaction buffer (RB) (see Recipes)
- RuBP stock (see Recipes)
- Alkaline scintillation cocktail (see Recipes)
- Radioactive stock (see Recipes)
- 2 M Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) (VWR International, J.T. Baker®, catalog number: 6081 ) (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Radioactivity licensed laboratory equipped with a security extraction hood
- Thermostatic water bath (SBS, model: TI-03 )
- Stopwatch chronometer (Oregon Scientific Inc., model: TR118 )
- Vacuum oven (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Heraeus, model: Vacutherm VT6025 ) connected to an alkaline trap
- Radioactivity scintillation counter (PerkinElmer, model: Tri-Carb 2810 TR )
Procedure
- Activation of Rubisco
- Rubisco extracted from C. reinhardtii cultures can be assayed at any level of purity. As a first step, the Rubisco should be transferred to a medium containing Mg2+ and dissolved CO2 (introduced as bicarbonate) to get the catalytically active form of the enzyme (Laing and Christeller, 1976). Therefore, desalt the starting extract loading 2.5 ml onto a Sephadex G-25 (PD-10) column equilibrated with activation buffer (AB), and elute with 3.5 ml of the same buffer.
Note: This section is equivalent to section D in the protocol on “Purification of Rubisco from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii” (Sudhani et al., 2015) and might be omitted if the Rubisco has been already transferred to AB after purification.
- Rubisco extracted from C. reinhardtii cultures can be assayed at any level of purity. As a first step, the Rubisco should be transferred to a medium containing Mg2+ and dissolved CO2 (introduced as bicarbonate) to get the catalytically active form of the enzyme (Laing and Christeller, 1976). Therefore, desalt the starting extract loading 2.5 ml onto a Sephadex G-25 (PD-10) column equilibrated with activation buffer (AB), and elute with 3.5 ml of the same buffer.
- Preparation of the substrate mixture and specific radioactivity controls
- Working in a security extraction hood, mix 1 ml of reaction buffer (RB), 0.1 ml of RuBP stock and 15 μl of the radioactive stock into a 1.5 ml Eppendorf tube. This will be the substrate reaction mixture (SR mix). In parallel, prepare an identical mixture but replace the 0.1 ml of RuBP stock by 0.1 ml of dH2O. This will be the no-RuBP reaction mixture (NR mix). Table 1 summarizes the composition of both reaction mixtures.
Table 1. Components and volumes of the reaction mixturesReaction mixture RB RuBP stock dH2O Radioactive stock SR mix 1 ml 0.1 ml 0 ml 15 μl NR mix 1 ml 0 ml 0.1 ml 15 μl
Note: Volumes given above are for the preparation of 1.115 ml of mixture, which is enough for assaying ca 21 vials (i.e., triplicates of seven independent determinations, including samples and controls). In the case that the number of vials intended for assay is higher than 21, the volumes should be scaled up accordingly. - Immediately place three 50 μl aliquots of the SR mix and three 50 μl aliquots of the NR mix in snap-cap plastic tubes (Bio-vial) used for radioactive counting. Add 3 ml of alkaline scintillation cocktail to each vial, mix, and count for radioactivity. These measurements are the SR and NR controls, and they will be used for determining the exact specific radioactivity of the fixed CO2.
Note: Commercial scintillation cocktails are usually acidic and, therefore, cannot be used for these controls because the radioactivity would be lost in the gas phase as 14CO2. - Meanwhile, the Eppendorf tube containing the substrate mixture should remain tightly closed at room temperature for at least 10 min in order to let the 14C-bicarbonate equilibrate with the non-radioactive CO2/bicarbonate pool.
- Working in a security extraction hood, mix 1 ml of reaction buffer (RB), 0.1 ml of RuBP stock and 15 μl of the radioactive stock into a 1.5 ml Eppendorf tube. This will be the substrate reaction mixture (SR mix). In parallel, prepare an identical mixture but replace the 0.1 ml of RuBP stock by 0.1 ml of dH2O. This will be the no-RuBP reaction mixture (NR mix). Table 1 summarizes the composition of both reaction mixtures.
- Preparation of the blank, non-RuBP fixation control and sample vials
- Place open vials in a rack for the samples and remaining controls. The latter include the blanks (measuring the radioactivity retained in the absence of sample) and the non-RuBP fixation control (monitoring potential CO2 fixation by the sample due to carboxylases other than Rubisco). You may prepare triplicates for each determination.
- Mix 180 μl of AB and 20 μl of sample extract (containing 0.2 to 10 μg of Rubisco) in each tube, except for the blank vials in which 200 μl of AB should be delivered. Submerge the tube rack in a thermostatic water bath at 30 °C inside the extraction hood and let stand for a few minutes to homogenize the temperature before starting the assay.
Note: Instead of a water bath, tubes may be alternatively placed in a thermoblock at 30 °C inside the hood.
- Place open vials in a rack for the samples and remaining controls. The latter include the blanks (measuring the radioactivity retained in the absence of sample) and the non-RuBP fixation control (monitoring potential CO2 fixation by the sample due to carboxylases other than Rubisco). You may prepare triplicates for each determination.
- Assay of the activity
- Place a stopwatch chronometer in a place easily readable while manipulating the samples, and start the assay at time 0 by delivering 50 μl of radioactive SR mixture to the first tube. Proceed subsequently by adding 50 μl to additional tubes every 20 sec. Switch from the SR to the NR mixture (delivering also 50 μl of it) when starting the set of samples for determining the non-RuBP carbon fixation. Tubes should be kept at 30 °C throughout the assay.
- Stop the enzymatic reaction by adding 50 μl of 2 M HCl to each tube exactly 5 min after the radioactive mixture was delivered. Table 2 summarizes the additions to each tube hitherto.
Table 2. Components and volumes added to each vial throughout the assayType of vial AB Extract SR mix NR mix 2 M HCl Blank 200 μl 0 μl 50 μl 0 μl 50 μl No-RuBP (NR) 180 μl 20 μl 0 μl 50 μl 50 μl + RuBP (SR) 180 μl 20 μl 50 μl 0 μl 50 μl - Place the rack of vials (without cap) in a vacuum oven connected to a water jet pump through an alkaline trap. This oven should also be placed inside the security extraction hood. Evacuate at 90 °C until total dryness of the content of the tubes in order to remove the unfixed radioactivity. This may take less than one hour, but the actual duration is highly dependent on the vacuum level achieved by the pump.
- Redissolve the dry content of each tube in 200 μl of dH2O and evacuate again at 90 °C until dryness.
- Redissolve again the dry content of each tube in 200 μl of dH2O and add 3 ml of a commercial scintillation cocktail (admitting a 7% of water in a single phase). Mix thoroughly before counting.
- Count all samples in a scintillation counter equipped with calibrated efficiency correction facilities. Sample vials should be counted long enough to accumulate more than 10,000 total counts (e.g., 5 min if more than 2,000 cpm are detected).
- Place a stopwatch chronometer in a place easily readable while manipulating the samples, and start the assay at time 0 by delivering 50 μl of radioactive SR mixture to the first tube. Proceed subsequently by adding 50 μl to additional tubes every 20 sec. Switch from the SR to the NR mixture (delivering also 50 μl of it) when starting the set of samples for determining the non-RuBP carbon fixation. Tubes should be kept at 30 °C throughout the assay.
- Assessment of the results and calculations
- After efficiency correction by the scintillation counter, radioactivity data will be in (or will be easily converted to) disintegrations per minute (dpm). Begin by calculating the average from triplicates, and subtracting the average of the blanks from all other means.
- Once the blanks have been deducted, divide the average radioactivity of the SR and NR controls by the number of μmoles of CO2/bicarbonate present in the reaction (0.2 ml of 10 mM bicarbonate in AB + 0.05 ml of 50 mM bicarbonate in the reaction mix which equals 4.5 μmoles) to obtain the specific radioactivity of the SR and NR assays. Specific radioactivity should be between 2.0.105 and 3.5.105 dpm/μmol.
- Divide the mean radioactivity of each sample (with blanks deducted) by the specific radioactivity of the corresponding control to obtain the number of μmoles of CO2 fixed in each assay.
- Subtract the μmoles of CO2 fixed in the no-RuBP assay from the μmoles of CO2 fixed in the corresponding assay with RuBP to get the net amount of RuBP-dependent CO2 fixation due to Rubisco.
- Divide the net μmoles of CO2 fixed by 5 min and by 0.02 ml to get the final activity (μmoles of CO2 fixed per min and ml of enzyme extract). If the concentration of Rubisco in the assays is known, results can be expressed as specific activities (e.g., μmoles of CO2 fixed per min and mg of enzyme). Typical specific activity of Rubisco from a wild type strain of C. reinhardtii is about 2 μmoles of CO2 fixed per min per mg of enzyme.
- After efficiency correction by the scintillation counter, radioactivity data will be in (or will be easily converted to) disintegrations per minute (dpm). Begin by calculating the average from triplicates, and subtracting the average of the blanks from all other means.
Representative data
Table 3 illustrates the calculation of the enzymatic activity from raw data with a numerical example. Note that the radioactivity of the SR and NR controls is not exactly the same probably due to limited reproducibility at pipetting small volumes of the radioactive stock. This leads to slightly different specific radioactivities for the assays in presence (SR series) and absence (NR series) of RuBP.
Table 3. Calculation of the Rubisco carboxylase activity from experimental triplicate determination of radioactivity (dpm)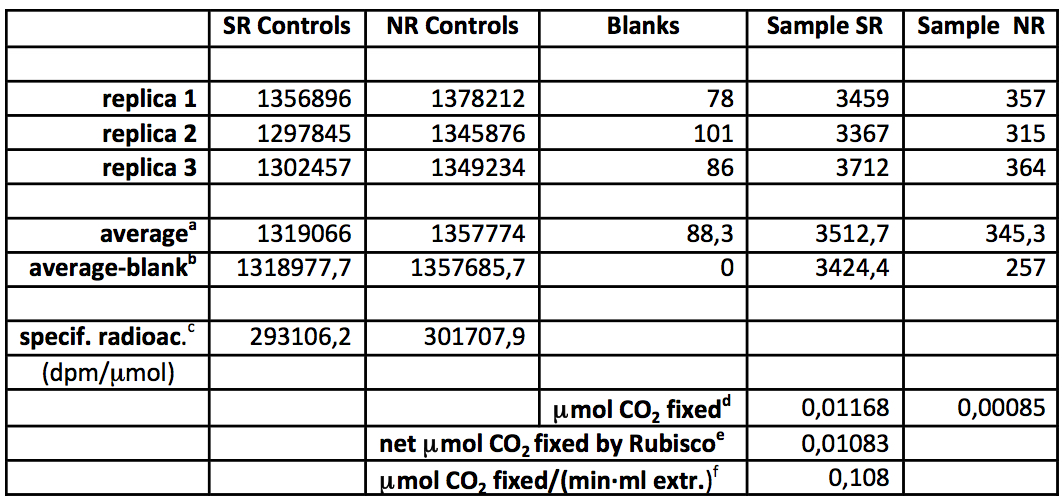
aAverages of the 3 replicas
bAverages with mean blank deduced (net radioactivity)
cSpecific radioactivity (radioactivity of controls divided by 4.5 μmol of CO2/bicarbonate)
dCO2 fixation (net radioactivity divided by the corresponding specific radioactivity)
eNet CO2 fixation due specifically to Rubisco (NR fixation subtracted)
fNormalized Rubisco activity = net Rubisco fixation divided by assay duration (5 min) and volume of extract (0.02 ml)
Notes
- This assay might be performed by a single person if the number of vials does not exceed 15 (typically 5 triplicates). For assaying more vials, it is convenient to engage 2 persons, one initiating the reactions by adding the substrate mixture every 20 sec and the other stopping them with HCl after a 5 min delay.
- When assaying moderately purified Rubisco, the RuBP-independent fixation is usually negligible. Consequently, the set of no-RuBP vials (NR series) can be suppressed, thereby reducing the assay length considerably.
- The carbon-fixation activity of eukaryotic Rubiscos decays slowly when assayed in vitro (in the absence of the auxiliary enzyme Rubisco activase and ATP) due to blocking of the catalytic site in an inactive form by the RuBP substrate, a process termed “fallover” (Edmondson et al., 1990). Fallover is negligible in the case of the C. reinhardtii enzyme for a 5 min-fixation assay (but it will become increasingly noticeable for prolonged incubations). Moreover, the Rubiscos of higher plants experience a much stronger fallover, and the fixation time should be shortened accordingly (typically to 1 min) when adapting this procedure to these enzymes. In any case, when facing the assay of a Rubisco from a new species, the interval of linearity should be checked.
Recipes
- Activation buffer (AB) (100 mM Tris-HCl, 10 mM MgCl2, 10 mM NaHCO3, pH 8.2)
For 100 ml:
Dissolve 1.210 g of Tris and 0.203 g of MgCl2.6H2O in some 80 ml of dH2O
Adjust the pH to 8.19 using diluted (e.g., 1 M) HCl
Add 0.084 g of NaHCO3 (previously weighed on aluminum foil) and dissolve. The final pH should be very nearly 8.2 (but do not readjust it further).
Bring the final volume to 100 ml and transfer to a 100 ml bottle leaving little headspace. Prepared this buffer shortly before use to prevent a significant loss of bicarbonate as CO2. - Reaction buffer (RB) (100 mM Tris-HCl, 10 mM MgCl2, 55 mM NaHCO3, pH 8.2)
For 100 ml:
Dissolve 1.210 g of Tris and 0.203 g of MgCl2.6H2O in some 80 ml of dH2O
Adjust the pH to 8.18 using diluted (e.g., 1 M) HCl
Add 0.462 g of NaHCO3 (previously weighed on aluminum foil) and dissolve. The final pH should be very nearly 8.2 (but do not readjust it further).
Bring the final volume to 100 ml
This buffer should be prepared immediately before preparing the reaction mixtures with it. - RuBP stock
RuBP comes as a dry powder, but it is very hygroscopic and should not be weighed. Therefore, once the sealed bottle is opened, immediately dilute the powder inside the original container with dH2O to a 10 mg/ml concentration (about 22 mM) according to the amount declared by the manufacturer. You may verify afterwards the actual amount by comparing the weight of the filled and the empty (dry) container, readjusting the nominal concentration if necessary.
Aliquot the RuBP solution in 150 μl portions, and freeze them in liquid nitrogen. Aliquots are stored at -80 °C and thawed as needed immediately before preparing the reaction mixture in order to minimize the spontaneous oxidation of the sugar, which results in an impurity that inhibits Rubisco activity (Kane et al., 1998). - Alkaline scintillation cocktail
For 115 ml:
Dissolve 0.980 g of PPO and 0.020 g of POPOP in 57 ml of toluene
Add 50 ml of 2-phenylethylamine and mix
Add 3 ml of methanol and 5 ml of dH2O
The final mixture should remain as a single phase.
Stored at 4 °C protected from light - Radioactive stock
14C-bicarbonate is usually delivered by the manufacturers as an aqueous solution at high pH (e.g., 9.5) inside a sealed glass ampoule. Once opened, the remaining solution should be transferred into a container leaving little headspace (e.g., an Eppendorf tube of an adequate volume) and stored tightly closed (e.g., wrapped in several layers of Parafilm) at room temperature inside the security hood. There will be nonetheless some unavoidable exchange with atmospheric CO2 resulting in a very slow decline of the specific radioactivity. This is the reason why the actual specific radioactivity should be measured for each assay. - 2 M HCl
For 10 ml:
Mix 2 ml of concentrated (36-38%, about 10 M) HCl with 8 ml of dH2O
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant (UV-INV-AE14-269247) of the University of Valencia.
References
- Edmondson, D. L., Badger, M. R. and Andrews, T. J. (1990). Slow inactivation of ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase during catalysis is caused by accumulation of a slow, tight-binding inhibitor at the catalytic site. Plant Physiol 93(4): 1390-1397.
- Kane, H. J., Wilkin, J. M., Portis, A. R. and John Andrews, T. (1998). Potent inhibition of ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase by an oxidized impurity in ribulose-1, 5-bisphosphate. Plant Physiol 117(3): 1059-1069.
- Laing, W. A. and Christeller, J. T. (1976). A model for the kinetics of activation and catalysis of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase. Biochem J 159(3): 563-570.
- Lilley, R. M. and Walker, D. A. (1974). An improved spectrophotometric assay for ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase. Biochim Biophys Acta 358(1): 226-229.
- Lorimer, G. H., Badger, M. R. and Andrews, T. J. (1977). D-Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase. Improved methods for the activation and assay of catalytic activities. Anal Biochem 78(1): 66-75.
- Sudhani, H. P. K., García-Murria, M. J., Marín-Navarro, J., García-Ferris, C., Peñarrubia, L. and Moreno, J. (2015). Purification of Rubisco from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Bio-protocol 5(23): e1673.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2015 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Sudhani, H. P. K., García-Murria, M. J., Marín-Navarro, J., García-Ferris, C., Peñarrubia, L. and Moreno, J. (2015). Assay of the Carboxylase Activity of Rubisco from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Bio-protocol 5(23): e1672. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1672.
Category
Plant Science > Phycology > Protein > Activity
Plant Science > Plant biochemistry > Protein > Activity
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link















