Advanced Search
Diffusion-weighted MRI protocol for acute brain edema detection after middle cerebral artery occlusion in mice
Last updated date: Jan 15, 2021 Views: 4097 Forks: 0
This protocol enables the detection of cytotoxic edema formation with 10-second time resolution diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) after middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) in mice.
MCAO surgery (Macrosphere injection model)
A ketamine/xylazine-anesthetized animal (C57BL6/J male mouse, 8 weeks old) was laid on its back on a heating pad.
A surgical midline incision was made from the clavicle to the chin to expose the right common carotid artery (CCA), internal carotid artery (ICA), and external carotid artery (ECA).
The distal side of ECA and proximal side of CCA were ligated using 7-0 silk suture.
The distal side of the ICA was clamped using a micro clamp (B-1, Fine Science Tools).
A small incision was subsequently made in the proximal portion of the CCA.
A 2m-long PE-10 polyethylene tube (PE-10, Beckton-Dickinson) filled with heparinized saline and six macrospheres (200 µm in diameter) was inserted into the CCA, and the clamp was subsequently removed. Tube length was dependent on the scanner environment. The opposite end of the tube was connected to a 1mL syringe filled with heparinized saline.
The tubing was secured in position using a 7-0 silk suture.
The skin incision was closed with 5-0 suture.
Diffusion-weighted MRI scan
MRI was performed using a 9.4-tesla animal scanner (BioSpec 94/30 USR, Bruker BioSpin, Ettlingen, Germany) equipped with a cryogenically cooled quadrature-resonator (CryoProbe, Bruker BioSpin, Ettlingen, Germany).
CCA catheter cannulated mice were placed on an MR–compatible stereotactic holder with ear bars (Bruker) to minimize head movement during scanning.
Body temperature was maintained at 37°C with hot water circulators, and respiratory rate was monitored using a remote system (SA Instruments, NY, USA).
All required adjustments (tuning, matching, shim adjustments) and T2-weighted TurboRARE were performed within 15 minutes after CCA catheter placement. If the T2-weighted image showed abnormal structure (e.g. ventricular enlargement), the animal was excluded.
TurboRARE: TR/TE: 8000/36 ms, Matrix 384 × 256, field of view (FOV) 19.2 mm × 12.8 mm, number of average (NEX) 1, 48 horizontal slices, slice thickness = 0.2 mm
Single-shot echo-planar diffusion weighted MRI (EPI-DWI) was performed continuously. Each measurement required 10 seconds.
EPI-DWI: TR/TE 2500/20 ms, NEX 1, FOV 18 mm × 15 mm, Matrix 108 × 96, 8 axial slices, slice thickness 0.8 mm. Z-direction motion probing gradient (MPG) was acquired with multiple b values (0, 100, 400, and 1000 s/mm2)
Thirty baseline images were acquired before MCA occlusion.
At the end of the 30th baseline scan, the macrospheres were advanced into the ICA via an injection of 0.02 ml heparinized saline. Animals remained in the same position within the magnet during occlusion.
Immediately after macrosphere delivery, MCA occlusion was confirmed by flow-compensated time-of-flight MR angiography (TOF-MRA) scans. This scan lasted 30 seconds. If MRA did not show complete occlusion of the MCA, the animal was excluded.
Flow compensated TOF-MRA: TR/TE 10/2.4 ms, Matrix 192 × 128, FA 80, FOV 19.2 mm × 12.8 mm, NEX 1, 10 horizontal slices (covered around circle of Willis and MCA), slice thickness = 0.3 mm
DWI scans restarted and continued over 360 measurements, with each measurement lasting 10 seconds.
Animals were euthanized immediately after MRI scanning.
Image processing
Maps of the mean diffusivity (ADC map) were derived using the standard algorithm of Paravision 6.0.1 software (Bruker).
ADC-map time series data were motion corrected using Advanced Normalization Tools (ANTs) normalization software (Avants et al., 2008, Avants et al., 2014).
Materials
1mL syringe
PE-10 tubing
heparinized saline
macrospheres (200 µm in diameter)
7-0 silk suture
5-0 suture
Images
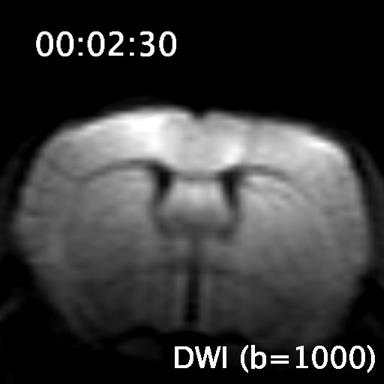
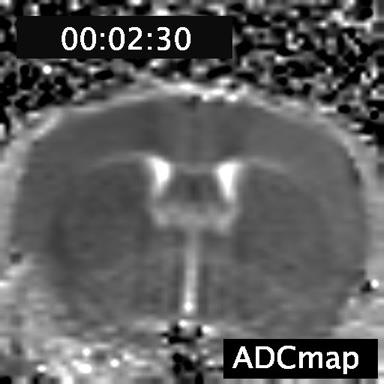
Acute cytotoxic edema could be detected as a hyperintense signal in DWI images and corresponding lower values on the ADCmap. Time course signal changes can be seen in the videos.
Videos
DWI.mp4 – time course DWI signal change. Time indicates time after macrosphere delivery. DWI hyperintense signal could be seen in ipsilateral hemisphere as a spreading wave within 1 to 3 minutes after MCAO occlusion.
ADCmap.mp4 – time course ADCmap change. ADC dropped as a wave started from the cortical surface and expanded throughout the ipsilateral hemisphere.
- Mestre, H, Du, T, Nedergaard, M and Mori, Y(2021). Diffusion-weighted MRI protocol for acute brain edema detection after middle cerebral artery occlusion in mice. Bio-protocol Preprint. bio-protocol.org/prep750.
- Mestre, H., Du, T., Sweeney, A. M., Liu, G., Samson, A. J., Peng, W., Mortensen, K. N., Stæger, F. F., Bork, P. A. R., Bashford, L., Toro, E. R., Tithof, J., Kelley, D. H., Thomas, J. H., Hjorth, P. G., Martens, E. A., Mehta, R. I., Solis, O., Blinder, P., Kleinfeld, D., Hirase, H., Mori, Y. and Nedergaard, M.(2020). Cerebrospinal fluid influx drives acute ischemic tissue swelling . Science 367(6483). DOI: 10.1126/science.aax7171
Category
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Tips for asking effective questions
+ Description
Write a detailed description. Include all information that will help others answer your question including experimental processes, conditions, and relevant images.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link
