Advanced Search
Total nucleated cells preparation enriching HSPC and S100A12high Neu2 for scRNA-seq
Last updated date: Jul 16, 2025 Views: 155 Forks: 0
Isolation of total nucleated cells (TNCs) from mobilized peripheral blood stem cell grafts collected by apheresis (PBSC), mobilized bone marrow (G-BM), and peripheral blood (PB) samples, as well as isolation of Lin⁻CD34⁺ cells and S100A12high Neu2 cell populations from grafts collected by apheresis and G-BM.
Reagent Preparation:
Red Blood Cell Lysis Buffer (ACK):
Dissolve 8.3 g ammonium chloride (NH₄Cl), 1.0 g potassium bicarbonate (KHCO₃), and 0.037 g disodium EDTA (EDTA-Na₂) in 1 L of sterile double-distilled water (ddH₂O). Filter sterilizes through a 0.22-µm membrane under a biosafety cabinet to ensure aseptic conditions.
Cell Staining Buffer:
Prepare phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) supplemented with 2 mM EDTA and 2% fetal bovine serum (FBS). Store at 4°C for up to two weeks.
0.04% Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA):
1× Dulbecco’s Phosphate-Buffered Saline (no calcium, no magnesium) containing 0.04% weight/volume BSA (400 µg/ml).
Operating steps:
1. Erythrocyte Lysis for Total Nucleated Cell Isolation
1.1 Sample Collection and Centrifugation
Collect PBSC, G-BM, or PB samples in EDTA-coated tubes. Centrifuge at 2,000 rpm (~500 × g) for 10 minutes at 4°C. Aspirate the supernatant and transfer to 1.5mL microcentrifuge tubes. Store at −80°C for future use.
1.2 Red Blood Cell Lysis
Add ACK buffer to cell pellets in the following ratios:
For BM: ACK: Sample = 4–5:1 (v/v)
For PB: ACK: Sample = 9:1 (v/v)
Gently invert tubes to ensure thorough mixing. Incubate the samples on ice for 10 minutes, mixing intermittently. Complete lysis is indicated by a translucent burgundy coloration of the solution.
1.3 Quenching and Washing
Quench the lysis by adding an equal volume of Dulbecco's PBS (DPBS). Centrifuge at 1,500 rpm (~300 × g) for 5 minutes at 4°C. Discard the supernatant and resuspend the cell pellet in fresh DPBS. Repeat the centrifugation step.
1.4 Additional Lysis (If Required)
If erythrocyte contamination persists, repeat the lysis step using an empirically adjusted volume of ACK buffer. Limit the number of lysis cycles to no more than three to maintain cell integrity. The presence of unlysed red blood cells in bone marrow samples may result from residual nucleated red blood cells, which is a common artifact associated with the sample preparation process.
1.5 Cell Viability Assessment
Resuspend a sample aliquot in 0.04% BSA and assess cell viability via Trypan Blue or automated cell counting. If viability falls below 80%, proceed with dead cell removal (see below).
1.6 Dead Cell Removal (If Viability <80%)
For samples with reduced viability, use a commercial dead cell removal kit (e.g., Miltenyi Biotec):
a) Resuspend ≤1×10⁷ cells in 100 µL of Dead Cell Removal Microbeads. Incubate for 15 minutes at room temperature (20–25°C) in the dark.
b) After incubation, add 1× Binding Buffer and pass the cell suspension through an MS column on a magnetic stand. Collect the flow-through, which contains viable cells, for downstream single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) via the 10× Genomics platform.
2. Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting (FACS) of Lin⁻CD34⁺ Cells
2.1 Antibody Staining
After cell counting, stain cells with the following fluorophore-conjugated antibodies for 30 minutes at 4°C, protected from light:
Antibody | Fluorescence channel | Volume(5×106 — 1×107cells) |
Human lineage cocktail | BV510 | 2µl |
Human CD34 | APC | 2µl |
Human CD38 | FITC | 2µl |
2.2 Washing and Preparation for FACS
Wash the stained cells with Cell Staining Buffer, then centrifuge at 1,500 rpm (~300 × g) for 5 minutes. Resuspend cells in Cell Staining Buffer containing 1 µg/mL DAPI to label dead cells immediately before FACS.
2.3 Gating Strategy
Perform FACS using a high-speed sorter. Apply the following gating strategy to isolate live Lin⁻CD34⁺ cells:
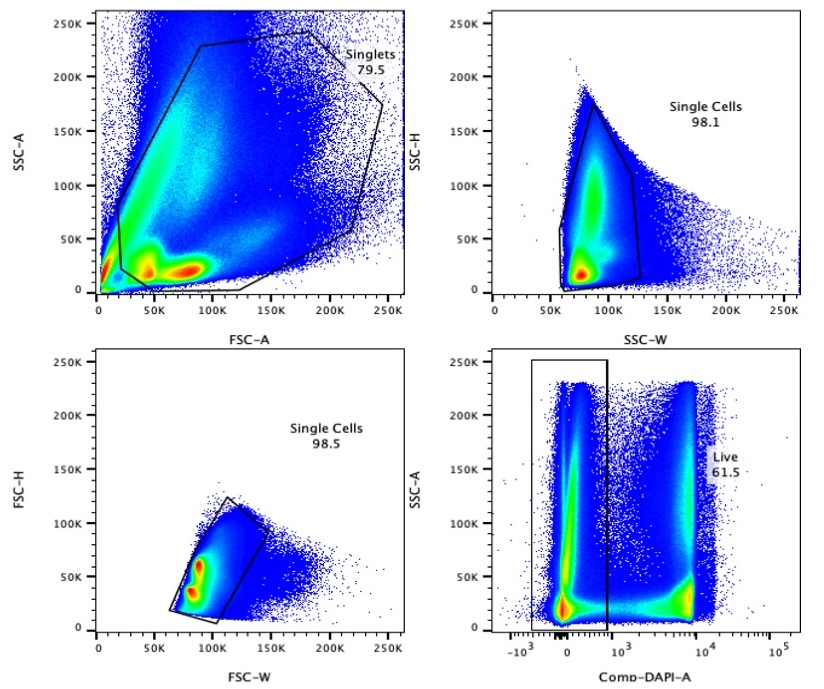
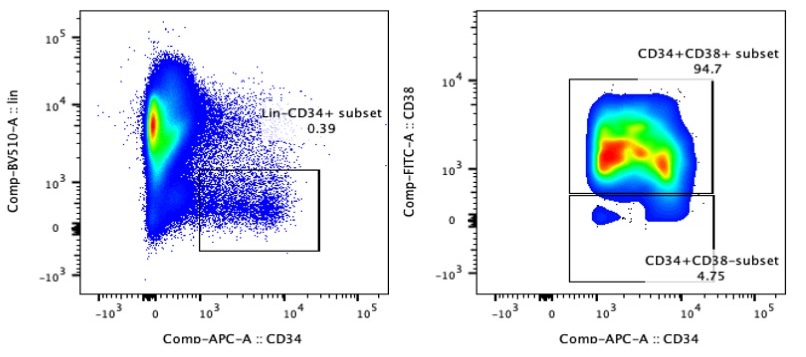
3. FACS of S100A12high Neu2 (Lin-CD34⁺CD66b⁺CD177⁺SSChigh)
3.1 CD34⁺ cell enrichment (Optional for PBSC Collections)
For samples with low frequency of the target population, perform CD34⁺ cell enrichment using magnetic separation:
Resuspend ≤1×10⁸ cells in 300 µL of PBE buffer.
Add 100 µL of Fc Receptor Blocking Reagent per 10⁸ cells and mix gently in the dark.
Add 100 µL of CD34 Microbeads per 10⁸ cells. Mix and incubate for 30 minutes at 4°C in the dark.
Wash the cell suspension with 20 mL PBE buffer and centrifuge.
Resuspend the cell pellet in 500 µL PBE buffer per 10⁸ cells.
Prime an LS column with 3 mL of PBE buffer. Apply the cell suspension onto the column and wash the column three times with 3 mL of PBE buffer per wash. Elute the retained cells using the plunger into a 15-mL tube with 3 mL of PBE buffer. Count the recovered cells.
3.2 Antibody Staining
Stain cells with the following antibodies for 30 minutes at 4°C in the dark:
Antibody | Fluorescence channel | Volume(5×106 — 1×107cells) |
Human lineage cocktail | BV510 | 2µl |
Human CD34 | APC | 2µl |
Human CD66b | FITC/PerCP-Cy5.5 | 2µl |
Human CD177 | PE/APC-Cy7 | 2µl |
3.3 Washing and Preparation for FACS
Wash the stained cells with PBE buffer and centrifuge at 1,500 rpm (~300 × g) for 5 minutes. Resuspend the pellet in PBE buffer containing 1 µg/mL DAPI immediately before FACS analysis.
3.4 Gating Strategy
Perform FACS sorting using the following gating strategy:
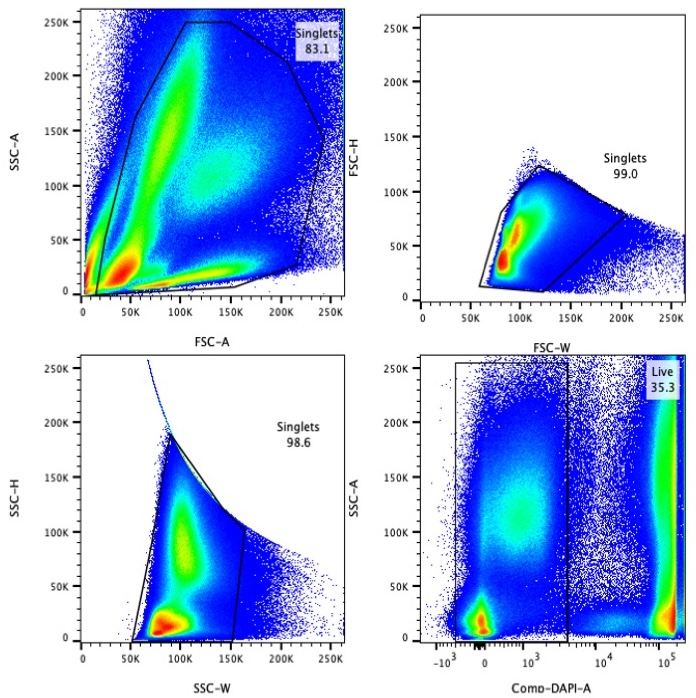
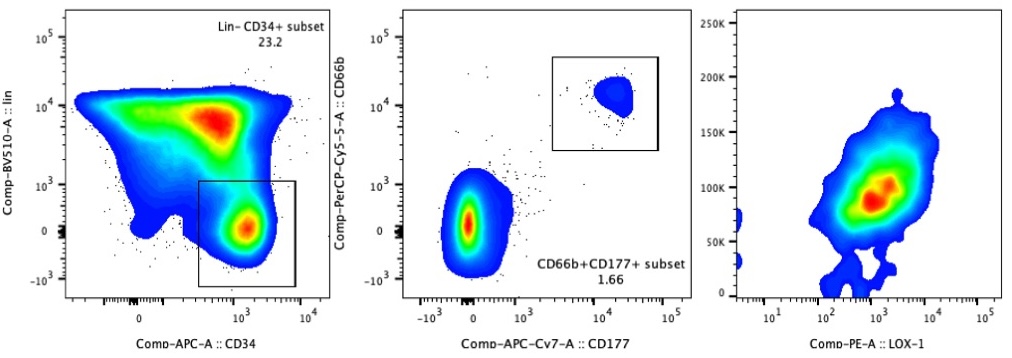
- Huo, Y, Wu, L, Jiang, E, Hao, S and Cheng, T(2025). Total nucleated cells preparation enriching HSPC and S100A12high Neu2 for scRNA-seq. Bio-protocol Preprint. bio-protocol.org/prep2843.
- Huo, Y., Wu, L., Pang, A., Li, Q., Hong, F., Zhu, C., Yang, Z., Dai, W., Zheng, Y., Meng, Q., Sun, J., Ma, S., Hu, L., Zhu, P., Dong, F., Gao, X., Jiang, E., Hao, S. and Cheng, T.(2023). Single-cell dissection of human hematopoietic reconstitution after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Science Immunology 8(81). DOI: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abn6429
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link
