- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Measurement of Endogenous H2O2 and NO and Cell Viability by Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy
Published: Vol 3, Iss 19, Oct 5, 2013 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.920 Views: 14308
Reviewed by: Tie Liu

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Quantification of Glyphosate, Aminomethylphosphonic Acid, and Ascorbate in Culture Medium and Microalgal Cells
Juan Manuel Ostera [...] Gabriela Malanga
Apr 5, 2025 1169 Views

Near-Infrared Autofluorescence Imaging of Nuclei in Living Plant Roots
Akira Yoshinari and Masayoshi Nakamura
Apr 20, 2025 2120 Views

Live-Cell Monitoring of Piecemeal Chloroplast Autophagy
Masanori Izumi [...] Shinya Hagihara
Nov 5, 2025 1687 Views
Abstract
Recently, there is compelling evidence that hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and nitric oxide (NO) function as signaling molecules in plants, mediating a range of responses including stomatal movement. Thus, the choice of sensitive methods for detection of endogenous H2O2 and NO in guard cells are very important for understanding the role of H2O2 and NO in guard cell signaling. In addition, besides stomatal closure caused by interfering guard cell signaling, it can also be caused by widespread, nonspecific damage to guard cells. To determine whether stomatal movement is caused by damage to guard cells, sensitive methods for detection of guard cell viability are often required.
The oxidatively sensitive fluorophore 2′,7′-dichlorofluorecin (H2DCF) is commonly employed to measure changes in intracellular H2O2 level directly. The non-polar diacetate ester (H2DCFDA) of H2DCF enters the cell and is hydrolysed into the more polar, non-fluorescent compound H2DCF, which, therefore, is trapped. Subsequent oxidation of H2DCF by H2O2, catalysed by peroxidases, yields the highly fluorescent DCF. Similarly, the cell-permeable, NO-sensitive fluorescent probe 4,5-diaminofluorescein diacetate (DAF-2DA) is widely used for the direct detection of NO presence in both animal and plant cells. The non-polar DAF-2DA enters the cell and is hydrolyzed by cytosolic esterase into the more polar, non-fluorescent compound DAF-2, which in the presence of NO is converted to the highly fluorescent triazole derivative DAF-2T. The fluorescent indicator dyes fluorescein diacetate (FAD) and propidium iodide (PI) are widely used for detection of cell viability. FAD passes through cell membranes and is hydrolyzed by intracellular esterase to produce a polar compound that passes slowly through a living cell membrane but fast through a damaged or dead cell membrane, and thus accumulates inside the viable cells and exhibits green fluorescence when excited by blue light. In contrast, PI passes through damaged or dead cell membranes and intercalates with DNA and RNA to form a bright red fluorescent complex seen in the nuclei of dying or dead cells but not living cells. Based on the above analysis, the fluorescent indicator dyes H2DCFDA, DAF-2DA, FAD and PI load readily into guard cells, and their optical properties make them amenable to analysis by confocal laser scanning microscopy.
This protocol describes how to combine confocal laser scanning microscopy with fluorescent indicator dyes H2DCFDA, DAF-2DA, FAD and PI respectively for measurement of H2O2 and NO and viability of guard cell in leaves of Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana).
Materials and Reagents
- Leaves of Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana)
- Ethanesulfonic acid (MES)
- 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescin diacetate (H2DCFDA) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D6883 )
- 4, 5-diaminofluorescein diacetate (DAF-2DA) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D2813 )
- Propidium iodide (PI) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P4170 )
- Fluorescein diacetate (FDA) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: F7378 )
- DMSO (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D8418 )
- 10 mM MES/KCl buffer pH 6.15 (see Recipes)
- Tris/KCl buffer pH 7.2 (see Recipes)
- 10 mM H2DCFDA (see Recipes)
- 10 mM DAF-2DA (stock solution) (see Recipes)
- 1 mg/ml PI (stock solution) (see Recipes)
- 5 mg/ml FDA (stock solution) (see Recipes)
Equipment
- TCS-SP2 Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (Leica Lasertechnik Gmbh3, Heidelberg)
- 25 °C incubator
- Glass slide and cover glass
- Eyelbrow brush (Yellow wolf hair, length of hair: 0.8 cm, width of hair: 0.8 cm)
- Tweezers
- 6-cm diameter Petri plate
Software
- Leica confocal software (Leica Lasertechnik Gmbh3, Heidelberg)
- Photoshop software
Procedure
- Sampling.
Arabidopsis seedlings were gown in plant growth chambers under a 16-h light/8-h dark cycle, a photon flux density of 0.1 mmol/m2/s, and a day/night temperature cycle of 18 °C/22 °C for 4-6 weeks. The youngest, fully expanded and flat leaves were harvested for immediate use.
- Opening the stomata.
For stomatal closing experiments, to ensure stomata at fully opened stage before starting of treatments, the freshly harvested flat leaves were first floated with their abaxial surfaces facing up on MES/KCl buffer (15 ml) in 6-cm diameter Petri plates for 2-3 h at 22 °C under light condition (0.1 mmol/m2/s) to open the stomata, and then for subsequent treatments.
- Treating samples.
Once the stomata were fully open (checked by microscope), the leaves were then floated on MES/KCl buffer alone or containing various compounds or inhibitors for required time at 22 °C under the same white light condition mentioned above or the desired conditions. Control treatments involved addition of buffer or appropriate solvents used with inhibitors.
Note: As the epidermal strips is easier peeled from the abaxial surface than the paraxial surface of Arabidopsis leaves, we only peeled epidermal strips from abaxial surface of leaves for subsequent measurement. Thus, for treatments of UV-B radiation as well as other lights, to ensure the abaxial surface of leaves receiving same dose of UV-B radiation as well as other lights, the leaves were floated with their abaxial surfaces facing up and perpendicular to the light on MES/KCl buffer in all treatments including opening stomata.
- Peeling epidermal strips.
After the above treatments, the leaf was taken out from MES/KCl buffer and a piece of filter paper was used to absorb the MES/KCl buffer on the surface of leaf. The leaf were flatly placed on a glass slide with its abaxial surfaces facing up, a tweezers was used to clamp a part of abaxial epidermis and mesophyll cells near the tip of leaf and the epidermal strips were quickly peeled along with the direction of the main leaf veins. Then, the peeled epidermal strips were immediately immersed in the corresponding treated buffer and pushed on the bottom of Petri plates by a forceps, the remained mesophyll cells were gently removed from epidermal strips by an eyebrow brush (Figure 1), and the tip of epidermal strip clamped by tweezers with more mesophyll cells was cut away, then epidermal strips were quickly used for loading of the fluorescent indicator dyes.
- Loading fluorescent indicator dyes.
The peeled epidermal strips were immediately placed into Petri plates containing Tris-KCl buffer in the presence of H2DCFDA at a final concentration of 50 μM for 10 min, DAF-2DA at a final concentration of 10 mM for 30 min, FAD at a final concentration of 10 μg/ml for 10 min, or PI at a final concentration of 5 μg/ml for 10 min respectively, in the dark at 25 °C to exclude the possibility of that the fluorescent probes were oxidized or hydrolyzed by UV-B or PAR radiation. Then, the epidermal strips were washed with fresh Tris–KCl buffer without the fluorescent indicator dyes at least three times in dark to remove the excess dyes.
- Examination of H2O2, NO and viability of guard cells by confocal laser scanning microscopy.
After loading of the fluorescent indicator dyes, the slides were made and an examination of the peels was immediately performed by TCS-SP2 confocal laser scanning microscopy with the following settings: excitation 488 nm and emission 530 nm for H2DCFDA, DAF-2DA and FAD or excitation 536 nm and emission 617 nm for PI; normal scanning speed, frame 512 x 512. For example, by using these fluorescent indicator dyes and the confocal laser scanning microscope, Figure 1 clearly showed that guard cells of wild-type Arabidopsis under light alone had low levels of H2O2 (Figure 1A) and NO (Figure 1D), and high viability of guard cells (Figure 1G). However, 3 h of 0.5 W/m2 UV-B radiation significantly induced production of H2O2 (Figure 1B) and NO (Figure 1E), and did not affect cell viability (Figure 1H) in wild-type guard cells, but did not induce H2O2 production in guard cells of AtrbohD/F double mutant (Figure 1C) or NO production in guard cells of Nia1-2/Nia2-5 double mutant (Figure 1F). Furthermore, when wild-type leaves were exposed to 0.8 W/m2 UV-B for 3 h, the guard cells were significantly damaged and clearly marked by the fluorescent dye PI (Figure 1I).
- Analysis
Images acquired from the confocal microscope were analyzed with Leica confocal software to measure the average fluorescent pixel intensities in the guard cells following various treatments (such as in Figure 1J; the detailed procedure of analysis seen the following note) and processed with Photoshop software. In each experiment, three epidermal strips were at least measured, each of which originated from a different plant. Each experiment was repeated three times. The selected confocal image represented the same results from approximately nine time measurements. Data of fluorescence pixel intensities are statistically analyzed by one-way ANOVA and displayed as means ± SE (n = 60).
Note: Procedure for analysis of fluorescent intensity: On the “LAS AF” screen of Leica confocal software, click the “quality” button, select “Histogram” analysis method and circle guard cell to be analyzed, then “Statistics” shows the average fluorescent intensity of the circled guard cell, select “Export as” to save the “Statistics” displayed data in a text format.
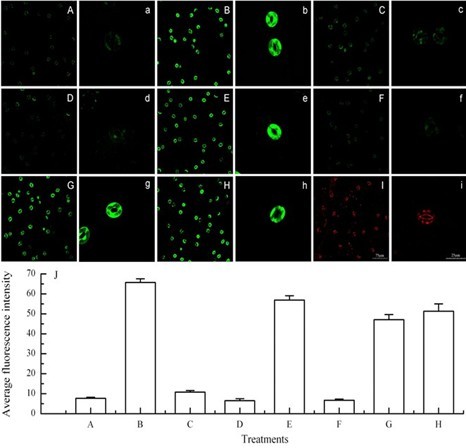
Figure 1. Effects of UV-B radiation on the production of H2O2 and NO and viability of Arabidopsis guard cells. A-C. Images of guard cells loaded with the fluorescent indicator dye H2DCFDA. D-F. Images of guard cells loaded with the fluorescent indicator dye DAF-2DA. G and H. Images of guard cells loaded with the fluorescent indicator dye FAD. A, D and G. Wild-type guard cells exposed to light alone for 3 h. B, E and H. Wild-type guard cells exposed to light with 0.5 W m-2 for 3 h. C and F. Double mutants AtrbohD/F and Nia1-2/Nia2-5 guard cells respectively exposed to light with 0.5 W m-2 for 3 h. I. Image of wild-type guard cells exposed to 0.8 W m-2 UV-B for 3 h and loaded with the fluorescent indicator dye PI. J. The figure shows the average fluorescent intensities (means ± SE) of guard cells in images from A to H. The guard cells shown in images a-i are representative of guard cells shown in images A-I, respectively. Scale bars in image I (75 μm) and i (25 μm) are for images A-I and a-i, respectively.
Recipes
- 10 mM MES/KCl buffer (10 mM MES, 50 mM KCl, 0.1 mM CaCl2, pH 6.15, 500 ml)
1.066 g MES
5.549 mg CaCl2
1.86375 g KCl
Mix these chemicals with 400 ml dH2O
Adjust pH to 6.15 with KOH
Add dH2O to 500 ml
Stored at room temperature
- Tris/KCl buffer (10 mM Tris and 50 mM KCl, pH 7.2, 500 ml)
0.6055 g Tris
1.86 g KCl
Mix these chemicals with 400 ml dH2O
Adjust pH to 7.2 with HCl
Add dH2O to 500 ml
Stored at room temperature
- 10 mM H2DCFDA (1 ml, stock solution).
Mix 4.8729 mg of H2DCFDA with 1 ml DMSO
Stored at -20 °C
This stock solution is diluted by Tris/KCl pH 7.2 buffer to get a working concentration of 50 μM
- 10 mM DAF-2DA (stock solution).
Mix 1 mg of DAF-2DA with 224 μl DMSO to form 10 mM stock solution
Stored at -20 °C
This stock solution is diluted by Tris/KCl pH 7.2 buffer to get a working concentration of 10 μM
- 1 mg/ml PI (stock solution)
Mix 1 mg of PI with 1 ml dH2O to make a stock solution
Stored at 4 °C in a dark bottle
This stock solution is diluted by Tris/KCl pH 7.2 buffer to get a working concentration of 5 μg/ml
- 5 mg/ml FDA (stock solution)
Mix 5 mg of FDA with 1 ml acetone to make a stock solution
Stored at 4 °C in a dark bottle
This stock solution is diluted by Tris/KCl pH 7.2 buffer to get a working concentration of 10 μg/ml
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation of China (grant no. 31170370) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (grant no. GK200901013). This protocol was adapted from previously published paper He et al. (2013).
References
- He, J. M., Ma, X. G., Zhang, Y., Sun, T. F., Xu, F. F., Chen, Y. P., Liu, X. and Yue, M. (2013). Role and interrelationship of Galpha protein, hydrogen peroxide, and nitric oxide in ultraviolet B-induced stomatal closure in Arabidopsis leaves. Plant Physiol 161(3): 1570-1583.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2013 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Wu, M., Ma, X. and He, J. (2013). Measurement of Endogenous H2O2 and NO and Cell Viability by Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy. Bio-protocol 3(19): e920. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.920.
- He, J. M., Ma, X. G., Zhang, Y., Sun, T. F., Xu, F. F., Chen, Y. P., Liu, X. and Yue, M. (2013). Role and interrelationship of Galpha protein, hydrogen peroxide, and nitric oxide in ultraviolet B-induced stomatal closure in Arabidopsis leaves. Plant Physiol 161(3): 1570-1583.
Category
Plant Science > Plant biochemistry > Other compound
Cell Biology > Cell imaging > Confocal microscopy
Biochemistry > Other compound > Reactive oxygen species
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link










