- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Protein Extraction, Acid Phosphatase Activity Assays, and Determination of Soluble Protein Concentration
Published: Vol 3, Iss 17, Sep 5, 2013 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.889 Views: 23717
Reviewed by: Tie Liu

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols
Immunofluorescence for Detection of TOR Kinase Activity In Situ in Photosynthetic Organisms
Ana P. Lando [...] Giselle M. A. Martínez-Noël
Dec 20, 2024 1803 Views
An Activity-Based Proteomics with Two-Dimensional Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (2D-PAGE) for Identifying Target Proteases in Arabidopsis Apoplastic Fluid
Sayaka Matsui and Yoshikatsu Matsubayashi
Mar 5, 2025 1966 Views
Advancing 2-DE Techniques: High-Efficiency Protein Extraction From Lupine Roots
Sebastian Burchardt [...] Emilia Wilmowicz
Oct 5, 2025 1756 Views
Abstract
Acid phosphatases (APases) catalyze the hydrolysis of inorganic phosphate (Pi) from a broad range of Pi-monoesters with an acidic pH optimum. The liberated Pi is reassimilated into cellular metabolism via mitochondrial or chloroplastic ATP synthases of respiration or photosynthesis, respectively. Eukaryotic APases exist as a wide variety of tissue- and/or cellular compartment-specific isozymes that display marked differences in their physical and kinetic properties. Increases in intracellular (vacuolar) and secreted APase activities are useful biochemical markers of plant nutritional Pi deficiency. The protocols for protein extraction, APase activity determination and measurement of soluble protein concentration from plant tissues or cell suspension cultures are presented.
Materials and Reagents
- Plant tissues
- Sodium acetate (Bioshop, catalog number: SAA305 )
- EDTA (Bioshop, catalog number: EDT001 )
- Dithiothreitol (DTT) (Bioshop, catalog number: DTT 002 )
- Phenylmethyl sulfonyl fluoride (PMSF) (G-Biosciences, catalog number: 786-0555 )
- Thiourea (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T-7875 )
- Polyvinyl (polypyrrodlidone) (PVPP) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P-6755 )
- β-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide reduced form (NADH) (Bioshop, catalog number: NAD002 )
- Phosphoelnolpyryvate (PEP) (Biovectra, catalog number: 2552 )
- MgCl2 ((Biolynx, catalog number: 18641 )
- Rabbit muscle lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: L-2500 )
- para-nitrophenyl-phosphate (pNPP, phosphatase substrate) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P-4744 )
- Coomassie Brilliant blue G-250 (Serva, catalog number: 35050 C.!.42655 )
- Bovine gamma globulin (BGG) (2.0 mg/ml) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 23212 )
- NaOH
- Extraction buffer (EB) (see Recipes)
- Bradford working solution (see Recipes)
- Acid phosphatase enzyme assay mix #1 (see Recipes)
- Acid phosphatase enzyme assay mix #2 (see Recipes)
- Bradford assay stock (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Whatman #1 filter paper
- 1.5 ml microfuge tubes
- 10 and 25 μl Hamilton syringes
- Pipetor
- Small mortar and pestle
- Eppendorf microfuge
- 96 well polystyrene microtitre plate (flat bottom)
- A computer supported microplate spectrophotometer (Spectromax Plus, Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale)
Procedure
- Extraction
This protocol applies to extraction of intracellular (vacuolar) APases from plant tissues and suspension cell cultures (e.g., Tran et al., 2010a; Veljanovski et al., 2006). Refer to Tran et al. (2010b) and Robinson et al. (2012) for information on the isolation and analysis of plant cell wall localized and secreted APase isoforms.
- Weigh tissue and freeze in liquid N2. Store at -80 °C until use.
- Place a small spatula of sea sand into the mortar, add small amount of liquid N2, followed by frozen tissue, and grind to a powder. Carefully add more liquid N2 if needed to keep frozen.
- Invert tube with extraction buffer (EB) to mix and add to sample at a ratio of 1:2, w/v (e.g. 0.5 g powdered tissue + 1.0 ml EB) although this may need to be increased to 1:3 for leaf tissue and 1:4 for roots. Grind for several minutes and place in 1.5 ml microfuge tubes.
- Centrifuge 5 min at 4 °C and 11,000 x g. Remove supernatant (clarified extract) to a fresh microfuge tube and keep it on ice. Measure APase activity immediately at room temperature (24 °C). Aliquots of clarified extracts can be snap frozen in liquid N2 and stored at -80 °C for future use.
- Weigh tissue and freeze in liquid N2. Store at -80 °C until use.
- APase activity assay 1
- Conveniently measure APase activity by coupling the hydrolysis of phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) to pyruvate to the lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) reaction at 24 °C and using a spectrophotometer to continuously monitor NADH oxidation at 340 nm. PEP seems to be an excellent APase substrate for since it occupies the highest position on the thermodynamic scale of phosphorylated intermediates (and thus its P atom is an excellent leaving group). For every PEP molecule hydrolyzed to pyruvate, one NADH molecule is oxidized to NAD+ by LDH as shown in Figure 1.
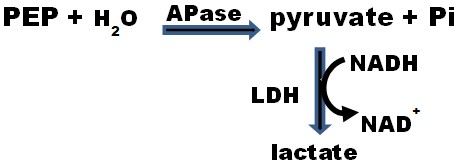
Figure 1. APase activity can be conveniently deterdmined by coupling the hydrolysis of PEP to pyruvate to the lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) reaction and using a spectrophotometer to continuously monitor NADH oxidation to NAD+ at 340 nm
- Accurately pipette 1-10 μl of clarified extract into a microplate well. We prefer to use a 10 or 25 μl Hamilton syringe as opposed to automated pipetors for accurate pipetting of enzyme protein extracts into wells of the microtitre plate.
- Use repeat pipetor to add 200 μl APase assay mix #1 to each well and immediately place in microplate spectrophotometer. Continuously monitor NADH oxidation to NAD+ as a decline in absorbance at 340 nm (A340), taking readings every 5-10 sec for up to 5 min.
- Correct for background NADH oxidation by omitting PEP from the reaction mixture. Ensure that the decline in A340 (amount of NADH being oxidized; ε340 = 6,220/M/cm) is proportional to assay time and concentration of enzyme assayed. Dilution of clarified extract in extraction buffer (lacking PVPP) may be necessary for samples containing abundant APase activity.
Note: One international unit (U) of enzyme activity is defined as the amount of enzyme resulting in the hydrolysis of 1 μmol of substrate (e.g. one μmol of NADH oxidized to NAD+) per min at 24 °C. APase activity in (U/ml clarified extract) = (ΔA340/min x clarified extract dilution factor)/6.22. Thus, if 2.0 μl of clarified extract mixed with 200 μl of APase reaction mixture yields a ΔA340/min of 0.1 at 340 nm, then the APase activity = (0.1 x 100)/6.22 U/ml = 1.6 U/ml.
- Conveniently measure APase activity by coupling the hydrolysis of phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) to pyruvate to the lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) reaction at 24 °C and using a spectrophotometer to continuously monitor NADH oxidation at 340 nm. PEP seems to be an excellent APase substrate for since it occupies the highest position on the thermodynamic scale of phosphorylated intermediates (and thus its P atom is an excellent leaving group). For every PEP molecule hydrolyzed to pyruvate, one NADH molecule is oxidized to NAD+ by LDH as shown in Figure 1.
- APase activity assay 2
This is a ‘stopped-time’ APase assay based upon the hydrolysis of the synthetic substrate, para-nitrophenyl-phosphate (pNPP), to para-nitrophenol (pNP) and Pi (Figure 2). The pNP product forms a yellow color at alkaline pH (λmax = 410 nm; extinction coefficient = ε410 = 18.2/mM/cm; meaning a 1 mM solution of pNP should have an A410 of 18.2). The amount of yellow color formed is thus directly proportional to the amount of pNP produced and is therefore an indicator of the APase activity. This assay tends to be more popular in the APase literature. However, care needs to be taken to ensure that the amount of pNP being formed is proportional to the assay time and volume of clarified extract being assayed.

Figure 2. APase activity is often assayed spectrophotometrically at 410 nm by determining the amount of pNP produced following the hydrolysis of Pi from pNPP. Addition of NaOH after a specified assay time (e.g., 10 min) serves to stop the APase reaction while simultaneously converting the product p-nitrophenol into the yellow colored p-nitrophenolate (λmax = 410 nm).
- Accurately pipette 1-10 μl of clarified enzyme extract into a well of the microtitre plate. Add 200 μl of APase assay mix #2 to each well containing enzyme extract and incubate for 10 min at room temperature (24 °C).
- At t = 10 min, add 50 μl of 3 M NaOH to each well containing APase reactions. This stops the reaction (denatures APase) while simultaneously converting pNP product into the yellow colored p-nitrophenolate.
- Determine ΔA410/min for each well to determine the amount (μmol) of pNP formed per min.
- Accurately pipette 1-10 μl of clarified enzyme extract into a well of the microtitre plate. Add 200 μl of APase assay mix #2 to each well containing enzyme extract and incubate for 10 min at room temperature (24 °C).
- Bradford Assay of Soluble Protein Concentration
- Prepare standard curve using the template below:
Well #
Vol BGG (0.4 mg/ml)
Amt Protein (BGG)
Vol H2O
(μl)
(μg)
(μl)
1a
0
0
25 (blank)
1b
2
0.8
23
1c
4
1.6
21
1d
8
3.2
17
1e
12
4.8
13
1f
16
6.4
9
1g
20
8.0
5
1h
25
10.0
0
2a
0
0
25 (blank)
- Pipette 2-20 μl of the clarified extract (dilute as necessary) and adjust final volume to 25 μl in each well with H2O. Dilute sample if necessary to remain in linear range of standard curve. A 25 μl Hamilton syringe is more accurate than automated pipetors for pipetting of BGG standard and clarified extract into wells of the microtitre plate.
- Add 250 μl of Bradford working solution to each well using a repeat pipetor and read A595 of protein standards and unknowns. Ensure that A595 values of clarified extract samples aliquot falls within range of A595 values of the BGG standards. The absorbance maximum for an acidic solution of Coomassie Brilliant blue G-250 shifts from 465 nm to 595 when protein binding occurs. Determine amount of protein in clarified extract aliquot from the standard curve (if 2 μl aliquot of clarified extract yields an A595 value equivalent to 5 μg of protein, then the extract would have a protein concentration of 2 mg/ml).
- Prepare standard curve using the template below:
Recipes
- Extraction buffer (EB, keep on ice)
50 mM Na-acetate (pH 5.6)
1 mM EDTA
1 mM DTT
1 mM PMSF (prepare 100 mM stock in absolute ethanol and store at -20 °C, add fresh to EB immediately prior to tissue extraction as PMSF is unstable in aqueous solution)
5 mM thiourea
1% (w/v) PVPP
- APase assay #1 reaction mixture (prepare freshly and keep at room temperature)
50 mM Na-acetate (pH 5.6)
10 mM MgCl2
0.2 mM NADH
5 mM PEP
3 U/ml rabbit muscle LDH (Desalt LDH by centrifuging an aliquot 3 min at 11,000 x g. Discard supernatant and resuspend the pellet in an equal volume of EB).
- APase assay #2 reaction mixture
10 mM pNPP (sodium salt), dissolved in 50 mM acetate-KOH (pH 5.8)
3 M sodium hydroxide (NaOH) also needed to stop the reaction
- Bradford assay stock
100 ml 95% EtOH
200 ml 88% H3PO4
350 mg Brilliant blue G-250
- Bradford working solution
30 ml Bradford Stock
425 ml H2O
15 ml EtOH
30 ml 88% H3PO4
Filter through Whatman #1 filter paper and store in brown or dark glass bottle.
Protein assay solutions are stable for months at room temperature.
- Bradford Protein standard
Dilute bovine Gamma Globulin with H2O to 0.4 mg/ml
Store 100 μl aliquots at -20 °C.
Acknowledgments
Research in our laboratory has been generously funded by research and equipment grants from The Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) and Queen’s Research Chairs program to William Plaxton.
References
- Robinson, W. D., Park, J., Tran, H. T., Del Vecchio, H. A., Ying, S., Zins, J. L., Patel, K., McKnight, T. D. and Plaxton, W. C. (2012). The secreted purple acid phosphatase isozymes AtPAP12 and AtPAP26 play a pivotal role in extracellular phosphate-scavenging by Arabidopsis thaliana. J Exp Bot 63(18): 6531-6542.
- Tran, H. T., Hurley, B. A. and Plaxton, W. C. (2010a). Feeding hungry plants: the role of purple acid phosphatases in phosphate nutrition. Plant Sci 179(1): 14-27.
- Tran, H. T., Qian, W., Hurley, B. A., She, Y. M., Wang, D. and Plaxton, W. C. (2010b). Biochemical and molecular characterization of AtPAP12 and AtPAP26: the predominant purple acid phosphatase isozymes secreted by phosphate-starved Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Environ 33(11): 1789-1803.
- Veljanovski, V., Vanderbeld, B., Knowles, V. L., Snedden, W. A. and Plaxton, W. C. (2006). Biochemical and molecular characterization of AtPAP26, a vacuolar purple acid phosphatase up-regulated in phosphate-deprived Arabidopsis suspension cells and seedlings. Plant Physiol 142(3): 1282-1293.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2013 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Knowles, V. and Plaxton, W. (2013). Protein Extraction, Acid Phosphatase Activity Assays, and Determination of Soluble Protein Concentration. Bio-protocol 3(17): e889. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.889.
Category
Plant Science > Plant biochemistry > Protein > Activity
Biochemistry > Protein > Isolation and purification
Plant Science > Plant biochemistry > Protein > Isolation and purification
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link










