- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Genomic 8-oxo-7,8-dihydro-2'-deoxyguanosine Quantification
Published: Vol 3, Iss 17, Sep 5, 2013 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.878 Views: 9696
Reviewed by: Anonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols
Colocalizing Telomeres With PML or γH2AX Foci by IF-FISH in Mouse Brain Neurons
Anna Konopka
Nov 5, 2025 1506 Views
Abstract
8-oxo-7,8-dihydro-2'-deoxyguanosine (8-oxo-dGuo) is among the most common reactive oxygen species-induced DNA lesions and can be used as a biomarker for oxidative stress. The lesion has been linked to several biological processes and diseases, including colorectal cancer, Huntington’s disease, estrogen-induced gene expression, and thymine dimer repair (reviewed in Delaney et al., 2012). The following assay is used to quantify 8-oxo-dGuo levels in DNA as described in Sousa et al. (2013).
Materials and Reagents
- NH4HCO3 (reagent grade ≥ 99% purity)
- MgCl2 (reagent grade ≥ 99% purity)
- CaCl2 (reagent grade ≥ 99% purity)
- DNase I from bovine pancreas (F. Hoffmann-La Roche, catalog number: 04716728001 )
- Nuclease P1 from P. citrinum (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: N8630-1VL )
- Phosphodiesterase I from C. adamanteus venom (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P3242-1VL )
- Alkaline phosphatase from E. coli (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P5931-100UN )
- 8-hydroxy-2’-deoxyguanosine (8-oxo-dGuo) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: H5653-1MG )
- [15N5]-8-hydroxy-2’-deoxyguanosine (Cambridge Isotope Laboratories, catalog number: NLM-6715-0 ) (this is the internal standard)
- DNeasy® Blood & Tissue Kit (QIAGEN, catalog number: 69506 )
- LC/MS-grade methanol
- Hydrolysis buffer (see Recipes)
- Solvent A (see Recipes)
- Solvent B (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Vortexer
- Microcentrifuge
- Vacuum centrifuge
- LC/MS/MS: We used an LC-20AD HPLC system (Shimadzu Corporation) coupled to an API 5000 triple-quadrupole mass spectrometer (Applied Biosystems)
- Zorbax SB-C18 reverse phase chromatography column (2.1 x 150 mm, i.d., 3.5 μm) (Agilent Technologies)
Procedure
- DNA isolation
DNA can be isolated using a variety of methods. We used the DNeasy® Blood Tissue Kit from QIAGEN, but other analogous kits are likely to yield similar results so long as they are not phenol based. Phenol-based DNA isolation has been shown to oxidize DNA in vitro and therefore overestimate 8-oxo-dGuo (Hamilton et al., 2001). Moreover, the final DNA elution step should be performed with water because most elution buffers contain EDTA, which inhibit nucleases. - Enzymatic hydrolysis of DNA
- In 40 μl hydrolysis buffer, add
- 1 U DNase I
- 0.2 mU phosphodiesterase I
- 0.1 U alkaline phosphatase
- 1.25 pmol [15N5]-8-hydroxy-2’-deoxyguanosine internal standard
(this gives a final concentration of 10 nM on the LC/MS/MS) - 0.5-5 μg DNA
- 1 U DNase I
- Incubate at 37 °C for 6 h to overnight.
- Add five volumes of ice-cold methanol to the samples and mix well by vortexing. This step precipitates enzymes and salts prior so that (1) they don’t interfere with analyte ionization and (2) they don’t precipitate upon exposure to organic mobile phase during chromatography, which can cause clogs.
- Centrifuge samples at 16,000 x g for 20 min at 4 °C.
- Transfer the supernatant to new tubes. The pellet contains precipitated enzymes and salts that can interfere with analysis and can be discarded.
- Vacuum centrifuge the supernatant until dry.
- Dissolve the resulting residue in 25 μl 5% methanol in water.
- Inject 20 μl sample into the LC/MS/MS for analysis.
- In 40 μl hydrolysis buffer, add
- A standard curve was made in 5% methanol in water containing 0.1-500 nM 8-oxo-dGuo, containing 10 nM internal standard.
- HPLC program (flow rate 300 μl/min)
- 5% solvent A for 0.5 min.
- Ramp to 90% solvent B over 6 min.
- Hold at 90% solvent B for 1.5 min.
- Re-equilibrate with 5% solvent A for 5 min.
- 5% solvent A for 0.5 min.
- MS/MS program
- MS/MS acquisition should be used with positive electrospray ionization in multiple reaction monitoring mode.
Note: The mass spectrometer settings are instrument specific and are therefore not included in this protocol. - Mass transition for 8-hydroxy-2’-deoxyguanosine: 284.1 -> 168.2.
- Mass transition for [15N5]-8-hydroxy-2’-deoxyguanosine: 289.2 -> 173.1.
- MS/MS acquisition should be used with positive electrospray ionization in multiple reaction monitoring mode.
- Quantification
- Integrate the area under the peaks.
- Divide the 8-oxo-dGuo peak area by the internal standard peak area for all samples.
- Make a standard curve from the standards of known concentrations.
- Use the slope and y-intercept from the standard curve to calculate the concentration of the unknowns.
- Integrate the area under the peaks.
- (Optional) Deoxynucleoside quantification
- Dilute 1 μl of sample prior to MS injection 1:1,000 in 5% methanol in water. The reason for the dilution is that the canonical deoxynucleosides are much more abundant than 8-oxo-dGuo and would saturate the mass spectrometer’s detector if injected undiluted.
- Inject 20 μl of diluted sample for LC/MS/MS analysis of deoxynucleosides.
- Use the same HPLC program as for 8-oxo-dGuo.
- Mass transitions for deoxyguanosine, deoxycytidine, deoxyadenosine, and thymidine: 252.1 ->136.1, 228.1 -> 112.1, 268.1 -> 152.0, and 243.1 -> 127.0, respectively.
- Use standard curves to quantify deoxynucleoside concentrations.
- Use the following formula to calculate 8-oxo-dGuo per 106 nucleosides:
(mol 8-oxo-dGuo/[mol dAdo + dGuo + dCyd + Thd]) x 1,000,000
- Dilute 1 μl of sample prior to MS injection 1:1,000 in 5% methanol in water. The reason for the dilution is that the canonical deoxynucleosides are much more abundant than 8-oxo-dGuo and would saturate the mass spectrometer’s detector if injected undiluted.
Recipes
- Hydrolysis buffer
100 mM NH4HCO3 (pH 7.6)
10 mM MgCl2
1 mM CaCl2 - Solvent A
0.1% formic acid in water - Solvent B
0.1% formic acid in methanol
Notes
- Hydrolysis procedure. The hydrolysis procedure used here is one of many viable alternatives. When choosing a hydrolysis method for nucleoside analysis one must consider the following:
- Does the method affect the bases? DNA can be chemically hydrolyzed, but this is more risky because the bases themselves are subject to damage. Some enzymes also have unintended activity. For example, commercial alkaline phosphatase has been shown to contain deaminase activity (or contamination by deaminases) (Dong and Dedon, 2006; Dong et al., 2003).
- How important is a short hydrolysis reaction time? Some nucleoside modifications can arise spontaneously in water and a short hydrolysis reaction time is therefore worth the extra cost and effort necessary. Our group has also measured genomic uracil, which can arise spontaneously from cytosine deamination in water. We therefore developed a method to hydrolyze DNA in 50 min instead of 6 h (Galashevskaya et al., 2013). Adding even more enzymes, one can lower the reaction time to 15-30 min at room temperature (using DNase I, SVPD, micrococcal nuclease, omnicleave, benzonase, alkaline phosphatase, and Antarctic phosphatase; unpublished results by Sarno, 2013). Note that adding more enzymes significantly increases the reaction cost.
- Does the method affect the bases? DNA can be chemically hydrolyzed, but this is more risky because the bases themselves are subject to damage. Some enzymes also have unintended activity. For example, commercial alkaline phosphatase has been shown to contain deaminase activity (or contamination by deaminases) (Dong and Dedon, 2006; Dong et al., 2003).
- Cleanliness. Mass spectrometry is a very sensitive technique, so great care should be taken to maintain a clean laboratory environment. Depending on the instrument and reagent quality, the assay can detect down to 0.1-0.5 fmol analyte. Thus, always ensure that all equipment and surfaces are clean and autoclaved if possible (e.g. pipettes, tips, tubes, centrifuges, etc.). Note that dust collects on surfaces over time, so even though a laboratory space may be contaminated even though it has not been used for some time. It is usually enough to wipe equipment and surfaces down with a laboratory wipe and deionized or milliQ water followed by either ethanol or isopropanol.
- Yield. We have performed the assay with 0.5-5 μg DNA and have always measured 8-oxo-dGuo above the assay’s limit of quantification. Nevertheless, one should always attempt to use as much DNA as possible (up to 5 μg) to ensure that there is enough measureable 8-oxo-dGuo. Regarding DNA yield: We have obtained an average of ~3 μg DNA per 106 cells from a multiple myeloma cell line using the DNeasy kit.
- Replicates. One should optimally have three technical replicates per sample. Thus, when analyzing 5 μg DNA, one should have at least 15 μg for three runs of 5 μg each. Additionally, one should always perform three independent experiments. Thus, one should have 3 x 15 μg per result.
- Quantification. Although it is possible to normalize the amount of 8-oxo-dGuo measured to μg DNA used in the initial hydrolysis reaction, it is more accurate and reproducible to compare 8-oxo-dGuo per (106) deoxynucleoside. This involves a single additional step and no extra material.
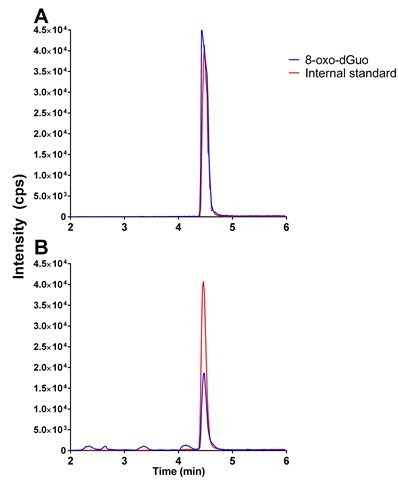
Figure 1. Typical chromatograms in 8-oxo-dGuo analysis. A. 50 nM 8-oxo-dGuo and 10 nM internal standard dissolved in 5% methanol in water. B. 8-oxo-dGuo from 5 μg commercially obtained salmon sperm DNA containing 10 nM internal standard.
Note that the peaks that don’t co-elute with the internal standard are discarded as contaminants.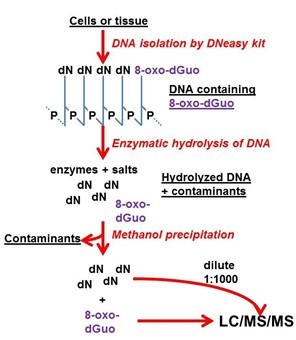
Figure 2. Visualized summary of the method.
Acknowledgments
This protocol is adapted from Sousa et al. (2013).
References
- Delaney, S., Jarem, D. A., Volle, C. B. and Yennie, C. J. (2012). Chemical and biological consequences of oxidatively damaged guanine in DNA. Free Radic Res 46(4): 420-441.
- Dong, M., Wang, C., Deen, W. M. and Dedon, P. C. (2003). Absence of 2'-deoxyoxanosine and presence of abasic sites in DNA exposed to nitric oxide at controlled physiological concentrations. Chem Res Toxicol 16(9): 1044-1055.
- Dong, M. and Dedon, P. C. (2006). Relatively small increases in the steady-state levels of nucleobase deamination products in DNA from human TK6 cells exposed to toxic levels of nitric oxide. Chem Res Toxicol 19(1): 50-57.
- Galashevskaya, A., Sarno, A., Vagbo, C. B., Aas, P. A., Hagen, L., Slupphaug, G. and Krokan, H. E. (2013). A robust, sensitive assay for genomic uracil determination by LC/MS/MS reveals lower levels than previously reported. DNA Repair (Amst) 12(9): 699-706.
- Hamilton, M. L., Guo, Z., Fuller, C. D., Van Remmen, H., Ward, W. F., Austad, S. N., Troyer, D. A., Thompson, I. and Richardson, A. (2001). A reliable assessment of 8-oxo-2-deoxyguanosine levels in nuclear and mitochondrial DNA using the sodium iodide method to isolate DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 29(10): 2117-2126.
- Sousa, M. M., Zub, K. A., Aas, P. A., Hanssen-Bauer, A., Demirovic, A., Sarno, A., Tian, E., Liabakk, N. B. and Slupphaug, G. (2013). An inverse switch in DNA base excision and strand break repair contributes to melphalan resistance in multiple myeloma cells. PLoS One 8(2): e55493.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2013 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Sarno, A. (2013). Genomic 8-oxo-7,8-dihydro-2'-deoxyguanosine Quantification. Bio-protocol 3(17): e878. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.878.
Category
Cancer Biology > General technique > Biochemical assays > DNA structure and alterations
Biochemistry > Other compound > Reactive oxygen species
Molecular Biology > DNA > DNA damage and repair
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link