- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Evaluation of Anticancer activity of Silver Nanoparticles on the A549 Human Lung Carcinoma Cell Lines through Alamar Blue Assay
Published: Vol 9, Iss 1, Jan 5, 2019 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3131 Views: 14709
Reviewed by: Prashanth N SuravajhalaNagendra KaushikAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols
Phagocytosis Assay to Measure Uptake of Necroptotic Cancer Cells by BMDCs
Tania Løve Aaes [...] Peter Vandenabeele
Nov 5, 2016 13339 Views
An Image-based Assay for High-throughput Analysis of Cell Proliferation and Cell Death of Adherent Cells
Paula Szalai and Nikolai Engedal
May 5, 2018 10975 Views
Real-time IncuCyte® Assay for the Dynamic Assessment of Live and Dead Cells in 2D Cultures
Arlene K. Gidda [...] Sharon M. Gorski
Feb 5, 2025 2799 Views
Abstract
Silver nanoparticles have been widely studied to possess antimicrobial as well as anticancer activity, and have found its applications in various fields including pharmaceutical industry, diagnostics, drug delivery, food industry, and others. For this purpose, several cell proliferation assays are widely used for the evaluation of anticancer activity of synthetic compounds as well as natural plant extracts. In general, a compound is said to possess an anticancer activity if it prevents the cancer cells to grow and divide actively, and indirectly activates the generic program of cell death. In this protocol, Alamar blue and MTT assay are described for the analysis of metabolic function and health of the cell. These procedures are generally used for the endpoint analysis. A549 cells are seeded in a 96-well plate, and after the adherence of the cells, they are treated with different concentrations of silver nanoparticles. Followed by 24 h of incubation, colorimetric dyes are added to the wells, and the absorbance is recorded to quantify the percentage cytotoxicity in the sample wells.
Keywords: Silver nanoparticlesBackground
Alamar blue has been commonly used for cell viability and cytotoxicity studies in various biological and environmental systems. There are several other commercially available tetrazolium salts that are frequently used as an indirect measure for viable cells. Some of them includes 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT), 4-[3-(4-iodophenyl)-2-(4-nitrophenyl)-2H-5-tetrazolio]-1,3-benzene disulfonate sodium, 3’-[1-phenylamino)-carbonyl]-3,4-tetrazolium]-bis (4-methoxy-6-nitrobenzene) sulfonic acid hydrate (XTT), and water-soluble tetrazolium salt (WST-1). Besides, Alamar blue and MTT are considered to be the most appropriate, reliable and economic methods. These offer certain advantages including ease of use, increased sensitivity and accuracy, rapid indication of cell toxicity. Both are employed on colorimetric detection of the number of viable cells based on the cellular metabolism activity.
Resazurin, an active component in Alamar blue assay monitors the reducing environment of living cell. The dye acts as an electron acceptor in electron transport chain without disrupting the normal transfer of electrons. As soon as the dye accepts the electrons, it gets reduced to pink color, fluorescent resorufin state. The change in the reduced state can be quantitatively measured spectrophotometrically by recording the absorbance at 570 and 600 nm wavelengths (Rampersad, 2012). Fluorescent signals can also be determined at an excitation wavelength of 530-560 nm and emission wavelength of 590 nm. In the current protocol, anticancer activity of silver nanoparticles was evaluated in A549 lung carcinoma cell lines through Alamar blue assay (Figure 1 A; Kumari et al., 2016; Arya et al., 2018).
In MTT assay (Figure 1 B), the tetrazolium salt is reduced to insoluble formazan dye by dehydrogenase enzyme present in the viable cells at 37 °C. Further, the insoluble formazan salt is dissolved by the addition of solubilizing agents, and the colored product is quantitatively measured spectrophotometrically. The dead cells lose the ability to reduce tetrazolium salts and fail to convert into colored formazan products. Thus, the intensity of the colored product is directly proportional to the number of viable cells present in the culture (Präbst et al., 2017). 
Figure 1. Schematic representation of general procedure for cytotoxicity assays using either Alamar blue (A) or MTT reagent (B)
Materials and Reagents
- Materials
- Pipette tips (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog numbers: 90030130-P, 90030230-C)
- 96-well tissue culture plates (Himedia, catalog number: TPP96 1X100NO)
- Tissue Culture Flask with filter caps (TPP, catalog number: 90026)
- Sterile 15 ml centrifuge tubes (Abdos, catalog number: P10402)
- 0.22 µm filter (Himedia, catalog number: SF9 1X75NO)
- Cells
A549 Human lung carcinoma cell lines (NCCS)
Note: These cell lines are cultured in complete medium containing DMEM media with 10% FBS, 1% pen-strep and are maintained at 37 °C, 5% CO2 in an incubator. - Reagents
- DMEM medium (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 12100046)
- Penicillin-Streptomycin (Pen-Strep) (Himedia, catalog number: A007)
- Fetal Bovine Serum (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 11573397)
- 0.25% Trypsin-EDTA (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 25200056)
- Dulbecco’s Phosphate Buffer Saline (Himedia, catalog number: TL1022)
- Resazurin sodium salt (Alamar Blue) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: R7017)
- MTT (Himedia, catalog number: TC247 5X30MG)
- Dimethylformamide solution (Sisco Research Laboratories, catalog number: 16616)
- Glacial acetic acid (Sisco Research Laboratories, catalog number: 90868)
- Sodium dodecyl sulfate (Sisco Research Laboratories, catalog number: 32096)
- Resazurin (0.15 mg/ml) stock solution in PBS (see Recipes)
Note: Resazurin is a light-sensitive dye, so should be stored in the dark. - MTT solution (5 mg/ml) in PBS (see Recipes)
Note: It should be light protected, and stored at -20 °C for long-term storage. - Solubilization buffer (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Micropipettes (SL-20,SL-200, SL-1000, Rainin)
- Balance (XB 220A Precisa, UK)
- Hemocytometer (Marienfeld, catalog number: 0610010)
- CO2 Incubator (Panasonic, Multigas Incubator)
- Biosafety cabinet level 2 (CHC Lab, CHC-777A2-04 Biolus)
- Inverted Microscope (Zeiss, Primovert)
- Benchtop centrifuge (Remi)
- Elisa Plate Reader (Thermo Scientific, Thermo Multiskan GO)
- U.V. Visible Spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific, model: Evolution 201)
Procedure
- Alamar blue assay
- Harvest the cells when they are in log phase of growth and count the cells using a hemocytometer when the cells in the flask are confluent (Figure 2).
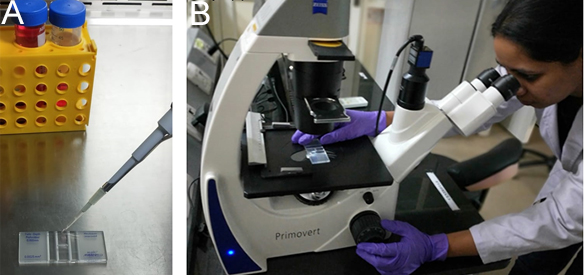
Figure 2. Cell counting. A. Load the hemocytometer chamber by pipetting the cell suspension under the coverslip. B. Place the hemocytometer under the microscope and count the cells. - Seed the cells in a 96-well plate at a cell density of 1 x 104 cells per well in 100 µl complete medium, so that 70-80% confluency will be attained after 1 day (Figure 3).
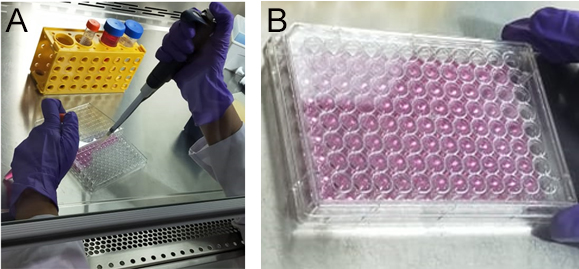
Figure 3. Cell seeding. A. Dilute and seed the wells to a cell density of 1 x 104 cells. B. The figure represents a complete seeded micro-well plate. - Keep the seeded plate in a CO2 incubator at 37 °C, 5% CO2, 95% humidity for 24 h to facilitate growth and adherence of cells to the plate surface (Figure 4).

Figure 4. Incubate the 96-well plate in a CO2 incubator - Wash each well twice with 1x PBS and treat the cells with different concentrations of silver nanoparticles in 100 µl complete medium. Include proper controls of blank medium, untreated seeded wells. Incubate the cells for another 24 h in an incubator (Figure 5).
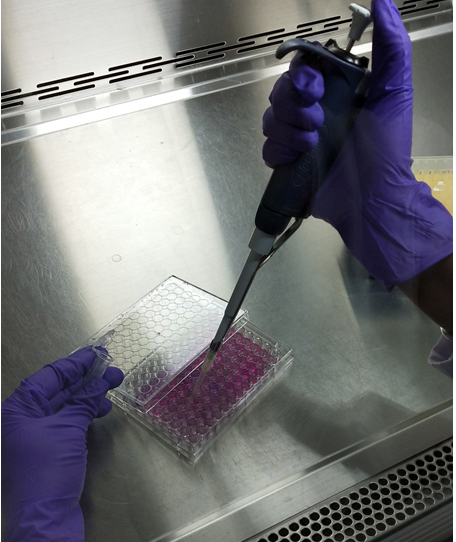
Figure 5. Treatment of cells with silver nanoparticles - Add Alamar blue aseptically in an amount equal to 10% volume of the wells (Figure 6).
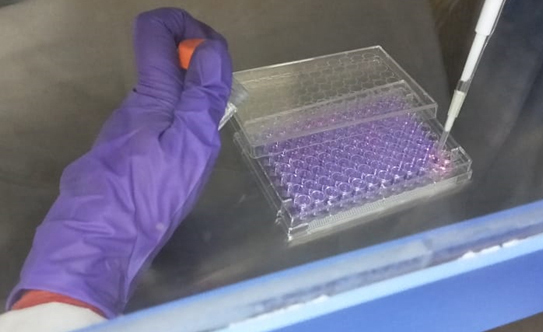
Figure 6. Add Alamar blue to each well - Incubate it for 2-4 h in a CO2 incubator. The optimum incubation time varies with cell type and seeding density.
- Determine the cell toxicity and proliferation by recording the absorbance at wavelength 570 nm and 600 nm after incubation. Complete media without cells, including Alamar blue, should be considered as blank (Figure 7).
Spectrophotometric determination of cell proliferation through Alamar blue assay
The difference in percentage reduction of cells between treated and control cells: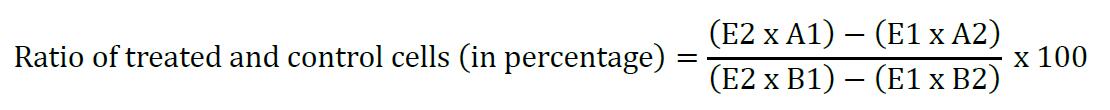
where,
E1 = Molar extinction coefficient (E) of oxidized Alamar blue at 570 nm, 80586
E2 = Molar extinction coefficient of oxidized Alamar blue at 600 nm, 117216
A1 = Absorbance of sample wells at 570 nm
A2 = Absorbance of sample wells at 600 nm
B1 = Growth control absorbance at 570 nm
B2 = Growth control absorbance at 600 nm
Fluorescence-based measurement of cell toxicity through Alamar blue assay
Observe the fluorescence at excitation and emission wavelength of 560 and 590 nm respectively.

Figure 7. Absorbance recorded through Elisa plate reader
- Harvest the cells when they are in log phase of growth and count the cells using a hemocytometer when the cells in the flask are confluent (Figure 2).
- MTT assay
- Freshly harvest the cells in cell culture flask and count the cells using a hemocytometer when the cells in the flask become confluent.
- Seed the cells in a 96-well microplate at a cell density of 1 x 104 with 100 µl complete medium per well.
- Incubate the plate at 5% CO2, 37 °C, 95% humidity for 24 h till the culture in the plate is 70%-80% confluent.
- Wash each well with 1x PBS and treat the cells with varying concentrations of silver nanoparticles. Take proper controls, including blank and untreated wells. Keep the plate in the incubator for another 24 h.
- Add MTT reagent to an amount equal to 10% of the total volume of wells. For a total volume of 100 µl, add 10 µl of MTT reagent to the wells, including the controls.
- Incubate the plate for 2-4 h again (Incubation time varies with the type of cell lines used for the study).
- After the formation of formazan crystals during incubation, add 100 µl of solubilization buffer to the wells.
- Stir gently to ensure proper solubilization.
- Record the absorbance at 570 nm using spectrophotometer or ELISA plate reader. Measure the reference wavelength higher than 650 nm to calculate the background noise of cell debris and undissolved particles.
Spectrophotometric determination of cell proliferation through MTT assay
- Merits and Limitations
MTT method is an endpoint analysis method, though it is one of the most widely investigated methods, it has limitations owing to its cytotoxic nature. It has been reported that the formed formazan crystals puncture the cell membrane during exocytosis, thus harming the cell. On the contrary, Alamar blue allows certain advantages over MTT assay including time course measurement analysis, increased sensitivity and accuracy, no cell lysis and is suitable for post-measurement functional studies. A basic disadvantage of using tetrazolium and resazurin dye for the evaluation of cytotoxicity is there need to incubate the cells with these reduction dyes to produce the signals. This tends to result in an increased probability of occurrence of artifacts due to the interaction between the test compound, chemical used for the assay and the cell biochemistry.
Data analysis
The % Reduction of Alamar blue is calculated as per the formula described in previous section.
An example is shown in the following:
E1 = 80586
E2 = 117216
A1 = 0.53
A2 = 0.25
B1 = 0.82
B2 = 0.13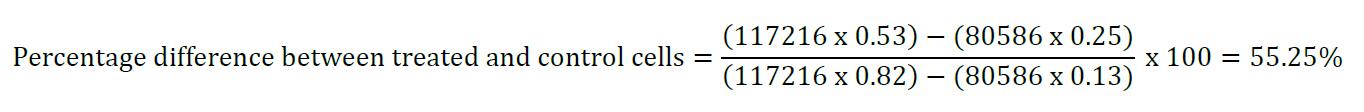
This represents the amount of reduction in treated wells is 55.25% as compared with the control wells. In other words, the cell growth has been inhibited by 44.4% by the test compound, indicating its anticancer activity at a particular concentration.
Notes
- All the experiments should be done in duplicates to obtain the statistically significant data, i.e., P ≤ 0.05.
- Optimize factors such as plating density, incubation time before starting any experiment because incubation time and cell density varies with the type of cell lines used for the study.
Recipes
- Resazurin (0.15 mg/ml) stock solution in PBS
- Weigh 1.5 mg resazurin in a 15 ml sterile centrifuge tube and add 10 ml sterile PBS to it
- Rotate the tube until the resazurin gets completely dissolved
- Filter sterilize the stock solution into a new 15 ml sterile centrifuge tube
- The stock solution should be kept at 2-8 °C for long-term storage
- MTT solution (5 mg/ml) in PBS
- Dissolve 5 mg MTT in 1 ml of Dulbecco’s Phosphate Buffer Saline, pH 7.4
- Filter sterilize the MTT solution through a 0.22 µm filter into a fresh sterile container
- Store the solution at -20 °C for long-term storage and at 4 °C for frequent use
- Solubilization buffer
- Make 40% (v/v) Dimethylformamide (DMF) solution in 2% (v/v) glacial acetic acid
- Add 16% (w/v) Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) to the solution, and mix it properly
- Adjust the pH of the whole solution to 4.7
- To avoid the precipitation of SDS, store the buffer at room temperature
Acknowledgments
Surendra Nimesh acknowledges the financial assistance from Department of Biotechnology (DBT), (grant No. 6242-P82/RGCB/PMD/DBT/SNMH/2015) Government of India. This protocol has been modified from one of our previous publication in Arya et al. (2018). Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 46(5): 985-993.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no conflicting interests.
References
- Arya, G., Kumari, R. M., Gupta, N., Kumar, A., Chandra, R. and Nimesh, S. (2018). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Prosopis juliflora bark extract: reaction optimization, antimicrobial and catalytic activities. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 46(5): 985-993.
- Kumari, R. M., Thapa, N., Gupta, N., Kumar, A. and Nimesh, S. (2016). Antibacterial and photocatalytic degradation efficacy of silver nanoparticles biosynthesized using Cordia dichotoma leaf extract. Advances in Natural Science: Nanoscience and Nanotechnology 7(4) 045009.
- Präbst, K., Engelhardt, H., Ringgeler, S. and Hubner, H. (2017). Basic colorimetric proliferation assays: MTT, WST, and resazurin. Methods Mol Biol 1601: 1-17.
- Rampersad, S. N. (2012). Multiple applications of Alamar Blue as an indicator of metabolic function and cellular health in cell viability bioassays. Sensors (Basel) 12(9): 12347-12360.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2019 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Sharma, N., Arya, G., Kumari, R. M., Gupta, N. and Nimesh, S. (2019). Evaluation of Anticancer activity of Silver Nanoparticles on the A549 Human Lung Carcinoma Cell Lines through Alamar Blue Assay. Bio-protocol 9(1): e3131. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3131.
Category
Cancer Biology > Cell death > Cell biology assays > Cell viability
Cell Biology > Cell viability > Cell death
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link









