- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Lipidomic Analysis of Caenorhabditis elegans Embryos
Published: Vol 7, Iss 18, Sep 20, 2017 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2554 Views: 11350
Reviewed by: Neelanjan BoseLu HanTanxi Cai

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols
Total Triglyceride Quantification in Caenorhabditis elegans
Anjali Sandhu and Varsha Singh
Nov 20, 2020 5211 Views
Oil Red O Staining for Lipid Content in Caenorhabditis elegans
Feng-Yung Wang and Tsui-Ting Ching
Aug 20, 2021 7617 Views

Rapid Lipid Quantification in Caenorhabditis elegans by Oil Red O and Nile Red Staining
Nicole L. Stuhr [...] Sean P. Curran
Mar 5, 2022 8373 Views
Abstract
Metabolomic is an emerging field of system biology. Lipidomic, a branch of metabolomic, aims to characterize lipophilic metabolites in biological systems. Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans) is a genetically tractable and versatile animal model for novel discovery of lipid metabolism. In addition, C. elegans embryo is simple and homogeneous. Here, we demonstrate detailed procedures of C. elegans culture, embryo isolation, lipid extraction and metabolomic data analysis.
Keywords: C. elegansBackground
The metazoan model Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans) offer a unique platform to discover novel functions and biological roles of metabolic enzymes. Current studies of genomic, transcriptomic and proteomic have advanced our understanding to appreciate the complexity of metabolic networks in C. elegans (Watson et al., 2015). Metabolomic is an emerging tool of system biology aiming to determine small molecule metabolites within biological systems. A number of C. elegans studies have used different metabolomic approaches, including nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, gas/liquid chromatography coupled mass spectrometry (GC/LC-MS), to dissect the metabolic networks in whole worm (Atherton et al., 2008; Hughes et al., 2009; Castro et al., 2012; Patti et al., 2014; Morgan et al., 2015; Wang et al., 2015; Wan et al., 2017). Currently, there is no metabolomic-based approach to characterize the lipid metabolites in C. elegans embryos. In this study, LC-MS-based untargeted lipidomic method is chosen for several reasons. First, LC-MS is sufficiently sensitive to analyze small quantity of C. elegans embryos. Second, untargeted metabolomic provides an unbiased view of detectable metabolites, which is crucial to generate a large amount of information. Subsequently, a hypothesis can be formulated based on the global metabolomic analysis. Last but not least, C. elegans embryo is considered simple and homogeneous compared to the whole worm. Taken together, these technical advantages provide opportunities for in-depth analysis of lipid metabolism in developing C. elegans embryos.
Materials and Reagents
- C. elegans culture
- Aluminum foil
- Autoclave tape (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 15904 )
- 90 x 15 mm disposable plastic Petri dishes (China biotech corporation)
- 14 ml polypropylene round-bottom tubes (Corning, Falcon®, catalog number: 352059 )
- 15 ml centrifuge tubes (Corning, catalog number: 430791 )
- 50 ml centrifuge tubes (Corning, catalog number: 430829 )
- 250 ml NalgeneTM PPCO centrifuge bottles (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: 3120-0250 )
- Microcentrifuge tube (Corning, Axygen®, catalog number: MCT-150-C )
- Glass slide
- 0.3 mm diameter platinum/iridium wire (Shineteh Instruments)
- 0.22 μm pore size syringe filter unit (EMD Millipore, catalog number: SLGP033RB )
- C. elegans N2 (wild type strain)
- C. elegans control-RNAi (Mock) and G6PD-RNAi (Gi) adults and embryos
- E. coli OP50 (University of Minnesota, C. elegans Genetics Center)
- E. coli HT115(DE3) harboring control-RNAi (Mock) and G6PD-RNAi (Gi) plasmids
Note: The details of these plasmids, including design and construction, are described in a previous report (Yang et al., 2013). - Ultrawater
- Bleach (NaOCl) (Clorox)
- Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) (Merck, catalog number: 1064980500 )
- M9 buffer
- Sodium chloride (NaCl) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 31434-5KG-R )
- Agar (BioShop, catalog number: AGR001.1 )
- Peptone (Oxoid, catalog number: LP0037 )
- Potassium phosphate dibasic (K2HPO4) (Merck, catalog number: 1051041000 )
- Potassium phosphate monobasic (KH2PO4) (Avantor Performance Materials, J.T. Baker, catalog number: 3246-05 )
- Cholesterol (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: C8667-5G )
- Ethanol (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 32221-2.5L )
Note: This product has been discontinued. - Magnesium sulfate (MgSO4) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M2643-500G )
- Calcium chloride dihydrate (CaCl2·2H2O) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: C3881-500G )
- Tetracyclin-hydrochloride (Boehringer Mannheim)
- Carbenicillin disodium salt (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: C1389-5G )
- Ampicillin sodium salt (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A9518-25G )
- Isopropyl-b-D-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) (BioShop, catalog number: IPT001.50 )
- LB broth (BD, DifcoTM, catalog number: 244610 )
- Nematode growth medium (NGM) (see Recipes)
- 1 M KPI buffer pH 6.0 (see Recipes)
- 5 mg/ml cholesterol (see Recipes)
- 1 M MgSO4 (see Recipes)
- 1 M CaCl2 (see Recipes)
- 10 mg/ml tetracycline-hydrochloride (see Recipes)
- 25 mg/ml carbenicillin (see Recipes)
- 200 mg/ml ampicillin (see Recipes)
- 1 M IPTG (see Recipes)
- C. elegans sample preparation
- Falcon cell-strainer cap (12 x 75 mm) (Corning, Falcon®, catalog number: 352235 )
- Pyrex glass tube (20 x 125 mm) (Corning, PYREX®, catalog number: 9826-20 )
- Glass Pasteur pipettes (Kimble Chase Life Science, catalog number: 63A54 )
- Glass organic solvent-resistant pipette tips (HBG, catalog number: 1010-19 )
- Organic solvent-resistant polypropylene tip (Gilson, catalog number: F161110 )
- Organic solvent-resistant polypropylene microcentrifuge tube (STARLAB INTERNATIONAL, catalog number: S1615-5500 )
- HPLC vial (WATERS, catalog number: 186000272C )
- Chloroform (LC grade) (Merck, catalog number: 1024444000 )
- Methanol (HPLC grade) (Avantor Performance Materials, J.T. Baker, catalog number: 9093 )
- Chromasolv grade water (H2O) (Sigma-Aldrich, Fluka ,catalog number: 39253-1L-R )
- Chromasolv grade acetonitrile (ACN) (Avantor Performance Materials, J.T. Baker, catalog number: 9829-03 )
- Chromasolv grade isopropanol (Sigma-Aldrich, Fluka, catalog number: 34965-2.5L )
- Ammonium formate (Fluka, catalog number: 70221 )
- Formic acid (Sigma-Aldrich, Fluka, catalog number: 56302 )
- Falcon cell-strainer cap (12 x 75 mm) (Corning, Falcon®, catalog number: 352235 )
Equipment
- Pyrex narrow mouth Erlenmeyer flasks (Corning, PYREX®, catalog number: 4980-1L )
- Lamina flow hood (Chin-Chih H&W ENTERPRISE, catalog number: BSC-4 )
- 20 °C incubator (Firstek, catalog number: RI-560 )
- 37 °C incubator with shaker (Yihder, catalog number: LM-570RD )
- Centrifuge (Beckman Coulter, model: Avanti® J-26XP )
- Rotor (Beckman Coulter, model: JA-14 )
- Stereomicroscope (Nikon Instruments, model: SMZ745 )
- Stainless steel surgical blade (No. 10) and holder (Feather Safety Razor, Japan)
- Vorterxer (Scientific Industries, model: Vortex-Genie 2 )
- Centrifuge (Eppendorf, model: 5810 R )
- High-capacity swing-bucket rotor with four 250 ml buckets (Eppendorf, model: A-4-62 )
- -80 °C freezer
- 100 ml glass beaker (Corning, PYREX®, catalog number: 1000-100 )
- Macropipette (Socorex, catalog number: 835.05 )
- Sonicator (Sonics & Materials, model: VCX 400 )
- Ultrasonic cleaner (Delta, model: DC200H )
- Nitrogen gas spray unit for aluminum block bath evaporation head (TAITEC, model: DTU-2B )
- Centrifuge (Eppendorf, model: 5427 R )
- Acquity CSH C18 column (particle size of 1.7 μm, 2.1 x 100 mm) (WATERS, catalog number: 186002352 )
- Ultra-performance liquid-chromatography (UPLC) system (WATERS, catalog numbers: 176001285 , 700003616 , 700002764 )
- SYNAPT G1 HDMS system (WATERS)
- Autoclave (Tomin Medical Equipment, catalog number: TM-328 )
- 4 °C cooling cabinet (Firstek, catalog number: CC-2 )
Software
- MassLynx4.1 (WATERS)
- Extended Statistics (EZinfo, WATERS)
- MetaboAnalyst (http://www.metaboanalyst.ca)
Procedure
- C. elegans media preparation
- Prepare NGM media (see Recipes) in a 1 L flask (see Note 1).
- Cover and seal the opening of the flask with two layers of aluminum foil, use a short stretch (2 cm) of autoclave tape to mark on top of aluminum foil.
- Autoclave NGM media, MgSO4, CaCl2 and KPI solutions (see Recipes) (see Note 2).
- Cool media to ~65 °C and add MgSO4, CaCl2, KPI, cholesterol (see Recipes) (see Note 3).
- For regular NGM agar plates: pour 20 ml media into each 90 mm Petri dish.
- For RNAi NGM agar plates: pour 20 ml media (supplemented with carbenicillin, tetracycline and IPTG [(see Recipes)] into each 90 mm Petri dish.
- Allow agar plates to solidify and dry overnight in a lamina flow hood at room temperature (see Note 4).
- Inoculate a single bacterial colony of OP50 or HT115(DE3) to 1 ml of LB (for HT115(DE3): 200 μg/ml ampicillin was supplemented) (see Recipes) in a sterilized polypropylene round-bottom tube and grow for 6 h at 37 °C with shaking (200 rpm).
- Inoculate 1 ml of bacterial culture to 300 ml of autoclaved LB in a 1 L flask and grow for 16 h at 37 °C with shaking (200 rpm).
- Harvest the overnight culture in 250 ml centrifuge bottles (Nalgene) by centrifugation (4,000 x g, 20 min, 4 °C) (Beckman Coulter, Avanti J-26 XP), discard the supernatant.
- Resuspend the pellet with fresh LB to a final volume = 7.5 ml (see Note 5).
- Seed each regular NGM agar plate with 300 µl concentrated E. coli OP50 culture and spread with a sterilized stainless steel spreader (see Note 6).
- Seed each RNAi NGM agar plate with 300 µl concentrated E. coli HT115(DE3) culture supplemented with 200 µg/ml ampicillin and spread with a sterilized stainless steel spreader.
- Allow bacteria-seeded plates to dry overnight in a lamina flow hood at room temperature (see Note 7).
- C. elegans culture
- Use a sterilized surgical blade (passing over the flame of burner) to cut a small chunk of agar (chunking) from OP50 seeded-NGM agar plate containing larvae worms and transfer the chunk of agar to fresh OP50 seeded-NGM agar plate (see Note 8).
- Propagate the worms at 20 °C until sufficient gravid adults from offspring are obtained.
- Harvest gravid adults by washing the plates with autoclaved ultrawater and collect into a 15 ml centrifuge tube (see Note 9).
- Allow the worms settle and then remove the supernatant by aspiration.
- Perform hypochlorite bleach by adding 3.5 ml autoclaved ultrawater to resuspend the pellet.
- Add 0.5 ml of 5 N NaOH.
- Add 1 ml of 5% NaOCl (Bleach), total volume in the tube is 5 ml.
- Vortex the tube briefly and leave at room temperature for less than 5 min, vortex 5 sec every few minutes until the majority (80%) of worms are dissolved (observed under dissecting microscope).
- Immediately add 8 ml autoclaved ultrawater and invert the tube 5 times for mixing thoroughly.
- Centrifuge at 1,258 x g (Eppendorf, 5810 R) for 1 min and discard the supernatant.
- Resuspend the pellet with 10 ml autoclaved ultrawater and invert the tube 5 times.
- Centrifuge again at 1,258 x g for 1 min (Eppendorf, 5810 R), discard the supernatant and resuspend the pellet (eggs) with 2 ml M9 buffer.
- Incubate the egg suspension at 20 °C overnight with shaking (50 rpm) to obtain synchronized L1 worms.
- Aliquots L1 worms to RNAi NGM agar plates (see Note 10).
- Incubate the plates at 20 °C for 3 days to obtain Mock and G6PD-knockdown (Gi) adult worms (Figure 1A).
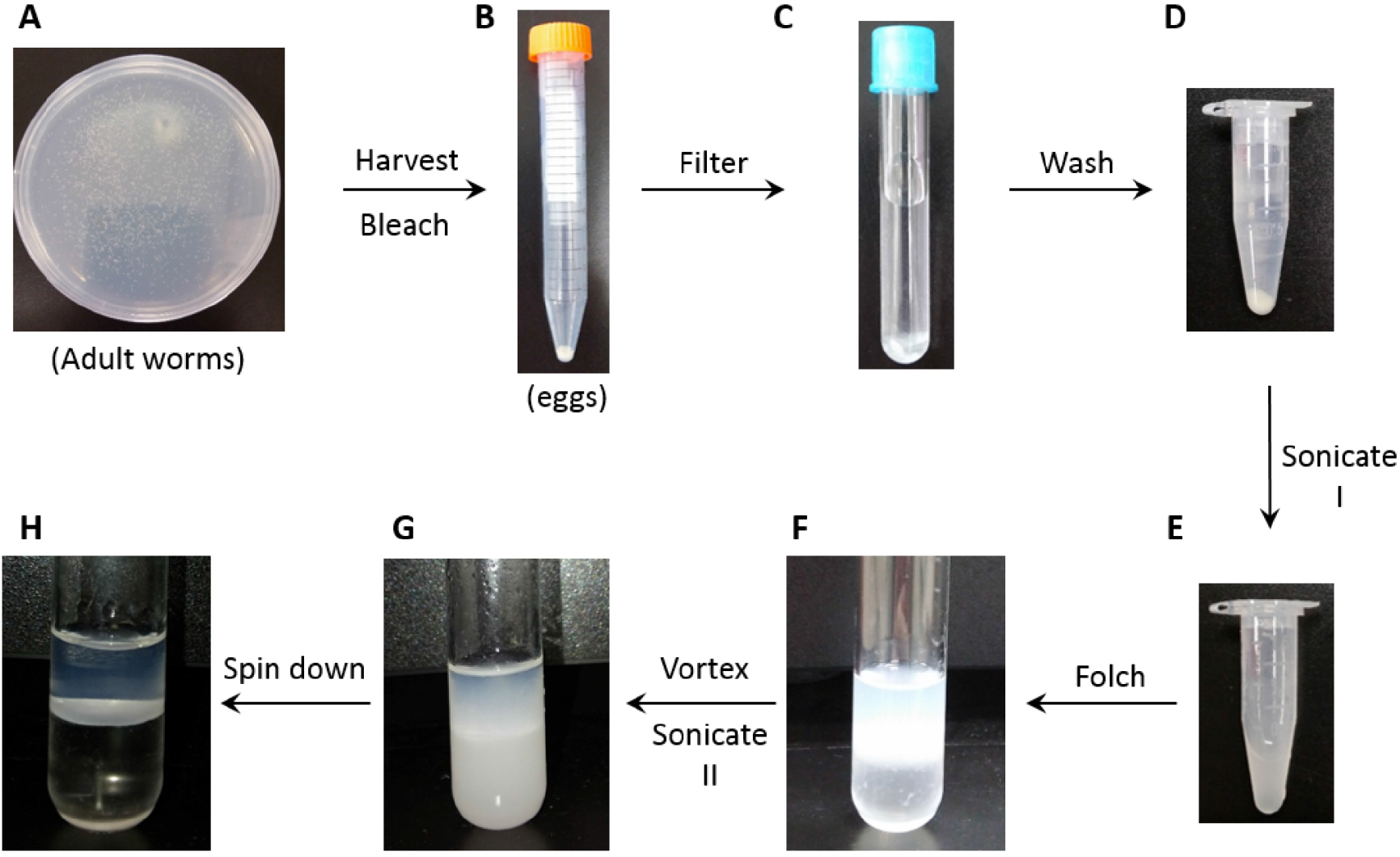
Figure 1. Representative images of sample preparation procedures. A. Worms grown on bacteria-seeded NGM plate at 20 °C for 3 days from synchronized L1. B. Washed eggs harvested in a 15 ml tube (as a pellet) from 5 NGM plates; C. Eggs filtered by Falcon cell-strainer cap; D. Washed eggs transferred to a microcentrifuge tube; E. Egg suspended in ultrawater after Sonication I (see step D2); F. Folch solution added to lysate in a glass tube; G. Initial phase separation formed after vortex and Sonication II (see step D7); H. Enhanced phase separation after centrifugation. - C. elegans sample preparation
- Four biological replicates of C. elegans gravid adults (see Note 11) are washed off from NGM plates by ultrawater (see Note 12). Place the 15 ml centrifuge tube on an ice bucket (see Note 13).
- Allow the worms to settle and remove the supernatant. Add 10 ml ultrawater to wash worms. Repeat this step to completely remove floating bacteria and eggs in the suspension.
- Perform hypochlorite bleach as described in previous section (steps B5-B11) (see Note 14).
- Centrifuge the tube at 1,258 x g for 1 min (Eppendorf, 5810 R), discard supernatant (Figure 1B).
- Add 1 ml ultrawater to suspend the eggs and keep the tube on ice.
- To filter the eggs, add 0.1 ml ultrawater to the top of Falcon cell-strainer cap to equilibrate the membrane.
- Once water is eluted from the membrane, transfer the egg suspension to the top of Falcon cell-strainer cap and allow to elute by gravity (Figure 1C).
- Add 1 ml ultrawater to wash the membrane.
- Centrifuge the tube at 1,258 x g for 5 min at 4 °C (Eppendorf, 5810 R). Discard the supernatant and the cap.
- Add 1 ml ultrawater to the tube and transfer the suspension to a microcentrifuge tube.
- Add additional 0.1 ml ultrawater to wash the tube and pool all suspension together in a microcentrifuge tube.
- Centrifuge the microcentrifuge tube at 1,258 x g for 5 min at 4 °C (Eppendorf, 5810 R).
- Aspirate the supernatant carefully (Figure 1D).
- Store the pellet in a -80 °C freezer until use (see Note 15).
- Four biological replicates of C. elegans gravid adults (see Note 11) are washed off from NGM plates by ultrawater (see Note 12). Place the 15 ml centrifuge tube on an ice bucket (see Note 13).
- Lipid extraction
- Thaw the pellet on ice and resuspend with 0.5 ml ultrawater.
- Perform sonication with samples (tube) being placed in a 100 ml glass beaker filled with ice.
- The sonication cycle is set at 2 sec pulse (frequency: 20 kHz; amplitude: 10%) and 5 sec interval, 20 cycles, total 40 sec (Sonicate I, Figure 1E).
- Transfer the supernatants to glass tubes with screw cap.
- Perform Folch extraction by adding 1 ml ultrawater to each glass tube, followed by adding 6 ml of chloroform/methanol (ratio = 2:1) mixture to each glass tube (see Note 16).
- Vortex each glass tube for 30 sec, repeated 4 times (see Note 17) (Figure 1F).
- Place the glass tubes on a test tube rack in an ultrasonic cleaner pre-filled with ice and water, sonicate the samples for 15 min (frequency: 40 kHz) (see Note 18) (Sonicate II, Figure 1G)
- Centrifuge the tubes at 1,258 x g for 15 min (Eppendorf, 5810 R) to further enhance phase separation (Figure 1H).
- Transfer the lower fraction (hydrophobic) to a clean glass tube by a glass Pasteur pipette (see Notes 19 and 20).
- Dry the lower fraction under nitrogen flow in a nitrogen evaporator (see Note 21).
- Store the dried pellet in a -80 °C freezer until use.
- Thaw the pellet on ice and resuspend with 0.5 ml ultrawater.
- Lipidomic analysis (see Note 22) (steps of lipidomic data analysis are summarized in Figure 2)
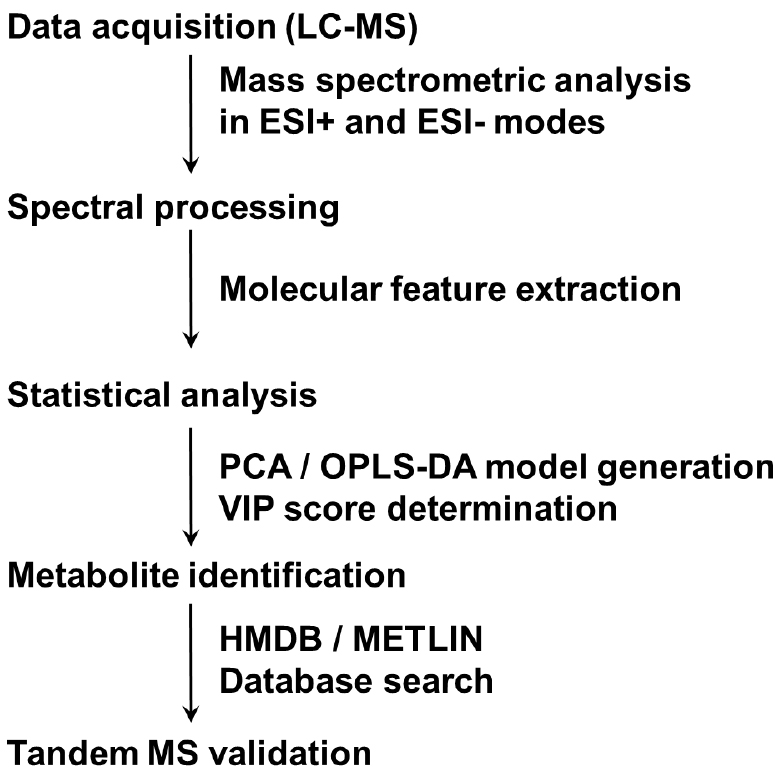
Figure 2. Summary of steps in lipidomic data analysis. A flow chart from sample separation to metabolites by tandem MS is presented.- Add 1,000 μl solvent (isopropanol/acetonitrile/water, 2/1/1, v/v/v) to the lower fraction. Vortex the glass tube for 30 sec, repeat 4 times. Transfer the supernatant to a new microcentrifuge tube (organic solvent-resistant) by using organic solvent-resistant tips and centrifuge at 15,294 x g for 15 min at 4 °C (Eppendorf, 5427 R). Transfer 800 μl supernatant to the HPLC vial for UPLC-qTOF/MS analysis.
- Each sample is carried out in three technical replicates for lipidomic profiling.
- Prepare mobile phase A (water:acetonitrile [60:40] supplemented with 10 mM ammonium formate and 0.1% formic acid).
- Prepare mobile phase B (isopropanol:acetonitrile [90:10] with 10 mM ammonium formate and 0.1% formic acid).
- Samples are injected and separated by using Acquity CSH C18 column.
- The column temperature is maintained at 55 °C, the flow rate is set at 0.4 ml/min.
- The solvent gradient is as follows: 0-2 min, 40-43% solvent B; 2-2.1 min, 43-50% solvent B; 2.1-12 min, 50-54% solvent B; 12-12.1 min, 54-70% solvent B; 12.1-18 min, 70-99% solvent B; 18-20 min, 99-40% solvent B.
- An injected volume of 1.5 μl sample is used in electrospray ionization (ESI) positive (+) mode, and 3 μl sample was used in ESI negative (-) mode (see Note 23).
- Mass spectrometric analysis is performed in both ESI+ and ESI- modes using the SYNAPT G1 HDMS system. The major parameter settings are as follows: The capillary and cone voltage are set at 3,000 V (2,000 V in ESI- mode) and 30 V, respectively. The desolvation gas flow rate is set at 800 L/h. The desolvation and source temperatures are 400 and 100 °C, respectively.
- Chromatograms are acquired over a range of m/z of 20-990 Da at a rate of 10 scans per second (see Note 24) (Figure 3).
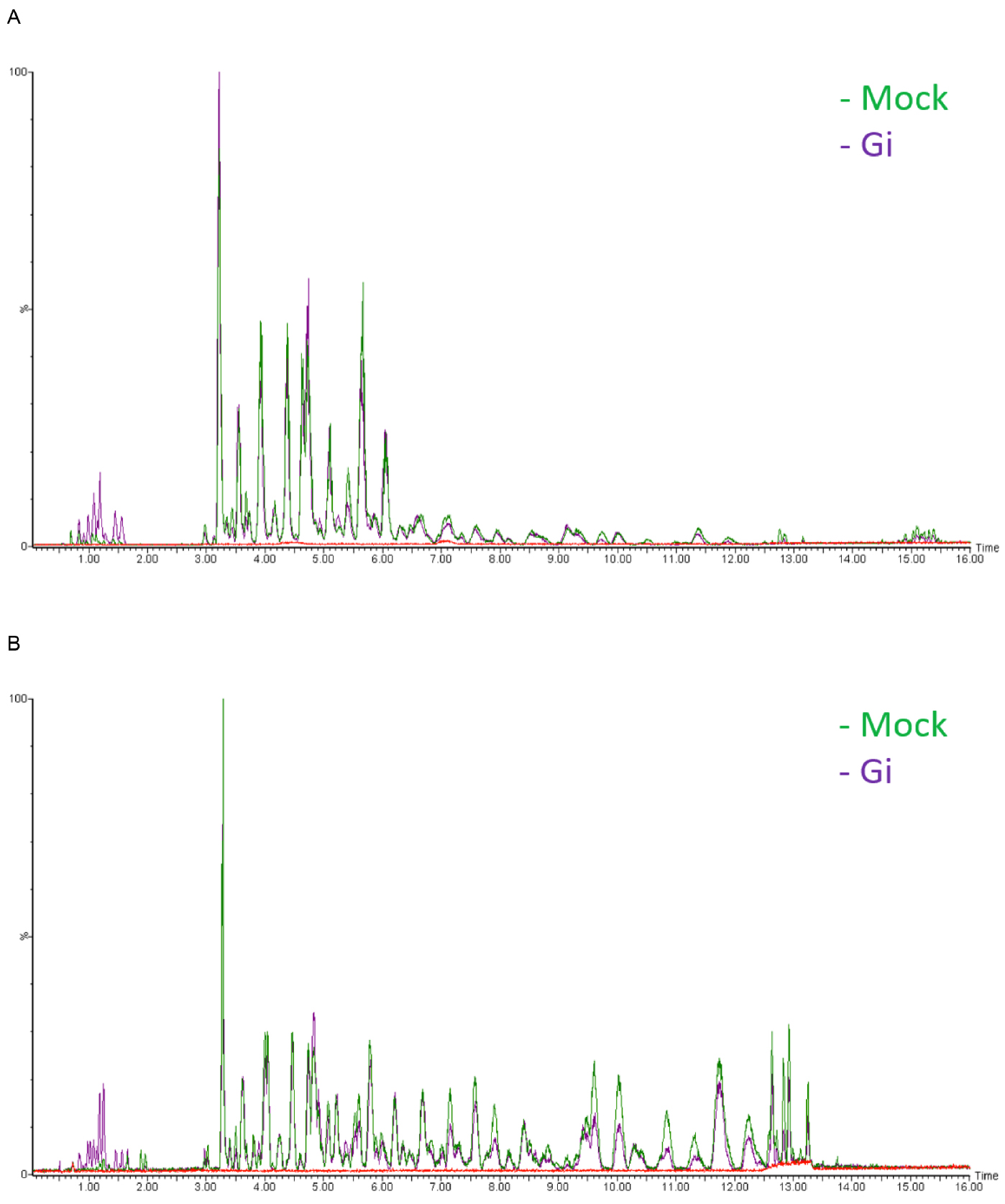
Figure 3. Base peak intensity (BPI) chromatograms of Mock and Gi embryos. A. ESI positive mode; B. ESI negative mode. The y axis represents relative intensity. Blank (solvent control, red line) is shown to indicate the base line. - Raw data are obtained in the centroid mode.
- The frequency of LockSpray is set at 0.5 sec per scan and corrected by averaging over 10 scans.
- Leucine encephalin (m/z 556.2771 for ESI+ and m/z 554.2615) in water/acetonitrile = 50/50 + 0.1% formic acid is used as LockSpray lockmass for exact mass measurement accuracy.
- Add 1,000 μl solvent (isopropanol/acetonitrile/water, 2/1/1, v/v/v) to the lower fraction. Vortex the glass tube for 30 sec, repeat 4 times. Transfer the supernatant to a new microcentrifuge tube (organic solvent-resistant) by using organic solvent-resistant tips and centrifuge at 15,294 x g for 15 min at 4 °C (Eppendorf, 5427 R). Transfer 800 μl supernatant to the HPLC vial for UPLC-qTOF/MS analysis.
Data analysis
- Use the molecular feature extraction function in MassLynx4.1 (WATERS) to extract information, including time-aligned ion features, mono-isotopic neutral mass, retention time as well as ion signal intensity, from raw data (see Note 25).
- The extracted data is further processed by the Extended Statistics (EZinfo, WATERS) to generate unsupervised principal component analysis (PCA) and orthogonal partial least-squares discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA) model (see Note 26) (Figure 4).
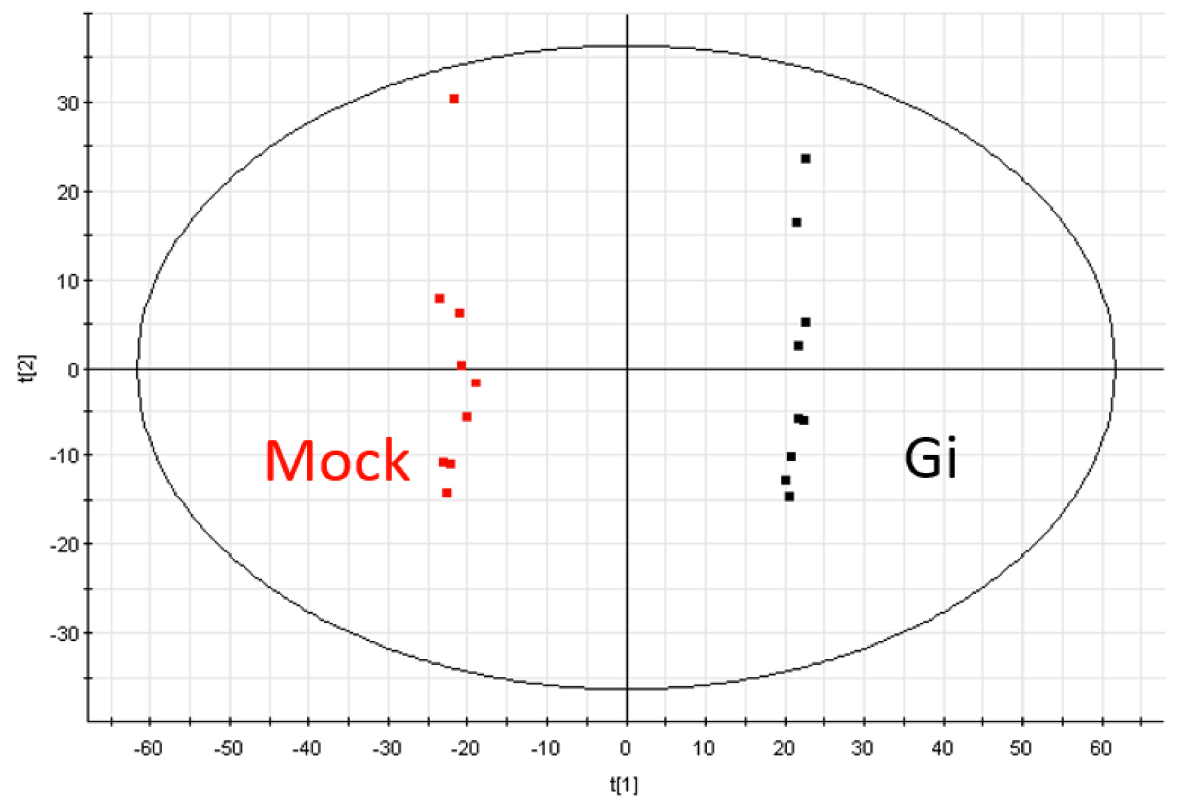
Figure 4. The principal component analysis (PCA) diagram of Mock and Gi embryos in ESI positive mode - From these models, the variable importance in the projection (VIP) score of each variable is obtained to represent its contribution to the grouping (see Note 27).
- High VIP score candidates are initially searched against Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) (http://www.hmdb.ca) and METLIN (http://metlin.scripps.edu/index.php) (see Note 28).
- Target candidates with high intensity (relative abundance above 200) are selected and validated by tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) with SYNAPT G1 HDMS system (WATERS) (see Note 29).
- MS/MS spectra are acquired and confirmed by METLIN (http://metlin.scripps.edu/index.php) and LIPID MAPS (http://www.lipidmaps.org/) as well as our in-house database for lipid standards.
Notes
- We prepare 500 ml of NGM media in a 1 L flask. If a smaller amount of NGM media is desired, flask size can be changed accordingly. Make sure not to fill media over 2/3 of the flask volume. Overfill media can lead to losing of volume due to spill over during autoclaving and is difficult to thoroughly mix by swirl.
- The sterilization cycle lasts 30 min at 121 °C. We usually take out the flask 1 h after sterilization (total time for autoclave is 2 h).
- We normally cool the flask (500 ml media) at room temperature for 30 min before adding supplements. Alternatively, the flask can be cooled in ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam ice bucket (4 L) filled with tap water for 10 min. However, it should be noted that both cooling methods require intermittent swirl and checking temperature through the hand touching by an experienced operator. For smaller volumes, it is recommended to shorten the cooling time accordingly.
- The plates are kept in a lamina flow hood (air flow is not required but can speed up the drying) to avoid contamination.
- The condensed culture can support sufficient worm growth up to 3 days (from L1 to gravid adult). The concentration factor is 40.
- We prefer to spread the bacterial lawn in rectangular shape and avoid touching the wall of plate. Keeping worms on the lawn can prevent losing worms (crawling on walls) upon harvest.
- The bacteria-seeded plates are kept in a lamina flow hood to avoid contamination. If the plates are still wet after overnight incubation, plates can be dried with extended time. Alternatively, turn on air flow to accelerate the drying of bacterial lawn in the lamina flow hood.
- It is recommended to perform chunking by using plates without contaminated bacteria or mold to avoid cross contamination. Alternatively, after chunking, allow the worms to crawl for a few hours and transfer them again to new plates by picking.
- A Petri dish (90 mm diameter) with as many gravid adults as possible yields high level of egg production.
- Prior to transferring L1 to RNAi plates, invert the tubes before each aspiration to obtain homogenous L1 suspension. Pipette a drop of suspension (10 μl) on a clean glass slide and count the number of worms in a drop. Make sure to transfer appropriate number of worms on a plate with sufficient food to sustain the growth for 3 days. Overcrowded worms consume bacteria rapidly and lead to starvation. Hence, it is highly recommended to determine the maximum number of worms that can grow for 3 days with enough food on one plate. We grow approximately 500 worms on a 300 μl concentrated bacterial culture-seeded RNAi plate.
- We harvest adult worms from 5 plates (90 mm) and pool them in a 15 ml centrifuge tube as one sample. In this case, the worms yield sufficient quantity of embryos to proceed metabolite extraction. 4 separate samples (N = 4) are prepared for each group.
- Use ultrawater only, because detergent (like Tween) contaminate the mass spectrometer system.
- Low temperature solution enhances the precipitation of worms.
- As the number of worms increases, the total bleaching time prolongs accordingly. Nevertheless, instead of increase the bleaching time, which may cause damage to embryos, we vortex the tube more frequently (10 sec every 30 sec) to enhance worm lysis and the release the embryos. It should be noted that worms exhibit embryonic lethality, such as G6PD-knockdown worms, due to the disruption of egg shell integrity (Yang et al., 2013; Chen et al., 2017). Hence the bleach should be done carefully to avoid the potential lysis of embryos. We recommend to examine the integrity of embryos under microscope.
- To ensure the consistency of metabolites extraction, samples collected at different date are extracted at the same day with the same batch of extraction solutions.
- The mixture of chloroform and methanol is prepared by mixing 2 volume of chloroform with 1 volume of methanol based on the total volume needed for the experiment. The ratio of chloroform, methanol and water is 8:4:3.
- An initial phase separation appears after the addition of chloroform and methanol mixture to the suspension.
- Sonication enhances the homogenization after vortex. It also removes the debris on the inner side of test tube wall.
- The lower fraction (hydrophobic) is lyophilized and stored for lipid-soluble metabolites analysis. The upper fraction (hydrophilic) can be lyophilized and stored for water-soluble metabolites analysis if desired.
- When aspirate the lower fraction, be careful not to disturb the middle protein layer, because the protein layer may be unstable and fall into the lower fraction. First, we carefully insert the tip of glass pipette into the lower fraction along the wall of glass tube and minimize touching the protein layer. Second, a minute amount of upper fraction fluid may fill in the front of glass pipette. We simply dispense it in the lower fraction forming ascending bubbles. This action avoids undesired contamination of hydrophilic metabolites.
- Upon completion of nitrogen evaporation, immediately cover the glass tube with screw cap to trap nitrogen gas as much as possible in the tube. Inert gas prevents unwanted chemical reactions, like oxidation, damaging the metabolites in the sample.
- The lipidomic profiling for UPLC-qTOF/MS analysis is modified from WATERS Application Note (720004107en).
- The detection of ESI- mode is less sensitive than that of ESI+ mode, hence, increased amount of sample is required for ESI- mode.
- We choose to show base peak intensity (BPI) chromatogram not total ion current (TIC) because BPI looks cleaner than TIC. Therefore, it is easier for us to identify the difference in peaks between sample groups.
- We obtain total features of 3,992 metabolites from ESI+ mode and 730 metabolites from ESI- mode.
- In addition to the commercial software, we also use MetaboAnalyst for the analysis and visualization of MS data sets in data matrices as well as generating PCA diagram.
- A higher VIP score represents a stronger contribution to discrimination between sample groups. We select candidates with VIP > 1.0 and obtain 848 metabolites from ESI+ mode and 198 metabolites from ESI- mode.
- When search lipid metabolites against Human Metabolome Database, we select the main adduct type as M+H and M-H for ESI+ and ESI- mode, respectively. The molecular weight tolerance is set as 0.01 Da. For searching the lipid classes, the ESI- mode provides more information on fragment ion property, for example, the composition of the fatty acids.
- Depend on the nature of compounds, the collision energy ranges from 6 to 32 V.
Recipes
- Nematode growth medium (NGM) media (for 0.5 L)
- Dissolve 1.5 g NaCl, 8.5 g agar, and 1.25 g peptone in 488 ml ultrawater (autoclave)
- Subsequently add 12.5 ml of 1 M KPI, 0.5 ml of 5 mg/ml cholesterol, 0.5 ml of 1 M MgSO4, 0.5 ml of 1 M CaCl2
- For growing E. coli HT115 strain harboring plasmid, 0.5 ml of 10 mg/ml tetracycline-hydrochloride, 1 ml of 25 mg/ml carbenicillin and 0.5 ml of 1 M IPTG are supplemented
- Dissolve 1.5 g NaCl, 8.5 g agar, and 1.25 g peptone in 488 ml ultrawater (autoclave)
- 1 M KPI buffer pH 6.0
- Dissolve 108.3 g KH2PO4 and 35.6 g K2HPO4 in 950 ml ultrawater
- Adjust pH (5.5) to pH 6.0 with 5 N KOH solution
- Adjust final volume to 1 L
- Autoclave, store at room temperature
- Dissolve 108.3 g KH2PO4 and 35.6 g K2HPO4 in 950 ml ultrawater
- 5 mg/ml cholesterol
Dissolve 0.2 g cholesterol in 40 ml ethanol
Note: Do not autoclave.
Store at room temperature - 1 M MgSO4
Dissolve 12.04 g MgSO4 in 100 ml ultrawater
Autoclave
Store at room temperature - 1 M CaCl2
Dissolve 14.7 g CaCl2 in 100 ml ultrawater
Autoclave
Store at room temperature - 10 mg/ml tetracycline-hydrochloride
Dissolve 150 mg tetracycline-hydrochloride in 15 ml ultrawater
Note: Do not autoclave.
Filter with 0.22 μm filter unit (Millipore)
Aliquot 1 ml to microcentrifuge tubes and store at -80 °C - 25 mg/ml carbenicillin
Dissolve 375 mg carbenicillin disodium salt in 15 ml ultrawater
Note: Do not autoclave.
Filter with 0.22 μm filter unit (Millipore)
Aliquot 1 ml to microcentrifuge tubes and store at -80 °C - 200 mg/ml ampicillin
Dissolve 3 g ampicillin in 15 ml ultrawater
Note: Do not autoclave.
Filter with 0.22 μm filter unit (Millipore)
Aliquot 1 ml to microcentrifuge tubes and store at -80 °C - 1 M IPTG
Dissolve 3.57 g IPTG in 15 ml ultrawater
Note: Do not autoclave.
Filter with 0.22 μm filter unit (Millipore)
Aliquot 1 ml to microcentrifuge tubes and store at -80 °C
Acknowledgments
This work was made possible by grants from the Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan (MOST103-2320-B-182-026-MY2 and MOST105-2320-B-182-031-MY2 to DTYC), from the Ministry of Education of Taiwan (EMRPD1E1751, EMRPD1G0181 and EMRPD1G0281 to DTYC), and from Chang Gung Memorial Hospital (BMRP098, CMRPD1F0621 and CMRPD1F0461 to DTYC). This protocol was modified from procedures published in Yang et al. (2013) and Chen et al. (2017).
References
- Atherton, H. J., Jones, O. A., Malik, S., Miska, E. A. and Griffin, J. L. (2008). A comparative metabolomic study of NHR-49 in Caenorhabditis elegans and PPAR-α in the mouse. FEBS Lett 582(12): 1661-1666.
- Castro, C., Sar, F., Shaw, W. R., Mishima, M., Miska, E. A. and Griffin, J. L. (2012). A metabolomic strategy defines the regulation of lipid content and global metabolism by Δ9 desaturases in Caenorhabditis elegans. BMC Genomics 13: 36.
- Chen, T. L., Yang, H. C., Hung, C. Y., Ou, M. H., Pan, Y. Y., Cheng, M. L., Stern, A., Lo, S. J. and Chiu, D. T. (2017). Impaired embryonic development in glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase-deficient Caenorhabditis elegans due to abnormal redox homeostasis induced activation of calcium-independent phospholipase and alteration of glycerophospholipid metabolism. Cell Death Dis 8(1): e2545.
- Hughes, S. L., Bundy, J. G., Want, E. J., Kille, P. and Sturzenbaum, S. R. (2009). The metabolomic responses of Caenorhabditis elegans to cadmium are largely independent of metallothionein status, but dominated by changes in cystathionine and phytochelatins. J Proteome Res 8(7): 3512-3519.
- Morgan, P. G., Higdon, R., Kolker, N., Bauman, A. T., Ilkayeva, O., Newgard, C. B., Kolker, E., Steele, L. M. and Sedensky, M. M. (2015). Comparison of proteomic and metabolomic profiles of mutants of the mitochondrial respiratory chain in Caenorhabditis elegans. Mitochondrion 20: 95-102.
- Patti, G. J., Tautenhahn, R., Johannsen, D., Kalisiak, E., Ravussin, E., Bruning, J. C., Dillin, A. and Siuzdak, G. (2014). Meta-analysis of global metabolomic data identifies metabolites associated with life-span extension. Metabolomics 10(4): 737-743.
- Wang, W., McReynolds, M. R., Goncalves, J. F., Shu, M., Dhondt, I., Braeckman, B. P., Lange, S. E., Kho, K., Detwiler, A. C., Pacella, M. J. and Hanna-Rose, W. (2015). Comparative metabolomic profiling reveals that dysregulated glycolysis stemming from lack of salvage NAD+ biosynthesis impairs reproductive development in Caenorhabditis elegans. J Biol Chem 290(43): 26163-26179.
- Wan, Q. L., Shi, X., Liu, J., Ding, A. J., Pu, Y. Z., Li, Z., Wu, G. S. and Luo, H. R. (2017). Metabolomic signature associated with reproduction-regulated aging in Caenorhabditis elegans. Aging (Albany NY) 9(2): 447-474.
- Watson, E., Yilmaz, L. S. and Walhout, A. J. (2015). Understanding metabolic regulation at a systems level: Metabolite sensing, mathematical predictions, and model organisms. Annu Rev Genet 49: 553-575.
- Yang, H. C., Chen, T. L., Wu, Y. H., Cheng, K. P., Lin, Y. H., Cheng, M. L., Ho, H. Y., Lo, S. J. and Chiu, D. T. (2013). Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency enhances germ cell apoptosis and causes defective embryogenesis in Caenorhabditis elegans. Cell Death Dis 4: e616.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2017 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Yang, H., Hung, C., Pan, Y., Lo, S. J. and Chiu, D. T. (2017). Lipidomic Analysis of Caenorhabditis elegans Embryos. Bio-protocol 7(18): e2554. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2554.
Category
Biochemistry > Lipid > Lipid measurement
Systems Biology > Metabolomics > Whole organism
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link









