- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Induction and Quantification of Patulin Production in Penicillium Species
Published: Vol 7, Iss 11, Jun 5, 2017 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2324 Views: 9066
Reviewed by: Zhaohui LiuAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols
Silencing Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungal Gene Using Chitosan Nanoparticle-Mediated dsRNA Delivery System
Chumei Yan [...] Xianan Xie
Jun 5, 2025 2630 Views
In Vitro Screening of Microbial Extracts Against the Oomycetes Phytophthora capsici and Pythium ultimum
Mónica Trigal Martínez [...] María Ángeles Vinuesa Navarro
Sep 20, 2025 1261 Views

A Reliable In Planta Inoculation and Antifungal Screening Protocol for Rhizoctonia solani-Induced Sheath Blight in Rice
Alinaj Yasin [...] Palash Deb Nath
Nov 5, 2025 1562 Views
Abstract
Patulin, a worldwide regulated mycotoxin, is primarily produced by Penicillium and Aspergillus species during fruit spoilage. Patulin contamination is a great concern with regard to human health because exposure of the mycotoxin can result in severe acute and chronic toxicity, including neurotoxic, mutagenic, and immunotoxic effects. Penicillium expansum is known as the main producer of patulin. This protocol addresses the cultivation procedure of P. expansum under patulin permissive conditions and describes the method of collection and detection of patulin.
Keywords: Penicillium expansumBackground
Patulin is a polyketide lactone mycotoxin and is produced by several species of fungi including Penicillium, Aspergillus and other species. Among them, Penicillium expansum, which is a well-known postharvest pathogen causing decay of pomaceous fruits during storage, is the main producer. Patulin levels in apple products are of great concern because of the severe acute and chronic effects caused by the toxin. Therefore the patulin level in food is limited in many countries around the world. The European Commission (2006) has set maximum permitted levels in apple juices (50 μg/kg), solid apple products (25 μg/kg) and, above all, fruit-derived baby foods (10 μg/kg), as children are major consumers of apple derived products.
Studies on patulin in recent years have focused on environmental factors regulating patulin production, molecular basis of patulin biosynthesis and biodegradation of patulin. The methods of induction and quantification of patulin production are important in these studies. Patulin analysis in fruits usually follows the AOAC method 995.10 (Brause et al., 1996). After treatment with pectinase, patulin is extracted with ethyl acetate from the puree of decayed portion of fruits. Many methods have been developed for measuring patulin such as TLC, mass spectrometry and gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Now, high performance liquid chromatography with ultra violet light detection (HPLC-UV) is the most frequently used method (Baert et al., 2007).
In this protocol, we address two methods of patulin induction in vitro and describe the specific parameters appropriate for HPLC-UV analysis of patulin.
Materials and Reagents
- 1,000 µl pipette tips (Corning, Axygen®, catalog number: TF-1000-R-S )
- 200 µl pipette tips (Corning, Axygen®, catalog number: TF-200-R-S )
- 10 µl pipette tips (Corning, Axygen®, catalog number: TF-300-R-S )
- Cheesecloth (Aladdin, catalog number: G6902 )
- 90 x 15 mm Petri dish (any brand will suffice)
- 10 ml centrifuge tubes (Sangon Biotech, catalog number: F601889 )
- 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes (Corning, Axygen®, catalog number: MCT-150-C )
- Filter (pore size 0.45 μm) (EMD Millipore, catalog number: SLHV033RB )
- Cellophane sheets (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 1650963 )
- 24-well culture plates (Corning, Costar®, catalog number: 3524 )
- Penicillium expansum T01: was isolated by our laboratory and whole-genome sequenced (Li et al., 2015)
- Glycerol (AMRESCO, catalog number: M152 )
- Tween 20 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T2700 )
- Liquid nitrogen
- Sterile distilled water
- Water (HPLC grade) (Alfa Aesar, catalog number: 19391 )
- Acetonitrile (HPLC grade) (Alfa Aesar, catalog number: 22927 )
- Potato
- Dextrose (Macklin, catalog number: D823520 )
- Agar (HUAAOBIO, catalog number: HA0552 )
- Sodium nitrate (NaNO3) (Beijing Chemical Works, GB/T 647-1993)
- Potassium phosphate dibasic trihydrate (K2HPO4·3H2O) (Beijing Chemical Works, HG/T 3487-2000)
- Potassium chloride (KCl) (Aladdin, catalog number: P112133 )
- Magnesium sulfate heptahydrate (MgSO4·7H2O) (Macklin, catalog number: M813599 )
- Iron(II) sulfate heptahydrate (FeSO4·7H2O) (Aladdin, catalog number: F116341 )
- Sucrose (Beijing Chemical Works, HG/T 3462-1999)
- Yeast extract (Oxoid, catalog number: LP0021 )
- Hydrochloric acid (HCl) (AMRESCO, catalog number: 0369 )
- PDA medium (see Recipes)
- CY medium (see Recipes)
- Acidified distilled water (pH 4.0) (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Glass spreading rod (any brand will suffice)
- Hemacytometer (QIUJING, model: XB-K-25 )
- 100-1,000 µl pipette (Eppendorf, catalog number: 3120000267 )
- 10-100 µl pipette (Eppendorf, catalog number: 3120000240 )
- 0.5-10 µl pipette (Eppendorf, catalog number: 3120000224 )
- Centrifuge (Beckman Coulter, model: Microfuge 16 , catalog number: A46473)
- Tweezer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 402011 )
- High-performance liquid chromatography (WATERS Corp., MA, USA)
- Auto sampler (WATERS, catalog number: 2498 )
- Binary HPLC pump (WATERS, catalog number: 1525 )
- UV/Visible detector (WATERS, catalog number: 2487 )
- C18 column (5 μm, 250 x 4.6 mm) (GL Sciences, model: Inertsil® ODS-3 )
- Vortexer (Select BioProducts, catalog number: SBS100-2 )
- Optical microscope (Chongqing Optec Instrument, model: B Series Biological Microscope , catalog number: B203LED)
- Clean bench (Donglian Electronic & Technology Development, model: SCB-1520 )
- Constant temperature incubator (TAICANG, model: THZ-C )
Software
- Microsoft Excel
- Empower 3.0
- SPSS 13.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA)
Procedure
- Patulin induction with PDA (solid) medium (Zong et al., 2015)
- Five-microliter spore suspension (5 x 106/ml in 16% glycerol, stored at -80 °C) of Penicillium expansum is inoculated on PDA plate (Figure 1A) and cultured for 2 weeks at 25 °C in the dark.
Conidia are harvested with a glass spreading rod with 3-5 ml 0.05% Tween 20 (Figure 1B) and filtered through four layers of sterile cheesecloth (Figure 1C). Conidia are counted with a hemocytometer and diluted to a concentration of 1 x 105 conidia/ml with sterile distilled water.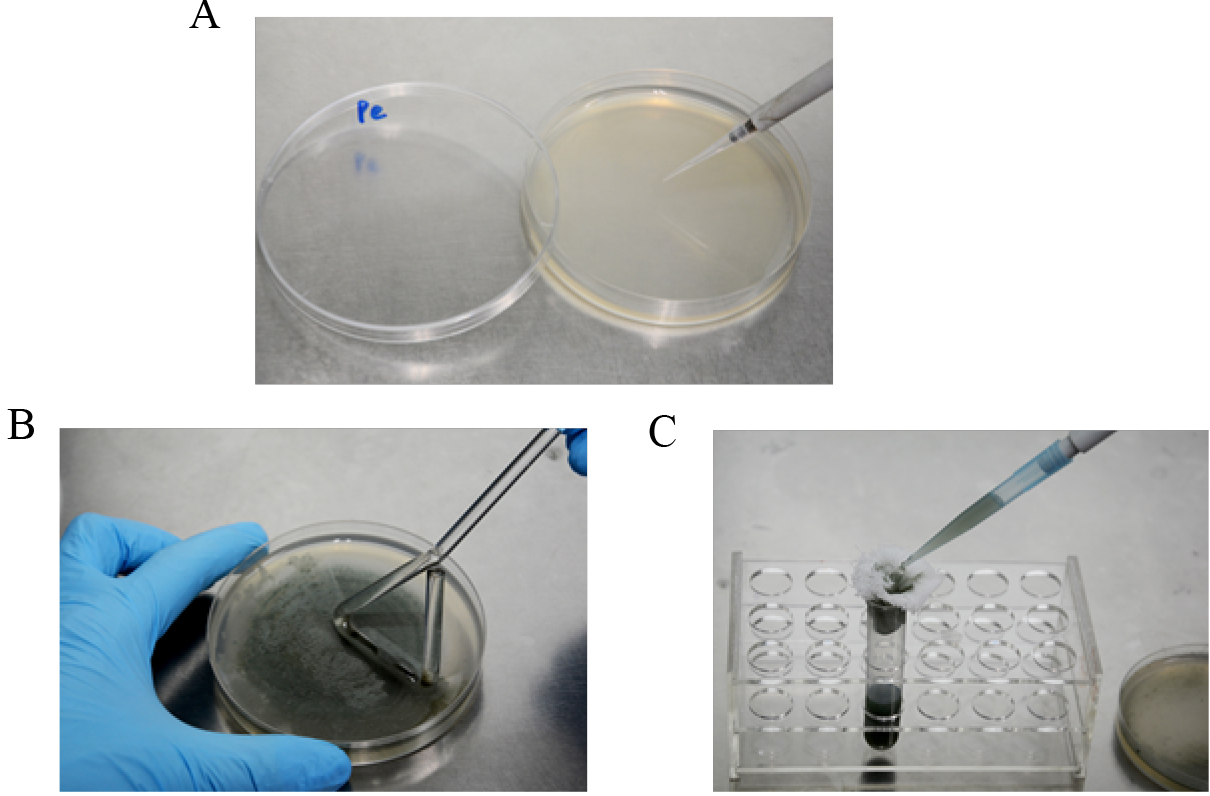
Figure 1. Preparation of P. expansum spore suspension. A. Activation of P. expansum on PDA plate; B. Conidia harvesting with 0.05% Tween 20; C. Filtration of spore suspension with four layers of sterile cheesecloth. - Five-microliter spore suspension is inoculated at the center of 9-cm PDA plates and incubated at 25 °C in the dark for 10 days (Figure 2A).
- Each of the Petri dish is washed with a glass spreading rod with 5 ml of acidified distilled water (pH 4.0) and the spore suspension is transferred to a 10 ml centrifuge tube with a 100-1,000 µl pipette (Figure 2B). Then, the spore suspension is centrifuged at 10,000 x g for 10 min and the supernatant is filtered through a 0.45 μm filter for patulin detection.
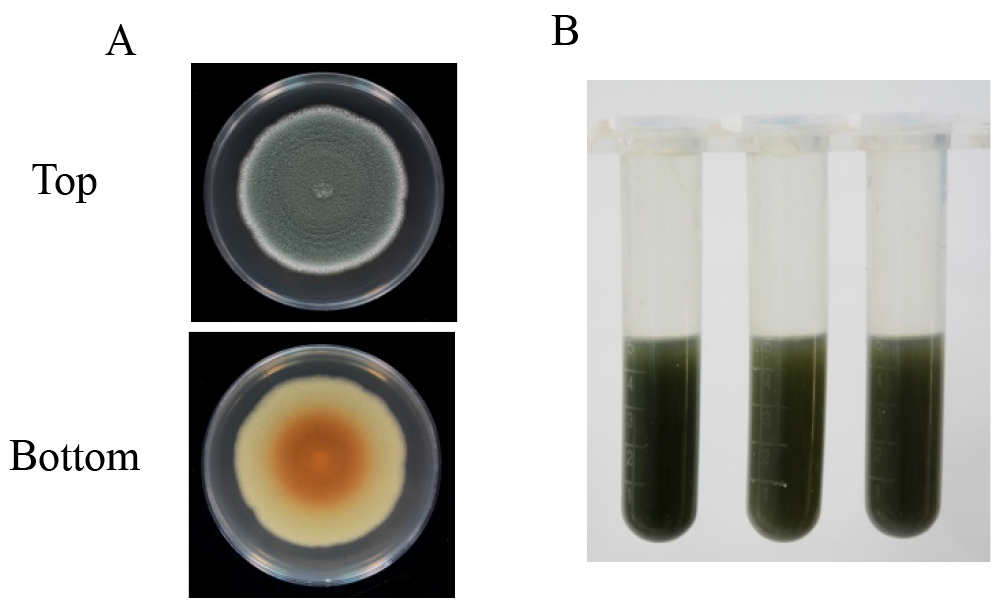
Figure 2. Patulin induction with PDA medium. A. Asexual sporulation (top) and mycelial pigmentation (bottom) patterns of P. expansum after 10 days of cultivation on PDA plate; B. The spore suspension washed with 5 ml of acidified distilled water (pH 4.0).
- Five-microliter spore suspension (5 x 106/ml in 16% glycerol, stored at -80 °C) of Penicillium expansum is inoculated on PDA plate (Figure 1A) and cultured for 2 weeks at 25 °C in the dark.
- Patulin induction with CY (liquid) medium
- P. expansum spore suspension is prepared as described above and diluted to a concentration of 1 x 106 conidia/ml with sterile distilled water.
- Aliquots of 1 μl of spore suspension are spread on cellophane sheets (1 x 1 cm) placed on PDA plates and cultured at 25 °C for 36 h (Figure 3A).
- Then the cellophane sheets covered with P. expansum mycelia are transferred to CY liquid medium. Each cellophane sheet is floated on 1 ml CY liquid medium in a 24-well culture plate (Figure 3B). The whole plate is covered and sealed with Parafilm, then cultured under static conditions at 25 °C in the dark.
- At 48 h after transfer, mycelium and spores are collected with a tweezer and quickly frozen with liquid nitrogen for some other use (RNA/DNA/protein extraction) and the medium (Figure 3C) is filtered through a 0.45 μm filter for patulin detection.
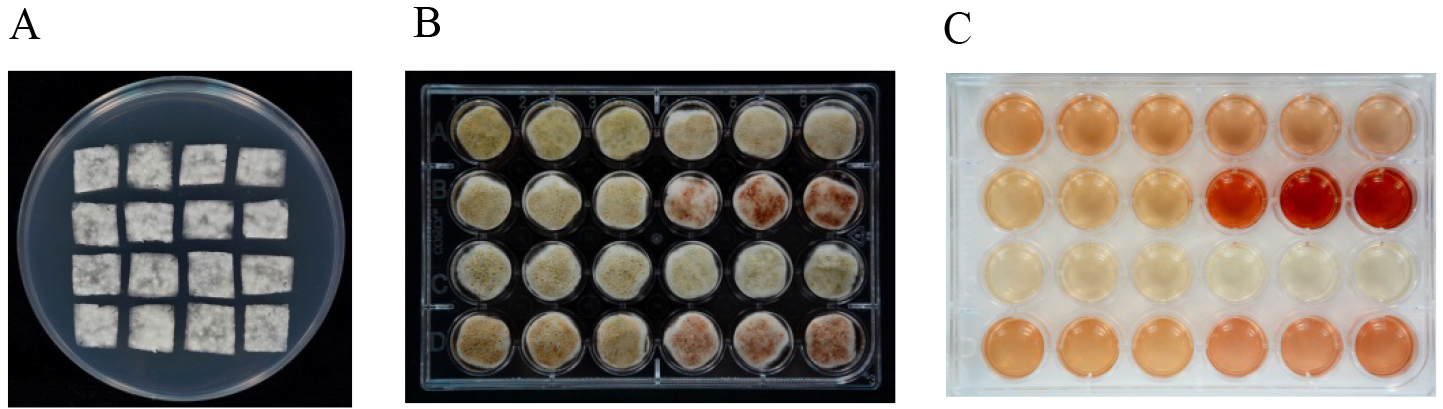
Figure 3. Patulin induction with CY medium. A. P. expansum mycelium incubated on cellophane sheets (1 x 1 cm) placed on PDA plates; B. Cellophane sheets covered with mycelium incubated on CY liquid medium in a 24-well culture plate; C. CY medium after removal of mycelium.
- P. expansum spore suspension is prepared as described above and diluted to a concentration of 1 x 106 conidia/ml with sterile distilled water.
- HPLC analysis
- High-performance liquid chromatography analysis is performed for determining patulin production.
- 10 μl of the filtrate extract is injected into a liquid chromatography equipped with an auto sampler (WATERS 2498), a binary HPLC pump (WATERS 1525), and a UV/Visible detector (WATERS 2487). A C18 column (5 μm, 250 x 4.6 mm, GL Sciences, Japan) is used for patulin detection.
- The mobile phase is a mixture of water and acetonitrile (90:10, v/v) at a flow rate of 1 ml/min in isocratic elution mode.
- The detection wavelength of patulin is 276 nm and the column oven is set at 25 °C.
- High-performance liquid chromatography analysis is performed for determining patulin production.
Data analysis
- To construct a standard curve
The solutions of patulin were prepared at concentrations of 20, 50, 100, 200 and 250 μg/ml. The volume injected into the column was 10 μl. The retention time of patulin is about 9.28 min in the HPLC analysis with above experimental conditions (Figure 4A). Linear regression was used to prepare the standard curve by using the mean values of peak areas of five injections of the five solutions (Figure 4B). Equation of the standard curve was:
E = 50990C + 39869 R² = 1
where, E is the peak area of patulin injected (10 μl) and C is the concentration (μg/ml) of the standard patulin injected.
The concentrations of experimental samples can be calculated with the corresponding peak area on the retention time of patulin (9.28 min) read by HPLC.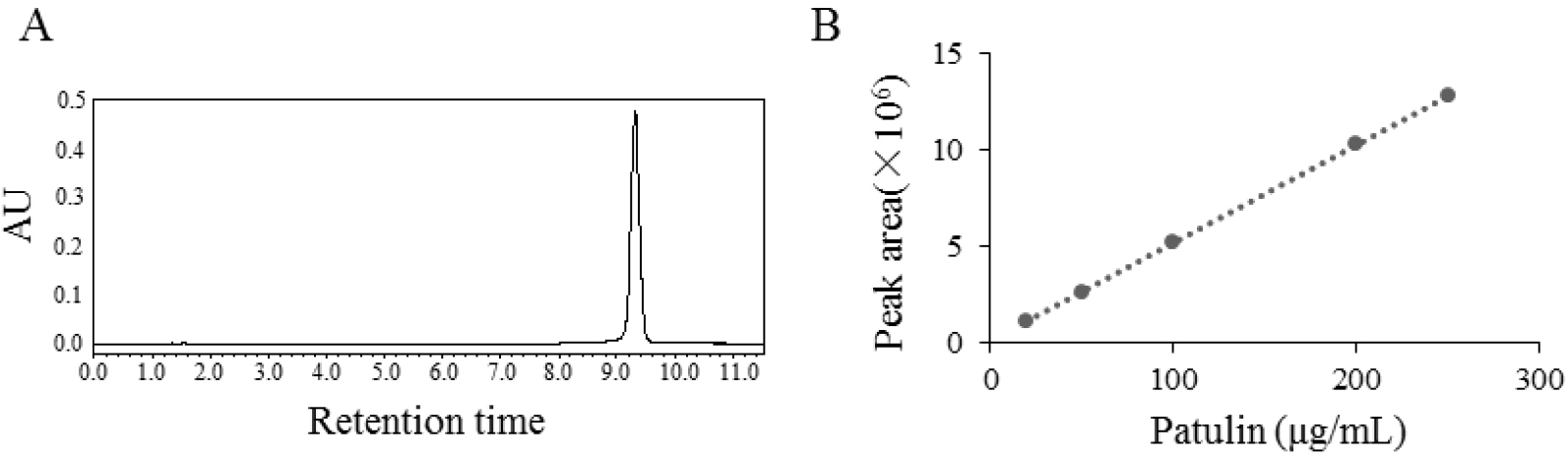
Figure 4. HPLC analysis (A) and standard curve of patulin (B) - Statistical analysis
Data from three independent experiments, each with five replicates, can then be analyzed with the statistic software SPSS version 13.0. ANOVA test was performed using Duncan’s multiple range test; P < 0.05.
Recipes
- PDA medium (1 L)
200 g potato
20 g dextrose
15 g agar
Boiling 200 g of sliced potatoes in 1 L distilled water for 30 min, then decanting the broth through cheesecloth and adding 20 g dextrose and 15 g agar powder in the broth. Add distilled water to make up 1 L, and the medium is sterilized by autoclaving at 121 °C for 20 min - CY medium (1 L)
3 g NaNO3
1 g K2HPO4·3H2O
0.5 g KCl
0.5 g MgSO4·7H2O
0.01 g FeSO4·7H2O
30 g sucrose
5 g yeast extract
dH2O up to 1 L
Adjust to pH 5.2 by adding HCl, autoclave at 121 °C for 20 min - Acidified distilled water (pH 4.0, 100 ml)
Prepare 100 ml distilled water, adjust to pH 4.0 with HCl, filter sterile through a 0.22 μm filter
Acknowledgments
This protocol was adapted from Li et al. (2015) and Zong et al. (2015). The work was supported by Chinese Ministry of Science and Technology (grant number 2016YFD0400902).
References
- Baert, K., Meulenaer, B., Kasase, C., Huyghebaert, A., Ooghe, W. B. and Devlieghere, F. (2007). Free and bound patulin in cloudy apple juice. Food Chem 100: 1278-1282.
- Brause, A. R., Trucksess, M. W., Thomas, F. S. and Page, W. S. (1996). Determination of patulin in apple juice by liquid chromatography: collaborative study. J AOAC Int 79: 451-455.
- European Commission Regulation (2006). Commission Regulation EC 1881/2006 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs. Off J Eur Commun L364: 5-24.
- Li, B., Zong, Y., Du, Z., Chen, Y., Zhang, Z., Qin, G., Zhao, W. and Tian, S. (2015). Genomic characterization reveals insights into patulin biosynthesis and pathogenicity in Penicillium species. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 28(6): 635-647.
- Zong, Y., Li, B. and Tian, S. (2015). Effects of carbon, nitrogen and ambient pH on patulin production and related gene expression in Penicillium expansum. Int J Food Microbiol 206: 102-108.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2017 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Chen, Y., Li, B., Zhang, Z. and Tian, S. (2017). Induction and Quantification of Patulin Production in Penicillium Species. Bio-protocol 7(11): e2324. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2324.
Category
Microbiology > Microbial biochemistry > Other compound
Plant Science > Plant immunity > Host-microbe interactions
Biochemistry > Other compound > Patulin
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link