- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
miRNA Characterization from the Extracellular Vesicles
Published: Vol 7, Iss 4, Feb 20, 2017 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2139 Views: 9027
Reviewed by: HongLok LungShalini Low-NamAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Polysome Fractionation to Analyze mRNA Distribution Profiles
Amaresh C. Panda [...] Myriam Gorospe
Feb 5, 2017 31837 Views

In situ Hybridization (ISH) and Quantum Dots (QD) of miRNAs
Sajni Josson [...] Leland W.K. Chung
Feb 20, 2017 11637 Views

Detection of Individual RNA in Fixed Cells and Tissues by Chromogenic ISH
Meng Jiang [...] Rongqin Ke
Feb 5, 2020 5196 Views
Abstract
Cancer cells and cancer associated stromal cells co-evolve secrete extracellular vesicles to the surrounding regions and regulate several processes involved in cancer metastasis. miRNAs have been known to be mediators of cancer progression and metastasis. miRNAs consist of short noncoding RNA. miRNAs are stable in extracellular fluids such as serum, plasma and urine. miRNAs are secreted by cells in normal and diseased conditions. miRNAs signatures have been identified specific to certain disease conditions. Therefore they are valuable biomarkers for different diseases. In our study we identified certain miRNAs, miR-409-3p and miR-409-5p, which were secreted by activated stromal fibroblast cells and were taken up by cancer cells to induce explosive tumor growth, through activation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition of cancer cells. Here we describe a procedure to determine miRNAs (miR-409-3p and miR-409-5p) in extracellular vesicles, which were secreted by prostate cancer stromal cells expressing miR-409. In this procedure, conditioned media from the stromal fibroblasts was used to extract the vesicular fraction. RNA was purified from the vesicular fraction, and specific miRNA was reverse transcribed and quantitated using real-time PCR assay.
Keywords: miRNABackground
miRNA are short non-coding RNA of 20-23 nucleotides in size. miRNAs have been detected in tissues and body fluids. miRNA expression levels have been determined using Northern blotting and quantitative real-time PCR. miRNA are powerful biomarkers for disease conditions. Under frozen conditions, they are stable in biofluids. Recent emphasis is on the miRNA in the vesicular fractions of cells and extracellular fluids (Josson et al., 2015). Extracellular vesicles (EV) contain different proteins, lipids, DNA, RNA and miRNA. EVs range from sizes of 30 nm to a few µm. EVs has been isolated using kits or differential centrifugation (Morello et al., 2013). In this study we describe the detection of miRNA in the vesicular fraction of activated stromal fibroblast cells. miRNAs are typically detected by Northern blot or quantitative real-time PCR assay (Josson et al., 2015). Using the recently available exosome purification kits we isolated exosomes and purified the miRNA from this fraction. The specific miRNA was reverse transcribed and quantitated using real-time PCR assay.
Materials and Reagents
- 6 well plates
- 6-well dish
- MicroAmp® optical 96-well reaction plate (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Applied BiosystemsTM)
- MicroAmp® optical adhesive tape (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Applied BiosystemsTM)
- SON normal human stromal fibroblast cells expressing miR-409 miRNA
- Penicillin-streptomycin (1%, stock: 10,000 U/ml)
- Exosome depleted FBS media supplement (System Biosciences, catalog number: EXO-FBS-50A-1 )
- Exo-Quick-TC (System Biosciences, catalog number: EXOTC10A-1 )
- SeraMir exosome RNA purification kit (System Biosciences, catalog number: RA808A-1 )
- Heat inactivated fetal bovine serum (Bio-Whittaker)
- DMEM
- F-12K
- Sodium bicarbonate
- Insulin
- Triiodothyronine
- Transferrin
- Biotin
- Adenine
- dNTP mixture (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Applied BiosystemsTM)
- M_MLV reverse transcriptase (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Applied BiosystemsTM)
- 10x RT buffer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Applied BiosystemsTM)
- RNase inhibitor (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Applied BiosystemsTM)
- dH2O (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Applied BiosystemsTM)
- Taqman miRNA primer sets for hsa-miR-409-3p, hsa-miR-409-5p and RNU6B (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Applied BiosystemsTM)
- Taqman universal PCR master mix, No AmpErase® UNG (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Applied BiosystemsTM)
- T-medium (see Recipes)
- Reverse transcription mix for 1 reaction (see Recipes)
- Real Time PCR reaction mixture for a single reaction (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Centrifuge
- Nanodrop 2000/2000c spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, model: NanodropTM 2000 / 2000c Spectrophotometer )
- Applied Biosystems 7500 Real-Time PCR machine (Thermo Fisher Scientific, model: 7500 Real-Time PCR System )
- PCR machine
Software
- Taqman software
- Graphpad Prism software
Procedure
- Cell culture
Prostate normal human stromal fibroblast cells, SON was stably transduced with miR-409 lentiviral particles. Stromal cells were derived from a patient. Stromal cells were cultured at a concentration of 3 x 105 cells in 6 well plates, and maintained in T-medium. The stromal cells were maintained in T-medium with exosome depleted FBS media supplement for 72 h. The conditioned media was collected, and used to extract EVs. - Extraction of exosomes
- The conditioned media (CM) from the cells was centrifuged for 15 min. at 3,000 x g to remove cellular debris.
- The supernatant (5 ml) was used for extracting EVs using the Exo-Quick-TC for tissue culture media. Exo-Quick-TC (1 ml) was mixed with 5 ml of CM, and the tube was inverted 3 times and kept at 4 °C overnight.
- The next day the solution was centrifuged at 13,000 rpm for 2 min. The supernatant was removed and the exosome pellet was used.
- Lysis buffer (350 μl) from SeraMir exosome RNA purification kit was added to the exosome pellet and vortexed for 15 sec. The solution was placed at RT for 5 min.
- The conditioned media (CM) from the cells was centrifuged for 15 min. at 3,000 x g to remove cellular debris.
- miRNA extraction
SeraMir exosome RNA purification kit was used to extract miRNA from EVs as per manufacturer’s instructions. The RNA concentration and purity were measured using a Nanodrop spectrophotometer. - miRNA detection
- MiRNA was detected separately for hsa-miR-409-5p, hsa-miR-409-3p and RNU6B. Equal amounts of miRNA (25 ng) were added to the reaction. Procedure was followed as per the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Reverse transcription: The reverse transcription mix was made as described below (see Recipes). The RT reaction was as follows: 16 °C-30 min, 42 °C- 30 min, 85 °C-5 min.
- Quantitative real-time PCR (RT-PCR): The RT-PCR reaction was performed as described below (see Recipes). Assays were run in duplicates. The reaction mixtures were put into the MicroAmp Optical 96 well reaction plate and sealed with a MicroAmp® optical adhesive tape. The assay was run in an Applied Biosystems 7500 Real-Time PCR machine, using the Taqman software, under standard run speed and using a reaction volume of 10 µl. The Ct values were used to determine the relative fold change and the results were normalized to RNU6B. The differential miRNA expression from the vesicular fraction was determined and plotted in a graph.
- MiRNA was detected separately for hsa-miR-409-5p, hsa-miR-409-3p and RNU6B. Equal amounts of miRNA (25 ng) were added to the reaction. Procedure was followed as per the manufacturer’s instructions.
Data analysis
Analysis of data is performed as mentioned in the Applied Biosystems manual. Real-time PCR assays are performed in duplicates. The Taqman software determines the Ct value of the specific miRNA (miR-409-3p for example). RNU6B is used as the endogenous control. The difference between the target miRNA and RNU6B is determined by subtraction. The normalized value (x), is then calculated as 2x. Values were expressed as means ± standard deviation. Different groups are compared, and miRNA concentration is plotted graphically, as relative change of miRNA normalized to RNU6B using Graphpad Prism software. If 2 groups are being compared, Student’s t-test is used for statistical analysis. If more than 2 groups are compared, One-Way ANOVA test is used. All experiments were done in duplicates at least two to three independent times.
Notes
miRNA concentrations vary in cells versus extracellular vesicles. For miRNA detection from conditioned media of stromal fibroblasts we used slightly higher RNA concentration for reverse transcription (25 ng). When determining certain miRNA, which is present in low concentration from EVs from conditioned media or body fluids, higher concentration of RNA will be needed to detect the miRNA of interest. Concentrations of 25 ng to 100 ng will be required for a pilot test. Since different miRNA are present in different levels, an initial dose response curve will be useful to determine an appropriate RNA starting concentration.
Recipes
- T-medium
DMEM:F-12K, 4:1, supplemented with:
5% FBS
3 g/L sodium bicarbonate
5 µg/ml insulin
13.6 pg/ml triiodothyronine
5 µg/ml transferrin
0.25 µg/ml biotin
25 µg/ml adenine - Reverse transcription mix for 1 reaction
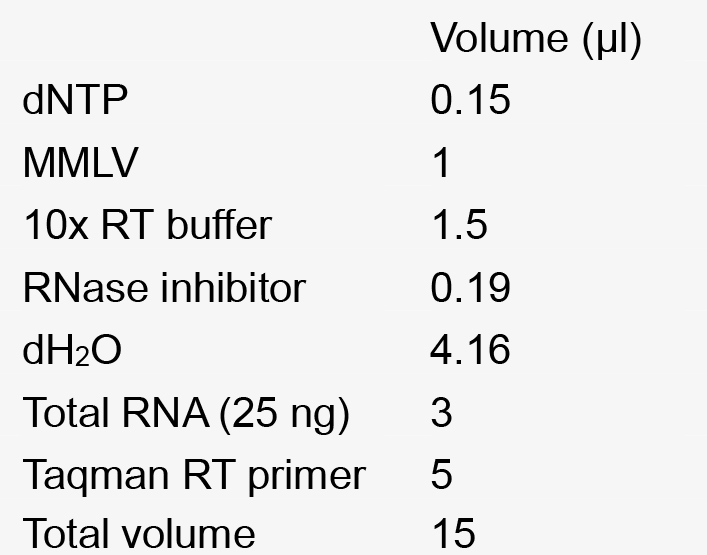
- Real Time PCR reaction mixture for a single reaction

Acknowledgments
These experimental procedures have been published Josson et al., 2015. Grant support for this work is from P01-CA98912, DAMD-17-03-02-0033, RO1-CA122602 (L.W.K. Chung).
References
- Josson, S., Gururajan, M., Sung, S. Y., Hu, P., Shao, C., Zhau, H. E., Liu, C., Lichterman, J., Duan, P., Li, Q., Rogatko, A., Posadas, E. M., Haga, C. L. and Chung, L. W. (2015). Stromal fibroblast-derived miR-409 promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and prostate tumorigenesis. Oncogene 34(21): 2690-2699.
- Morello, M., Minciacchi, V. R., de Candia, P., Yang, J., Posadas, E., Kim, H., Griffiths, D., Bhowmick, N., Chung, L. W., Gandellini, P., Freeman, M. R., Demichelis, F. and Di Vizio, D. (2013). Large oncosomes mediate intercellular transfer of functional microRNA. Cell Cycle 12(22): 3526-3536.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2017 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Josson, S., Gururajan, M. and Chung, L. W. (2017). miRNA Characterization from the Extracellular Vesicles. Bio-protocol 7(4): e2139. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2139.
Category
Cancer Biology > General technique > Biochemical assays > RNA
Biochemistry > RNA > miRNA tagging
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link












