- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Analysis of Myosin II Minifilament Orientation at Epithelial Zonula Adherens
Published: Vol 6, Iss 23, Dec 5, 2016 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2054 Views: 9673
Reviewed by: Nicoletta CordaniThomas J. BartoshXuecai Ge

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols
An Automated Imaging Method for Quantification of Changes to the Endomembrane System in Mammalian Spheroid Models
Margaritha M. Mysior and Jeremy C. Simpson
Jun 5, 2025 1646 Views

Quantifying Intracellular Distributions of HaloTag-Labeled Proteins With SDS-PAGE and Epifluorescence Microscopy
Julia Shangguan and Ronald S. Rock
Jul 20, 2025 2497 Views
Fluorescence Lifetime-Based Separation of FAST-Labeled Cellular Compartment
Aidar R. Gilvanov [...] Yulia A. Bogdanova
Oct 5, 2025 1319 Views
Abstract
Non-muscle myosin II (NMII) form bipolar filaments, which bind F-actin to exert cellular contractility during physiological processes (Vicente-Manzanares et al., 2009). Using a combinatorial approach to fluorescently label both N- and C-termini of the NMII heavy chain, recent works have demonstrated the ability to visualize NMII bipolar filaments at various subcellular localizations (Ebrahim et al., 2013; Beach et al., 2014). At the zonula adherens (ZA) of epithelia, NMII minifilaments bind the circumferential actin bundles in a pseudo-sarcomeric manner (Ebrahim et al., 2013), a conformation required to maintain junctional tension and tissue integrity (Ratheesh et al., 2012). By expressing green fluorescent protein (GFP)-NMIIA heavy chain and immunolabel it using a NMIIA C-terminus specific antibody, we were able to visualize the NMII minifilaments bound to F-actin bundles in Caco-2 cells (Michael et al., 2016), as previously reported (Ebrahim et al., 2013; Beach et al., 2014). In addition, we designed an FIJI/MATLAB analysis module to quantify the size, distance and alignment of these minifilaments with respect to junctional F-actin at the ZA. Measurements of the dispersion of minifilaments angles were proven to be a useful parameter that closely correlated to the extent of contractility at junctions (Michael et al., 2016).
Keywords: Myosin II minifilamentsBackground
For decades, the assembly of NMII into bipolar filaments has been studied using electron microscopy (EM) techniques. These mainly involve the assembly of NMII minifilaments from purified proteins or the visualization of minifilaments in cells following extraction of the actin cytoskeleton (Pollard, 1982; Svitkina et al., 1989). Whilst these methods enabled measurements of NMII bipolar filament assemblies, they were technically challenging and did not accurately reflect the cellular distribution of these entities, notwithstanding the artifacts introduced due to the sample preparation. With the advent of super-resolution microscopy, we are now able to observe and measure these NMII minifilaments in various subcellular locations with high resolution, using a rapid process that is amenable for most laboratories equipped with a microscope that performs structured illumination microscopy (SIM, Yap et al., 2015). In this protocol, we describe a method that we have developed to assess NMII minifilaments properties at adherens junctions by measuring the lengths of the minifilaments as well as quantifying their angles with respect to the junctional F-actin and their distance from the junctions (Michael et al., 2016).
Materials and Reagents
- 1.6-well plates (Corning, Costar®, catalog number: 3516 )
- Glass coverslips (13 mm, #1.5) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: 1014355130NR15 )
- ShandonTM ColorFrostTM glass slides (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: 6776214 )
- Caco-2 human colon adenocarcinoma cells (ATCC, catalog number: ATCCH®TB-37TM )
- Plasmid: GFP-NMIIA (Addgene, catalog number: 11347 )
- Roswell Park Memorial Institute (RPMI) 1640 medium (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 11875093 )
- Fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 26140079 )
- 100x penicillin/streptomycin (10,000 U/ml) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 15140122 )
- 100x L-glutamine (200 mM) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 25030081 )
- Lipofectamine® 3000 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: L3000015 )
- Opti-MEM®, reduced serum media (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 31985070 )
- Alexa Fluor® 647 phalloidin (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Molecular ProbesTM, catalog number: A22287 )
- Triton X-100 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: X100 )
- Antibodies
- Anti-Myosin IIA rabbit polyclonal antibody (Biolegend, catalog number: PRB-440P )
Note: This antibody targets the C-terminal portion of the NMIIA heavy chain. - Goat anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) secondary antibody, Alexa Fluor® 546 conjugate (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Invitrogen, catalog number: A11035 )
- TetraSpeckTM multi-speck 100 nm beads (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Molecular ProbesTM, catalog number: T7279 )
- ProLong® Gold antifade mountant (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Molecular ProbesTM, catalog number: P36934 )
- Paraformaldehyde (PFA) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 158127 )
- Piperazine-N,N’-bis(2-ethanesulfonic acid) (PIPES) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P6757 )
- Potassium chloride (KCl) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P9541 )
- Sucrose (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S0389 )
- Ethylene glycol-bis(β-aminoethyl ether)-N,N,N’,N’-tetraacetic acid (EGTA) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: E3889 )
- Magnesium chloride (MgCl2) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M8266 )
- Tris-Cl (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T5941 )
- Sodium chloride (NaCl) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S3014 )
- Bovine serum albumin (BSA) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A2153 )
- Phosphate buffered saline (PBS), without Ca2+ and Mg2+ (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 14190250 )
- 10x trypsin/EDTA (0.5%) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 15400054 )
- 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) (see Recipes)
- Tris buffered saline (TBS) (see Recipes)
- Blocking buffer (see Recipes)
Equipment
- NuncTM 75 cm2 cell culture flasks (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: 156472 )
- Incubator
- Zeiss ELYRA superresolution microscope (ZEISS, model: ELYRA Superresolution Microscope )
Software
- Zen (black version; Zeiss)
- FIJI (http://imagej.net/Fiji)
- Prism, GraphPad (http://www.graphpad.com/scientific-software/prism/)
- Matlab, Mathworks (https://www.mathworks.com/index-c.html)
- FIJI and Matlab scripts for minifilament analysis (see Appendix I and II of this Bioprotocol)
Procedure
- Preparation and transfection of Caco-2 cells
Note: This technique was used in our recent Developmental Cell article (Michael et al., 2016).- Culture Caco-2 cells in RPMI media supplemented with 10% FBS, penicillin/streptomycin, L-glutamine and maintained at 37 °C in 5% CO2.
- For transfection, plate cells at 200,000 cells/well in a 6-well plate containing 4x coverslips evenly dispersed and lying flat within each well.
- Once cells reached ~50-80% confluence (~36-48 h post-plating, Figure 1), transfect cells with GFP-NMIIA plasmid using Lipofectamine 3000 reagent, according to manufacturer’s instructions.
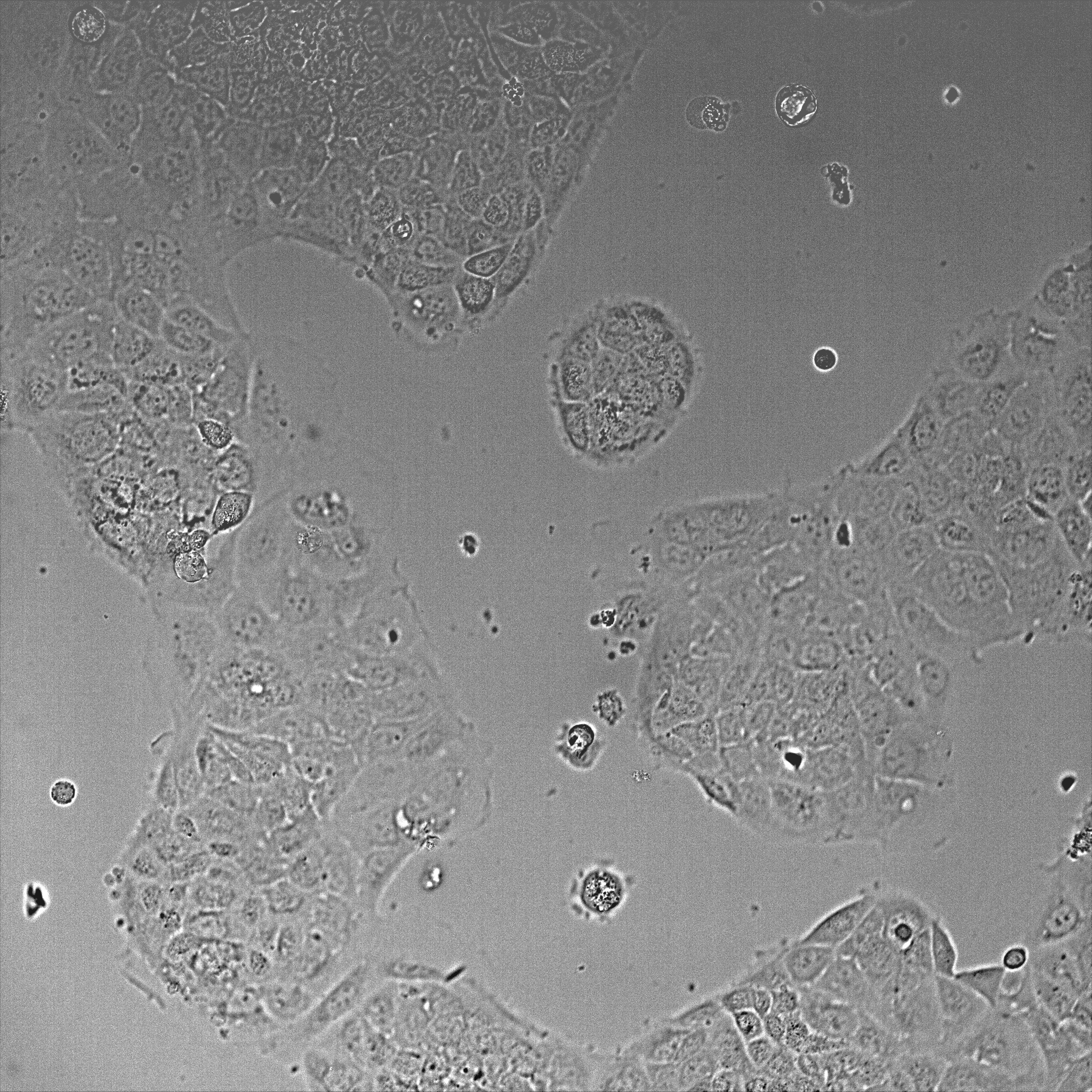
Figure 1. DIC image of Caco-2 cells after 48 h plating using a 20x objective. The image shows a field of view of 600 x 600 μm. - For the transfection, 2 μg of DNA is diluted in 190 μl Opti-MEM containing 5 μl P3000 reagent. In a separate tube, 5 μl of Lipofectamine 3000 is diluted in 190 μl Opti-MEM. Both mixes are then combined and incubated at room temperature for 10 min and applied to cells containing 1 ml Opti-MEM per well.
- Return cells to the 37 °C incubator and after 6 h, replace the transfection media with growth media. Leave cells to grow within the incubator for a further 24 h before fixation. Expression of the GFP-tagged plasmid can be observed in 30-40% of the cells after 24 h transfection using a fluorescent microscope (Figure 2).
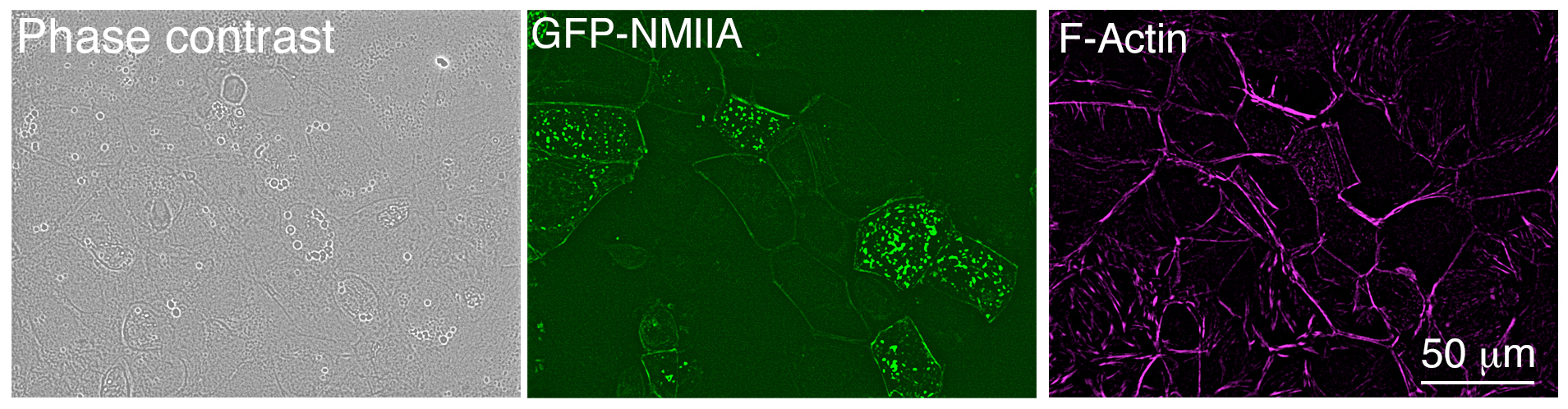
Figure 2. Low magnification image of Caco-2 cells after 24 h transfection, taken with an epifluorescence microscope. Cells were fixed and stained using Alexa Fluor® 647 phalloidin.
- Culture Caco-2 cells in RPMI media supplemented with 10% FBS, penicillin/streptomycin, L-glutamine and maintained at 37 °C in 5% CO2.
- Immunofluorescence
- Fix cells on ice with 4% PFA for 20 min followed by permeabilization on ice with 0.25% Triton X-100 in TBS for 5 min.
- Block cells with blocking buffer (see Recipes) at room temperature for 1 h followed by incubation with anti-Myosin IIA antibody (1:1,000 dilution) for 1 h at room temperature. All antibodies used were diluted in blocking buffer.
- Wash 3 times with TBS. Then, incubate cells for 1 h with the goat anti-rabbit Alexa Fluor® 546 secondary antibody (1:500 dilution) and phalloidin Alexa Fluor® 647 (1:500 dilution).
- Wash cells again 3 times with TBS and then mount coverslips by inverting them onto glass slides containing 5 μl drops of ProLong® Gold mounting reagent.
- Fix cells on ice with 4% PFA for 20 min followed by permeabilization on ice with 0.25% Triton X-100 in TBS for 5 min.
- Imaging of Myosin IIA and F-actin at the zonula adherens
- Perform structured illumination microscopy (SIM) of the immunostained coverslips on a Zeiss Elyra superresolution microscope using a 60x objective, 1.4 NA Plan Apochromat oil immersion lens.
- Do 3-channel imaging, using 488, 561, 640 nm lasers, to detect GFP-NMIIA fluorescence, the NMIIA C-terminal antibody (Alexa Fluor® 546) and phalloidin (Alexa Fluor® 647) at the zonula adherens (ZA).
- Acquire images of a single z-slice through channel-specific gratings at 5 phases and 3 120° rotations of the grid pattern.
- Perform image reconstruction with the Zen software using a noise filtering level of -4.5 and an optical sectioning value of 100.
- Perform channel alignment on reconstructed images using pre-calibrated values that were previously obtained by measuring 4-colour bead alignment samples (multi-speck beads).
- The final images reveal a pseudo-sarcomeric organization of NMII decorating the phalloidin labeled F-actin filaments at the ZA (Figure 3A). Furthermore, due to the increased resolution of the SIM technique and the N-terminally tagged GFP-NMIIA and C-terminal NMIIA antibody labeling combination, the NMIIA bipolar filaments can be visualized in detail as a set of green-red-green puncta (Figures 3A and 3B).
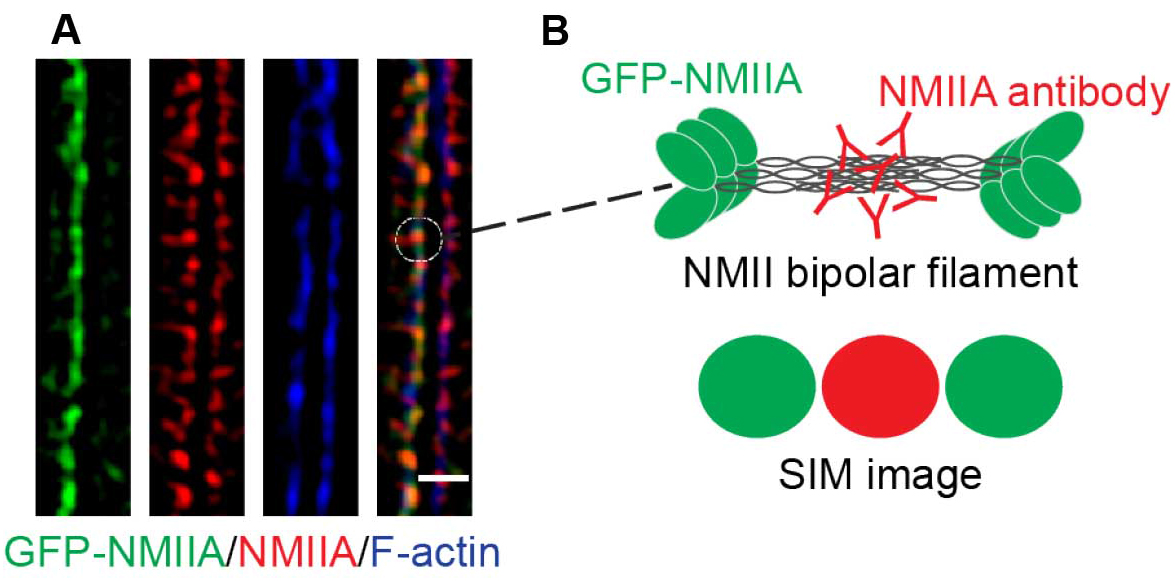
Figure 3. A magnified area of a final SIM image. A. SIM image of a cell-cell junction expressing GFP-NMIIA (green) and immunostained for the C-terminus of NMII (red). Phalloidin labeling (blue) served as a marker for junctional F-actin. B. Illustration of NMII bipolar filament organization and its visualization by SIM. Scale bar = 1 μm.
- Perform structured illumination microscopy (SIM) of the immunostained coverslips on a Zeiss Elyra superresolution microscope using a 60x objective, 1.4 NA Plan Apochromat oil immersion lens.
Data analysis
- Quantification of NMIIA minifilament orientations at the ZA
- Overview
- Step 1 (FIJI software): Use an RGB image of the SIM data to draw (Figure 4) regions of interest (ROIs) corresponding to:
- The cell-cell junction according to the phalloidin (blue) staining as a guide, using the segmented line tool in FIJI.
- Each individual actomyosin minifilament (green-red-green dots), using the straight line tool in FIJI.

Figure 4. A cropped area of the 3 color SIM image showing the details of ROIs used for analysis. Left, RGB image with ROI. Right, schematic of ROIs. The first ROI that needs to be drawn is the one that corresponds to the cell-cell junction (Blue) followed by the different ROIs that correspond to individual minifilaments.
- The cell-cell junction according to the phalloidin (blue) staining as a guide, using the segmented line tool in FIJI.
- Step 2 (FIJI software): Save the ROIs as XY coordinates, using the FIJI script provided in this protocol (Appendix I), in a .txt format (Figure 5).
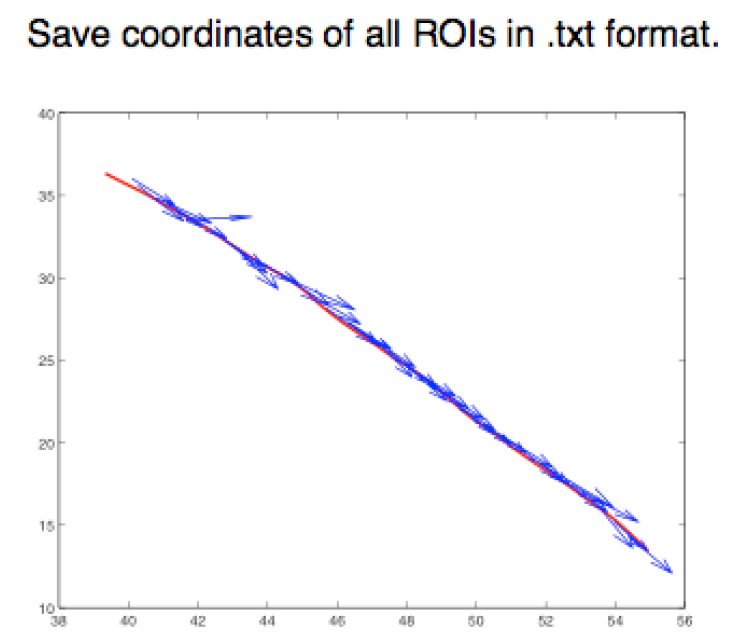
Figure 5. Graphical representation of different ROIs in the XY plane. ROIs exported as .txt files using a FIJI script (Appendix I) are imported into MATLAB and shown as a figure (The figure is generated automatically after running the MATLAB script, Appendix II). - Step 3 (MATLAB software): Measure the angle between the tangent of the junction (θ) and the orientation of the minifilament (γ). Angle = θ - γ (Figure 6).
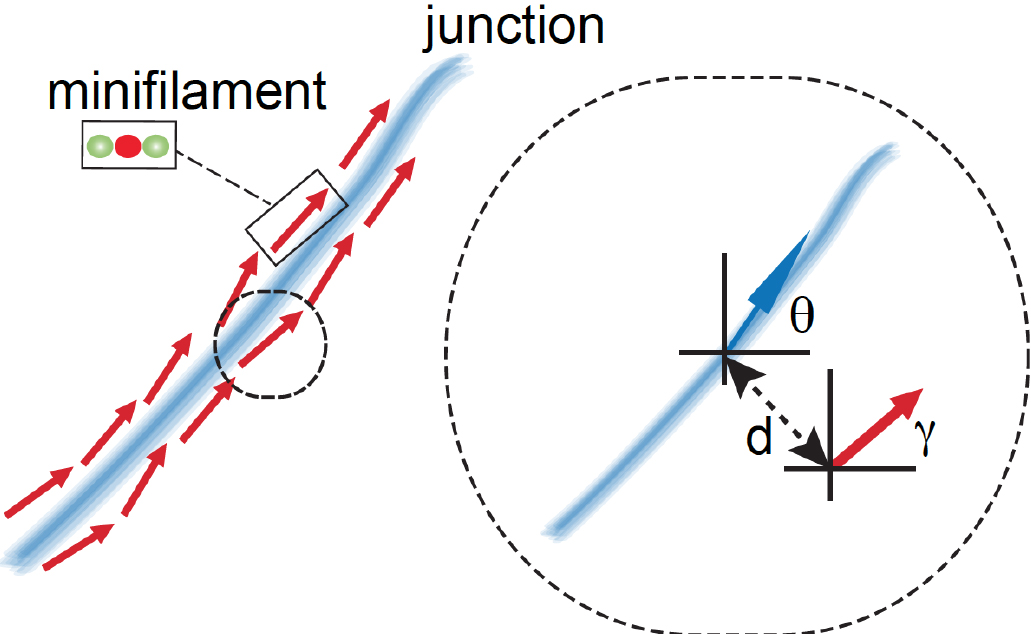
Figure 6. Schematic of how relative orientation of minifilaments is calculated based on the spatial information of the different ROIs. The red arrow represents a minifilament and γ indicates the angle that defines the local orientation of its vector. The blue arrow shows the local angle of the junction, indicated by θ, defined by the closest point of the junction to the corresponding minifilaments. - Step 4 (MATLAB software): Measure the distance of the minifilament to the junction (Figure 7).
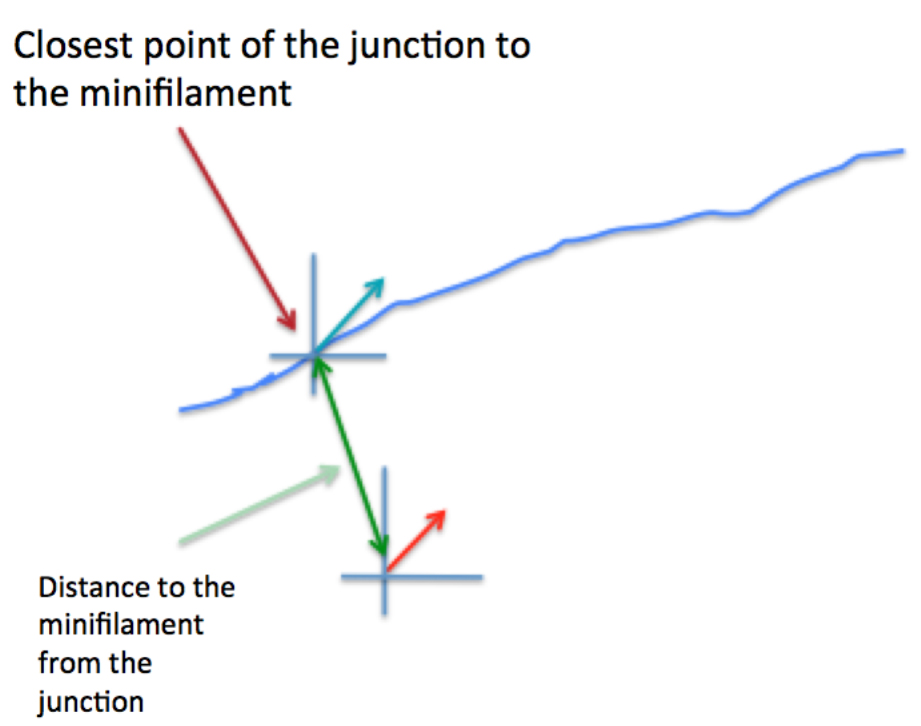
Figure 7. Graphical representation of the calculation of the distance between minifilaments and the cell-cell junction - Step 5 (MATLAB software): Measure the length of the ROIs (‘minifilament length’) corresponding to the different minifilaments (Figure 8).

Figure 8. A magnified view of the SIM image with the position of the different ROIs - Step 6 (PRISM or Excel software): Preparation of results
Here the quantities that are obtained from this analysis are: (1) the standard deviation of the angle values, which is an index of the relative organization of minifilaments parallel to the junction; (2) the average distance of minifilaments to the junction, an index of how closely associated the minifilaments are to the cell-cell junctions and (3) the average length of minifilaments, which reflects the capacity of myosin (and mechanical tension) to organize actomyosin into sarcomeric structures.
- Step 1 (FIJI software): Use an RGB image of the SIM data to draw (Figure 4) regions of interest (ROIs) corresponding to:
- Procedure in practice
- Quantification of minifilaments alignment was performed using custom-made scripts for FIJI and MATLAB (see Appendix I and Appendix II).
- The 3 channel images were opened in FIJI. The F-actin at junctions is visualized as a bundle of linear F-actin filaments (Figure 3). Using the phalloidin channel as a reference, a freehand line is drawn in the middle of the F-actin bundle (corresponding to the junction) and this line is added to the ROI manager (refer to Figure 4, also step A1a.i).
- Using the merged 3-channel (RGB) image, each minifilament (defined by the green-red-green puncta) is marked using the line tool (step A1a.ii) and added to the ROI manager (refer to Figure 4). The ROI manager along with the RGB image is saved in a folder.
- Using the ‘FIJI script for minifilament analysis’, a custom-made macro for FIJI (Appendix I), the coordinates for the junctional F-actin and the minifilaments were extracted from the ROIs and these coordinates were saved as .txt that were used later in MATLAB to determine the minifilament angle, length and distance with respect to the junction. The macro can be easily created by selecting Plugins->New->Macro. A window appears where the script in Appendix I can be pasted. Then, from this window the macro can be run.
- Open MATLAB and select the directory that contains the RGB SIM images (where the .txt files with the XY coordinates of ROIs are stored).
- Open MATLAB and create a new script by copying and pasting the ‘MATLAB script for minifilament analysis’.
- Modify the first line of the code to include the correct number of ROIs to be analyzed.
- Run the script (‘command + alt + R’ in MacOS).
- After running the script 3 figures appear (Figure 9).
These figures can be saved as EPS, JPEG or TIFF formats in MATLAB. We recommend saving these as EPS format, as these are fully editable, and amenable to subsequent figure preparation in Adobe Illustrator.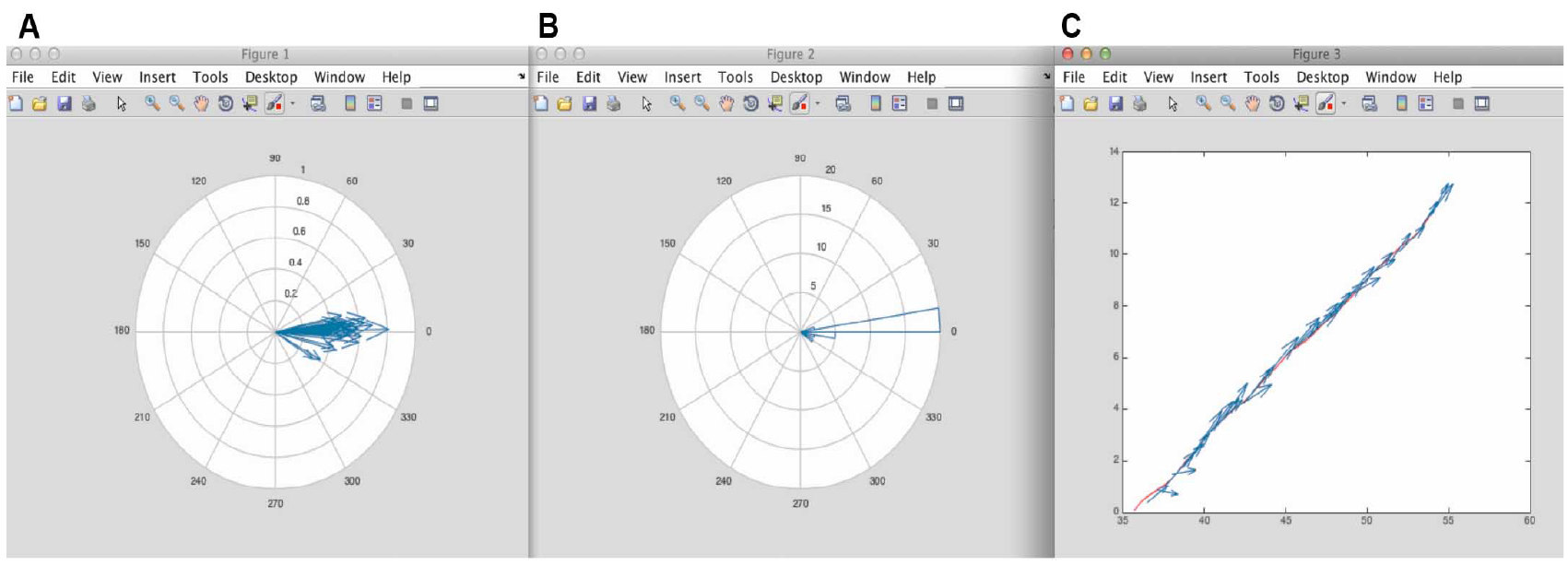
Figure 9. Figure results from MATLAB using the script in Appendix II. A. Corresponds to the different minifilaments put on the same origin of coordinates. From here it is possible to appreciate the distribution of orientation of the minifilaments with respect to the cell-cell junction. B. Corresponds to the polar histogram of minifilament orientations shown in Figure 4. C. Shows the vectorial map of the different minifilaments alongside the position of the junction. - Numeric results
- In the workspace of MATLAB, the variable ‘AAResults’ will contain the numerical results for statistical analysis (Figure 10).
This variable has 5 columns:
1st Column: Minifilament length
2nd Column: Distance of the minifilament from the junction
3rd Column: Relative orientation (angle) of the minifilament with respect to the junction
4th Column: X component of the minifilament vector
5th Column: Y component of the minifilament vector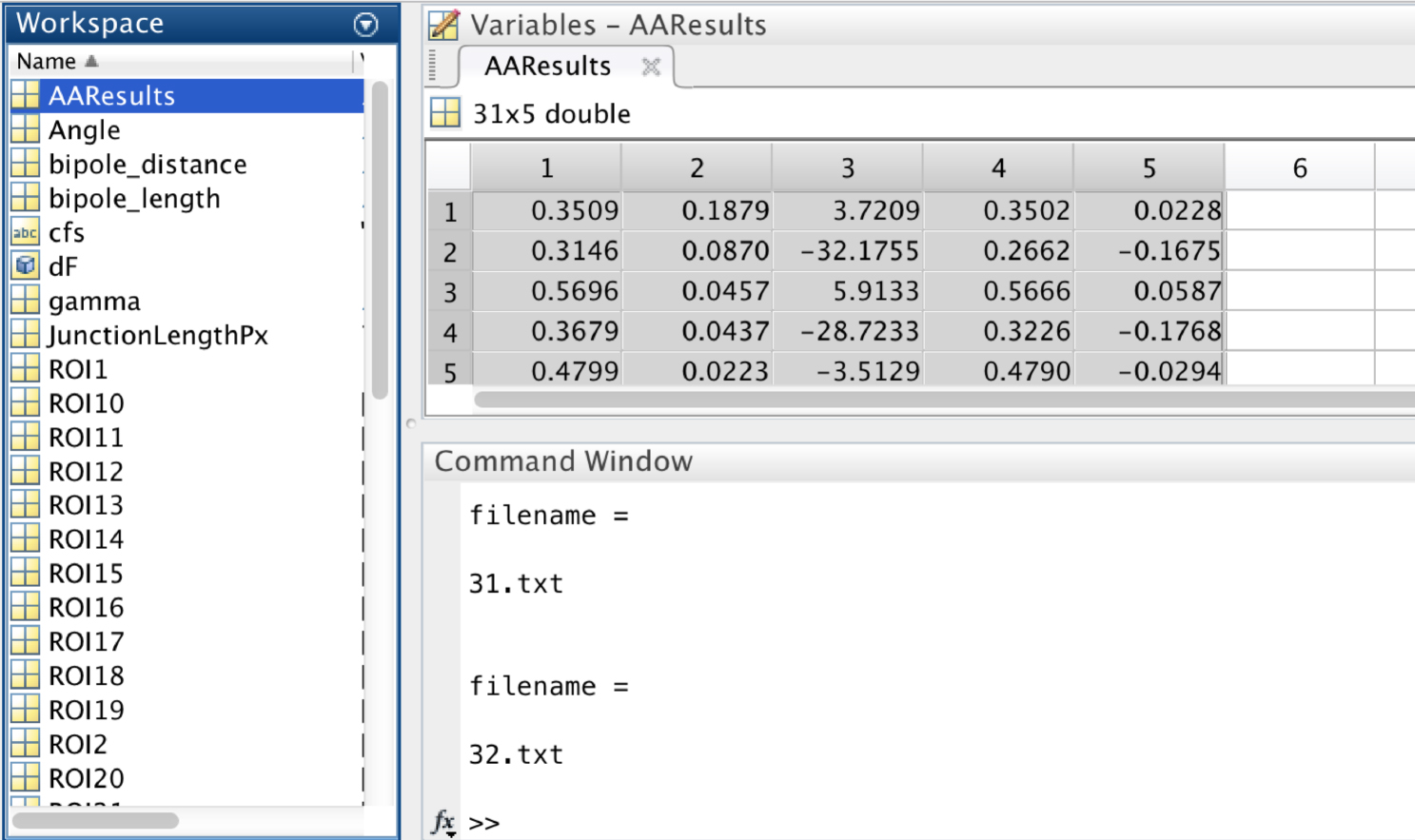
Figure 10. A screen snapshot of the ‘AAResults’ table in MATLAB. This table contains the numerical results for the different analysis. - Copy Columns 1 to 3 and paste into PRISM or Excel software to perform statistical analysis of the following parameters:
Average the values of minifilament length (average of Column 1).
Average the values of distance between minifilaments and the cell-cell junction (average of Column 2).
Standard deviation of angles between minifilaments and the cell-cell junction (standard deviation of Column 3). - These values then can be compared between different experimental conditions as in (Michael et al., 2016).
- In the workspace of MATLAB, the variable ‘AAResults’ will contain the numerical results for statistical analysis (Figure 10).
- Quantification of minifilaments alignment was performed using custom-made scripts for FIJI and MATLAB (see Appendix I and Appendix II).
- Overview
Notes:
- If junctions to be analyzed are too vertical, modify the second line of the Matlab code to make it
Rotate45 = 1.
This would prevent a premature stop of the code while running. - Analyze Column 4 of the AA results for the presence of negative values. The code and analysis are designed to run in such a way that values within this column should be positives. If some negative values are present for this column, the rows containing them should be excluded from analysis.
Recipes
- 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA, in cytoskeletal stabilization buffer)
Dissolve PFA in 10 mM PIPES at pH 6.8
100 mM KCl
300 mM sucrose
2 mM EGTA
2 mM MgCl2
Adjust pH to 7.0
Store at -20 °C in 10 ml aliquots - Tris buffered saline (TBS)
50 mM Tris-Cl
150 mM NaCl
Dissolve in Milli-Q water
Adjust pH to 7.5 - Blocking buffer
Dissolve 5% (wt/vol) BSA into 1x TBS
Acknowledgments
This protocol is an adapted version of the one published in (Michael et al., 2016). This work was supported by grants from the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia (1037320, 1067405), the Australian Research Council (DP120104667, 150101367) and the Kids Cancer Project of the Oncology Children’s Foundation. Optical imaging was performed at the ACRF/IMB Cancer Biology Imaging Facility, established with the generous support of the Australian Cancer Research Foundation, and the Queensland Brain Institute microscopy facility supported by ARC LIEF grant (LE130100078).
References
- Beach, J. R., Shao, L., Remmert, K., Li, D., Betzig, E. and Hammer, J. A., 3rd (2014). Nonmuscle myosin II isoforms coassemble in living cells. Curr Biol 24(10): 1160-1166.
- Ebrahim, S., Fujita, T., Millis, B. A., Kozin, E., Ma, X., Kawamoto, S., Baird, M. A., Davidson, M., Yonemura, S., Hisa, Y., Conti, M. A., Adelstein, R. S., Sakaguchi, H. and Kachar, B. (2013). NMII forms a contractile transcellular sarcomeric network to regulate apical cell junctions and tissue geometry. Curr Biol 23(8): 731-736.
- Michael, M., Meiring, J. C., Acharya, B. R., Matthews, D. R., Verma, S., Han, S. P., Hill, M. M., Parton, R. G., Gomez, G. A. and Yap, A. S. (2016). Coronin 1B reorganizes the architecture of F-actin networks for contractility at steady-state and apoptotic adherens junctions. Dev Cell 37(1): 58-71.
- Pollard, T. D. (1982). Structure and polymerization of Acanthamoeba myosin-II filaments. J Cell Biol 95(3): 816-825.
- Ratheesh, A., Gomez, G. A., Priya, R., Verma, S., Kovacs, E. M., Jiang, K., Brown, N. H., Akhmanova, A., Stehbens, S. J. and Yap, A. S. (2012). Centralspindlin and α-catenin regulate Rho signalling at the epithelial zonula adherens. Nat Cell Biol 14(8): 818-828.
- Svitkina, T. M., Surguchova, I. G., Verkhovsky, A. B., Gelfand, V. I., Moeremans, M. and De Mey, J. (1989). Direct visualization of bipolar myosin filaments in stress fibers of cultured fibroblasts. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton 12(3): 150-156.
- Vicente-Manzanares, M., Ma, X., Adelstein, R. S. and Horwitz, A. R. (2009). Non-muscle myosin II takes centre stage in cell adhesion and migration. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10(11): 778-790.
- Yap, A. S., Michael, M. and Parton, R. G. (2015). Seeing and believing: recent advances in imaging cell-cell interactions. F1000Res 4(F1000 Faculty Rev): 273.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2016 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Michael, M., Liang, X. and Gomez, G. A. (2016). Analysis of Myosin II Minifilament Orientation at Epithelial Zonula Adherens. Bio-protocol 6(23): e2054. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2054.
Category
Cell Biology > Cell structure > Cell adhesion
Cell Biology > Cell imaging > Fluorescence
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link