- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Microglial Phagocytosis Assay
Published: Vol 6, Iss 21, Nov 5, 2016 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1988 Views: 18952
Reviewed by: Soyun KimPengpeng LiAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols
Identification and Sorting of Adipose Inflammatory and Metabolically Activated Macrophages in Diet-Induced Obesity
Dan Wu [...] Weidong Wang
Oct 20, 2025 2104 Views
Selective Enrichment and Identification of Cerebrospinal Fluid-Contacting Neurons In Vitro via PKD2L1 Promoter-Driven Lentiviral System
Wei Tan [...] Qing Li
Nov 20, 2025 1249 Views
Revisiting Primary Microglia Isolation Protocol: An Improved Method for Microglia Extraction
Jianwei Li [...] Guohui Lu
Dec 5, 2025 1129 Views
Abstract
Phagocytosis is essential for microglial clearance of apoptotic cells, extracellular protein aggregates, and infectious bacteria in the central nervous system (CNS). While the preparation of primary microglial culture has been described elsewhere, this protocol describes the microglial phagocytosis experimental procedure and the subsequent measurement of microglial phagocytic ability using fluorescent latex beads or fluorescent amyloid beta 42 (Aβ42) peptides.
Background
Microglia play multiple roles in the central nervous system (CNS). Upon stimulation, microglia present complicated inflammatory responses including altered gene expression and morphological changes (Heneka et al., 2014; Cunningham, 2013). Cytokines are a critical cluster of proteins among the list of altered expression molecules by activated microglia. Through the potent signaling-capable cytokine receptors expressed on astrocytes, neurons, and other brain cell types, microglia communicate, recruit, and coordinate inflammatory events (Smith et al., 2012). Besides cytokine secretion, phagocytosis, which involves morphological changes in microglia, also adds to their role as guardians of environmental homeostasis within the CNS milieu. Microglial phagocytosis of pathogens, extracellular protein aggregates, and apoptotic cell debris dampens inflammation and protects neurons (Fu et al., 2014). Apart from pathogenic conditions, microglial phagocytosis is also involved in CNS development and synaptogenesis through eliminating nonfunctional synapses. Deficient or excess microglial phagocytic ability could lead to abnormal synaptic connections and deposits of aggregated proteins (Schafer et al., 2012; Lian et al., 2016). Here we describe a protocol for measuring microglial phagocytic ability using in vitro cultured primary microglia. To mimic exogenous particles and protein aggregates, we used latex beads and amyloid β protein as the substrates for microglia to engulf.
Materials and Reagents
- 24-well plates (Corning, Costar®, catalog number: 3527 )
- 12 mm glass coverslips (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 12-545-81 )
- 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes (Corning, Axygen®, catalog number: MCT-150-R )
- Fluorescent latex beads of 1 μm diameter (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: L1030 )
- Poly-D-lysine (PDL) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P6407-5MG )
- Distilled water (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 15230147 )
- Dulbecco’s modified Eagle medium (DMEM) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 11995065 )
- Fetal bovine serum (FBS) (GE Healthcare, HycloneTM, catalog number: SH30088.03 )
- FAM-labelled Aβ42 peptides (AnaSpec, catalog number: AS-23526-01 )
- Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 472301 )
- Phosphate buffered salt (PBS)
- 4% PFA (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, catalog number: sc-281692 )
- Mounting medium with DAPI (Vector Laboratories, catalog number: H-1200 )
- Microglial culture media (500 ml) (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Ventilation hood (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: 1323 )
- CO2 cell culture incubator (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: 50144906 )
- 37 °C water bath (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, model: TSGP02 )
- Cell counter
Software
- ImageJ (http://fiji.sc/)
Procedure
- Coat coverslips with 10 μg/ml PDL (250 μl/well for a 24-well plate well) for 2 h at room temperature. Wash the coverslips with distilled water 3 times and aspirate the water before use.
Note: Extra coated plates could be stored at 4 °C for months. - Prepare purified primary microglial cells. Seed microglia onto coverslips at a density of 50,000 cells/cm2. Put the cultures into an incubator containing 5% CO2 and 100% humidity at 37 °C. Microglia attach to the wells within 2 h of seeding. Replenish the wells with fresh, pre-warmed microglial culture medium (No. 14 in ‘Materials and Reagents’ and No. 1 in ‘Recipes’) after cells are attached. Replace cultures into the incubator.
- Allow 24 h for the microglial cells to recover, after which the cells will be ready for the phagocytosis assay the following day.
- If using fluorescent beads:
Pre-opsonize aqueous green fluorescent latex beads in FBS for 1 h at 37 °C. The ratio of beads to FBS is 1:5. Dilute the bead-containing FBS with DMEM to reach the final concentrations for beads and FBS in DMEM of 0.01% (v/v) and 0.05% (v/v), respectively.
If using fluorescent Aβ42:
Prepare the fluorescent Aβ42 stock solution according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. We dissolve the peptide in DMSO to obtain a 0.1 mM stock (200x). Dilute the reconstituted Aβ42 peptides in DMEM to reach a final concentration of 500 nM and incubate the solution at 37 °C for 1 h to promote Aβ42 aggregation. - Replace microglial conditioned culture media with beads- or Aβ-containing DMEM and incubate cultures at 37 °C for 1 h. For a well of a 24-well plate, we add 250 μl beads- or Aβ-containing DMEM.
- Wash cultures thoroughly with ice-cold PBS 5 times and then fix the cells using 4% PFA for 15 min.
- Perform immunohistochemistry for microglial proteins which can mark cell shape and counterstain the culture with DAPI. We visualize green fluorescent beads and FAM-Aβ with the green channel and use the red channel for Iba1 staining (Figures 1 and 2).
Note: Iba1 works well in our hands. It not only demonstrates cell morphology but also excludes other cell types since it is a microglial-specific marker. You should use a secondary antibody detectable by a different channel than the fluorescent beads or Aβ. - Image the microglial culture using a confocal microscope. For latex beads, we recommend imaging at low to medium magnification (10x or 20x) so that more cells can be imaged in one field. For Aβ42, we recommend imaging at medium or high magnification (e.g., 20x or 40x) to maintain sufficient resolution for visualizing the Aβ signal.
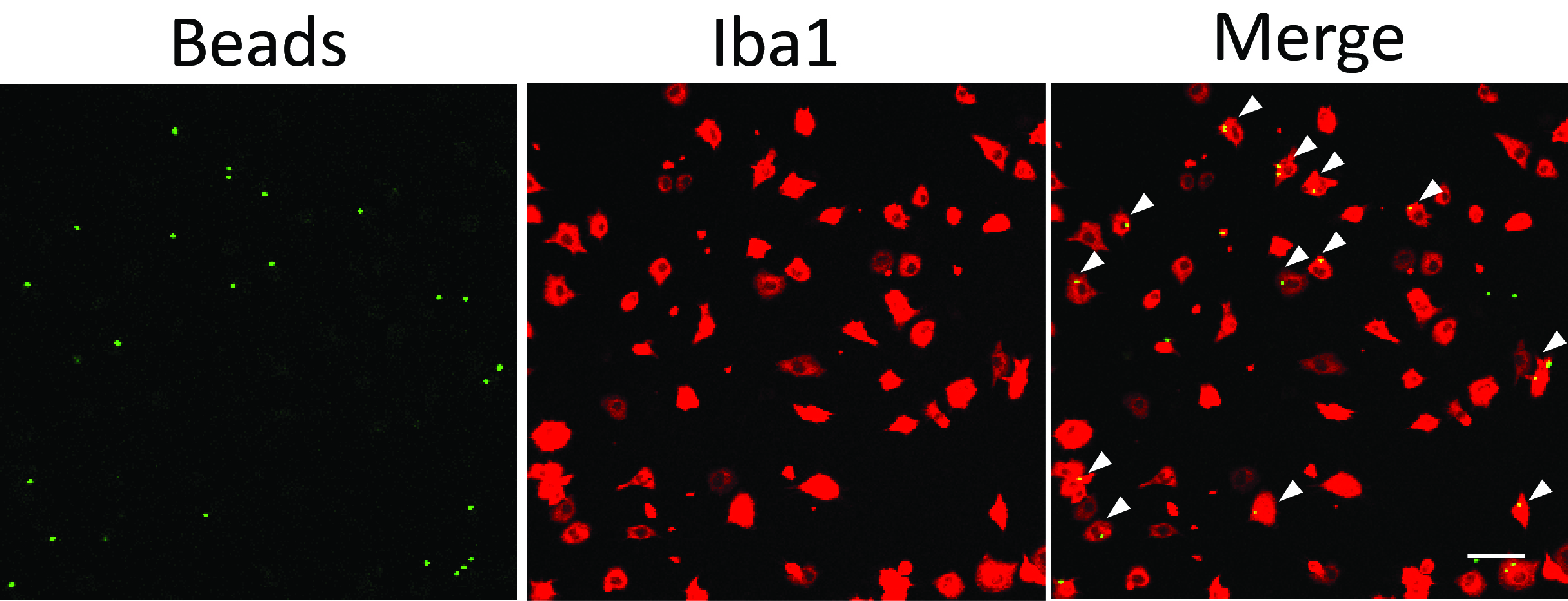
Figure 1. Microglial phagocytosis assay using fluorescent latex beads. White arrowheads point to phagocytic microglial cells containing beads inside the cell body. Scale bar = 50 μm.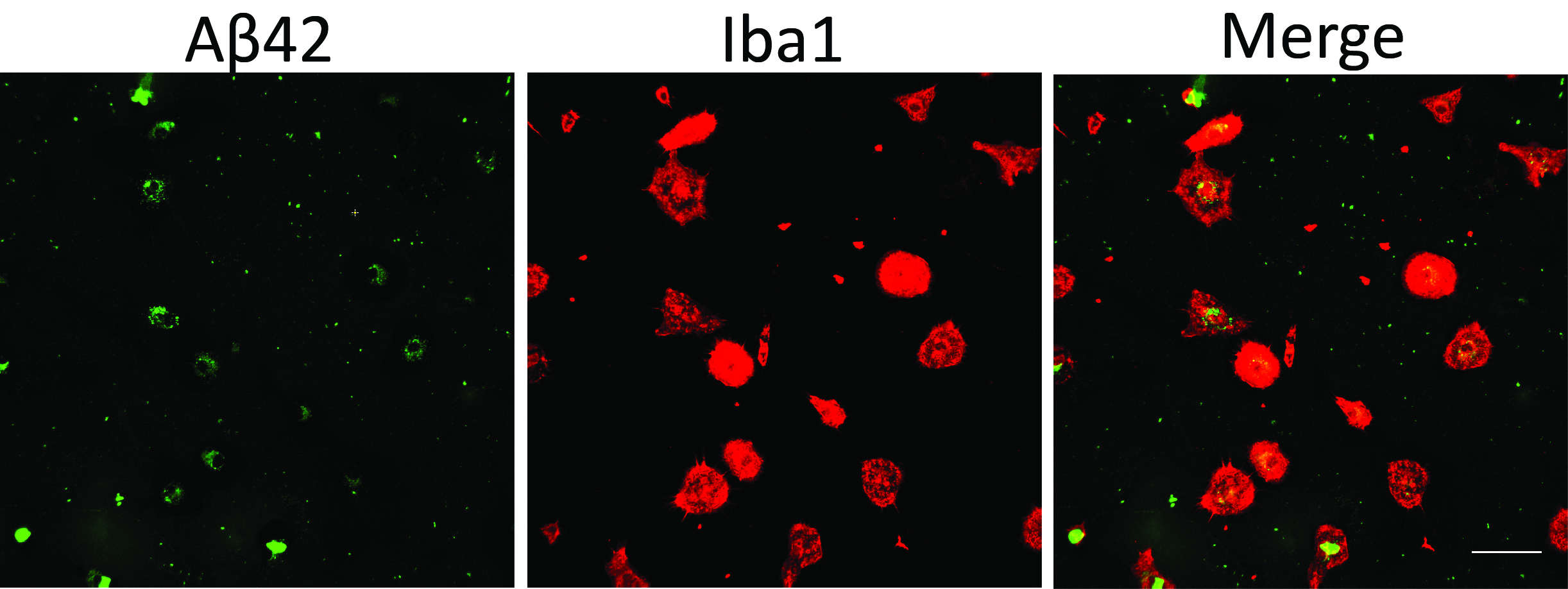
Figure 2. Microglial phagocytosis assay using fluorescent Aβ42. Scale bar = 50 μm.
Data analysis
Below we use the example of images of green fluorescent beads or Aβ and red Iba1 staining signal to explain the data processing procedure.
Open the file with ImageJ (We recommend the Fiji version of ImageJ. It has higher compatibility with many file formats generated by different microscope systems and is loaded with a variety of useful plugins).
- For microglial phagocytosis of latex beads
- Count the total cell number in each field. You can use the cell counter ImageJ plugin to count cells manually or count the total number of cell nuclei by using the ‘Analyze particles’ tool to automatically identify DAPI-positive areas after threshold adjustment (Ntotal) (Figure 3).
- Make a composite image of Iba1 and bead signals, and manually count cells having beads inside the cell body (Ncell with beads) using the cell counter plugin (Figure 4).
- Percentage of phagocytic cells is determined as: Ncell with beads/Ntotal.
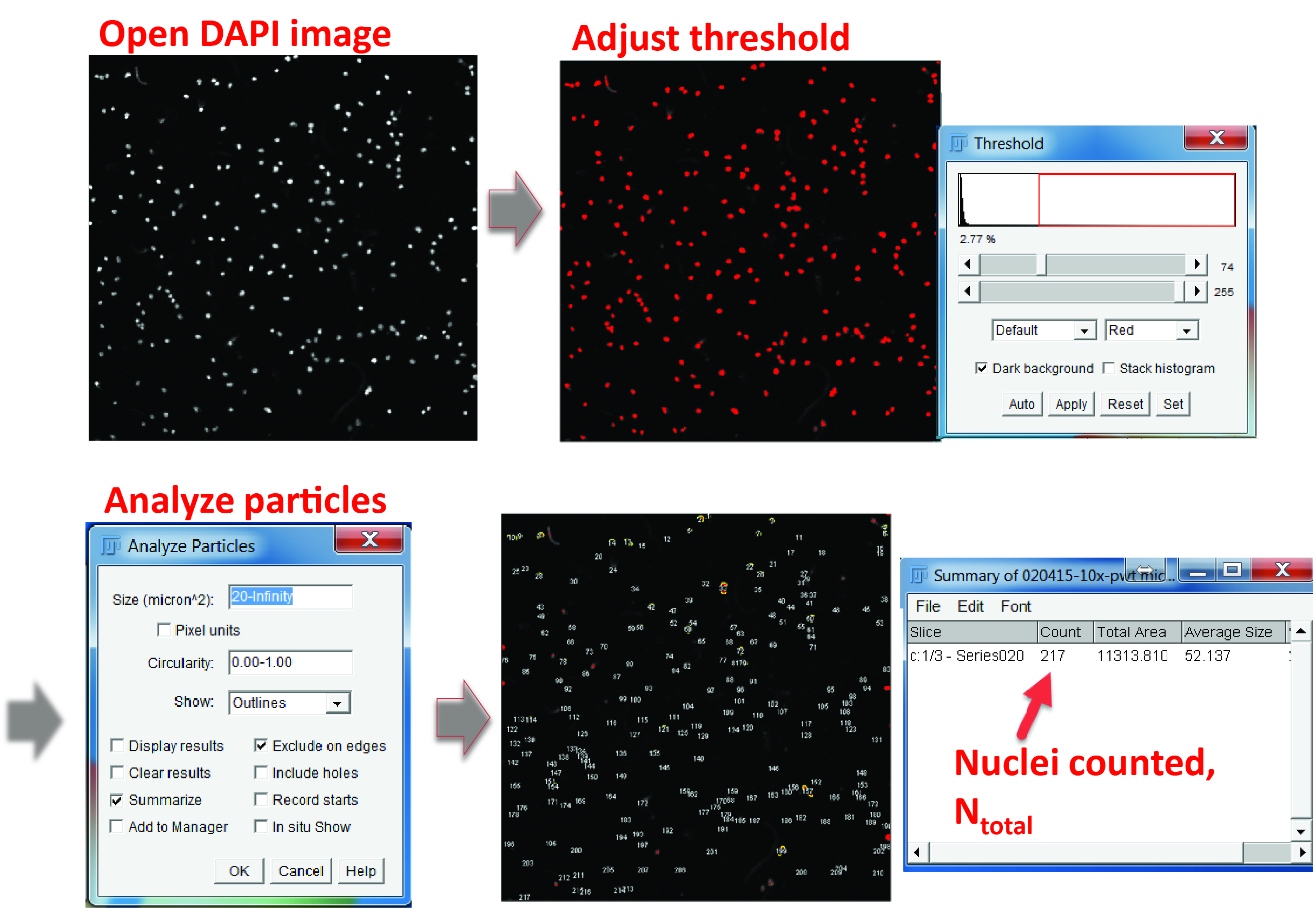
Figure 3. Counting the total cell number in a field. In the DAPI channel, adjust the color threshold until all the nuclei are highlighted. Select ‘Analyze particles’ in the menu, define the particle size from 20 μm2 to infinity (20 μm2 is usually large enough to exclude non-specific signals) and check the options of ‘Exclude on edges’ and ‘Summarize’. The output window will show the total number of cells counted.
Figure 4. Counting phagocytic cells using the cell counter plugin. Make a composite image of beads and Iba1, open the cell counter plugin, initialize the image, chose a cell type, and click on the cells having beads inside the cell body. The number of selected cells will show up in the plugin window.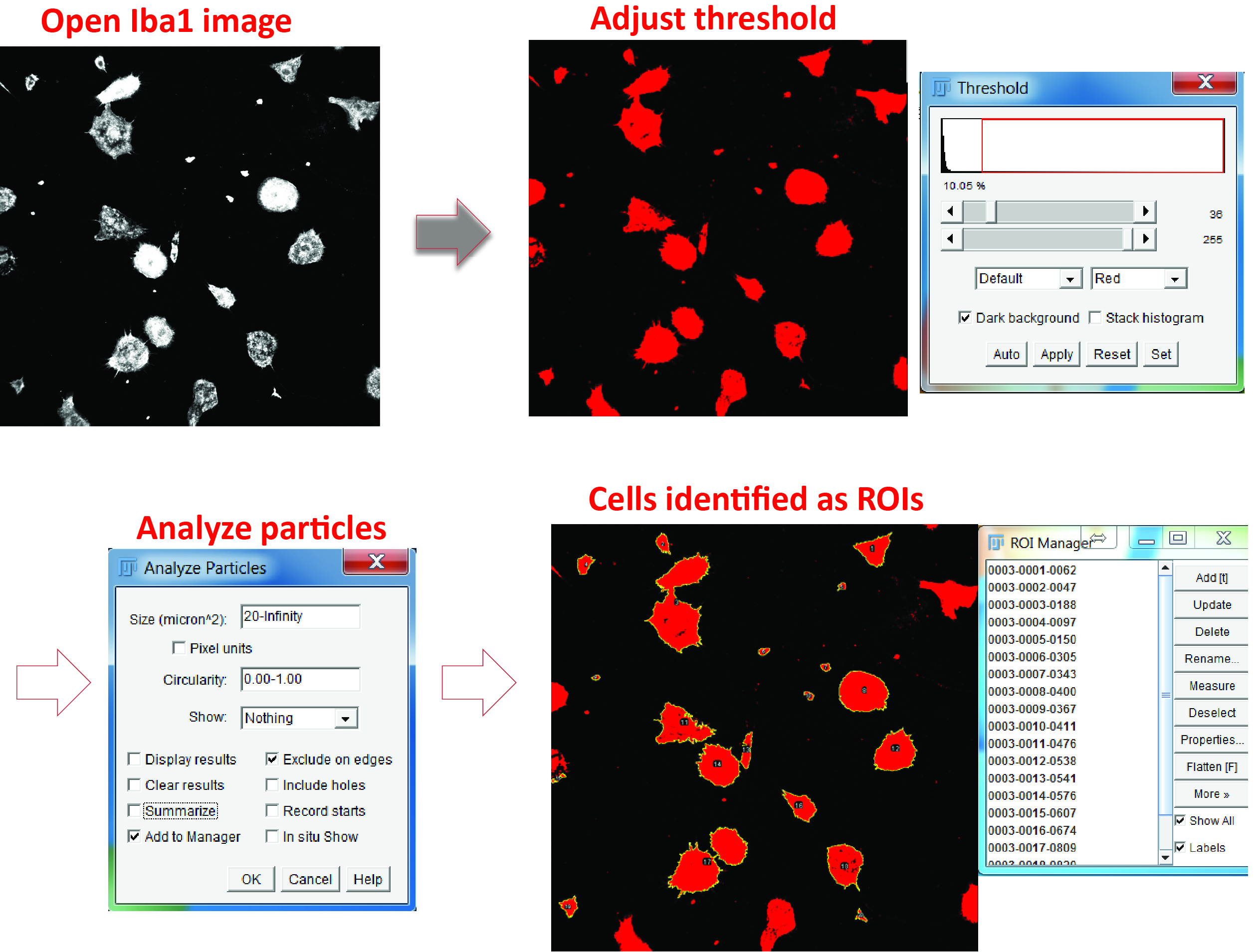
Figure 5. Identify microglial cell body. Open the Iba1 image, adjust the color threshold to highlight the cell body, and define the particle size. Check the option of adding the positive areas to the ROI manager (‘Add to Manager’) and the areas will be numbered and listed in the ROI Manager. - For phagocytosis assays using Aβ42
- Identify individual microglial cells as regions of interest (ROIs) using the Analyze particles function and the ROI manager in the Iba1 channel (Figure 5).
- Exclude ROIs that represent cell debris (check the DAPI channel and exclude the ROIs without a nucleus) or have large FAM-labelled inclusions of Aβ aggregates, as these artefacts will introduce large variance into your measurement (check the Aβ channel and exclude the ROIs with bulky Aβ) (Figure 6).
- Switch to the Aβ channel. Adjust the color threshold to highlight Aβ-positive regions and measure both the fluorescence intensity and percentage area of Aβ inside each ROI (Figure 7).
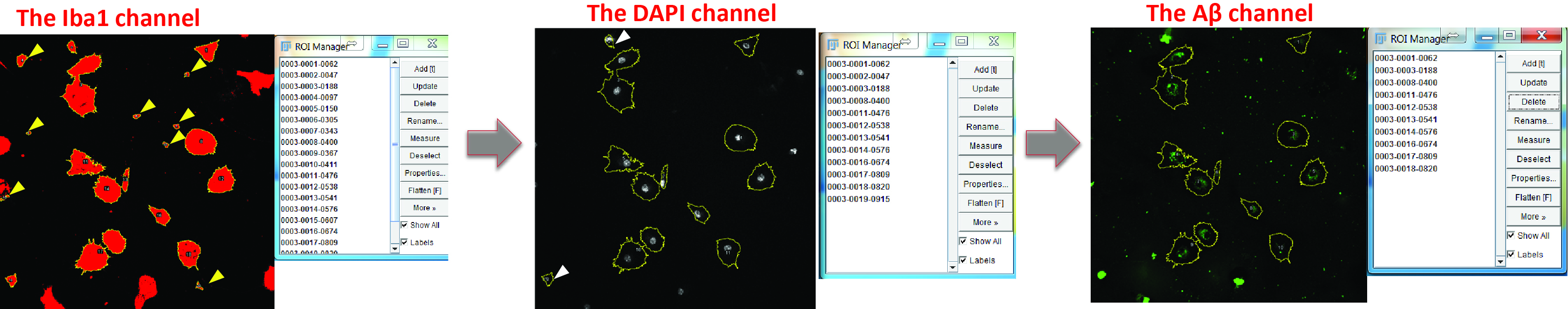
Figure 6. Optimize the selection of positive areas. Switch to the DAPI channel and exclude the regions without nucleus (yellow arrowheads). Switch to the Aβ channel and delete the cells which engulf large Aβ aggregates (white arrowheads).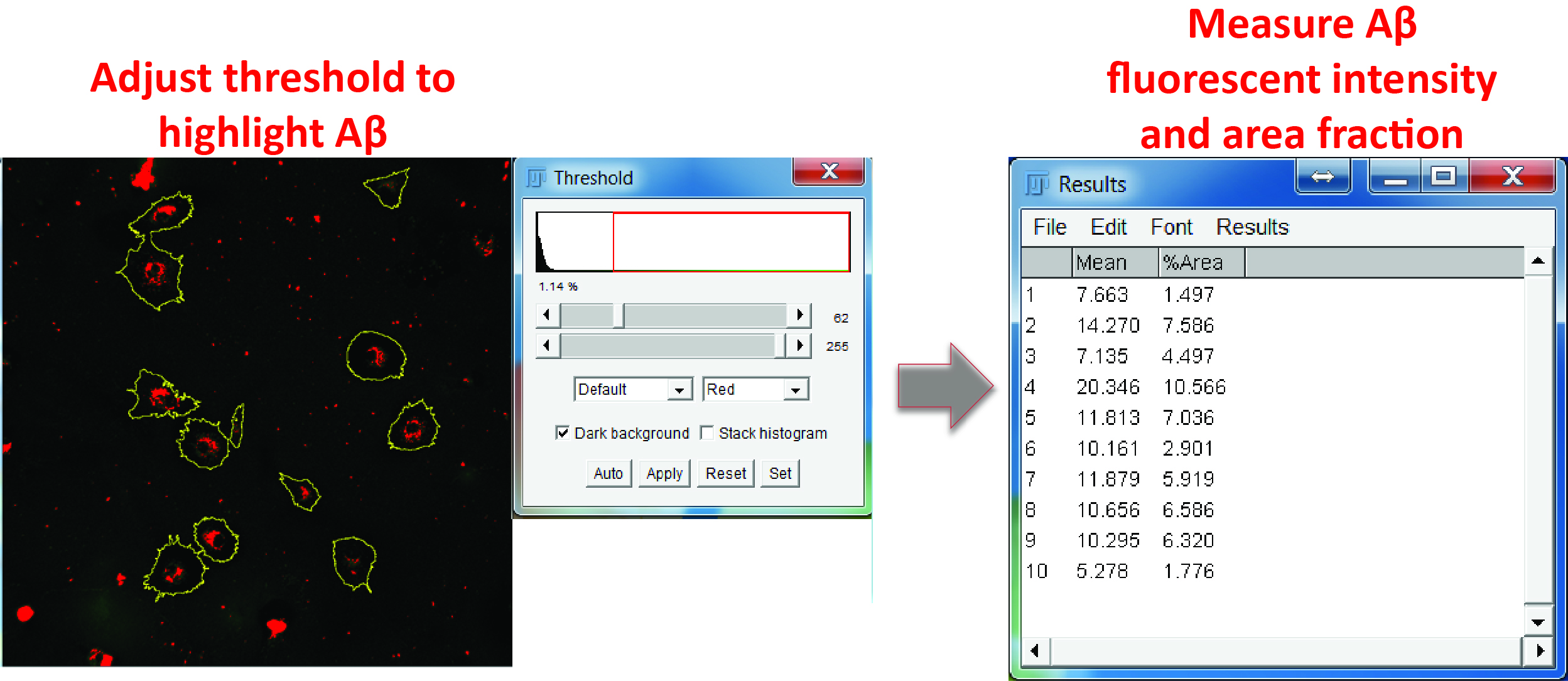
Figure 7. Aβ measurement. In the Aβ channel, adjust the color threshold to select Aβ positive signals, select all the regions in the ROI manager, and measure the mean grey value and area fraction of the Aβ signals in the ROIs.
Recipes
- Microglial culture media (500 ml)
Add 50 ml FBS to 450 ml DMEM for a final serum concentration of 10%
Acknowledgments
We thank the R01s from the NIH (AG032051, AG020670, and NS076117 to H.Z.) for supporting this work.
References
- Cunningham, C. (2013). Microglia and neurodegeneration: the role of systemic inflammation. Glia 61(1): 71-90.
- Fu, R., Shen, Q., Xu, P., Luo, J. J. and Tang, Y. (2014). Phagocytosis of microglia in the central nervous system diseases. Mol Neurobiol 49(3): 1422-1434.
- Heneka, M. T., Kummer, M. P. and Latz, E. (2014). Innate immune activation in neurodegenerative disease. Nat Rev Immunol 14(7): 463-477.
- Lian, H., Litvinchuk, A., Chiang, A. C., Aithmitti, N., Jankowsky, J. L. and Zheng, H. (2016). Astrocyte-microglia cross talk through complement activation modulates amyloid pathology in mouse models of Alzheimer's disease. J Neurosci 36(2): 577-589.
- Schafer, D. P., Lehrman, E. K., Kautzman, A. G., Koyama, R., Mardinly, A. R., Yamasaki, R., Ransohoff, R. M., Greenberg, M. E., Barres, B. A. and Stevens, B. (2012). Microglia sculpt postnatal neural circuits in an activity and complement-dependent manner. Neuron 74(4): 691-705.
- Smith, J. A., Das, A., Ray, S. K. and Banik, N. L. (2012). Role of pro-inflammatory cytokines released from microglia in neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Res Bull 87(1): 10-20.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2016 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Lian, H., Roy, E. and Zheng, H. (2016). Microglial Phagocytosis Assay. Bio-protocol 6(21): e1988. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1988.
- Lian, H., Litvinchuk, A., Chiang, A. C., Aithmitti, N., Jankowsky, J. L. and Zheng, H. (2016). Astrocyte-microglia cross talk through complement activation modulates amyloid pathology in mouse models of Alzheimer's disease. J Neurosci 36(2): 577-589.
Category
Neuroscience > Cellular mechanisms > Cell isolation and culture
Cell Biology > Cell isolation and culture > Cell isolation
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link