- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
PCR-based Assay for Genome Integrity after Methyl Methanesulfonate Damage in Physcomitrella patens
Published: Vol 6, Iss 19, Oct 5, 2016 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1954 Views: 8703
Reviewed by: Marisa RosaAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols
A Microplate-Based Expression Monitoring System for Arabidopsis NITRATE TRANSPORTER2.1 Using the Luciferase Reporter
Yoshiaki Ueda and Shuichi Yanagisawa
Dec 5, 2024 1714 Views
A Novel Gene Stacking Method in Plant Transformation Utilizing Split Selectable Markers
Guoliang Yuan [...] Xiaohan Yang
Feb 20, 2025 1902 Views

Optimized Protocol for DNA Extraction in Three Theobroma Species
Angie F. Riascos-España [...] Pedro A. Velasquez-Vasconez
May 5, 2025 1953 Views
Abstract
In plant cells, genomic DNA exists in three organelles: the nucleus, chloroplast, and mitochondrion. Genomic DNA can be damaged by endogenous and exogenous factors, but the damaged DNA can be repaired by DNA repair systems. To quantify the extent of their repair activity of on individual genomic DNA, a PCR-based assay utilizing long amplicons is valuable for evaluable. This assay is based on the inhibitory effects of methyl methanesulfonate (MMS)-induced DNA damage on the amplicons. This assay is useful for assessing DNA double-strand repair pathways, such as homologous recombination repair, as it detects DNA double-strand breaks produced by MMS in vivo.
Keywords: ChloroplastBackground
The quantification of genomic DNA damage is useful for analyzing DNA repair mechanisms. This assay utilizes real-time PCR to quantify the nuclear, chloroplast, and mitochondrial DNA copy number for the normalization of long PCR products, providing more accurate quantification compared with that by the previous protocol by Hunter et al. (2010).
Materials and Reagents
- 90 mm plastic Petri dish
- 50 ml tube
- 1.5 ml tube
- Physcomitrella patens protonemal cells (cultivated for 4 days)
- BCDAT medium (Nishiyama et al., 2000)
- Methyl methanesulfonate (MMS) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 129925 )
- Chloroform (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: V800117 )
- Ethanol (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 09-0770 )
- RNase A
- LA Taq (TAKARA BIO, catalog number: RR002A )
- Agarose powder (Promega, catalog number: V3125 )
- 0.7% agarose gel
- Ethidium bromide (EtBr)
- Power SYBR® green PCR master mix (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Applied BiosystemsTM, catalog number: 4367659 )
- Hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: H-5882 )
- Sodium chloride (NaCl) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 28-2270 )
- Tris-HCl, pH 8.0 (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 206-07884 )
- Ethylenediamine-N,N,N’,N’-tetraacetic acid, disodium salt, dihydrate (EDTA) (DOJINDO, catalog number: 345-01865 )
- PEG8000 (MP Biomedicals, catalog number: 02194839 )
- Oligonucleotide DNA primers for long amplicon quantitative PCR:
Nuclear DNA (5′-GTGGAAGTGAGATGCAGTTTGG-3′ and 5'-GTGGCTCTGGACAGTGAAATTG-3′)
Chloroplast DNA (5′-AATTGGAGTCGGTCCTTCCATA-3′ and 5′-TGGCAAATACAATGGCAAAAAG-3′)
Mitochondrial DNA (5′-GACTGCCCTCACTAGGATGCTT-3′ and 5′-TGGGTGATTTACTCCATTGACG-3′) - Oligonucleotide DNA primers for short amplicon quantitative PCR:
Nuclear DNA (5′-CAACCGTCTTCTGTGTCTAGGTC-3′ and 5′-GAAACCGGCCTGCATTACATG-3′)
Chloroplast DNA (5′-AGTAATCCCATCGCGTGACAT-3′ and 5′-AGGTATGGAAAAAATCGCTGAAAA-3′)
Mitochondrial DNA (5′-CGTGCTAAAAATCCAGTCCATTC-3′ and 5′-AGCAAAGAAGTCAAGACCTAACAAAAC-3′) - 2x CTAB buffer (see Recipes)
- 10% CTAB (see Recipes)
- CTAB ppt buffer (see Recipes)
- NaCl-TE (see Recipes)
- TE buffer (see Recipes)
- PEG solution (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Forceps
- Multi-beads shocker (Yasui Kikai)
- Vacuum pump (Tokyo Rikakikai, catalog number: AS-3 )
- Bench top centrifuge for 1.5 ml tubes
- Heat block for 1.5 ml tubes (TAITEC, catalog number: DTU-2CN )
- Standard thermal cycler (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 170-8720JA )
- Real-time PCR thermal cycler (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Applied BiosystemsTM, model: Applied Biosystems® 7500 Fast Real-Time PCR Systems )
Software
- ImageJ (https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/)
- Excel (Microsoft)
Procedure
- MMS treatment of plants
- Cultivate P. patens protonemal cells on four BCDAT agar plates for each strain under continuous light at 25 °C.
- Immerse P. patens protonemal cells in 12 ml BCDAT liquid medium containing 20 mM MMS in 90 mm plastic Petri dishes under vacuum for 1 h. Note that undamaged control samples are harvested prior to the MMS treatment. These should include three biological replicates.
Note: MMS is a carcinogen. - After washing with BCDAT liquid medium (twice with 15 ml BCDAT liquid medium in 50 ml tubes), cultivating the protonemal cells under continuous light at 25 °C.
- Using forceps, harvest the cells at 0, 6, 24 and 48 h after washing.
- Cultivate P. patens protonemal cells on four BCDAT agar plates for each strain under continuous light at 25 °C.
- Extraction of total genomic DNA
- Grind frozen protonemal cells using a homogenizer (Multi-beads shocker: 1,500 rpm, 10 sec, thrice). Alternatively, mortar and pestle can be used.
- Add an equal volume (approximately 300 µl in a 1.5 ml tube) of 2x CTAB buffer to the powdered protonemal cells. Mix and then incubate at 60 °C for 1 h.
- Mix with an equal volume of chloroform and centrifuge at 4,500 x g for 20 min. Recover aqueous phase (approximately 500 µl).
- Add 1/10 volume of 10% CTAB.
- Extract DNA with an equal volume of chloroform and recover the aqueous phase. Repeat this step twice.
- Add an equal volume of CTAB ppt buffer and mix well by inverting.
- Centrifuge at 4,500 x g for 20 min. Discard the supernatant.
- Dissolve the pellet in 400 µl of NaCl-TE. Incubate at 60 °C for 30 min.
- Add two volumes of ethanol.
- Centrifuge at 14,000 x g for 10 min. Discard the supernatant.
- Dissolve the pellet in 100 µl of TE. The pellet may be insoluble at this step, but will dissolve in the next step.
- Add 2 µl of RNase A (1 mg/ml) and incubate at 37 °C for 1 h.
- Add an equal volume of PEG solution.
- Centrifuge at 14,000 x g at 4 °C for 10 min.
- After removing the supernatant, rinse the pellet with 70% ethanol.
- Dissolve the pellet in 100 µl of TE.
- Grind frozen protonemal cells using a homogenizer (Multi-beads shocker: 1,500 rpm, 10 sec, thrice). Alternatively, mortar and pestle can be used.
- Long amplicon quantitative PCR
Long amplicon PCR is performed to quantify the amount of undamaged DNA template.- Design primers to generate 8-10 kb PCR amplicons from the nuclear, chloroplast, and mitochondrial genomes.
Note: Long amplicons efficiently detect DNA damage; however, amplification efficiency is poor. - Prepare a dilution series (20, 10, 5, 2.5, 1.25 and 0.625 ng/µl by diluting with TE buffer) of undamaged DNA, spanning the range from the lowest to the highest amount of PCR product in the damaged samples, to use as standard. Diluted samples to 10 ng/µl by adding TE buffer, and use 1 µl for each PCR reaction.
- Perform a 2-step PCR (first step, 98 °C for 10 sec; second step, 68 °C for 10 min) using a Taq DNA polymerase optimized for long amplicon (LA-Taq). Subject all samples and control dilutions to a single PCR reaction. Use the number of PCR cycles at which the resulting DNA amplicon is exponentially amplified. Thus, the resulting amount/yield of the PCR amplicon reflects the amount of DNA template used in the reaction. Use 17, 20 and 27 cycles for amplifying the chloroplast, mitochondria and nuclear DNA, respectively.
- Electrophorese on 0.7% agarose gels stained with EtBr to resolve the PCR products (Figure 1). Load a suitable fraction of the PCR product on the gel.
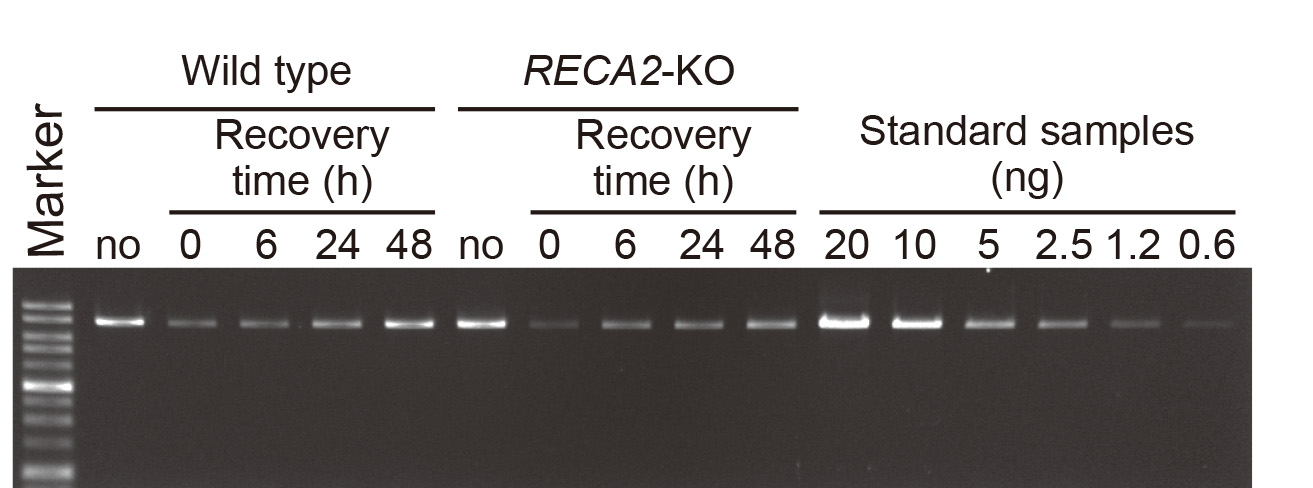
Figure 1. Electrophoresis of long PCR amplicons on agarose gel. An example of agarose gel electrophoresis of long PCR products from nuclear actin locus. No MMS damage control (no) and MMS-damaged samples (0, 6, 24 and 48 h after washing) were analyzed with serially diluted standard samples. RECA2-KO is shown as an example of a mutant (Odahara et al., 2015).
- Design primers to generate 8-10 kb PCR amplicons from the nuclear, chloroplast, and mitochondrial genomes.
- Short amplicon quantitative PCR
Short amplicon PCR allows copy number quantification of the nuclear, chloroplast and mitochondrial DNA. Both standard and real-time PCRs are applicable for this short amplicon quantitative PCR, but the latter provides more accurate values.- Design primers to amplify approximately 100 bp of the nuclear, chloroplast and mitochondrial loci, based on the standard protocol for quantitative real-time PCR assay using intercalating dyes, such as SYBR Green I.
- Prepare a dilution series to use as standard controls, including all sample concentrations. It is important to use the 10 ng/µl sample DNA prepared in the long amplicon PCR.
- Perform real-time PCR using DNA polymerase mixture optimized for real-time PCR (Power SYBR® Green PCR Master Mix) and thermal cycler real-time PCR system with a PCR program (first step, 95 °C for 15 sec; second step, 60 °C for 1 min). Calculate the relative copy number of the nuclear, chloroplast, and mitochondrial DNA of each sample using standard curves prepared using the standard samples.
- Design primers to amplify approximately 100 bp of the nuclear, chloroplast and mitochondrial loci, based on the standard protocol for quantitative real-time PCR assay using intercalating dyes, such as SYBR Green I.
Data analysis
Analysis of recovery from MMS damage- Measure the volume of each band in the electrophoresis gel with ImageJ using the “measure” tool, and calculate the relative amount of long PCR products from all samples by fitting them to the standard curve prepared using those from the serially diluted standard samples.
- Divide the relative amount of long amplicon PCR products by the relative copy number of the nuclear, chloroplast and mitochondrial DNA calculated from short amplicon PCR products to obtain the relative copy number of undamaged DNA.
- Relative recovery is calculated by dividing the amount of undamaged DNA in damaged samples by that of undamaged controls. Use t-test for statistical analysis of data from three biological replicates and Excel.
Recipes
- 2x CTAB buffer
2% CTAB
1.4 M NaCl
100 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0
20 mM EDTA
Store at room temperature (RT). - 10% CTAB
10% CTAB
0.7 M NaCl
Store at RT. - CTAB ppt buffer
1% CTAB
50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0
10 mM EDTA
Store at RT. - NaCl-TE
1 M NaCl
10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0
1 mM EDTA
Store at RT. - TE buffer
10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0
1 mM EDTA
Store at RT. - PEG solution
2 M NaCl
20% PEG8000
Store at RT.
Acknowledgments
The long amplicon PCR assay is based on Hunter et al. (2010) with slight modifications. The genomic DNA extraction protocol is based on PHYSCObase (http://moss.nibb.ac.jp/). This work was supported by the Strategic Research Foundation Grant-aided Project for Private Universities from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan, and the Funding Program for Next-Generation World-Leading Researchers (NEXT Program).
References
- Hunter, S. E., Jung, D., Di Giulio, R. T. and Meyer, J. N. (2010). The QPCR assay for analysis of mitochondrial DNA damage, repair, and relative copy number. Methods 51(4): 444-451.
- Nishiyama, T., Hiwatashi, Y., Sakakibara, I., Kato, M. and Hasebe, M. (2000). Tagged mutagenesis and gene-trap in the moss, Physcomitrella patens by shuttle mutagenesis. DNA Res 7(1): 9-17.
- Odahara, M., Inouye, T., Nishimura, Y. and Sekine, Y. (2015). RECA plays a dual role in the maintenance of chloroplast genome stability in Physcomitrella patens. Plant J 84(3): 516-526.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2016 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Odahara, M., Inouye, T., Nishimura, Y. and Sekine, Y. (2016). PCR-based Assay for Genome Integrity after Methyl Methanesulfonate Damage in Physcomitrella patens. Bio-protocol 6(19): e1954. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1954.
Category
Molecular Biology > DNA > DNA damage and repair
Plant Science > Plant molecular biology > DNA
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link










