- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Measurement of Cellular Copper in Rhodobacter capsulatus by Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy
Published: Vol 6, Iss 19, Oct 5, 2016 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1948 Views: 10527
Reviewed by: Valentine V TrotterFilipa VazAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols
β-lactamase (Bla) Reporter-based System to Study Flagellar Type 3 Secretion in Salmonella
Fabienne F. V. Chevance and Kelly T. Hughes
Jun 20, 2023 1709 Views
Determination of Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) Content in Cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 Using Acid Hydrolysis Followed by High-performance Liquid Chromatography
Janine Kaewbai-ngam [...] Tanakarn Monshupanee
Aug 20, 2023 1739 Views
An HPLC-based Assay to Study the Activity of Cyclic Diadenosine Monophosphate (C-di-AMP) Synthase DisA from Mycobacterium smegmatis
Avisek Mahapa [...] Dipankar Chatterji
Dec 20, 2024 1702 Views
Abstract
Copper is an essential micronutrient and functions as a cofactor in many enzymes such as heme-Cu oxygen reductases, Cu-Zn superoxide dismutases, multi-copper oxidases and tyrosinases. However, due to its chemical reactivity, free copper is highly toxic (Rae et al., 1999) and all organisms use sophisticated machineries for controlling uptake, storage and export of Cu. The strict control of the cellular Cu homeostasis prevents toxic effects but sustains synthesis of cuproproteins. Monitoring the copper levels within the cell and within different cellular compartments is an essential approach for identifying the contribution of different proteins in maintaining the cellular copper equilibrium. Therefore, whole cells and whole-cell lysates, which can be further fractionated into cytoplasm and periplasm, were digested and the protein concentration was determined by Lowry assay. Subsequently, the copper content was measured by atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) and the Cu content per mg of protein was calculated. This provides a simple and cost-effective method of producing quantifiable results about the cellular Cu content. To exemplify this method, we used the phototrophic α-proteobacterium Rhodobacter capsulatus, which is commonly used as a model organism for studying Cu-trafficking in bacterial cells (Ekici et al., 2012).
Keywords: Copper homeostasisBackground
Due to a growing interest in cellular Cu homeostasis different methods for measuring the cellular Cu content have been developed during the past years. They include electrochemical and fluorimetric protocols, inductively coupled plasma mass spectroscopy (ICP-MS), inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry (ICP-AES), electron microprobe analyses (EMPA), X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) or synchrotron-based X-ray fluorescent microscopy (SXRF) (reviewed in Ralle et al., 2009). Although these methods allow for a reliable and accurate determination of Cu in biological and environmental samples, they usually require advanced experimental set-ups and are not generally suited for analyzing a large number of samples. Atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) is a well established and widely available method that allows for a quick, sensitive and cost-effective Cu determination. It is suitable for determining Cu in whole cells but also in subcellular extracts.
Materials and Reagents
- Petri dishes (60 x 15 mm) (SARSTEDT, catalog number: 82.1194.500 )
- 50 ml Falcon tubes (SARSTEDT, catalog number: 62.559.001 )
- 15 ml Falcon tubes (SARSTEDT, catalog number: 62.554.502 )
- 0.45 µm filters (Carl Roth, catalog number: P667.1 )
- 10 ml syringes (Carl Roth, catalog number: C542.1 )
- Rhodobacter capsulatus wild type (MT1131) or mutant strains
- BactoTM peptone (BD, catalog number: 211820 )
- BactoTM yeast extract (BD, catalog number: 212720 )
- Calcium chloride dihydrate (CaCl2·2H2O) (Carl Roth, catalog number: 5239.1 )
- Magnesium chloride hexahydrate (MgCl2·6H2O) (Carl Roth, catalog number: 2189.2 )
- MPYE agar media (1.5% agar in MPYE medium; 25 ml/Petri dish)
- Chelex® 100 resin (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 1422832 )
- Tris/HCl, pH 7.5 (Carl Roth, catalog number: 5429.2 ; P074.1 )
- Sucrose (MP Biomedicals, catalog number: 04821713 )
- Lysozyme (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: L2879 )
- EDTA (Carl Roth, catalog number: 8043.2 )
- Lowry protein assay reagents [Reagent A, Folin & Ciocalteu’s phenol reagent (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: F9252 ), 1% SDS/0.1 N NaOH]
- SDS (SERVA Electrophoresis, catalog number: 20765.03 )
- Protein assay bovine serum albumin (Carl Roth, catalog number: 8076.4 ), standards (0, 0.02, 0.04, 0.08, 0.12, 0.2 mg/ml protein)
- Sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) (Carl Roth, catalog number: 8563.1 )
- Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) (Carl Roth, catalog number: 6771.1 )
- Copper(II) sulphate pentahydrate (CuSO4·5H2O) (Carl Roth, catalog number: P024.1 )
- Na-tartrate (EMD Millipore, catalog number: 106663 )
- 53% nitric acid in ultra-pure water (Carl Roth, catalog number: 9274.1 )
- 30% hydrogen peroxide (Carl Roth, catalog number: 9681.1 )
- Ultra-pure water (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, model: BarnsteadTMGenPureTM )
- Palladium (II) chloride (VWR, catalog number: AA11034-09 )
- Magnesium chloride (MgCl2) (VWR, catalog number: AA42843-22 )
- Copper standards [(20, 40, 60 ppb Cu in ultra-pure water; diluted from TraceCert copper standard for AAS (1,000 mg/ml Cu in 2% nitric acid, prepared with high purity Cu metal)] (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 38996 )
- MPYE media (see Recipes)
- Cu-free MPYE (see Recipes)
- Cu-free water (see Recipes)
- Spheroplast buffer (see Recipes)
- Lysis buffer (see Recipes)
- Reagent A for Lowry assay (see Recipes)
- AAS modifier solution (see Recipes)
Equipment
- 1.5 ml cuvettes (Carl Roth, catalog number: Y195.1 )
- Magnetic stir plate (Heidolph, model: Hei-VAP )
- Sterile inoculation loop (Carl Roth, catalog number: 6163.1 )
- Shaking incubator multitron standard for bacterial growth at 35 °C (Infors, mode: INFORS HT )
- 250 ml Erlenmeyer flasks (Carl Roth, catalog number: K184.1 )
- Centrifuge (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, model: Sorvall Lynx 6000 )
- Microscope at 100x magnification with numerical aperture 1.4 (OLYMPUS, model: BX51 )
- 1,000 µl automatic pipet (Gilson, catalog number: F123602 )
- Incubator for sample incubation at 60 °C and 80 °C (Kühner, model: ISF-1X )
- Atomic absorption spectrophotometer (PerkinElmer, model: 4110 ZL Zeeman )
- VIS spectrophotometer able to read OD660 and OD685 (e.g., GE Healthcare Life Science, model: Ultrospec 3100 Pro )
Software
- Excel 2007 (Microsoft)
- Perkin-Elmer AAWinLab software
Procedure
- Growth of Rhodobacter capsulatus and spheroplast preparation, preparation of Cu-free MPYE and Cu-free water
- Grow cultures under sterile conditions of the required Rhodobacter strains on MPYE agar plates (~24 h, at 35 °C) including antibiotics if required.
- Prepare MPYE medium for liquid culture, Cu-free MPYE and Cu-free water (see Recipes).
- Pick a single colony using a sterile inoculation loop and inoculate 10 ml MPYE in a 50 ml Falcon tube. Add appropriate antibiotics if required. Grow cultures at 35 °C and 110 rpm in a rotary shaker overnight.
- Next day: Inoculate the main culture (100 ml MPYE in 250 ml flask) with 108 cells from the overnight culture and incubate at 35 °C, 110 rpm until the culture reaches an OD685 of 1 (approx. 24 h, assuming that an OD685 = 1 corresponds to 7.5 x 108 cells/ml). This corresponds to the late exponential growth phase of R. capsulatus.
- Harvest the cells using a pre-cooled Lynx 6000 centrifuge (4 °C), at 5,000 rpm (corresponds to 3,000 x g in the F12-6 x 500 LEX rotor) for 20 min.
- Decant the supernatant and resuspend the pellet in 40 ml pre-cooled Cu-free MPYE and centrifuge once more at 5,000 rpm (3,000 x g, F12-6 x 500 LEX rotor) for 20 min at 4 °C.
- Decant the supernatant and resuspend the pellet in 2 ml spheroplast buffer and take a small aliquot of 50 µl for determining the protein concentration, e.g., by the Lowry assay (see Data analysis).
- Split the cell suspension in two equal parts into two clean 15 ml Falcon tubes. One tube is for measuring the copper concentration in whole cells, while cells in the other tube are used for spheroplast preparation. This allows measuring the copper content in the cytoplasm (spheroplasts), periplasm (supernatant after spheroplast preparation) and whole cells.
- Spheroplast preparation
- Add lysis buffer to the spheroplast sample fraction in a dilution of 1:10 to reach a final concentration of 0.1 mg/ml of lysozyme, e.g., add 100 µl lysis buffer to 900 µl sample.
- Incubate the cell suspension 15 min on ice with gentle mixing i.e., turning the tubes upside down several times every few minutes. After 15 min, the majority of cells are converted into spheroplasts; longer incubations might be required for other Gram-negative bacteria.
- Monitor spheroplast formation by using a microscope.
- Collect the spheroplasts by centrifugation at 5,000 rpm (3,000 x g, F12-6 x 500 LEX rotor) for 20 min at 4 °C.
- Carefully collect the supernatant (periplasm), preferentially using a 1,000 µl automatic pipet into a clean 15 ml Falcon tube.
- Resuspend the pellet (cytoplasm) with 1 ml spheroplast buffer.
- Take aliquots of 50 µl from each fraction and measure the protein concentration of all samples.
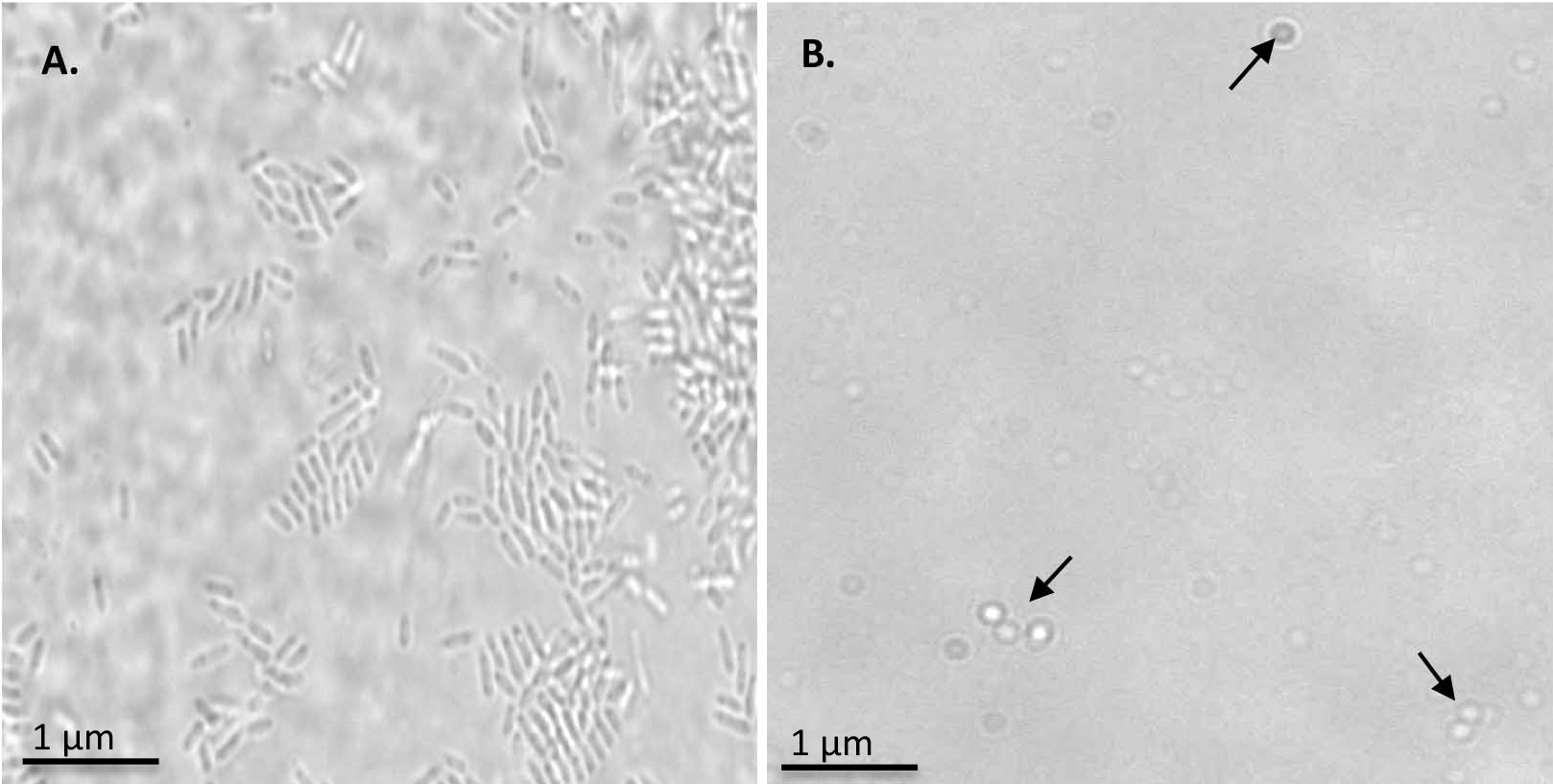
Figure 1. Monitoring the spheroplast formation. A. R.capsulatus cells observed at 100x magnification. B. Spheroplasts formation observed at 100x magnification. Spheroplasts are indicated by arrows.
- Add lysis buffer to the spheroplast sample fraction in a dilution of 1:10 to reach a final concentration of 0.1 mg/ml of lysozyme, e.g., add 100 µl lysis buffer to 900 µl sample.
- Grow cultures under sterile conditions of the required Rhodobacter strains on MPYE agar plates (~24 h, at 35 °C) including antibiotics if required.
- Determination of Cu-concentration by atomic absorption spectroscopy
- To approximately 1 ml of whole cells, spheroplasts and the supernatant (after the spheroplast preparation) in 15 ml Falcon tubes, add 1.5 ml of 53% nitric acid. This treatment and the following incubation at high temperatures completely denature the protein solutions and releases any bound metal. Incubate for 1 h at 80 °C and subsequently at 60 °C overnight without shaking.
- After overnight-incubation, stop the digestion by the addition of 300 µl H2O2 (30% in water) and adjust the samples to a final volume of 10 ml by adding Cu-free water.
- If any insoluble impurities are observed, the solution is filtrated through a 0.45 µm disposable syringe-filter. The prepared samples are now stable and can be stored for several days at room temperature.
- The copper content is measured using an atomic absorption spectrophotometer measuring 3 times for 3 sec of atomization. Load 20 µl sample and 5 µl modifier containing 0.005 mg palladium and 0.003 mg magnesium (functioning as ionization agent).
- Blank measurement (0.2% nitric acid in ultra-pure water), calculate mean and set to 0.
- Calibrate the spectrophotometer by measuring 3 standards containing 20, 40 and 60 ppb of Cu.
- Measure the samples. If the values are out of range, dilute the samples 1:2 or 1:3.
- Analysis of the copper content is achieved by the Perkin-Elmer AAWinLab software. For every value the standard deviation (SD) and relative standard deviation (RSD) is calculated by the software.
- Blank measurement (0.2% nitric acid in ultra-pure water), calculate mean and set to 0.
- Plot the data in excel using protein concentrations and copper measurements. Calculate the total copper amount of your 10 ml sample and divide it through the total protein mass, calculated by protein quantification assay and the sample volumes before adding the nitric acid using the following formula:
µg Cu/mg protein = (X Cu ppb x 10 ml)/(X mg/ml protein x X ml sample volume)
Note: Cu ppb refers to Cu µg/L.
- To approximately 1 ml of whole cells, spheroplasts and the supernatant (after the spheroplast preparation) in 15 ml Falcon tubes, add 1.5 ml of 53% nitric acid. This treatment and the following incubation at high temperatures completely denature the protein solutions and releases any bound metal. Incubate for 1 h at 80 °C and subsequently at 60 °C overnight without shaking.
Data analysis
- A representative experiment demonstrating the determination of the cellular copper content in Rhodobacter capsulatus can be found in Trasnea et al. (2016). Cooperation between two periplasmic copper chaperones is required for full activity of the cbb3-type cytochrome oxidase and copper homeostasis in Rhodobacter capsulatus.
- An example of the excel BSA standard curve for determining protein concentration in Rhodobacter capsulatus cells/cell extracts is described below. The samples were diluted in 200 µl of 1% SDS/0.1 N NaOH, 1 ml reagent A was added, followed by 5 min of incubation at room temperature. Afterwards, 100 µl of Folin & Ciocalteu’s phenol reagent 1 N was added and after 45 min of incubation the absorbance at A660 was determined. The absorbance was correlated to a protein concentration using a standard curve (as described below).
Table 1. BSA protein standards and their relative absorbance at A660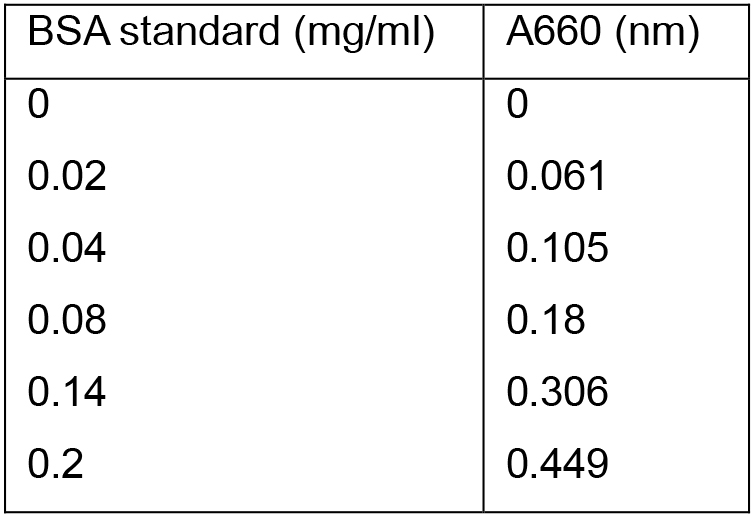
Absorbance reads were determined using a VIS spectrophotometer and data were subsequently plotted as seen in Figure 2.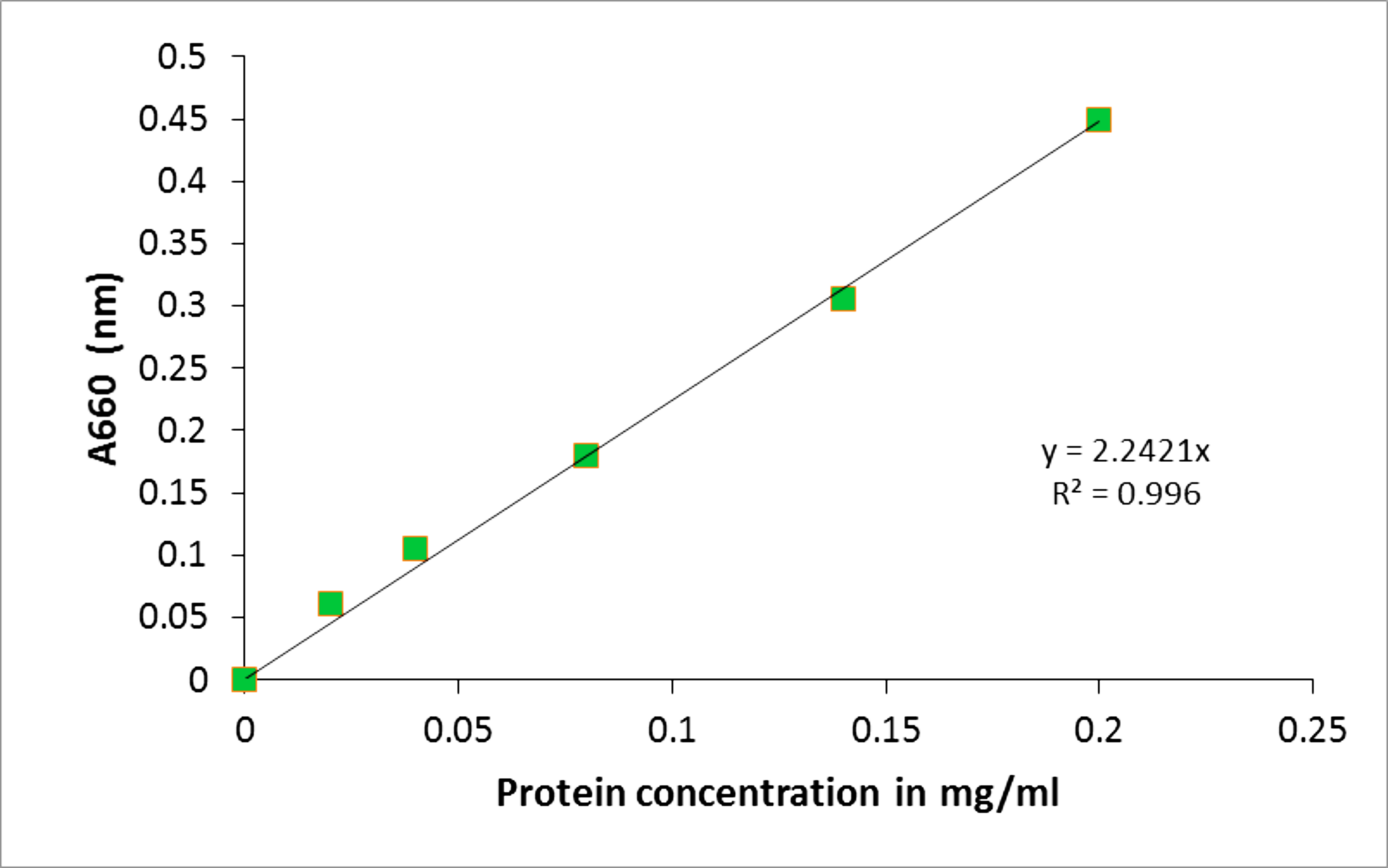
Figure 2. BSA protein standard curve. The absorbance at A660 (nm) was determined for a range of BSA protein standards from 0-0.2 mg/ml. The line of the best fit was plotted using y = mx (MS Excel 2007). The protein concentration of the samples was determined by correlating their absorbance to the protein concentration on the x-axis. - A representative of the Cu standards and their extinction values for atomic absorption spectroscopy using the Perkin-Elmer AAWinLab software is provided in Table 2. Figure 3 contains an exemplified standard curve using Microsoft Excel (in process automatically generated by the Perkin-Elmer AAWinLab software).
Table 2. Cu standards and their extinctions at 324.8 nm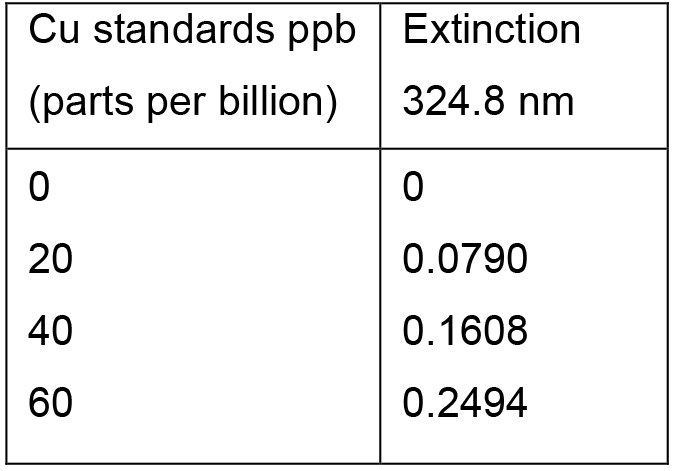
The data were subsequently plotted using the Perkin-Elmer AAWinLab software or MS Excel as displayed in Figure 3.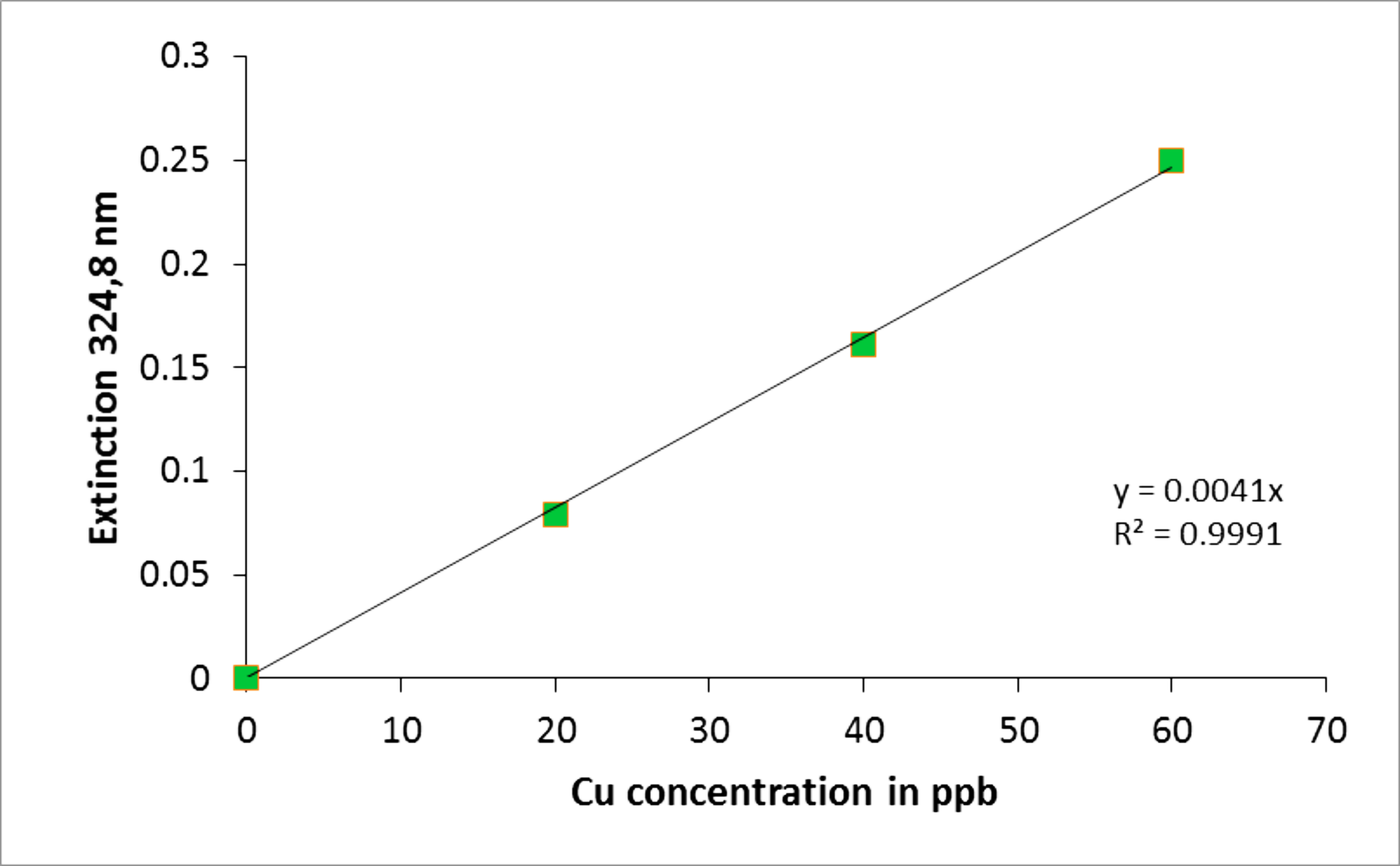
Figure 3. Cu concentration standard curve. The curve was generated using Microsoft Excel using the values obtained by AAS. The extinction standards at 324.8 nm were determined for a range of 0-60 ppb of Cu. Using this curve the copper concentration from cells and different cell compartments can be determined by correlating their extinction to the Cu concentration values on the x-axis.
Notes
- This protocol is optimized for measuring the intracellular copper concentration of Rhodobacter capsulatus. For other bacteria, use the appropriate growth media with appropriate antibiotics and growth conditions. Cu was determined in cells harvested at the late exponential growth phase of OD685 = 0.8. The method should also work with cells harvested at different growth phases, but this was not analyzed here.
- The lysozyme treatment for periplasm extraction is optimized for R. capsulatus and therefore for Gram-negative bacteria. As lysozyme does not reliably work on all Gram-negative bacteria, different muramidases such as mutanolysin can be tested in these cases.
- With the obtained copper concentrations, the molar concentration of copper in cell compartments can be calculated by dividing the copper content of the sample by the volume of the cell compartment using the following formula:
µmol/L Cu = (X µg/L Cu x A)/(63.546 g/mol x B x C)
A = sample volume (usually 0.01 L) [L]
B = number of cells in the sample (determined by OD measurement or by microscopic counting of cells)
C = estimated volume of one cell or the cell compartment [L]
63.546 g/mol corresponds to the molecular mass of Cu
Example:
Assuming that the cytosol plus the inner membrane of one Rhodobacter capsulatus cell has a volume of 1.9 x 10-16 L (calculated, based on the CyberCell Database; http://ccdb.wishartlab.com/CCDB/), the molar concentration of copper in the cytoplasm is around 300 µM.
Recipes
- MPYE medium
0.3% (w/v) BactoTM peptone
0.3% (w/v) BactoTM yeast extract
0.1% (v/v) 1 M CaCl2·2H2O
0.1% (v/v) 1 M MgCl2·6H2O
Distilled water, autoclave - Cu-free MPYE and Cu-free water
Add 5 g Chelex 100 resin to 100 ml solution and stir continuously for at least 1 h.
Afterwards, filter the solution through a 0.45 µm filter and autoclave.
After Chelex-treatment, the copper concentration is below the limit of detection. - Spheroplast buffer (stored at 4 °C or freshly prepared)
100 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5
0.5 M sucrose
Prepared with Cu free water and diluted from stock solutions (1 M Tris-HCl, pH 7.5; 2.5 M sucrose). Store at 4 °C. - Lysis buffer
10 mg/ml lysozyme dissolved in 8 mM EDTA, pH 8. Final concentration 0.1mg/ml. - Reagent A for Lowry assay
2% (w/v) Na2CO3
0.1 N NaOH
0.01% (w/v) CuSO4
0.02% (w/v) Na-tartrate
Dissolved in water - AAS modifier solution
0.005 mg palladium
0.003 mg magnesium
Volume up to 5 µl in ultra-pure water
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG, to HGK), the German Academic Exchange Service (DAAD, to PIT), the Else-Kröner-Fresenius Stiftung (to DM and MU) and the German-French PhD College on Membrane Proteins and Biological membranes (DFDK, to HGK).
References
- Ekici, S., Yang, H., Koch, H. G. and Daldal, F. (2012). Novel transporter required for biogenesis of cbb3-type cytochrome c oxidase in Rhodobacter capsulatus. MBio 3(1).
- Rae, T. D., Schmidt, P. J., Pufahl, R. A., Culotta, V. C. and O'Halloran, T. V. (1999). Undetectable intracellular free copper: the requirement of a copper chaperone for superoxide dismutase. Science 284(5415): 805-808.
- Ralle, M., Lutsenko, S. (2009). Quantitative imaging of metals in tissues. Biometals 22(1): 197-205.
- Trasnea, P. I., Utz, M., Khalfaoui-Hassani B., Lagies, S., Daldal, F. and Koch, H. G. (2016). Cooperation between two periplasmic copper chaperones is required for full activity of the cbb3-type cytochrome c oxidase and copper homeostasis in Rhodobacter capsulatus. Mol Microbiol 100(2): 345-361.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2016 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Trasnea, P., Marckmann, D., Utz, M. and Koch, H. (2016). Measurement of Cellular Copper in Rhodobacter capsulatus by Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy . Bio-protocol 6(19): e1948. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1948.
Category
Microbiology > Microbial biochemistry > Other compound
Biochemistry > Other compound > Ion > Copper
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link












