- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Killer Cell Ig-like Receptors (KIR)-Binding Assay for Tumor Cells
Published: Vol 6, Iss 18, Sep 20, 2016 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1931 Views: 7701
Reviewed by: HongLok LungBenoit ChassaingAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols
Reprogramming Cancer Cells to Antigen-presenting Cells
Alexandra G. Ferreira [...] Carlos-Filipe Pereira
Nov 20, 2023 4996 Views
Isolation and Ex Vivo Testing of CD8+ T-Cell Division and Activation Using Mouse Splenocytes
Melissa Dolan [...] John M.L. Ebos
Aug 20, 2025 3852 Views
Abstract
Natural killer (NK) cells play key roles in innate and adaptive immune responses against virus and tumor cells. Their function relies on the dynamic balance between activating and inhibiting signals through receptors that bind ligands expressed on target cells. The absence of inhibitory receptor engagement with their ligands and the presence of activating signals transmitted by activating receptors interacting with specific ligands, leads to NK cell activation (Lanier, 2005; Raulet et al., 2001). Thus, the balance of the ligands expressed for inhibitory and activating receptors determines whether NK cells will become activated to kill the target cells. This protocol allows to assign a precise ligand specificity to any given receptor on NK cells. Thus, if a tumor cell expresses the ligand, this protocol will allow to evaluate its interaction with the specific receptor. In particular, killer cell immunoglobulin (Ig)-like receptors (KIR) recognize their ligands (HLA class I molecules) through the direct contact with HLA class I heavy chain residues and amino acid residues of the bound peptide. This protocol will allow to test the effect of amino acid substitutions or other mutations on the binding of KIR to HLA class I. We used this protocol to depict the role of ERAP1, a key component of the MHC class I antigen processing, in regulating NK cell function by controlling the engagement of inhibitory receptors (Cifaldi et al., 2015).
Keywords: NK cellsMaterials and Reagents
- T25 Flasks (Corning, Falcon®, catalog numbers: 353108 )
- T75 Flasks (Corning, Falcon®, catalog numbers: 353136 )
- 15 ml centrifuge tubes (Corning, Falcon®, catalog number: 352096 )
- 96 well plates (Corning, catalog number: 3799 )
- FACS tubes
- Tumor cell line (grown in flasks, in incubator at 37 °C and 5% CO2)
- RPMI 1640 (EuroClone, catalog number: ECM9106L )
- Fetal bovine serum (FBS) heat-inactivated for 1 h at 56 °C (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 10270-106 )
- Penicillin/streptomycin (EuroClone, catalog number: ECB3001D )
- L-glutamine (EuroClone, catalog number: ECB3000D )
- EDTA (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: E5134 )
- Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) (EuroClone, catalog number: ECB4004L )
- Bovine serum albumin (BSA) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A2153-100G )
- Trypan-blue
- KIR-Fc fusion proteins
- Recombinant Human KIR2DL1/CD158a Fc chimera protein (R&D System, catalog number: 1844-KR-050 )
- Recombinant Human KIR2DL3/CD158b2 Fc chimera protein (R&D System, catalog number: 2014-KR-050 )
- Recombinant Human KIR3DL1 Fc chimera protein (R&D System, catalog number: 1225-KR-050 )
- Goat anti-Human Molecular ProbesTM secondary antibody, RPE conjugate (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Invitrogen, catalog number: H10104 )
- Complete RPMI (see Recipes)
- 833 μM EDTA (see Recipes)
- FACS buffer (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Centrifuge, used with maximal acceleration and deceleration (Eppendorf, model: 5810R )
- Incubator (5% CO2, 37 °C) (FormaTM Steri-CultTM CO2 Incubator-Thermo Fisher Scientific)
- Flow cytometer, equipped with 2 lasers (8 detectors), interfaced with PC by using DIVA Software version 6.1.3 (BD, model: FACSCanto II )
Software
- DIVA software version 6.1.3
- FlowJo software
Procedure
- Human tumor cells are cultured in fresh RPMI medium at a cell density ≥ 0.5-0.7 x 106 cells/ml in an incubator at 37 °C, 5% CO2. For each experiment are required 0.5 x 106 tumor cells.
- Wash adherent cells with PBS (5 ml) and detach cells by adding 833 μM EDTA (1 ml for T25 flask and 2 ml for T75 flask) for 3-5 min in an incubator at 37 °C, 5% CO2.
- Wash cells twice with PBS (2 x 5 ml in 15 ml tube) by centrifugation at 468 x g for 7 min and re-suspend them in cold FACS buffer.
- Count total viable cell number with Trypan-blue exclusion method.
- Seed cells in round-bottom 96 well plates at a cell density of 1 x 106 cells/well. Prepare 1 well for the control (without KIR-Fc fusion-proteins) and 1 well for each fusion protein to be tested.
- Spin cells at 832 x g for 2 min at 4 °C.
- Discard the supernatant and add 100 µl/well of cold FACS buffer containing single KIR-Fc fusion proteins (KIR2DL1-Fc, KIR2DL3-Fc, and KIR3DL1-Fc) diluted 1:5 and 100 μl of cold FACS buffer with none in control cells.
- Incubate for 1 h at 4 °C.
- Wash cells with 150 µl of cold FACS buffer and centrifuge at 832 x g at 4 °C.
- Discard the supernatant and re-suspend cells in 50 µl of cold FACS buffer containing Goat anti-Human secondary antibody, RPE conjugate antibody (diluted 1:100) and mix carefully avoiding formation of bubbles.
- Incubate for 25 min on ice in the dark.
- Wash cells with 150 µl of cold FACS buffer and centrifuge at 832 x g at 4 °C.
- Discard the supernatant and re-suspended cells in 150 µl of cold FACS buffer in FACS tubes and perform flow cytometric analysis. Viable human single cells will be selected by gating in forward scatter versus side scatter dot plot and the binding of KIR-Fc fusion proteins will be evaluated by mean fluorescence intensity (Figure 1).
- Acquire data using DIVA software and analyse using FlowJo software.
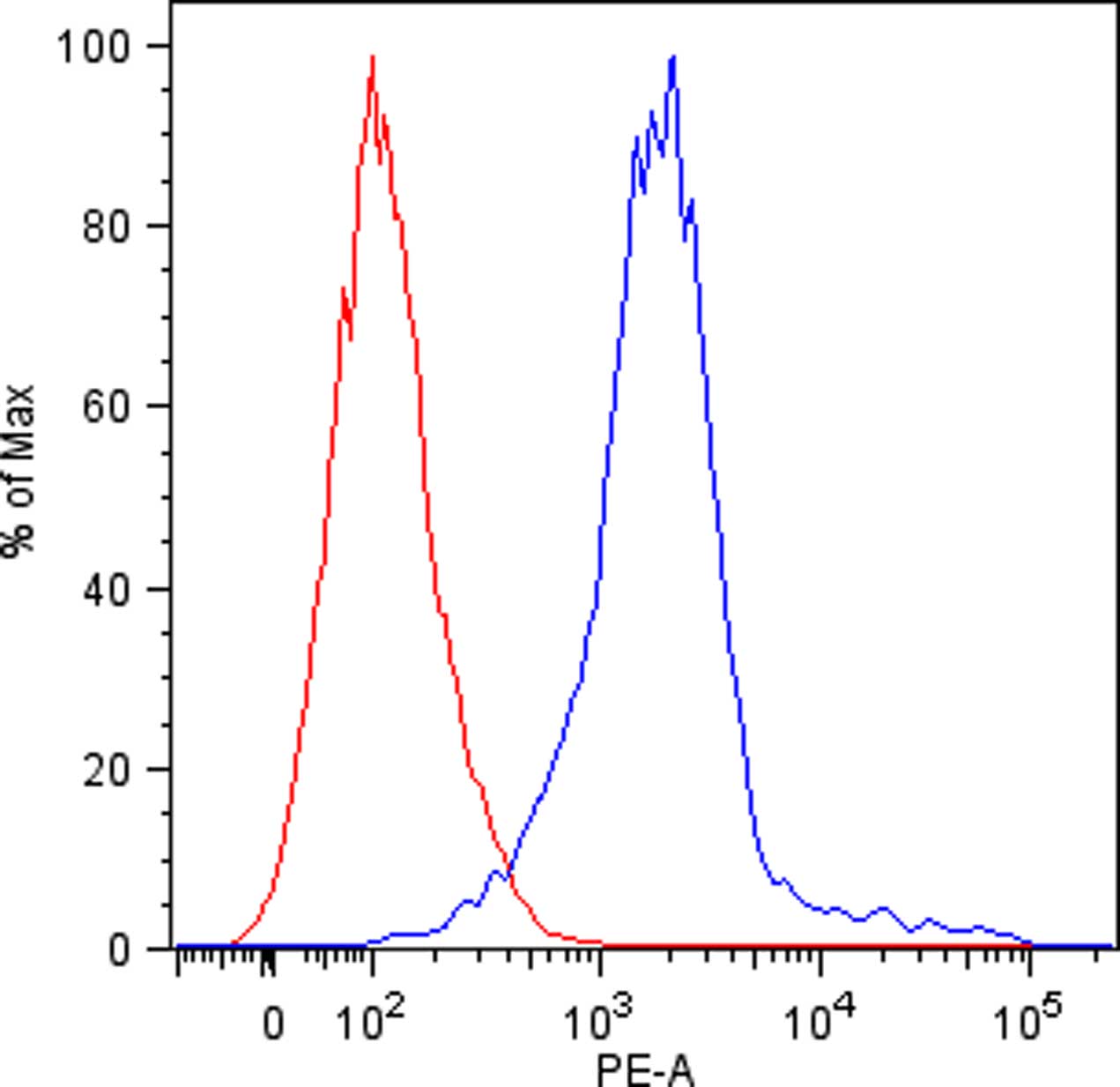
Figure 1. KIR3DL1 binding to DAOY cells. Flow cytometric analysis of KIR3DL1-Fc fusion protein binding to DAOY cells (blue line). Isotype-matched negative control antibody is displayed as the red line.
Recipes
- Complete RPMI
440 ml RPMI 1640
50 ml FBS
5 ml penicillin-streptomycin
5 ml L-glutamine - 833 µM EDTA
Dissolve 7.3 g EDTA in 50 ml sterile water, adjust pH to 8.0
Add 83.3 µl of this solution into 50 ml sterile PBS
Filter sterilize through a 20 µm filter
Store at 4 °C - FACS buffer
50 ml PBS
1 g BSA
Acknowledgments
This protocol was adapted from Cifaldi et al. (2015). We acknowledge funding from Italian Ministry of Health (Rome, Italy) grant and the special project 5 x 1,000 Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (AIRC, Milan, Italy) grant.
References
- Cifaldi, L., Romania, P., Falco, M., Lorenzi, S., Meazza, R., Petrini, S., Andreani, M., Pende, D., Locatelli, F. and Fruci, D. (2015). ERAP1 regulates natural killer cell function by controlling the engagement of inhibitory receptors. Cancer Res 75(5): 824-834.
- Lanier, L. L. (2005). NK cell recognition. Annu Rev Immunol 23: 225-274.
- Raulet, D. H., Vance, R. E. and McMahon, C. W. (2001). Regulation of the natural killer cell receptor repertoire. Annu Rev Immunol 19: 291-330.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2016 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Cifaldi, L., Locatelli, F. and Fruci, D. (2016). Killer Cell Ig-like Receptors (KIR)-Binding Assay for Tumor Cells. Bio-protocol 6(18): e1931. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1931.
Category
Immunology > Immune cell function > Antigen-specific response
Cancer Biology > Tumor immunology > Cell biology assays
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link










