- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Target Gene Inactivation in Cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. PCC 7120
Published: Vol 6, Iss 15, Aug 5, 2016 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1890 Views: 10874
Reviewed by: Maria SinetovaClaudia CatalanottiYoko Eguchi

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols
Gene Replacement by a Selectable Marker in the Filamentous Fungus Magnaporthe oryzae
Nalleli Garcia [...] Jessie Fernandez
Sep 5, 2023 2137 Views
Efficient Genetic Transformation and Suicide Plasmid-mediated Genome Editing System for Non-model Microorganism Erwinia persicina
Tingfeng Cheng [...] Lei Zhao
Mar 20, 2024 2426 Views

Egg Microinjection for the Silkworm Bombyx mori
Hayato Yamada [...] Teruyuki Niimi
May 20, 2025 3267 Views
Abstract
Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120 has long served as a model organism for investigating N2-fixation, photosynthesis, and various plant-type metabolic pathways and biofuel production, as well as cellular differentiation (Xu et al., 2008, Halfmann et al., 2014, Golden and Yoon, 2003). Since more than 30,000 sequenced bacterial genomes are currently available (Land et al., 2015), specific gene inactivation and analyses of the corresponding mutant’s phenotype have become powerful tools in elucidating the function of a target gene. Here we describe a protocol to inactivate a target gene in Anabaena sp. PCC 7120 using a single-crossover approach. This approach requires only one-step cloning of an internal fragment of a target gene into an integrative vector to produce a cargo plasmid. Upon a single crossover (homologous recombination) between the cargo plasmid and the Anabaena chromosome, the endogenous target gene is disrupted by generating 3’- and 5’-deleted fragments. This gene inactivating protocol is based on an integrative vector pZR606 (Chen et al., 2015), which may be broadly applied to gene inactivation in other cyanobacterial species as well as other prokaryotic organisms.
Keywords: Genetic tools for bacteriaMaterials and Reagents
- Petri dishes (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: FB0875713 )
- Glass flask (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: FB-500-50 )
- 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 02-682-550 )
- 15 ml conical centrifuge tubes (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 05-527-90 )
- 50 ml conical centrifuge tubes (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 12-565-270 )
- Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120 (hereafter Anabaena 7120)
- Escherichia coli (E. coli) NEB10β [Δ(ara-leu) 7697 araD139 fhuAΔlacX74 galK16 galE15 e14-Φ80dlacZΔM15 recA1 relA1 endA1 nupG rpsL(StrR)rph spoT1Δ(mrr-hsdRMS-mcrBC); New England BioLabs, catalog number: C3019H ]
- E. coli HB101 [F-mcrB mrr hsdS20(rB-mB-) recA13, leuB6, ara-14, proA2, lacY1, galK2, xyl-5, mtl-1, rpsL20(SmR) glnV44 λ- ; Promega, catalog number: L2015 ]
- Conjugal plasmid pRL443 and helper plasmid pRL623 (Elhai et al., 1997)
- pZR606, an integrative vector for Anabaena 7120 (Chen et al., 2015). pZR606 is available upon request (GenBank, catalog number: KJ500179.1 )
- pZR670 (available upon request), a replicative vector in Anabaena 7120 (Xu et al., 205) [The map of pZR670 is provided (Figure S1).]
- LB broth (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: L3522-1KG )
- LB agar, used for growing E. coli (MP, catalog number: 100262 )
Note: This brand of agar does not work for cyanobacteria. - Agar, required for growing Anabaena 7120 and other cyanobacteria (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: A360-500 )
- Immobilon-NC transfer membrane (Millipore, catalog number: HATF08550 )
- Ampicillin sodium salt (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A9518-25G )
- Chloramphenicol (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: BP904-100 )
- Erythromycin (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: E6376-25G )
- Kanamycin sulfate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: K4000-25G )
- Spectinomycin dihydrochloride pentahydrate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S9007-25G )
- MgSO4·7H2O (MP, catalog number: 194833 )
- CaCl2·2H2O (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: BP510-500 )
- NaCl (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: S271-1 )
- K2HPO4 (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: BP363-500 )
- KNO3 (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: BP368-500 )
- NaNO3 (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: BP360-500 )
- MnCl2·4H2O (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: M87-100 )
- Na2Mo4·2H2O (99% purity) (Acros Organics, catalog number: 206371000 )
- ZnSO4·7H2O (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: Z76-500 )
- CuSO4·5H2O (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: BP346-500 )
- H3BO3 (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: BP168-500 )
- NH4VO3 (Acros Organics, catalog number: 194910500 )
- CoCl2·6H2O (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: C371-100 )
- KOH (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: P250-500 )
- Na2EDTA·2H2O (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: BP120-500 )
- FeSO4·7H2O (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: I146-500 )
- Allen and Arnon medium plus nitrate: AA/8(N) (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Centrifuges (Beckman, model: Allegra X-15R ; Thermo Fisher Scientific, SorvallTM LegendTM, model: Micro17 )
- Innova-44R shaker equipped with continuous fluorescent light illumination (ca. 50-100 μE/m2 s) (Eppendorf, New BrunswickTM Innova®, model: 44R )
- Cyanobacteria Culture Room (constant at 30 °C) equipped with a digital temperature controlling system and Sylvania fluorescent light bulbs (F40CWX, 40W/4100K, T12)
Note: Light shelves in cyanobacteria culture room are able to provide continuous light illumination (ca. 50-150 μE/m2 s). - ESCO laminar flow cabinet (ESCO, Clean BenchAirstream® model: AHC-4B2 )
- Water bath sonicator (Bransonic® Ultrasonic Cleaner, model: 1510R-MT )
- Microscope, Olympus upright compound microscope (Olympus, model: AX70; BX53 )
- PCR thermal cycler (Bio-Rad Laboratories, TouchTM, model: C1000 )
- UV-Vis spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, model: GeneSyS 10S )
Procedure
- Preparation of E. coli strains
- Amplify the internal fragment (at least 500 bp) of the target gene from Anabaena chromosomal DNA.
- Clone the internal fragment into the multiple cloning sites (BglII-NotI-AgeI-SpeI-ApaI-SmaI/XmaI) of pZR606 (KmR/SpR) to produce the cargo plasmid [see details in (Chen et al., 2015)]. The map for multiple cloning sites in pZR606 is provided (Figure S2). The cargo plasmid must be transformed to E. coli NEB10β or E. coli DH10B.
- Grow E. coli HB101 harboring pRL443 (ApR) and pRL623 (CmR) in 2 ml LB broth with 100 µg/ml ampicillin and 25 µg/ml chloramphenicol overnight (~16 h) at 37 °C with 200 rpm shaking. Meanwhile, grow NEB10β bearing the cargo plasmid (KmR/SpR) in 2 ml LB broth with 50 µg/ml kanamycin overnight at 37 °C with 200 rpm shaking.
- Transfer 100 µl of the above overnight E. coli cultures into 5 ml fresh LB with appropriate antibiotics respectively; continue to grow for ~3 h (OD600 ~0.5).
- Harvest the 5 ml culture by centrifugation at 4,000 x g in Allegra X-15R for 10 min at 25 °C (room temperature).
- Wash the cell pellets three times with 1 ml LB to remove antibiotics completely, then add 200 μl LB to re-suspend the pellets, respectively.
- For mating experiment, mix 100 µl NEB10β bearing cargo plasmid with 100 µl HB101 harboring pRL443 and pRL623 and incubate at room temperature for 30 min (experimental group). For a negative control, mix 100 µl LB with 100 µl HB101 harboring pRL443 and pRL623 and incubate at room temperature for 30 min (control group).
- Amplify the internal fragment (at least 500 bp) of the target gene from Anabaena chromosomal DNA.
- Preparation of Anabaena 7120 culture
- Grow Anabaena 7120 in 30 ml AA/8(N) medium (Allen & Arnon, 1955a, Allen & Arnon, 1955b) or BG11 medium (Rippka et al., 1979) for ca. 5 days until it reaches early exponential stage (OD700 ~0.5). The Anabaena 7120 is grown under continuous light illumination (ca. 50 μE/m2 s) at 30 °C and shaken at 120 rpm in a temperature controlled Innova-44R lighted incubator (New Brunswick Scientific) or in the Cyanobacteria Culture Room with continuous light illumination (ca. 50 μE/m2 s) at 30 °C and shaken at 120 rpm.
- Harvest the culture by centrifugation at 4,000 x g with Allegra X-15R for 10 min at 25 °C.
- Re-suspend the cell pellet with 2 ml AA/8(N) in a 25 ml glass flask, break filaments into an average 3-5 cell lengths (confirmed microscopically) by sonicating the cultures for 60-120 sec using water bath sonicator (Figure S3). Set up the sonicator under standard model and add water to the operating level line during the sonication process.
- Transfer the sonicated culture into a 15 ml centrifuge tube and centrifuge in Allegra X-15R at 4,000 x g for 10 min at 25 °C. Re-suspend the cell pellet with 1 ml AA/8(N), transfer the cells into a 1.5 ml Eppendorf tube, and then centrifuge at 6,000 x g for 1 min (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Micro17) at 25 °C. Re-suspend the pellet with 400 µl AA/8(N); then divide cells equally into two tubes.
- Grow Anabaena 7120 in 30 ml AA/8(N) medium (Allen & Arnon, 1955a, Allen & Arnon, 1955b) or BG11 medium (Rippka et al., 1979) for ca. 5 days until it reaches early exponential stage (OD700 ~0.5). The Anabaena 7120 is grown under continuous light illumination (ca. 50 μE/m2 s) at 30 °C and shaken at 120 rpm in a temperature controlled Innova-44R lighted incubator (New Brunswick Scientific) or in the Cyanobacteria Culture Room with continuous light illumination (ca. 50 μE/m2 s) at 30 °C and shaken at 120 rpm.
- Conjugal transformation of a cargo plasmid into Anabaena 7120
- Mix 200 µl of Anabaena 7120 resuspension (step 11) with 200 µl of the mated E. coli mixture (experimental group, step 7), or the control mixture (control group, step 7), respectively, and incubate at room temperature for another 30 min.
- Spread the conjugal mixtures onto the autoclaved Immobilon-NC transfer membrane atop AA (N) agar containing 5% LB (v/v) without antibiotic and incubate at 30 °C, with continuous light illumination (ca. 50 μE/m2 s) for 24 h.
- Transfer the membrane onto AA (N) agar plate with 10 μg/ml spectinomycin (Sp10), and incubate under the same growth conditions until spectinomycin-resistant colonies gradually appear during 10-15 days as shown in Figure 1 (top and middle panels).
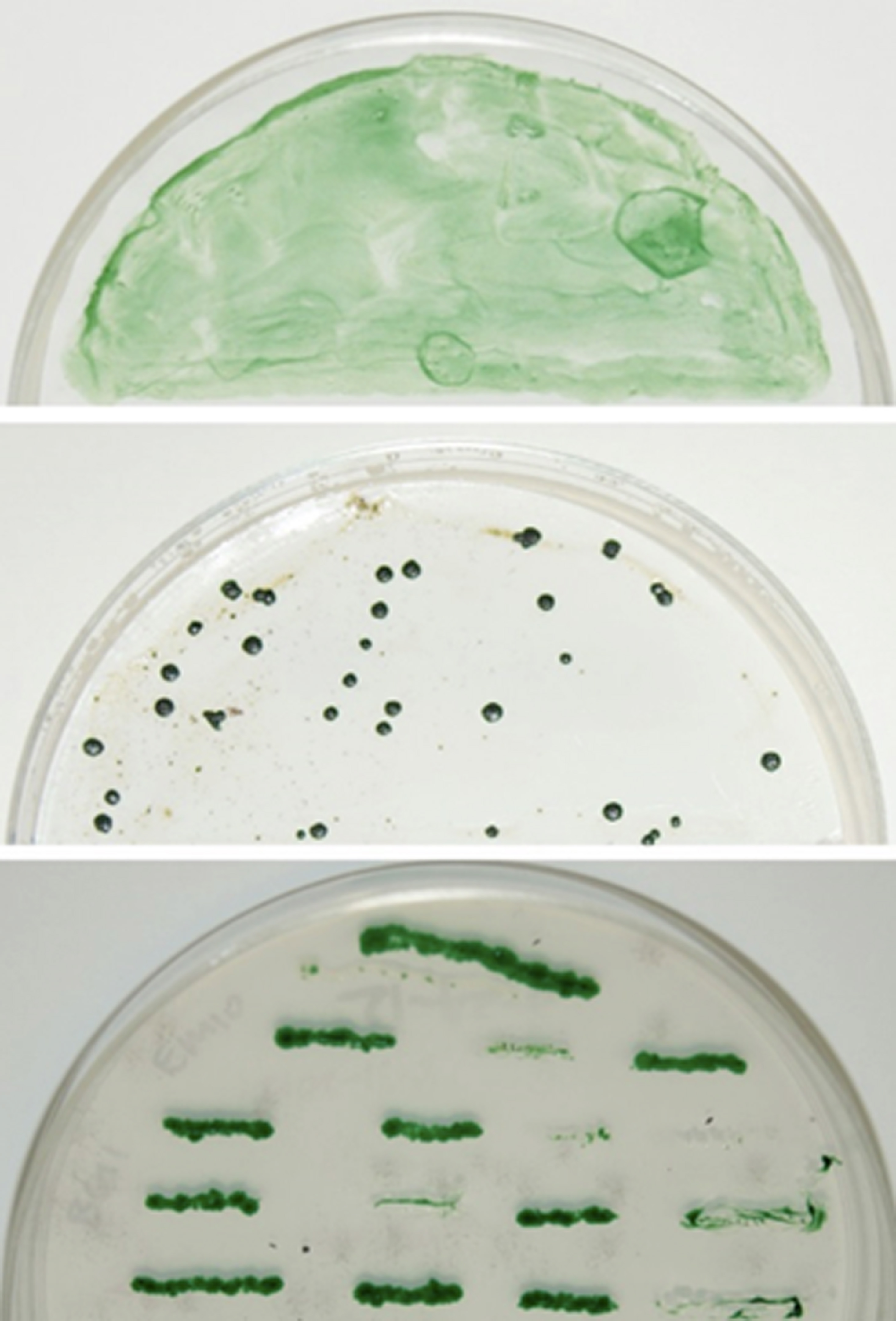
Figure 1. Screen for the potential knockout mutants. The conjugal transfer mixture with the cargo plasmid was spread onto Immobilon-NC membrane atop AA (N) agar containing Sp10 for 0 (top panel) and 19 days (middle panel). The bottom panel shows the above individual colonies re-streaked onto a new AA (N) agar plate containing Sp10 for segregation. As a negative control, the conjugal transfer mixture without cargo plasmid (control) showed no individual colonies on AA (N) agar plate containing Sp10 (data not shown).
- Mix 200 µl of Anabaena 7120 resuspension (step 11) with 200 µl of the mated E. coli mixture (experimental group, step 7), or the control mixture (control group, step 7), respectively, and incubate at room temperature for another 30 min.
- Verification of the knockout mutants
- Re-streak at least ten potential knockout mutant colonies onto a fresh AA (N) agar plate containing Sp10, allowing complete segregation of mutant chromosomes (Figure 1, bottom panel) since Anabaena 7120 has multiple copies of chromosomes per cell (Hu et al., 2007).
- Screen for the positive knockout mutant colonies by colony PCR. Three primers were designed to verify the target gene knockout mutants. Targeted gene open reading frame (ORF) primer pair [forward primer (FP) and reverse primer (RP)] was used to verify the wild-type gene; while forward primer FP paired with a vector-specific primer ZR90 (AAGTTCTTCTCCTTTGCTAGC) (Chen et al., 2015) was used to distinguish the positive knockout mutants from WT. A standard PCR program was used with the exception that the chromosomal DNA template was prepared by preheating cyanobacterial cell suspension in 6 μl ddH2O at 95 °C for 10 min.
- Completely suspend PCR positive mutant colonies in 100 µl AA/8(N) medium to make serial dilutions (1x, 10x and 100x). Then re-streak each dilution onto AA (N) agar plate containing Sp10 for single colonies to separate E. coli contamination from Anabaena. These single Anabaena knockout mutant colonies were confirmed again with the colony PCR described above.
- Repeat steps 15 to 17 until no wild-type target gene was detected in the knockout mutant colony PCR. An example of colony PCR verification for the inactivated mutants of all4160 in Anabaena 7120 is shown in Figure 2.
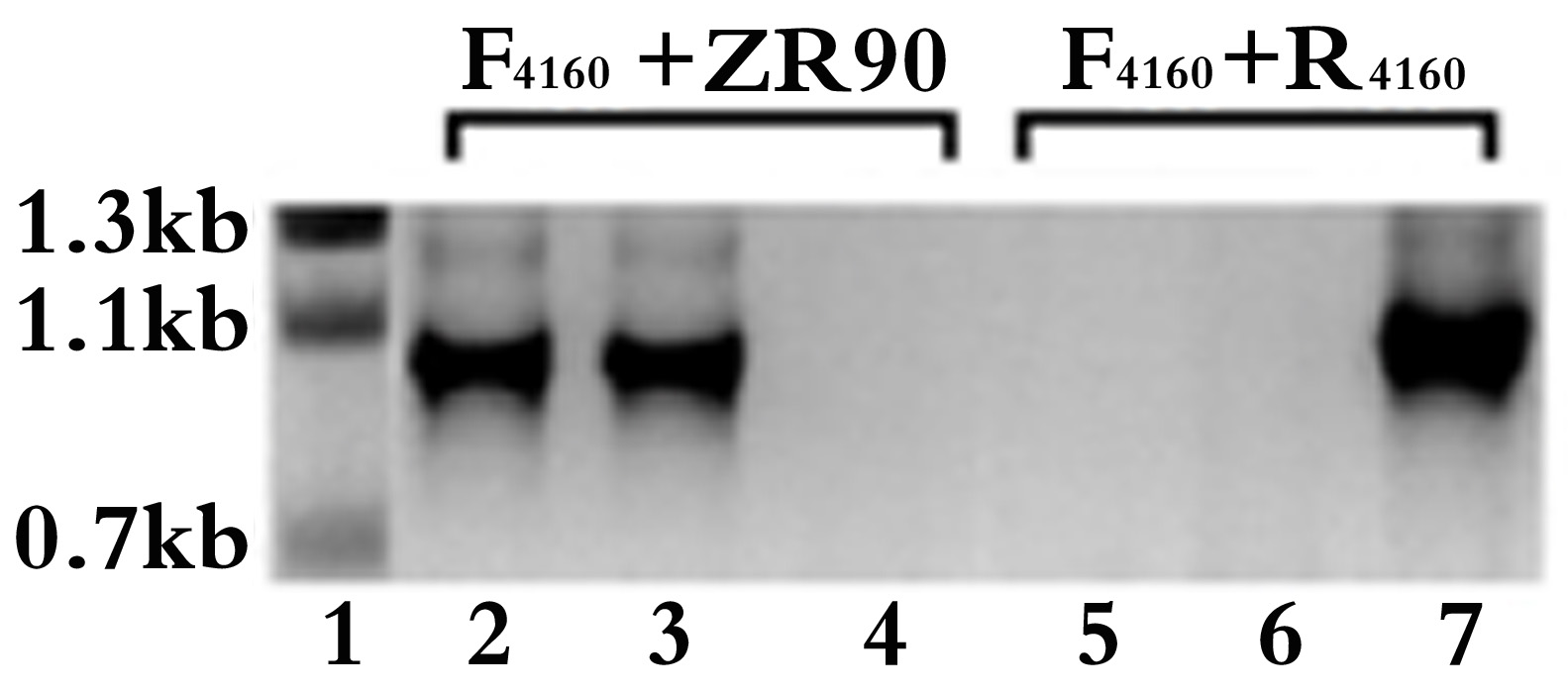
Figure 2. Colony PCR verification for the single crossover inactivated all4160 mutant in Anabaena 7120. The target gene specific F4160 + R4160 and F4160 + ZR90 primer pairs were used for PCR amplification from the knockout mutant colonies of all4160 (lanes 2-3 and 5-6, respectively) or from the WT 7120 (lanes 4 and 7) as controls. The PCR product sizes amplified with F4160 + R4160 and F4160 + ZR90 primer pairs are expected to be 1,056 bp (lane 7) and 910 bp (lanes 2-3), respectively. The sizes of DNA ladder (lane 1) are also indicated. Lanes 2 & 3 or lanes 5 & 6 were two independent knockout mutants. Lanes 5 & 6 show that the target gene was successfully knocked out, the mutants were completely segregated. F1460: ggatccatatgTACATGGCAACCAAAGTG, R4160: gtcgacATAAGCGCCACTATTTCTATTAAA (uppercase letters represent nucleotides corresponding to all4160).
- Re-streak at least ten potential knockout mutant colonies onto a fresh AA (N) agar plate containing Sp10, allowing complete segregation of mutant chromosomes (Figure 1, bottom panel) since Anabaena 7120 has multiple copies of chromosomes per cell (Hu et al., 2007).
- Complementation experiment
- A complementation experiment is required to confirm that the target gene, rather than a downstream gene, is responsible for the mutant phenotype, as in some cases, a knockout mutant’s phenotype might be due to a polar effect on the expression of a downstream gene. Complementation by a single gene was tested by sub-cloning the entirety of the target gene-coding region into a shuttle vector pZR670 (Xu et al., 2015) or pRL2833a (Wolk et al., 2007), which contains both the chloramphenicol (CmR) and the erythromycin (EmR) resistance genes. To construct the complementing plasmid, the coding sequence of the target gene is cloned into the multiple cloning sites (MCS) (NsiI/NdeI/AvrII/AatII/XhoI/AscI/NaeI/BamHI) of pZR670 (Figure 3), in-frame with the glnA start codon. For example, coding sequencing of alr4853 was in-frame cloned into NdeI-XhoI digested pZR670, producing pZR1617 (Xu et al., 2015).
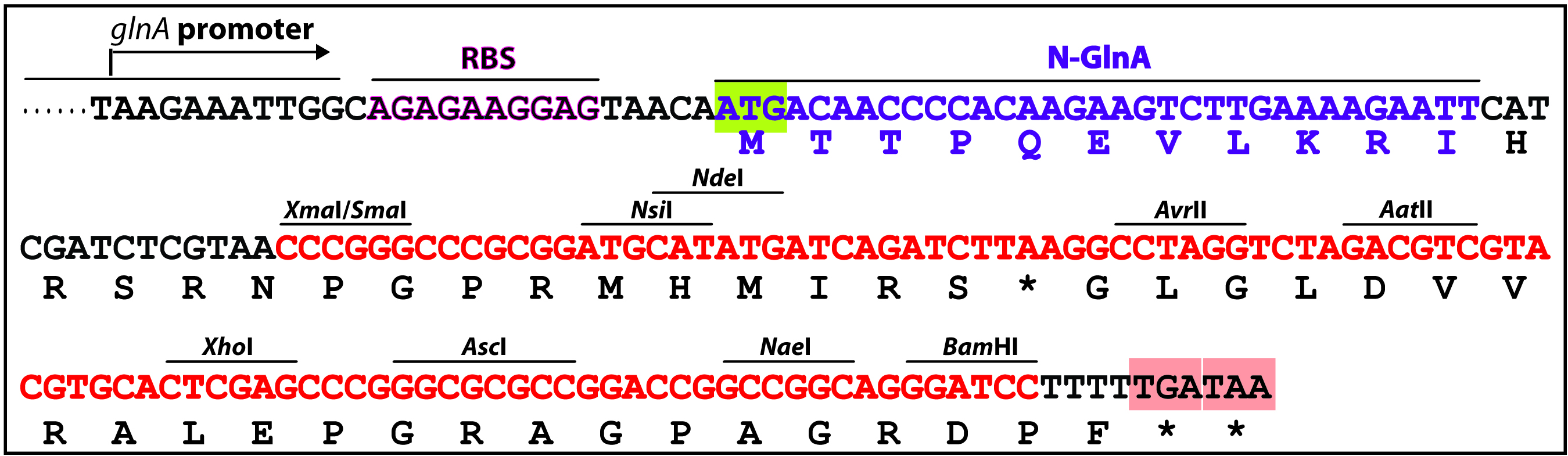
Figure 3. The multiple cloning sites of a complementing vector pZR670. PglnA: promoter region of glnA (alr2328), RBS: Ribosomal binding site, 5’-glnA: N-terminal portion (MTTPQEVLKRI) of Anabaena GlnA (glutamine synthetase), MCS (nucleotides highlighted in red): multiple cloning sites. The target gene-coding sequence (ORF) can be in-frame inserted between NdeI and one of AvrII/AatII/XhoI/AscI/NaeI/BamHI digested pZR670 (Xu et al., 2015). - A similar approach described in Part C is used to transfer the complementing plasmid into the knockout mutant. E. coli and Anabaena mutant culture were prepared as described before (steps 3 to 11), except that the cargo plasmid was substituted by the complementing plasmid. Then dilute the mutant Anabaena culture by 5x, 10x and 100x with AA/8(N) in 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes. Spot 5 µl of the diluted cultures onto the Immobilon-NC membrane atop AA(N) agar containing 5% LB without antibiotic. Make 3 replicate spots for each sample. Air-dry the membrane for a few minutes; then spot 5 µl of the mated E. coli mixture atop the Anabaena spots. Air-dry for a few minutes, and incubate the plate under continuous light illumination (ca. 50 μE/m2 s) at 30 °C for 24 h.
- Transfer the membrane onto AA (N) agar plate containing both Sp10 and 10 μg/ml of erythromycin, and incubate under the same growth conditions. The Sp-Em-resistant colonies will grow in 10-15 days, similarly as seen in Figure 1.
- Then verify the Sp-Em-resistant colonies that contain the complementing plasmid by colony PCR with specific primers targeting the Em resistance gene.
- Examine the phenotype for at least three verified colonies to see if the complementing plasmid is capable of complementing the single crossover generated mutant. If the complemented mutant displays a restored wild-type phenotype, in which the target gene has been successfully inactivated by a single crossover approach, you can conclude that the target gene is responsible for the mutant’s phenotype, which hints the function of the target gene.
- If the complementing plasmid fails to restore the mutant’s phenotype to its wild-type’s phenotype in step 22, this indicates that the mutant’s phenotype might be caused by a polar effect on a downstream gene. No functional clue could be made for the target gene under this condition although it has been successfully inactivated.
- A complementation experiment is required to confirm that the target gene, rather than a downstream gene, is responsible for the mutant phenotype, as in some cases, a knockout mutant’s phenotype might be due to a polar effect on the expression of a downstream gene. Complementation by a single gene was tested by sub-cloning the entirety of the target gene-coding region into a shuttle vector pZR670 (Xu et al., 2015) or pRL2833a (Wolk et al., 2007), which contains both the chloramphenicol (CmR) and the erythromycin (EmR) resistance genes. To construct the complementing plasmid, the coding sequence of the target gene is cloned into the multiple cloning sites (MCS) (NsiI/NdeI/AvrII/AatII/XhoI/AscI/NaeI/BamHI) of pZR670 (Figure 3), in-frame with the glnA start codon. For example, coding sequencing of alr4853 was in-frame cloned into NdeI-XhoI digested pZR670, producing pZR1617 (Xu et al., 2015).
Notes
- Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120 can also be grown in BG11 medium (http://www-cyanosite.bio.purdue.edu/media/table/BG11.html) (Rippka et al., 1979).
- After transferring the membrane onto AA (N) agar plate with appropriate antibiotics, keep tracking the membrane color change. The wild-type Anabaena 7120 should be killed and the color of the membrane should gradually turn to yellow.
- Change the AA (N) agar plate with appropriate antibiotics every week to maintain effective antibiotics. If the membrane in the control plate (Anabaena 7120 + HB101 harboring pRL443 and pRL623) does not turn to yellow in one week, transfer all the membranes onto new AA(N) agar plate containing appropriate antibiotics immediately.
Recipes
- Allen and Arnon medium plus nitrate: AA/8(N)
Anabaena 7120 is grown in a modified Allen-Arnon medium (Allen & Arnon, 1955a). AA liquid medium was diluted 8 times with sterilized distilled H2O to make AA/8. For making AA/8(N), a final concentration of 2.5 mM nitrate was added to AA/8 medium from KNO3/NaNO3 stock solution. For preparation of AA(N) agar plates, a final concentration of 2.5 mM nitrate and 1% agar were added to AA medium.- AA medium preparation
Solution A 25.0 ml
Solution B 6.25 ml
Agar (if needed) 10.0 g
Distilled water 969.0 ml
Aliquot 200 ml into five bottles, and then autoclave them at 121 °C for 20 min - Solution A (A & A minus phosphate stock solution)
4% MgSO4·7H2O 500.0 ml (final concentration 1%, m/m)
1.2% CaCl2·2H2O 500.0 ml (final concentration 0.3%, m/m)
3.8% NaCl 500.0 ml (final concentration 0.95%, m/m)
Microelements stock solution 500.0 ml (final concentration of microelements in solution A is four times diluted microelements stock solution) - Solution B (K2HPO4 stock solution)
K2HPO4 21.40 g
Distilled water 500.0 ml - KNO3/NaNO3 stock solution (500 mM)
KNO3 25.276 g
NaNO3 21.249 g
Add distilled H2O to a final volume of 500 ml
Stock solution is autoclaved and stored at 4 °C - Microelements stock solution
A & A FeEDTA solution 160.0 ml
MnCl2·4H2O 360 mg
Na2MoO4·2H2O 61.1 mg
ZnSO4·7H2O 44.0 mg
CuSO4·5H2O 15.8 mg
H3BO3 572.0 mg
NH4VO3 4.6 mg
CoCl2·6H2O 8.0 mg
Distilled water 1,090.0 ml - A & A FeEDTA stock solution
Dissolve 5.2 g KOH in 186 ml distilled water, add 20.4 g Na2EDTA·2H2O
Dissolve 13.7 g FeSO4·7H2O in 364 ml distilled water
Mix the above two solutions, then bubbling millipore-filtered air through solution until color changes. The final pH of FeEDTA solution is approximately 7.5.
- AA medium preparation
Acknowledgments
The protocol is based on the publications “Conjugal transfer of DNA to cyanobacteria” (Elhai and Wolk, 1988); “Simultaneous gene inactivation and promoter reporting in cyanobacteria” (Chen et al., 2015), and “Characterization of five putative aspartate aminotransferase genes in the N2-fixing heterocystous cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120” (Xu et al., 2015). The authors would like to thank Jaimie Gibbons for her critical reading of the manuscript. This work was partially supported by the NSF, Energy for Sustainability Grant CBET1133951 (to R. Z.), and by the USDA-NIFA grant 11665597 (to R. Z.).
References
- Allen, M. B. and Arnon, D. I. (1955). Studies on nitrogen-fixing blue-green algae. I. growth and nitrogen fixation by Anabaena cylindrica Lemm. Plant Physiol 30(4): 366-372.
- Chen, K., Xu, X., Gu, L., Hildreth, M. and Zhou, R. (2015). Simultaneous gene inactivation and promoter reporting in cyanobacteria. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99(4): 1779-1793.
- Elhai, J., Vepritskiy, A., Muro-Pastor, A. M., Flores, E. and Wolk, C. P. (1997). Reduction of conjugal transfer efficiency by three restriction activities of Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120. J Bacteriol 179(6): 1998-2005.
- Elhai, J. and Wolk, C. P. (1988). Conjugal transfer of DNA to cyanobacteria. Methods Enzymol 167: 747-754.
- Golden, J. W. and Yoon, H. S. (2003). Heterocyst development in Anabaena. Curr Opin Microbiol 6(6): 557-563.
- Halfmann, C., Gu, L. and Zhou, R. (2014). Engineering cyanobacteria for the production of a cyclic hydrocarbon fuel from CO2 and H2O. Green Chemistry 16: 3175-3185.
- Hu, B., Yang, G., Zhao, W., Zhang, Y. and Zhao, J. (2007). MreB is important for cell shape but not for chromosome segregation of the filamentous cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. PCC 7120. Mol Microbiol 63(6): 1640-1652.
- Land, M., Hauser, L., Jun, S. R., Nookaew, I., Leuze, M. R., Ahn, T. H., Karpinets, T., Lund, O., Kora, G., Wassenaar, T., Poudel, S. and Ussery, D. W. (2015). Insights from 20 years of bacterial genome sequencing. Funct Integr Genomics 15(2): 141-161.
- Rippka, R., Deruelles, J., Waterbury, J. B., Herdman, M. and Stanier, R. Y. (1979). Generic assignments, strain histories and properties of pure cultures of cyanobacteria. Microbiology 111: 1-61.
- Wolk, C. P., Fan, Q., Zhou, R., Huang, G., Lechno-Yossef, S., Kuritz, T. and Wojciuch, E. (2007). Paired cloning vectors for complementation of mutations in the cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120. Arch Microbiol 188(6): 551-563.
- Xu, X., Elhai, J. and Wolk, C. (2008). Transcriptional and developmental responses by Anabaena to deprivation of fixed nitrogen. Caister Academic Press, Norfolk, United Kingdom.
- Xu, X., Gu, L., He, P. and Zhou, R. (2015). Characterization of five putative aspartate aminotransferase genes in the N2-fixing heterocystous cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120. Microbiology 161(6): 1219-1230.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2016 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Chen, K., Zhu, H., Gu, L., Tian, S. and Zhou, R. (2016). Target Gene Inactivation in Cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. PCC 7120. Bio-protocol 6(15): e1890. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1890.
Category
Molecular Biology > DNA > Transformation
Microbiology > Microbial genetics > Transformation
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link













