- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Determination of Keto-deoxy-d-manno-8-octanoic acid (KDO) from Lipopolysaccharide of Escherichia coli
Published: Vol 5, Iss 24, Dec 20, 2015 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1688 Views: 17622
Reviewed by: Valentine V TrotterAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Simple Methods for the Preparation of Colloidal Chitin, Cell Free Supernatant and Estimation of Laminarinase
Ananthamurthy Koteshwara
Oct 5, 2021 5037 Views
Extraction and Electrophoretic Analysis of Bacterial Lipopolysaccharides and Outer Membrane Proteins
Yue-Jia Lee and Thomas J. Inzana
Dec 20, 2021 5602 Views
Surface Plasmon Resonance for the Interaction of Capsular Polysaccharide (CPS) With KpACE
Zhe Wang [...] Chao Cai
Jun 20, 2025 3477 Views
Abstract
2-Keto-3-deoxy-octonate (KDO) is an essential constituent of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) that forms the outermost leaflet of Gram-negative bacterial outer membrane. LPS is mainly composed of lipid A, O-antigen and a core oligosaccharide. Two molecules of KDO are present per one molecule of LPS. A proper level of LPS is required to maintain the outer membrane integrity and either high or low levels of LPS are toxic to the cell. Various methods are available for quantification of LPS; of these, determination of KDO is a simple and accurate method and it can be estimated either directly from crude bacterial cell lysates or from purified LPS by a simple colorimetric assay. Although this procedure can be theoretically used for any Gram-negative bacterium, we used it routinely to measure KDO from cell lysates of Escherichia coli (E. coli) K12 strains.
Method: The protocol is taken from Karkhanis et al. (1978). It is a simple, sensitive and reliable method to measure KDO. The assay is performed after complete acid hydrolysis of cell lysates or LPS to release the various components of LPS. Further, reaction with periodate, arsenite and thiobarbituric acid gives a pink to red color chromophore, which is measured at 548 nm after stabilizing with DMSO.
Materials and Reagents
- Bacterial strain(s) MG1655 (wild-type) (Escherichia coli K12 strain)
- Periodate (H5IO6) (Merck Millipore Corporation, catalog number: 10450-60-9 )
- Sodium Arsenite (NaAsO2) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S7400 )
- 2-Thiobarbituric acid (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T5500 )
- Sulphuric acid (H2SO4) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 7664-93-9 )
- Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) (Merck Millipore Corporation, catalog number: 802912 )
- HEPES (Merck Millipore Corporation, CalBiochem, catalog number: 7365-45-T )
- Quick Start-Bradford Reagent (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 5000205 )
- 2-Keto-3-deoxyoctonate ammonium salt (KDO) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: K2755 )
- Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A9647 )
- Tryptone (Difco Laboratories, catalog number: 211705 )
Note: Currently, it is “BD, Bacto, catalog number: 211705”. - Yeast extract (Difco Laboratories, catalog number: 212750 )
Note: Currently, it is “BD, Bacto, catalog number: 212750”. - Sodium chloride (NaCl) (Sisco Research Laboratories, catalog number: 7647-14-5 )
- Hydrochloric acid (HCl) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 7647-01-0 )
- Ultra Pure water (Milli Q water) Millipore Progard TL1Cl2, MilliQ system (Merck Millipore Corporation, catalog number: PROGTLCS1 )
- LB broth (see Recipes)
- 0.1 M periodate reagent (see Recipes)
- 4% sodium arsenite reagent (see Recipes)
- 0.6% thiobarbituric acid reagent (see Recipes)
- 0.5 N sulphuric acid (see Recipes)
- 10 mM HEPES buffer (see Recipes)
- 0.5 N HCl (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Sonicator (Probe size, 3 mm) (Sonics Vibra, model: VLB 3X )
- Centrifuge (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Eppendorf, model: 5417R )
- UV-Visible Spectrophotometer (PerkinElmer, model: LAMBDA-35 )
- Thermo heating bath (Labnet International, Accu BlockTM Digital Dry bath)
- Pipettes (Gilson)
Procedure
- Standard
Make KDO standard 200 μg/ml stock (in water) and use 0, 10, 20, 30, 40 μl for standards (Figure 1). Use ultra pure water to make up the volume to 50 μl.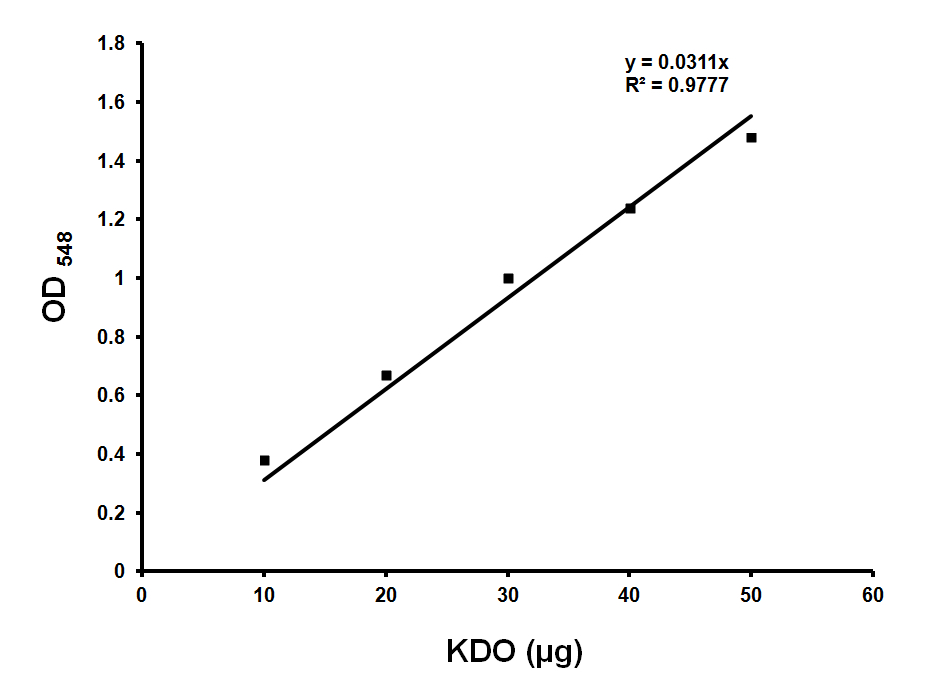
Figure 1. Standard curve for KDO estimation. Standard graph showing OD548 values obtained with various amounts of KDO. Approximately 36 μg of KDO corresponds to OD548 of 1.0. Y is the slope and R2 is the correlation coefficient of this standard curve. - Sample preparation
Preparation of crude cell lysates:- Grow bacterial strain(s) of interest in 2 ml LB (Luria-Bertani broth) overnight at the desired temperature.
- Next morning, subculture 1:100 into 25 ml LB and grow until appropriate optical density is reached.
For example: We have grown MG1655 (wild-type) and a mutant derivative known to make low LPS (MG1655 lpxC1272) to measure KDO. They were grown in 2 ml LB at 37 °C overnight. Next day subcultured 1:100 dilution into 25 ml LB and grown at 37 °C till an OD600 of 1.0. - Pellet down cells by centrifuging at 10,000 rpm/9,391 rcf for 10 min at 4 °C.
- Wash the pellet with 1 ml of 10 mM HEPES buffer (pH 7.4) and again resuspend in 1 ml of same buffer.
- Sonicate cells on ice for 5 min with 10 sec on and 10 sec off at 40% amplitude.
- Spin at 12,000 rpm/13,362 rcf for 10 min at 4 °C to remove unbroken cells. Transfer supernatant to a fresh microcentrifuge tube and store on ice. Quantify the concentration of protein.
Note: Although the cell lysates are stable on ice for 24 h, in most of our experiments we used them within 6-8 h of preparation. We used Quick start Bradford reagent for estimating the protein concentration of the cell lysates. The protein concentration is used to normalize KDO. Samples with protein concentration range from 8 to 20 mg/ml work well. Normally, with these volumes, we have obtained approximately 10 mg/ml protein.
- Grow bacterial strain(s) of interest in 2 ml LB (Luria-Bertani broth) overnight at the desired temperature.
- Assay
- To 50 µl of the above cell lysate (sample), add 50 µl of 0.5 N H2SO4 and vortex.
- Heat at 100 °C for 15 min for total hydrolysis of LPS. Cool to room temperature.
Note: Heating is not required for KDO standards; for different Gram-negative bacteria, the time taken for hydrolysis should be standardized. - Add 50 µl periodate reagent (H5IO6), vortex and let it stand for 10 min at room temperature.
- Add 200 µl sodium arsenite (NaAsO2) reagent and vortex until the brown color disappears (Figure 2 A).
- Add 800 µl thiobarbituric acid reagent and vortex.
- Heat at 100 °C for 15 min.
- Add 1 ml DMSO to each sample (Figure 2B) when it is warm to make the sample clear and also to stabilize the chromophore.
- Cool and measure absorbance at 548 nm on a spectrophotometer (Figure 2C).
- Calculate the KDO values based on the standard graph (Figure 1). Normalize the values with protein concentrations.
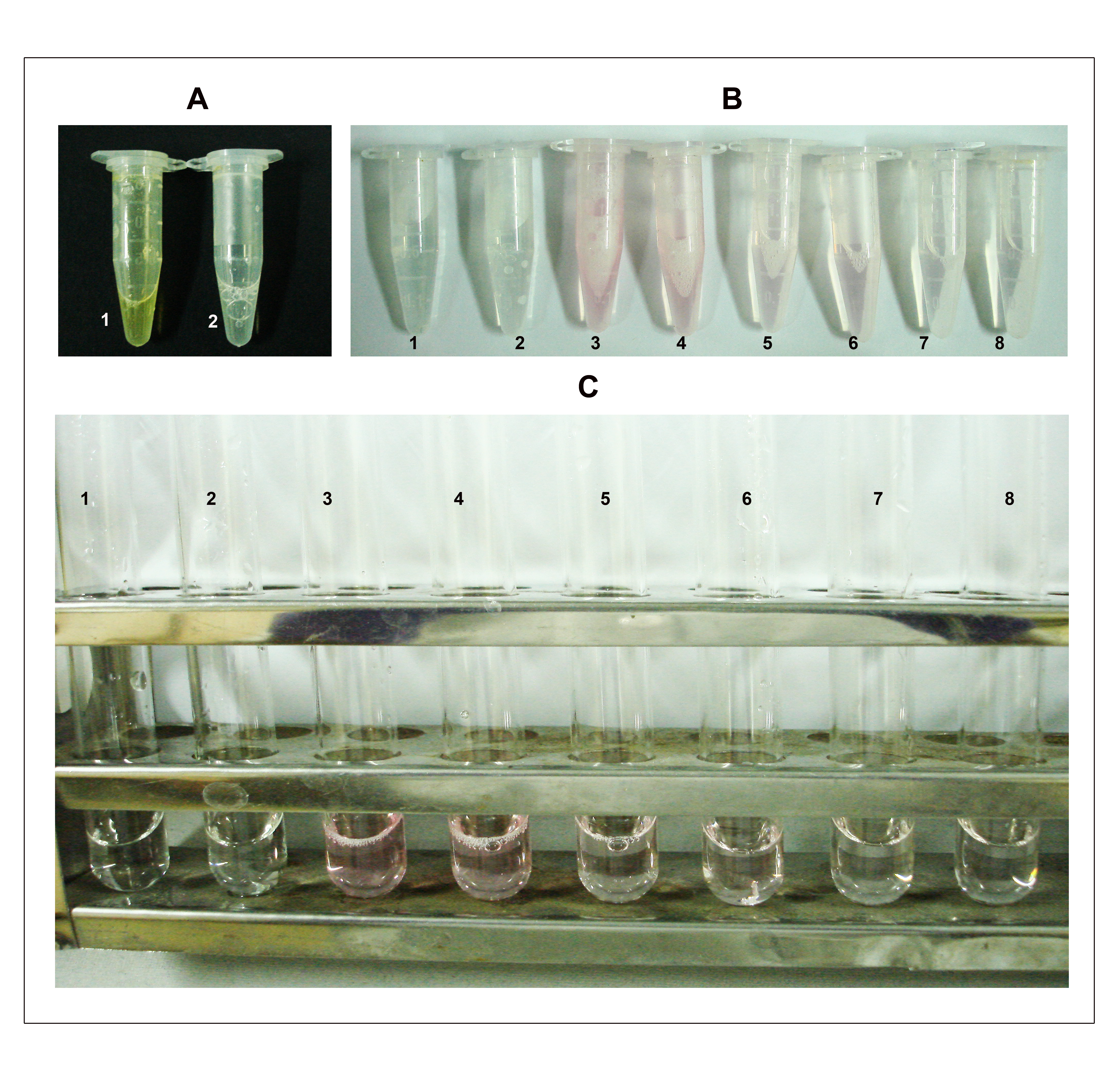
Figure 2. Depiction of steps B4, 7-8 in the KDO determination assay. A. Step 4: The assay mixture turns brown immediately after the addition of sodium arsenite (tube 1) and the color disappears after vortexing (tube 2). B. Step 7: After heating at 100 °C for 15 min, the samples turn pink/red depending on the amount of KDO. Tubes 1 and 2 are blank duplicates; 3 and 4 are duplicates each containing approximately 500 μg of total protein (50 μl from the cell lysate having a concentration of 10 mg/ml protein); 5 and 6 are duplicates each containing 250 μg of total protein and; 7 and 8 are duplicates each containing 100 μg of total protein. C. Samples after addition of DMSO. The numbering on tubes is as described earlier in B.
- To 50 µl of the above cell lysate (sample), add 50 µl of 0.5 N H2SO4 and vortex.
Representative data
- KDO values of various E. coli strains
The value of KDO obtained for wild type in our laboratory was more or less equal to that of the KDO obtained by Ogura et al. (1999).Strains µg of KDO per mg of protein Wild type MG1655 9.0 ± 0.5 MG1655 lpxC1272 6.8 ± 0.4
Notes
- The experimental values should be determined from three independent experiments to check the variability and reproducibility of the results.
- Procedure should be standardized when determining KDO from other Gram-negative bacteria.
Recipes
- LB broth
1% Tryptone
0.5% yeast extract
1% NaCl - 0.1 M periodate reagent
Dissolve 2.28 g of periodate in 100 ml of ultra pure water - 4% sodium arsenite reagent
Dissolve 2.0 g of sodium arsenite in 50 ml of 0.5 N HCl - 0.6% thiobarbituric acid reagent
Dissolve 150 mg of thiobarbituric acid in 25 ml ultra pure water
Note: Use warm water to dissolve, make it fresh before use. - 0.5 N sulphuric acid
1.38 ml of concentrated sulphuric acid in 98.62 ml ultra pure water - 10 mM HEPES buffer
Dissolve 0.238 gm HEPES free acid in 100 ml ultra pure water and adjust pH to 7.4 with NaOH - 0.5 N HCl
Add 4.16 ml of concentrated HCl to 95.84 ml of ultra pure water
Acknowledgments
KDO estimation protocol was adapted from Karkhanis et al. (1978). Cell lysates were prepared as described in Ogura et al. (1999). This work was supported by funds from Department of Biotechnology (DBT), and Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), Government of India.
References
- Karkhanis, Y. D., Zeltner, J. Y., Jackson, J. J. and Carlo, D. J. (1978). A new and improved microassay to determine 2-keto-3-deoxyoctonate in lipopolysaccharide of Gram-negative bacteria. Anal Biochem 85(2): 595-601.
- Mahalakshmi, S., Sunayana, M. R., SaiSree, L. and Reddy, M. (2014). yciM is an essential gene required for regulation of lipopolysaccharide synthesis in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 91(1): 145-157.
- Ogura, T., Inoue, K., Tatsuta, T., Suzaki, T., Karata, K., Young, K., Su, L. H., Fierke, C. A., Jackman, J. E., Raetz, C. R., Coleman, J., Tomoyasu, T. and Matsuzawa, H. (1999). Balanced biosynthesis of major membrane components through regulated degradation of the committed enzyme of lipid A biosynthesis by the AAA protease FtsH (HflB) in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 31(3): 833-844.
- cmdr.ubc.ca/bobh/methods/KDOASSAY.html.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2015 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Sunayana, M. R. and Reddy, M. (2015). Determination of Keto-deoxy-d-manno-8-octanoic acid (KDO) from Lipopolysaccharide of Escherichia coli. Bio-protocol 5(24): e1688. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1688.
Category
Microbiology > Microbial biochemistry > Carbohydrate
Biochemistry > Carbohydrate > Polysaccharide
Biochemistry > Lipid > Lipid measurement
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link











