- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Generation of Mouse Thyroid Calcitonin-producing Cell Tumors from Primary Mouse Tumors
Published: Vol 5, Iss 24, Dec 20, 2015 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1681 Views: 8286
Reviewed by: Hong Lok LungKristopher MarjonAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols
Generation of Luciferase-expressing Tumor Cell Lines
Todd V. Brennan [...] Yiping Yang
Apr 20, 2018 18858 Views

A Fast and Reliable Method to Generate Pure, Single Cell-derived Clones of Mammalian Cells
Zhe Han [...] Varun Kumar
Aug 20, 2022 3142 Views
An Optimized Protocol for Simultaneous Propagation of Patient-derived Organoids and Matching CAFs
Jenny M. Högström and Taru Muranen
Jan 20, 2025 3088 Views
Abstract
Medullary thyroid cancers (MTCs) are derived from calcitonin-producing cells (C cells) of neuroendocrine origin. Rb heterozygous mice develop low-grade C cell adenocarcinoma following biallelic inactivation of the Rb tumor suppressor gene loci. Additional inactivation of another tumor suppressor gene such as Trp53, Arf or Cdkn1a allows Rb-deficient mice to generate more aggressive C cell adenocarcinoma (Takahashi et al., 2006; Shamma et al., 2009; Kitajima et al., 2015). To characterize C cell adenocarcinoma cells derived from Rb-deficient mice of different genetic backgrounds, we attempted to extract C cell adenocarcinoma cells from primary thyroid tumor tissue. Since primary mouse small cell lung cancer (SCLC) cells those originate in neuroendocrine cells that also stems C cells, can be established both as non-adhesive and adhesive cells (Calbo et al., 2011), we applied their method to MTCs. Here we describe our isolation technique for non-adhesive and adhesive cell cultures from primary medullary thyroid tumor tissue. We found that the molecular markers of C cell such as Calcitonin and Ascl1 are predominantly enriched in the non-adhesive population (Kitajima et al., 2015). This is in line with the fact that one of most commonly distributed human MTC cell line TT is non-adhesive.
Keywords: RetinoblastomaMaterials and Reagents
- 12 well cell culture plate (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 150628 )
- 100 mm cell culture dish (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 172931 )
- 5 ml centrifuge tube (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 339650 )
- Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) (pH 7.2) (Life Technologies, catalog number: 20012027 )
Note: Currently, it is “Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 20012027”. - 100x Antibiotic-Antimycotic (Life Technologies, catalog number: 15240062 )
Note: Currently, it is “Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 15240062”. - Dulbecco’s modified Eagle's medium (DMEM) (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 04330085 )
- 3,000 U/ml Collagenase from Clostridium histolyticum (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: C5138 )
- 1,000 U/ml Hyaluronidase (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 08006201 )
- 20 mg/ml Deoxyribonuclease I from bovine pancreas (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: DN25 )
- Fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: SH3091003 )
Note: Currently, it is “GE Healthcare, catalog number: SH3091003”. - Penicillin-Streptomycin Mixed Solution (Nakarai tesque, catalog number: 2625384 )
- 0.5 g/l-Trypsin/0.53 mmol/l-EDTA Solution, with Phenol Red (Nakarai tesque, catalog number: 3277834 )
- 7-AAD (BD Pharmingen, catalog number: 5168981E )
- CELLBANKER1 (Nippon Zenyaku Kogyo Co., ZENOAQ, catalog number: CB011 )
- Wash buffer (see Recipes)
- Digestion solution (see Recipes)
- Growth medium (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Surgical scissors and forceps
- Pipettes
- Centrifuge
- Cell culture hood
- 37 °C, 5% CO2 cell culture incubator
- Microscope
- FACS Aria ll flow cytometer (BD Biosciences)
Procedure
- Euthanize the mouse when the thyroid tumor has reached appropriate size, approximately 50-500 mm3 (refer to Video 1 and Figure 1).
- Expose and remove the thyroid tumor from trachea using sterile scissors. Remove the surrounding tissues as carefully as possible.
- Place the thyroid tumor onto 12 well type plate, and wash it several times with 2 ml of cold wash buffer.
- Mince the thyroid tumor into small pieces as small as possible using sterile scissors on ice.
- Collect all of the tumor pieces into 15 ml centrifuge tube.
- Wash with 5 ml wash buffer by centrifugation at 300 rcf for 5 min at 4 °C.
- Resuspend the tumor pieces in 5 ml digestion solution.
- Incubate at 37 °C for 60 min. Meanwhile mix gently every 15 min.
- Centrifuge at 300 rcf for 5 min at room temperature, and remove the supernatant.
- Wash 2 times with 5 ml wash buffer by centrifugation at 300 rcf for 5 min at room temperature.
- Resuspend the tumor pieces in 10 ml growth medium, and plate them onto a 100 mm cell culture dish.
- Incubate at 37 °C in 5% CO2 for 4~5 days.
- You will see some cells attach to the dish and grow, while the major population of cells is floating.
- Collect all culture medium containing floating cells into 15 ml centrifuge tube.
- Add 1 ml growth medium to the 100 mm cell culture dish, wash and recollect it into 15 ml centrifuge tube. Repeat this step at least twice in order to recover all of the floating cells.
- Centrifuge at 300 rcf for 5 min at room temperature, discard the supernatant, resuspend the cells in 10 ml growth medium, and plate them onto a new 100 mm cell culture dish.
- Add 10 ml growth medium to the used 100 mm cell culture dish, and maintain the attached cells in the cell culture incubator as adhesive population.
- Repeat steps 13-17 after 3-4 day culture at least 3-4 times until attached cells never appear from floating cells in order to completely separate the non-adhesive population from the adhesive population.
- You will detect the markers of C cells such as Calcitonin and Ascl1 positive cells are highly enriched in the non-adhesive population.
- Dead cells should be removed by cell sorter using staining reagents such as 7-AAD for some applications.
- Non-adhesive and adhesive populations can be stored in liquid nitrogen tank with cell stock solution such as CELLBANKER1.Video 1. The video for how to remove the thyroid tumor
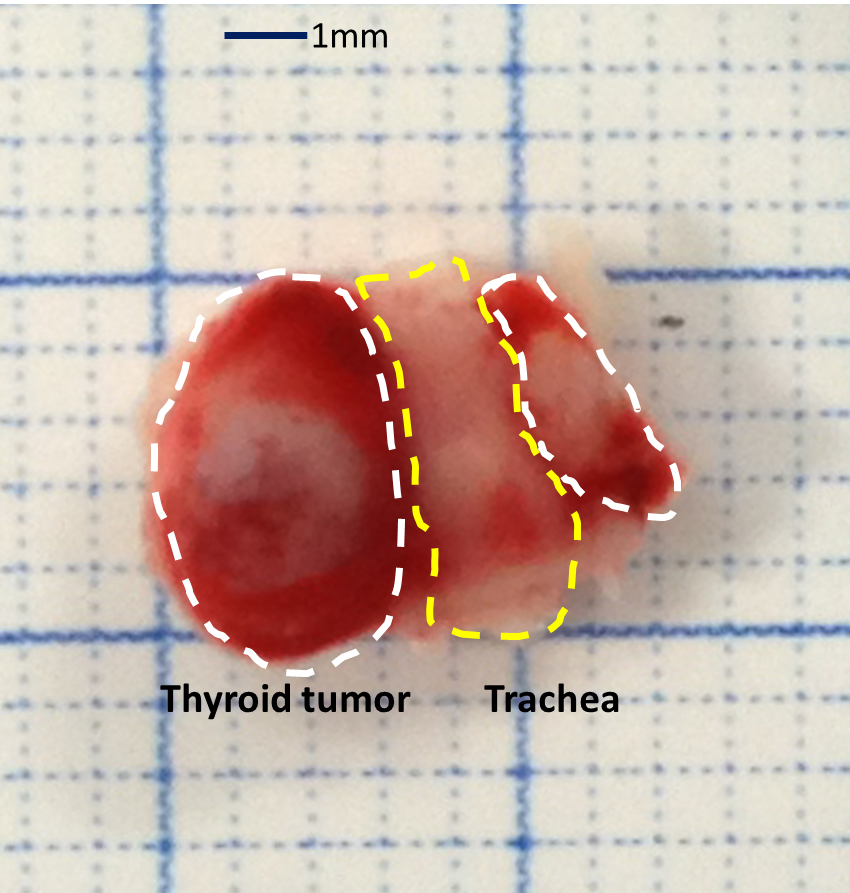
Figure 1. The picture of mouse thyroid tumor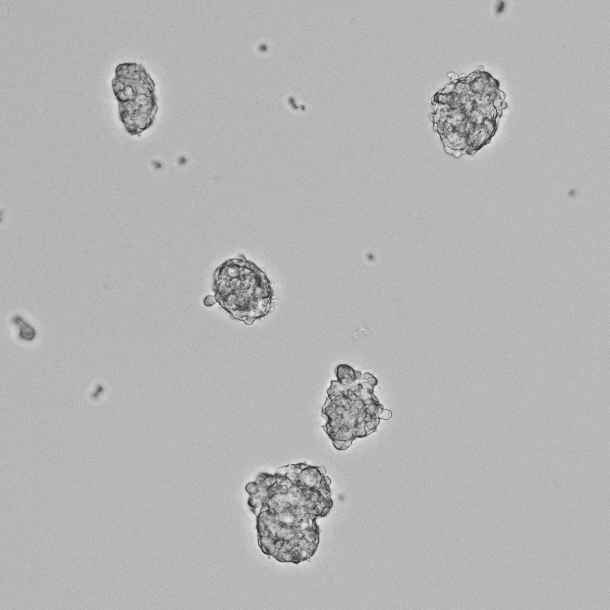
Figure 2. Phase-contrast image of the non-adhesive cell population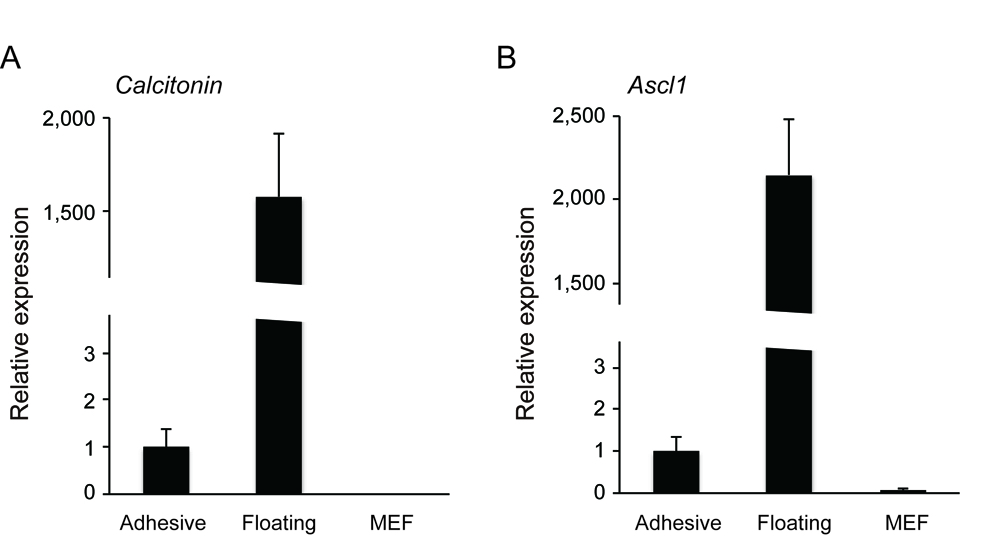
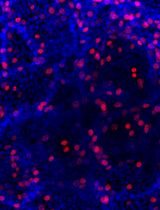
Figure 3. The non-adhesive population highly expressed C cell markers (A. Calcitonin, B. Ascl1) as compared to adhesive population and mouse embryonic fibroblast
Recipes
- Wash buffer
2x antibiotic
Antimycotic in PBS (pH 7.2) - Digestion solution
DMEM containing 300 units/ml collagenase, 100 units/ml hyaluronidase and 0.1 mg/ml DNase l - Growth medium
DMEM supplemented 10 % FBS, 100 U/ml Penicillin and 100 μg/ml Streptomycin
Acknowledgments
We thank S. Kohno, H. Muranaka and Y. Nishimoto for helping preparation of this manuscript. Also, we thank A. Berns’s group for stimulating us to create this protocol. This work was supported by Funding Program for Next Generation World-Leading Researchers (NEXT), Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (MEXT), Astellas Foundation for Research on Metabolic Disorders, Takeda Science Foundation, Naito Foundation, Daiichi-Sankyo Foundation for Life Science, NOVARTIS Foundation (Japan) for Promotion of Science and Hokkoku Foundation for Cancer Research.
References
- Calbo, J., van Montfort, E., Proost, N., van Drunen, E., Beverloo, H. B., Meuwissen, R. and Berns, A. (2011). A functional role for tumor cell heterogeneity in a mouse model of small cell lung cancer. Cancer Cell 19(2): 244-256.
- Kitajima, S., Kohno, S., Kondoh, A., Sasaki, N., Nishimoto, Y., Li, F., Abdallah Mohammed, M. S., Muranaka, H., Nagatani, N., Suzuki, M., Kido, Y. and Takahashi, C. (2015). Undifferentiated State induced by Rb-p53 double inactivation in mouse thyroid neuroendocrine cells and embryonic fibroblasts. Stem Cells 33(5): 1657-1669.
- Shamma, A., Takegami, Y., Miki, T., Kitajima, S., Noda, M., Obara, T., Okamoto, T. and Takahashi, C. (2009). Rb Regulates DNA damage response and cellular senescence through E2F-dependent suppression of N-ras isoprenylation. Cancer Cell 15(4): 255-269.
- Takahashi, C., Contreras, B., Iwanaga, T., Takegami, Y., Bakker, A., Bronson, R. T., Noda, M., Loda, M., Hunt, J. L. and Ewen, M. E. (2006). Nras loss induces metastatic conversion of Rb1-deficient neuroendocrine thyroid tumor. Nat Genet 38(1): 118-123.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2015 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Kitajima, S., Li, F. and Takahashi, C. (2015). Generation of Mouse Thyroid Calcitonin-producing Cell Tumors from Primary Mouse Tumors. Bio-protocol 5(24): e1681. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1681.
Category
Cancer Biology > General technique > Cell biology assays
Cancer Biology > General technique > Tumor formation
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Tips for asking effective questions
+ Description
Write a detailed description. Include all information that will help others answer your question including experimental processes, conditions, and relevant images.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link










