- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Determination of Fructokinase Activity from Zobellia galactanivorans
Published: Vol 5, Iss 21, Nov 5, 2015 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1633 Views: 9995
Reviewed by: Valentine V TrotterChristian RothAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols
Surface Plasmon Resonance for the Interaction of Capsular Polysaccharide (CPS) With KpACE
Zhe Wang [...] Chao Cai
Jun 20, 2025 3552 Views
Activation of X-Succinate Synthases for Fumarate Hydroalkylation Using an In Vitro Activation Method
Anshika Vats [...] Mary C. Andorfer
Jun 20, 2025 2504 Views
An Optimized Enzyme-Coupled Spectrophotometric Method for Measuring Pyruvate Kinase Kinetics
Saurabh Upadhyay
Aug 20, 2025 2434 Views
Abstract
Mannitol is a polyol that occurs in a wide range of living organisms, where it fulfills different physiological roles. Several pathways have been described for the metabolism of mannitol by bacteria, including the phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase system (PST) and a M2DH-based catabolic pathway. The latter involves two enzymes, a mannitol-2-dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.67) and a fructokinase (EC 2.7.1.4), and has been identified in different bacteria, e.g.,, the marine Bacteroidetes Zobellia galactanivorans (Zg) which had recently gained interest to study the degradation of macroalgal polysaccharides. This protocol describes the biochemical characterization of a recombinant fructokinase (FK) of Zobellia galactanivorans. The ZgFK enzyme catalyzes the conversion of fructose to fructose-6-phosphate using ATP as a cofactor.
[Principle] Fructokinase (FK) activity was determined by an enzyme-coupled assay (Figure 1). ADP formed through the FK reaction, i.e., phosphorylation of fructose to fructose-6-phosphate (F6P), is used by the pyruvate kinase (PK) which transforms phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) to pyruvate. Then, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) converts pyruvate to lactate using NADH as a cofactor. FK activity is measured by following the decrease in absorbance at 340 nm which corresponds to the transformation of NADH to NAD+.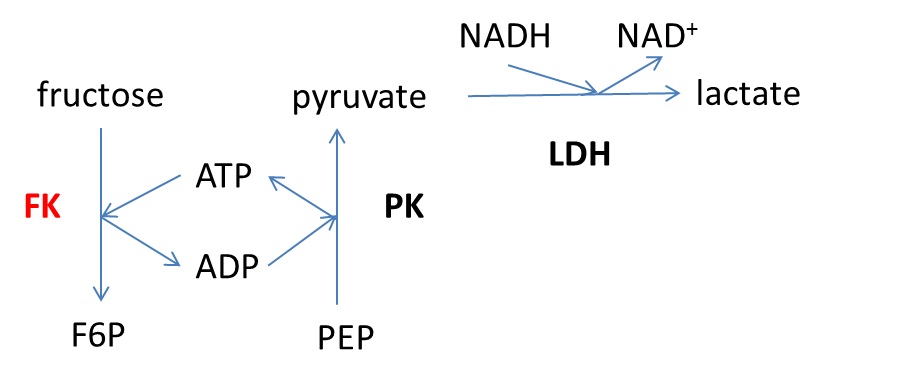
Figure 1. Enzyme-coupled reaction used for determination of fructokinase (FK) activity
Materials and Reagents
- UV-Star® PS Microplate (96 Well) (Greiner Bio-One GmbH, catalog number: 655801 )
- Purified recombinant His-tagged ZgFK
Note: This protein was produced in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) containing the recombinant pFO4_ZgFK vector, as described by Groisillier et al. (2010). This recombinant protein was purified by affinity chromatography using a HisPrep FF 16/10 column (GE Healthcare Dharmacon) onto an Äkta avant system (GE Healthcare Dharmacon). The complete purification protocol is described in details in Groisillier et al. (2015). - Pyruvate Kinase/Lactic Dehydrogenase enzymes from rabbit muscle (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P0294 )
- MilliQ water
- Phospho(enol)pyruvic acid tri(cyclohexylammonium) salt (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P7252 )
- Trizma® base (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T1503 )
- 4-morpholineethane-sulfonic acid (MES) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M2933 )
- Bis-Tris (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: B9754 )
- β-Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, reduced disodium salt hydrate (NADH) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: N8129 )
- Examples of chemicals to be tested to assess substrate specificity:
- D-(-)-fructose (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: F0127 )
- D- (+)-glucose (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G8270 )
- D-(+)-mannose (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M4625 )
- D-mannitol (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M9647 )
- D-sorbitol (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S1876 )
- D-mannitol-1-phosphate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 92416 )
- D-fructose-1-phosphate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S408689 )
- α-D-Glucose 1-phosphate disodium salt hydrate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G9380 )
- D-Mannose 6-phosphate sodium salt (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M3655 )
- D-Glucose 6-phosphate sodium salt (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G7879 )
- D-Fructose 6-phosphate disodium salt hydrate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: F3627 )
- Adenosine 5’-triphosphate (ATP) disodium salt hydrate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A1852 )
- D-(-)-fructose (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: F0127 )
- 1 M Tris-HCl (pH 7.5) (see Recipes)
- 100 mM MgCl2 (see Recipes)
- 1 M KCl (see Recipes)
- 100 mM PEP (see Recipes)
- 100 mM ATP (see Recipes)
- 10 mM NADH (see Recipes)
- PK/LDH (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Safire2 UV spectrophotometer microplate reader (Tecan Trading AG)
- NanoDrop 2000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific)
Software
- Hyper 32 (Hyper32.software.informer.com)
- Microsoft Excel
Procedure
- The reaction mixture contains 100 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 1 mM fructose, 1 mM ATP, 100 mM KCl, 1.5 mM MgCl2, 1 mM phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP), 0.5 mM freshly prepared NADH, 0.2 µl Pyruvate kinase/lactate dehydrogenase (PK/LDH) enzymes (stored at -20 °C before use), and 1 to 10 µg of purified recombinant enzyme, in a volume of 100 µl. Blank corresponds to reaction mixture where substrate is substituted by MilliQ water (Table 1).
Table 1. Composition of blank and reaction mixture for determination of ZgFK activityStock solutions µl added in blank µl added in reaction mix (test) Tris-HCl (pH 7.5) (1 M) 10 10 Fructose (25 mM) 0 4 ATP (100 mM) 1 1 MgCl2 (100 mM) 1.5 1.5 KCl (1 M) 10 10 PEP (100 mM) 1 1 NADH (10 mM) 2 2 PK/LDH (600-1,500 units/ml) 0.2 0.2 ZgFK (1 µg/µl) 1 1 MilliQ water 73.3 69.3 - The continuous assay reaction is started by adding the substrate, and activity is assayed by following changes in absorbance at 340 nm which corresponds to the conversion of NADH to NAD+, in a Safire2 UV spectrophotometer microplate reader. The assay is performed at 25 °C for up to 20 min. Only the early linear part of the curves is used to calculate activity (Figure 2).
- Calculate the consumption of NADH using the formula:
[(ΔA340nm test-ΔA340nm blank)/(t*6220*0.3*0.0001)]
Where
ΔA340nm= variation of absorbance during the duration of incubation
t=duration of incubation (min)
6220= extinction coefficient for NADH (L mol-1 cm-1)
0.3= optical path (cm)
0.0001= assay volume (L)
The rate of decrease of NADH is directly proportional to the rate of formation of lactate and thus to the FK activity. One unit (U) of FK activity corresponds to 1 µmol of NADH oxidized per min.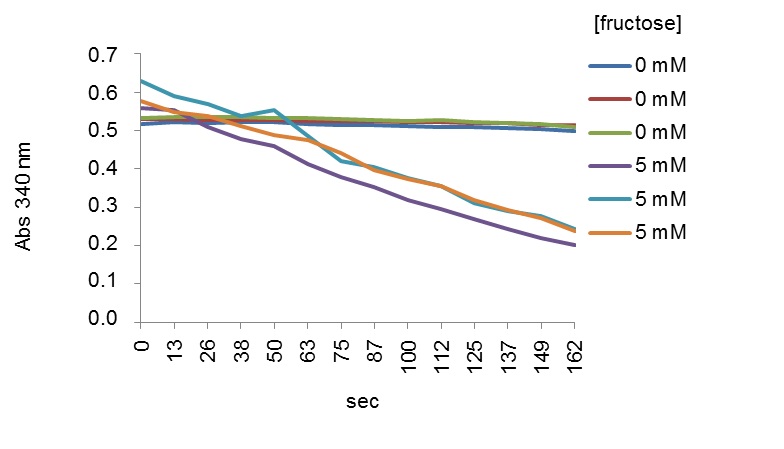
Figure 2. Early linear parts of curves representing changes in absorbance (340 nm) monitored as a function of time (sec) in presence of fructose. The curves represent two series of triplicates at 0 and 5 mM of fructose, respectively. - To calculate specific activities, divide the value obtained in the equation above by the quantity of ZgFK proteins present in the sample. Perform three replicates for each assay and determine the average ± S.E. (cf. Notes) of these three replicates. This applies also to the experiments described below. As an example, typical value for specific activity of ZgFK was 0.49 U/mg in presence of 5 mM fructose.
- To determine substrate specificity, assess ZgFK activity in presence of each of the substrates listed in the “Materials and Reagents” section, using concentration ranging from 1 mM to at least 100 mM.
- To determine the optimal pH, replace the 100 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5) buffer used in step 1 of the procedure by other buffers prepared at different pHs. As an indication, it is possible to use:
100 mM MES for pH 5.5, 6, 6.5
100 mM Bis-Tris propane for pH 6.5, 7, 7.5, 8, 8.5, 9, 9.5
100 mM Tris-HCl for pH 7, 7.5, 8, 8.5, 9 - To determine the optimal temperature, incubate the reaction mixtures described in step 1 at temperatures ranging, for instance, from 10 °C to 50 °C, with incremental of 5 or 10 °C.
- To examine the influence of NaCl, add in the reaction mixture described in step 1 sodium chloride to obtain final concentrations ranging from 0 to 2 M.
- To estimate the kinetic parameters of the enzyme for a selected substrate S, run individual enzyme reactions in presence of at least five different concentrations of this substrate and a fixed concentration of ATP. Determine the initial reaction rate for each reaction and plot 1/V versus 1/[S] to obtain a Lineweaver-Burk plot, from which Km and Vm for S can be calculated.
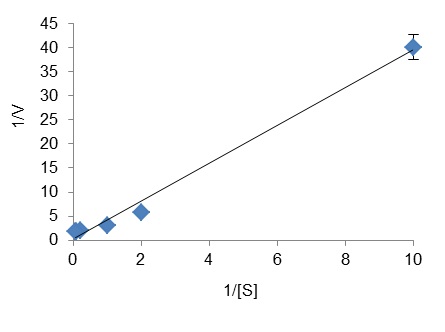
Figure 3. Lineweaver-Burk plot used to determine the Km (10 mM) and Vm (2.55 U/mg) of ZgFK for fructose. [S] is the fructose concentration (in mM) and V is the reaction rate (in µmol/min/mg of protein).
Notes
- PK/LDH enzymes activities must be compared under the selected assay conditions (temperature, pH, salt concentrations…) with activities recommended by the supplier (one unit convert 1.0 µmole of substrate per minute at pH 7.6 at 37 °C). If these activities change, do the protocol in two steps: first, perform the fructokinase reaction under selected condition (without PK/LDH enzymes, PEP and NADH) for different times of incubation; then, in a second step, measure [NADH] after these different times of incubation and plot the results as illustrated in Figure 2.
- Before determining Km and Vm for a given substrate S, be sure that cofactor (ATP) is in excess, i.e., that V does not increase with increasing quantities of cofactor in the reaction mixture; in the same vein, before determining Km and Vm for the cofactor, be sure that S is in excess, i.e., that V does not increase with increasing quantities of S in the reaction mixture. In theory, saturating concentration is equivalent to 100 Km, but 10 Km is usually sufficient (Bisswanger, 2014). It is then necessary to adjust the ZgFK concentration and the incubation time to obtain a linear decrease of absorbance at 340 nm, i.e., a linear consumption of NADH.
- S. E. corresponds to standard error calculated in Excel.
Recipes
- 1 M Tris-HCl (pH 7.5)
Stored at room temperature - 100 mM MgCl2
Stored at room temperature - 1 M KCl
Stored at room temperature - 100 mM PEP
Prepared fresh in MilliQ water on the week of use and stored at -20 °C - 100 mM ATP
Prepared fresh in MilliQ water on the day of use - 10 mM NADH
Prepared fresh in MilliQ water on the day of use - PK/LDH
Stored at -20 °C
Acknowledgments
This protocol was performed by Groisillier et al. (2015). This work was supported by the French National Research Agency via the investment expenditure program IDEALG (ANR-10-BTBR-02). We also acknowledge funding from the Émergence-UPMC-2011 research program.
References
- Bisswanger, H. (2014). Enzymes assays. Perspective in Sciences 1: 41-55.
- Groisillier, A., Herve, C., Jeudy, A., Rebuffet, E., Pluchon, P. F., Chevolot, Y., Flament, D., Geslin, C., Morgado, I. M., Power, D., Branno, M., Moreau, H., Michel, G., Boyen, C. and Czjzek, M. (2010). MARINE-EXPRESS: taking advantage of high throughput cloning and expression strategies for the post-genomic analysis of marine organisms. Microb Cell Fact 9: 45.
- Groisillier, A., Labourel, A., Michel, G. and Tonon, T. (2015). The mannitol utilization system of the marine bacterium Zobellia galactanivorans. Appl Environ Microbiol 81(5): 1799-1812.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2015 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Groisillier, A. and Tonon, T. (2015). Determination of Fructokinase Activity from Zobellia galactanivorans. Bio-protocol 5(21): e1633. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1633.
Category
Microbiology > Microbial biochemistry > Carbohydrate
Biochemistry > Carbohydrate > Mannitol
Biochemistry > Protein > Activity
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link











