- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
An Efficient Procedure for Protoplast Isolation from Mesophyll Cells and Nuclear Fractionation in Rice
Published: Vol 5, Iss 5, Mar 5, 2015 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1412 Views: 24882
Reviewed by: Ru ZhangMarisa Rosa

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Transgene-free Genome Editing in Grapevine
Edoardo Bertini [...] Sara Zenoni
Feb 20, 2025 2378 Views
Isolation and Biophysical Characterization of Extracellular Vesicles From Hairy Root Cultures
Marisa Conte [...] Alfredo Ambrosone
Mar 5, 2025 2101 Views
Rapid Miniprep of Intact Chloroplasts from Arabidopsis thaliana Leaves
Brenda A. Carranza-Correa [...] Manuel Gutiérrez-Aguilar
May 20, 2025 2518 Views
Abstract
Plant protoplasts, a proven physiological and versatile cell system, are widely used in high-throughput analysis and functional characterization of genes. Green protoplasts have been successfully used in investigations of plant signal transduction pathways related to hormones, metabolites and environmental challenges. This protocol, adapted from Zhang et al. (2011), describes a procedure for the isolation of rice protoplasts from green tissue and shows an efficient and rapid method for isolation of nuclei form these protoplasts which are commonly used in a variety of experimental procedures including the isolation of high-molecular-weight DNA (Watson and Thompson, 1986), in vitro DNA synthesis (Roman, 1980), isolation of labeled transcripts for differential screening of cDNA libraries (Somssich et al., 1989), preparation of nuclear extracts for in vitro transcription systems (Roberts and Okita, 1991), isolation of nuclear proteins (Harrison et al., 1992) and studies of protein targeting to the nucleus (Hicks and Raikhel, 1993).
Materials and Reagents
- 12-day-old plants with 1-2 cm leaves before flowering
- Cellulase RS (Yakult Pharmaceutical)
- Macerozyme R-10 (Yakult Pharmaceutical)
- D-Mannitol (Sigma-aldrich, catalog number: M4125 )
- KCl (Sigma-aldrich, catalog number: P9333 )
- MES hydrate (Sigma-aldrich, catalog number: M8250 )
- CaCl2 (Sigma-aldrich, catalog number: C1016 )
- BSA Bovine serum albumin (Sigma-aldrich, catalog number: A2153 )
- Spermidine (Sigma-aldrich, catalog number: S2626 )
- EDTA (Sigma-aldrich, catalog number: EDS )
- Sucrose (Sigma-aldrich, catalog number: 84097 )
- Triton X-100 (Sigma-aldrich, catalog number: X100 )
- DTT (Sigma-aldrich, catalog number: 43815 )
- Enzyme solution (ES) (see Recipes)
- Washing and incubation solution (WS1) (see Recipes)
- Washing solution (WS2) (see Recipes)
- MMG solution (see Recipes)
- Nuclei isolation solution (NIB) (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Razor blades (No18 sterile stainless steel scalpel balde) (Swann Morton, catalog number: 0323 )
- Micro-dissecting forceps (Sigma-aldrich, catalog number: F3767 )
- Nunc petri dishes (diam 90 mm × H 15 mm, surface area size 58 cm2, vented) (Sigma-aldrich, catalog number: Z717223 )
- 50 ml conical tubes (Bioland scientific, catalog number: A02-04 )
- Orbitron Rotator I (115 V) (Boekel Scientific)
- Nylon mesh CX-60 (120 µm) and CX-400 (38 µm) (Carolina Biological Supplies, catalog number: 65-2222N )
- Glass funnel
- Hemocytometer [Mfr Part Number: 3100; Cell depth: 0.100mm +/- 2% (1/10mm); Volume: 0.1 Microliter] (PGC Scientific, catalog number: 1907353 ).
- Stereo Microscope (Olympus, catalog number: SZ51 )
- 25G5/8 gauge needle (Kendall, catalog number: KND8881511235 )
Procedure
- Prepare protoplast
- Weigh 1 g cut leaves, removing the petiole (see Figure 1A).
- On the flat glass, chop leaves into 0.5-1 mm strips with fresh razor blades or with flamed scissors without shredding.
Note: Strips don’t need to be very small to avoid the accumulation of excessive cell debris on the filter. Leaves can be easily cut using a plate surface like a petri dish.
- Using a forceps, transfer immediately the plant material to a deep petri dish filled with washing solution WS1 (enough to cover the strips) and after gentle shaking (1-3 min by hand) remove all liquid by pipetting.
- Add freshly prepared enzyme solution (ES). 5 ml of ES is generally used per 1 g of cut leaf material. Incubate 4-5 h in the dark, at room temperature, with gentle shaking (60-80 rpm) in the rotator.
- Weigh 1 g cut leaves, removing the petiole (see Figure 1A).
- Harvesting protoplasts
- After the enzymatic digestion, transfer the digestion mixture to a 50 ml Falcon tube, add an equal volume of WS2 solution and shake vigorously by hand for 10 sec.
- Release the protoplasts from undigested leaf tissue by filtering the mixture through 120 µm nylon mesh sieves on glass funnel into a round bottom tubes. Two sequential filtering steps, first using CX-60 (120 µm) and then CX-400 (38 µm), are sufficient for protoplasts being isolated from leaf tissue.
Note: We usually go through a 3 step filtration procedure when working with suspension culture material since the sieves clog quickly. The sieves are used in the order CX-60, CX-150 (104 µm) and finally CX-400.
- Wash the protoplasts 3-5 times using 2 ml WS2 solution.
- Spin, after each washing, the tube for 10 min at 50 x g. Discard supernatant and wash protoplasts again with 2 ml WS2 solution.
- After washing, collect the pellets by centrifugation at 50 x g for 3 min with a swinging bucket rotor and re-suspend in MMG solution for counting or in NIB solution for the Isolation of nuclei.
- After the enzymatic digestion, transfer the digestion mixture to a 50 ml Falcon tube, add an equal volume of WS2 solution and shake vigorously by hand for 10 sec.
- Evaluating the quality (viability) and counting the protoplasts
Evaluating the quality
The protoplast isolation procedure often damages or kills a percentage of cells. To determine the viability of the cells, we used fluorescein diacetate (FDA) staining to estimate the percentage of viable protoplast (green protoplast) in a preparation.
- Mix 0.25 ml of 0.05% fluoriscin diacetate (dissolved in acetone) with 20 ml of the appropriate isolation medium to make the ‘’stain’’ solution.
- Pipete 0.25 ml of the protoplast suspension into 1.0 ml of the stain solution.
- Swirl gently to mix and mount some of the protoplasts on a glass slide. First, look at the protoplasts using a 10 or 20 x objectives lens. Now view the protoplasts using the UV source (420- to 490 mn excitation). In the rice green tissue protoplasts, the chloroplasts could be easily identified by their typical chlorophyll autofluorescence under a confocal microscope, while they could not be clearly observed in etiolated protoplasts.
- Observe at least 50 protoplasts and calculate the percentage of living cells. Multiply the estimate of number of protoplasts by this percentage to obtain an estimate of the number of living protoplasts.
Example: 5 x 105 protoplasts per milliliter multiplied by 0.95 viable protoplasts, equals 4.75 x 105 living protoplasts per milliliter. A good isolation will yield between 90 and 95 % viable protoplasts.
Counting protoplasts
- Place a cover glass over the hemocytometer counting chambers.
- Gently mix the protoplast sample thoroughly to insure a uniform distribution of the cells and withdraw a sample with a Pasteur pipet.
Note: Dilute the sample if the cell count is greater than 107 cells/ml.
- Examine at the appropriate magnification (100 x should work for the protoplasts) and count the number of protoplasts in four, appropriately-sized grids in each chamber.
Note: Include all cells touching the middle line along the left or top margin of a square, but not the right or bottom. At 100 x, a 1 mm3 square will fill the field.
- Count a total of 16 grids from 4 chambers
- Record the data in table 1 & 2 and calculate the number of cells per ml using the following equation (to be significant at the 5% level of confidence, the 8 counts cannot deviate more than 7% from the mean [Klein and Klein (1970)]): Cells/ml = Cells/square x 1 square/volume (mm3) x 1000 mm3/ ml x dilution factor
Table 1: Hemocytometer data
Grid size counted
0.1 mm x _____ mm x _____mm
volume of grid counted (mm3)
Dilution (if any)
Table 2: Protoplast density in a partially purified suspension of Red cabbage protoplasts measured with a hemocytometer
Grid
protoplasts grid-1
protoplasts ml-1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
mean +/- std
- Mix 0.25 ml of 0.05% fluoriscin diacetate (dissolved in acetone) with 20 ml of the appropriate isolation medium to make the ‘’stain’’ solution.
- Isolation of nuclei
- Re-suspend pellet at 106/ml of cold NIB in 2 ml eppendorf tube or bigger tubes.
- Put on ice for 7 min.
- Fill a large syringes with protoplasts and pass it 4 times through a 25G5/8 gauge needle.
- Filter the lysate through 20 µm filter into a new tube. Centrifuge at 400 x g for 10 min.
- Discard supernatant
- Re-suspend in NIB + glycerol or SDS solution for SDS gel electrophoresis.
- Re-suspend pellet at 106/ml of cold NIB in 2 ml eppendorf tube or bigger tubes.
Representative data
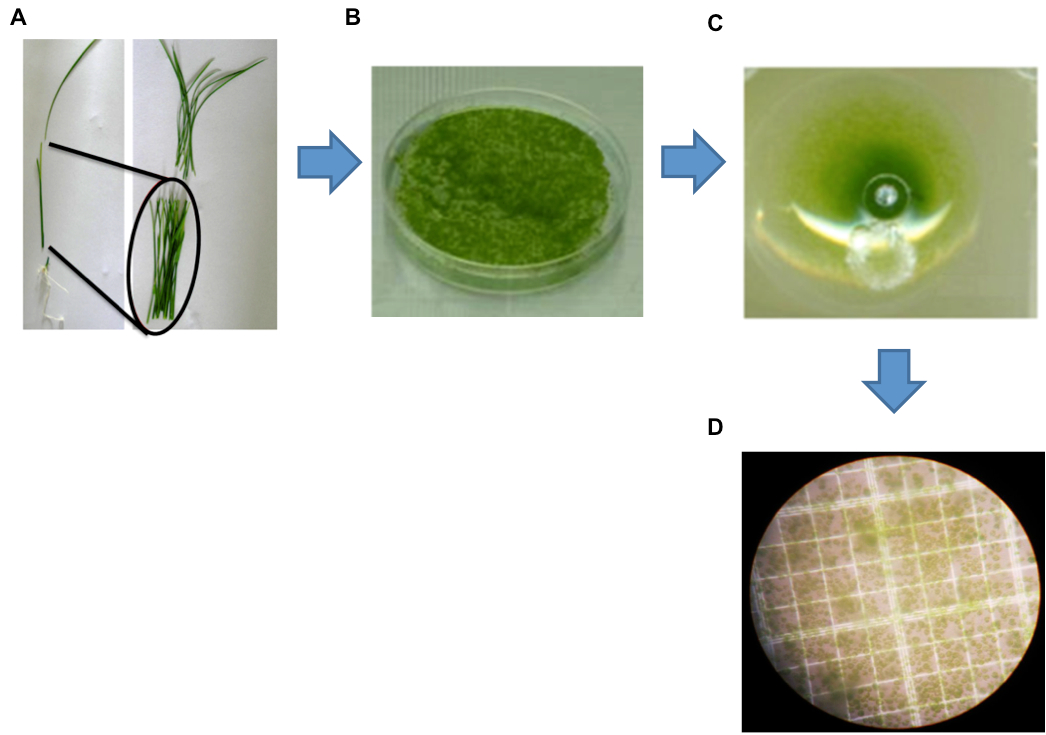
Figure 1. Isolation of protoplasts from rice green tissue. A. A representative healthy 12-day-old rice seedling used for protoplast isolation. Black markers indicate the optimal sections of seedlings (stem and sheath) yielding protoplasts. B. Cut strips were digested by enzyme solution (ES). C. Protoplasts collected after the filtration step. D. Image of protoplasts obtained using a Leica digital camera under an Olympus microscope with a 40x objective.
Recipes
- Enzyme solution (ES)
1.5% (w/v) cellulase R10
0.4% (w/v) macerozyme R10
0.4 M mannitol
20 mM KCl
20 mM MES (pH 5.5)
Heat to 55 °C for 10 min, then cool to room temperature before adding 10 mM CaCl2
0.1% BSA
Note: For longer-term storage, the enzyme powder should be aliqouted and stored at -20 °C in tightly capped plastic tubes. For regular use, a frozen 5 g tube is "thawed" and stored at 4 °C.
- Washing and incubation solution (WS1)
0.5 M mannitol
4 mM MES-KOH (pH 5.5)
20 mM KCl
- Washing solution (WS2)
154 mM NaCl
125 mM CaCl2
5 mM KCl
2 mM MES at pH 5.7
- MMG solution
0.4 M mannitol
15 mM MgCl2
4 mM MES at pH 5.7
Note: Solutions WS1, WS2 and MMG can be prepared before the experiment, autoclaved and stored at 4 °C. Just check the pH before using them.
- Nuclei isolation solution (NIB)
0.1 mM spermidine
10 mM MES-KOH (pH 5.5)
2.5 mM EDTA
10 mM NaCl
10 mM KCl
0.2 M sucrose
0.15% Triton X-100
2.5 mM DTT (add fresh just before using)
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the Swiss National Foundation grant (31003A-12293 and 31003A-138339) and the Sino-Swiss Science and Technology Cooperation Program (IZLCZ3 123946 to YP and 2009DFA32040 to QS).
References
- Harrison, M. J., Choudhary, A. D., Lawton, M. A., Lamb, C. J. and Dixon, R. A. (1992). Analysis of defense gene transcriptional regulation. In: Bowles, D. J. (ed). Molecular Plant Pathology: A Practic Approach. Oxford University Press, pp 147-162.
- Hicks, G. R. and Raikhel, N. V. (1993). Specific binding of nuclear localization sequences to plant nuclei. Plant Cell 5(8): 983-994.
- Roberts, M. W. and Okita, T. W. (1991). Accurate in vitro transcription of plant promoters with nuclear extracts prepared from cultured plant cells. Plant Mol Biol 16(5): 771-786.
- Roman, R. (1980). Replication of DNA by nuclei isolated from soybean suspension cultures. Plant Physiol 66(4): 726-730.
- Somssich, I. E., Bollmann, J., Hahlbrock, K., Kombrink, E. and Schulz, W. (1989). Differential early activation of defense-related genes in elicitor-treated parsley cells. Plant Mol Biol 12(2): 227-234.
- Watson, J. C. and Thompson, W. F. (1986). Purification and restriction endonuclease analysis of plant nuclear DNA. Method Enzymol 118:57-79.
- Zhang, Y., Su, J., Duan, S., Ao, Y., Dai, J., Liu, J., Wang, P., Li, Y., Liu, B., Feng, D., Wang, J. and Wang, H. (2011). A highly efficient rice green tissue protoplast system for transient gene expression and studying light/chloroplast-related processes. Plant Methods 7(1): 30.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2015 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Jabnoune, M., Secco, D., Lecampion, C., Robaglia, C., Shu, Q. and Poirier, Y. (2015). An Efficient Procedure for Protoplast Isolation from Mesophyll Cells and Nuclear Fractionation in Rice . Bio-protocol 5(5): e1412. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1412.
Category
Plant Science > Plant cell biology > Cell isolation
Plant Science > Plant cell biology > Organelle isolation
Cell Biology > Organelle isolation > Nuclei
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link









