- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
ELISA on Virus-Infected Cells
Published: Vol 4, Iss 10, May 20, 2014 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1127 Views: 12525
Reviewed by: Anonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Protocol for RYMV Inoculation and Resistance Evaluation in Rice Seedlings
Agnès Pinel-Galzi [...] Laurence Albar
Jun 5, 2018 8058 Views
An Optimised Indirect ELISA Protocol for Detection and Quantification of Anti-viral Antibodies in Human Plasma or Serum: A Case Study Using SARS-CoV-2
Claire Baine [...] Jennifer Serwanga
Dec 20, 2023 3631 Views
Abstract
The gammaherpesvirus murid herpesvirus 4 (MuHV-4) enters cells by endocytosis from the cell surface and fusion of the viral envelope with the membrane of late endosomes. The viral envelope glycoproteins undergo antigenic changes both upon virion endocytosis and upon fusion of the viral envelope with the endosomal membrane. These changes in virion antigenicity during virus entry were first described by immunofluorescence of infected cells. Although immunofluorescence provides valuable information on the subcellular distribution of the viral glycoproteins, the quantification of immunofluorescence signals in a large number of cells is not only dependent on relatively expensive microscopy equipment, but is also relatively time-consuming. In order to quantify the antigenicity of MuHV-4 virions entering NMuMG epithelial cells in a reliable, as well as time- and cost-effective way, we have developed an ELISA with infected cells as the solid phase. In this assay, cells are grown on 96-well tissue culture plates, exposed to virions at 4 °C, followed by incubation at 37 °C allowing virion endocytosis. Cells are fixed either directly after virion binding at 4 °C or after incubation at 37 °C. After subsequent permeabilization, the cells are incubated with monoclonal antibodies specific for the viral envelope glycoproteins, followed by detection with an alkaline phosphatase-coupled secondary antibody. Upon incubation of cells with p-nitrophenyl phosphate substrate, the absorbance is measured on a conventional ELISA microplate reader. The different ways of data interpretation are discussed.
Keywords: HerpesvirusMaterials and Reagents
- NMuMG cells (ATCC, catalog number: CRL-1636 )
- BAC-derived MuHV-4 strain 68 (Adler et al., 2000)
- Glutamine (PAA Laboratories GmbH, catalog number: E15-883 )
- Fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Amimed, catalog number: 2-01F10-I )
- 100 U/ml penicillin and 100 µg/ml streptomycin (PAA Laboratories GmbH, catalog number: P11-010 )
- Trypsin-EDTA (PAA Laboratories GmbH, catalog number: L11-003 )
- Trypan blue solution (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T8154 )
- Paraformaldehyde (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P6148 )
- Glycine (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 50046 )
- Triton-X100 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: X100 )
- Tween 20 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P1379 )
- Bovine serum albumin (BSA) (Fraction V) (Amresco, catalog number: 0332 )
- MuHV-4 envelope glycoprotein-specific monoclonal antibodies (hybridoma supernatants) (Glauser et al., 2012b; Glauser et al., 2013)
- Alkaline phosphatase-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG (γ chain specific) polyclonal antibody (SouthernBiotech, catalog number: 1030-04 )
- p-nitrophenyl phosphate tablets (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: N2770 )
- Complete medium (see Recipes)
- 10x PBS (pH 7.4) (see Recipes)
- 1x PBS (pH 7.4) (see Recipes)
- Trypsin-EDTA (see Recipes)
- PBS (pH 7.4)
- PBS containing 4% formaldehyde (see Recipes)
- PBS containing 0.1 M glycine (see Recipes)
- PBS containing 0.1% Triton-X100 (see Recipes)
- PBS containing 0.1% Tween 20 and 2% BSA (see Recipes)
- PBS containing 0.1% Tween 20 (see Recipes)
- PBS containing 4% formaldehyde (see Recipes)
- ELISA substrate (p-nitrophenyl phosphate) (see Recipes)
Equipment
- 150 cm2 tissue culture flasks (TPP Techno Plastic Products, catalog number: 90150 )
- 96-Well tissue culture plates (F-base) (TPP Techno Plastic Products, catalog number: 92096 )
- Standard tissue culture equipment
- Cooled tabletop microfuge
- Fume hood
- 37 °C, 5% CO2 incubator
- 4 °C cold room
- Sunrise microplate reader (Tecan Trading AG)
- Neubauer improved hemocytometer
- 10, 20, 200, and 1,000 µl volume pipettes and tips
- 200 µl volume 12-channel pipette
- 5 ml Bijoux tubes (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: Z645346 )
- Disposable sterile buffer reservoirs for multichannel pipettes
- Polystyrene boxes
Software
- Microsoft Excel 2010
Procedure
Part I. Considerations for the experimental design
- Cells are fixed at 3 different stages in the viral entry process: (i) after virion binding at 4 °C, (ii) after cell entry at 37 °C for 1 h, and (iii) after cell entry at 37 °C for 2 h. For each of these conditions, a separate tissue culture plate is used.
- At least 6 wells should be infected for each experimental condition (virus, treatment, antibody etc.).
- On each plate, at least 6 wells should be left uninfected in order to determine the background signal for each virus-specific monoclonal antibody.
- If the assay is used to study the entry process of viruses pretreated with neutralizing antibodies, it might be necessary to use IgG subclass-specific secondary antibodies in order to avoid binding of the secondary antibody to the neutralizing antibody (Glauser et al., 2012a).
Part II. Experimental procedure
Day 1
- Passage and seed cells
- Grow NMuMG cells in a 150 cm2 tissue culture flask until they form a 90-100% confluent monolayer. One 150 cm2 tissue culture flask yields approximately 2-3 x 107 cells, the experiment described below requires 6 x 106 cells. Wash cells 1x with 10 ml sterile PBS, then overlay with 5 ml Trypsin-EDTA and incubate for 10 min at 37 °C. Detach the cells by hitting the flask, then add 15 ml complete medium. Re-suspend cells by pipetting up and down, centrifuge 3 min at 350 x g at 4 °C and discard the supernatant. Re-suspend cells in 10 ml fresh complete medium, mix a small aliquot 1:1 with trypan blue and count with hemocytometer.
- Seed cells into 96-well tissue culture plates (20,000 cells in 100 µl complete medium/well) and incubate overnight at 37 °C.
- Grow NMuMG cells in a 150 cm2 tissue culture flask until they form a 90-100% confluent monolayer. One 150 cm2 tissue culture flask yields approximately 2-3 x 107 cells, the experiment described below requires 6 x 106 cells. Wash cells 1x with 10 ml sterile PBS, then overlay with 5 ml Trypsin-EDTA and incubate for 10 min at 37 °C. Detach the cells by hitting the flask, then add 15 ml complete medium. Re-suspend cells by pipetting up and down, centrifuge 3 min at 350 x g at 4 °C and discard the supernatant. Re-suspend cells in 10 ml fresh complete medium, mix a small aliquot 1:1 with trypan blue and count with hemocytometer.
Day 2
- Binding of virus to cells (work in 4 °C cold room)
- Dilute virus (MOI of 5 PFU or 15 eGFP units/cell) in complete medium (83 µl/well) in 5 ml Bijoux tubes.
- Pre-cool the 96-well tissue culture plates containing the cells and the tubes containing the diluted viruses for 1 h on ice at 4 °C.
- Gently tap off the cell medium and overlay cells with 83 µl/well diluted viruses or complete medium (uninfected controls), incubate for 2 h on ice at 4 °C.
- Gently wash the cells 3x with ice-cold PBS (approximately 300 µl/well).
- Dilute virus (MOI of 5 PFU or 15 eGFP units/cell) in complete medium (83 µl/well) in 5 ml Bijoux tubes.
- Fixation of cells after cell binding at 4 °C
- Take one plate and overlay the cells with ice-cold PBS containing 4% formaldehyde (100 µl/well), incubate for 1 h at room temperature (RT).
- In order to stop the fixation, gently tap off the fixative and incubate the cells with PBS containing 0.1 M glycine (100 µl/well) for 15 min at RT.
- Wash the cells 3x with PBS (approximately 300 µl/well).
- Permeabilize the cells by incubation with PBS containing 0.1% Triton-X100 (100 µl/well) for 30 min at RT.
- Block the cells by overnight incubation with PBS containing 0.1% Tween 20 and 2% BSA (100 µl/well) at 4 °C.
- Take one plate and overlay the cells with ice-cold PBS containing 4% formaldehyde (100 µl/well), incubate for 1 h at room temperature (RT).
- Fixation of cells after cell entry at 37 °C
- Take the remaining two plates and overlay the cells with ice-cold complete medium (83 µl/well), then incubate one plate for 1 h and the other for 2 h at 37 °C.
- Wash the cells 1x with ice-cold PBS (approximately 300 µl/well), then fix and treat as described in steps C1-5.
- Take the remaining two plates and overlay the cells with ice-cold complete medium (83 µl/well), then incubate one plate for 1 h and the other for 2 h at 37 °C.
Day 3
- Detection of virions by ELISA
Remark: For the primary antibodies use a concentration which gives a strong signal in immunofluorescence (IF). In our experience, hybridoma supernatants diluted 1:2 give good signals in IF and ELISA.- Dilute primary antibodies (hybridoma supernatants) in PBS containing 0.1% Tween 20 and 2% BSA, add to cells (50 µl/well) and incubate 3 h at RT.
- Wash cells 3x with PBS containing 0.1% Tween 20 (approximately 300 µl/well).
- Centrifuge secondary antibody (alkaline phosphatase conjugate) for 10 min at 16,000 x g in a cooled tabletop microfuge (4 °C) to remove any potential antibody aggregates.
- Dilute secondary antibody 1:1,000 in PBS containing 0.1% Tween 20 and 2% BSA, add to cells (100 µl/well) and incubate 3 h at RT.
- Wash cells 6x with PBS containing 0.1% Tween 20 (approximately 300 µl/well).
- Dilute p-nitrophenyl phosphate in H2O according to manufacturer's instructions, add to cells (100 µl/well) and incubate overnight at RT and protected from light.
- Measure absorbance at 405 nm on an ELISA microplate reader. If the microplate reader can measure at a reference wavelenght, use 650 nm.
- Dilute primary antibodies (hybridoma supernatants) in PBS containing 0.1% Tween 20 and 2% BSA, add to cells (50 µl/well) and incubate 3 h at RT.
Part III. Data interpretation
- The absorbance values should not be considered an absolute measure of virion antigenicity, instead they should only be used to compare the antigenicity of virions between the different stages of virus entry, i.e., virus binding at 4 °C and virus entry at 37 °C for 1 or 2 h.
- The absorbance signal which is measured on uninfected cells can be considered the background signal of the respective monoclonal antibody and can be subtracted from the absorbance values measured on infected cells (for an example, see Figure 1A-B).
- If the aim of the experiment is to compare the virion antigenicity of a single virus at different entry stages, the absolute absorbance values can be shown (Glauser et al., 2012b).
- If the aim of the experiment is to compare the entry kinetics of different virus mutants (Glauser et al., 2013), the absorbance values for each virus mutant should be normalized to the values measured after virion binding at 4 °C (for an example, see Figure 1C).
- If the aim of the experiment is to compare the effect of different neutralizing antibodies on virus entry (Glauser et al., 2012a), the absorbance values for each virus-antibody combination should be normalized to the values measured after virion binding at 4 °C, because virus neutralization can either increase or decrease cell binding.
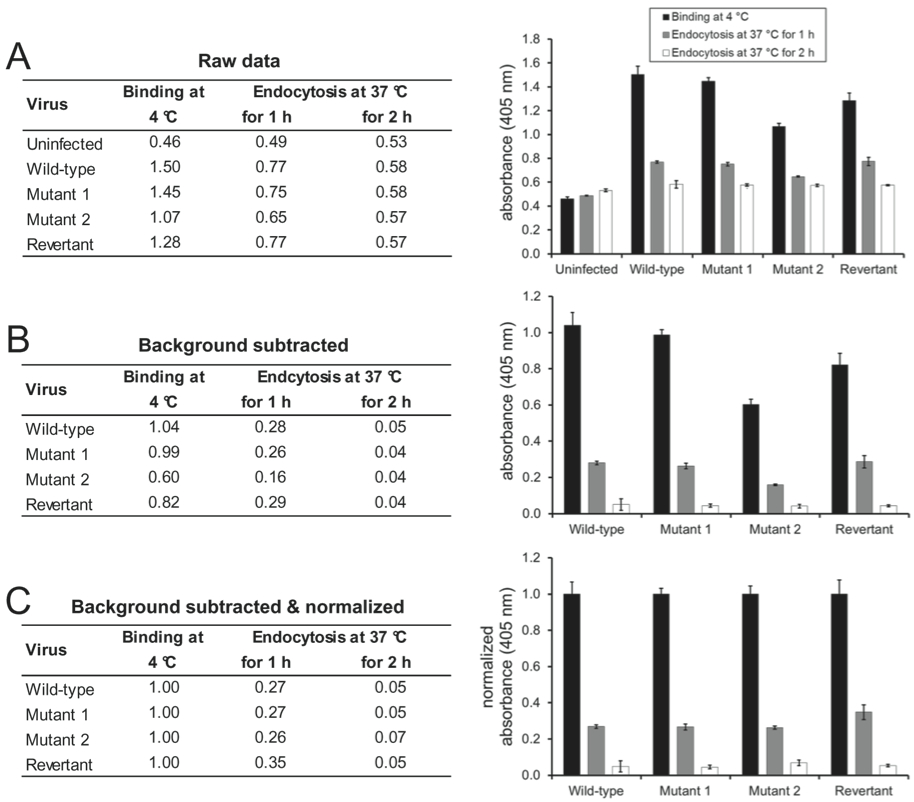
Figure 1. Wild-type, mutant 1, mutant 2, and mutant 1 revertant MuHV-4 (MOI 15 eGFP units/cell) were bound to NMuMG cells for 2 h at 4 °C. After 3 washes with ice-cold PBS to remove unbound virions, the cells were either fixed directly or after further incubations at 37 °C to allow virion endocytosis. The cells were then incubated with mAb BN-1A7 recognizing the pre-fusion conformation of MuHV-4 glycoprotein B and bound antibody detected with an alkaline phosphatase-conjugated secondary antibody and incubation with p-nitrophenyl phosphate substrate. The bars show mean values from 6 wells ± standard error of the mean. (A) Mean absorbance readings at 405 nm (raw data). (B) The signal measured on uninfected cells was taken as background and subtracted from the signals measured on the infected cells. (C) After subtraction of the background signal, all values were normalized to the values measured after virus binding at 4 °C. This allows better comparison of the entry kinetics different virus mutants.
Recipes
- Complete medium
DMEM, 4.5 g/L glucose, with stable glutamine 500 ml Heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum 50 ml 100x Penicillin-Streptomycin 5.5 ml Stored at 4 °C - 10x PBS (pH 7.4)Stir with magnetic stirrer until completely dissolved
Deionized H2O 800 ml NaCl 80 g KaCl 2 g Na2HPO4.7H2O 26.6 g KH2PO4 2.4 g
Adjust to pH 7.4 with HCl
Adjust volume to 1 liter with H2O
Sterilize by autoclaving
Stored at RT - 1x PBS (pH 7.4)Sterilize by autoclaving
Deionized H2O 900 ml 10x PBS (pH 7.4) 100 ml
Stored at RT - Trypsin-EDTAStored at 4 °C
Sterile PBS (pH 7.4) 90 ml 10x Trypsin-EDTA 10 ml - PBS containing 4% formaldehydeBoil PBS in microwave oven
PBS (pH 7.4) 100 ml Paraformaldehyde 4 g
Caution: Do not close the lid of the bottle.
Let PBS cool down for approximately 5 min, then add paraformaldehyde to warm PBS.
Caution: Work in fume hood and wear gloves and eye protection.
Stir with magnetic stirrer until completely dissolved
Stored at -20 °C - PBS containing 0.1 M glycineMix until completely dissolved
PBS (pH 7.4) 100 ml Glycine 0.75 g
Sterilize by autoclaving
Stored at RT - PBS containing 0.1% Triton-X100Mix until completely dissolved
PBS (pH 7.4) 100 ml Triton-X100 0.1 ml
Stored at RT - PBS containing 0.1% Tween 20 and 2% BSAMix until completely dissolved
PBS (pH 7.4) 100 ml Tween 20 0.1 ml BSA 2 g
Sterilize by filtration (0.2 µm filter)
Stored at 4 °C - PBS containing 0.1% Tween 20Mix until completely dissolved
PBS (pH 7.4) 1,000 ml Tween 20 1 ml
Stored at RT - ELISA substrate (p-nitrophenyl phosphate)Mix until completely dissolved
Deionized H2O 20 ml Buffer tablet 1 pc. Substrate tablet 1 pc.
Prepare immediately before use
Acknowledgments
This protocol is adapted from Glauser et al. (2012a); Glauser et al. (2012b); and Glauser et al. (2013).
References
- Adler, H., Messerle, M., Wagner, M. and Koszinowski, U. H. (2000). Cloning and mutagenesis of the murine gammaherpesvirus 68 genome as an infectious bacterial artificial chromosome. J Virol 74(15): 6964-6974.
- Glauser, D. L., Gillet, L. and Stevenson, P. G. (2012a). Virion endocytosis is a major target for murid herpesvirus-4 neutralization. J Gen Virol 93(Pt 6): 1316-1327.
- Glauser, D. L., Kratz, A. S. and Stevenson, P. G. (2012b). Herpesvirus glycoproteins undergo multiple antigenic changes before membrane fusion. PLoS One 7(1): e30152.
- Glauser, D. L., Milho, R., Frederico, B., May, J. S., Kratz, A.-S., Gillet, L. and Stevenson, P. G. (2013). Glycoprotein B cleavage is important for murid herpesvirus 4 to infect myeloid cells. J Virol 87(19): 10828-10842.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2014 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Glauser, D. L. and Stevenson, P. G. (2014). ELISA on Virus-Infected Cells. Bio-protocol 4(10): e1127. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1127.
Category
Microbiology > Microbe-host interactions > Virus
Biochemistry > Protein > Immunodetection > ELISA
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link