- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Generation and Screening of a Non-typeable Haemophilus influenzae Tn-seq Mutant Library
Published: Vol 4, Iss 5, Mar 5, 2014 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1065 Views: 11929
Reviewed by: Fanglian He

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols
A Novel Method of Inducible Directed Evolution to Evolve Complex Phenotypes
Ibrahim S. Al’Abri [...] Nathan Crook
Oct 20, 2022 3033 Views
Comprehensive Mapping of EZ-Tn5 Transposon Insertion Sites in Pseudomonas argentinensis SA190 Using RATE-PCR
Büsra Elkatmis [...] Maged M. Saad
Jul 20, 2025 1701 Views
Editing the Serratia proteamaculans Genome Using the Allelic Exchange Method
Ksenia Chukhontseva [...] Ilya Demidyuk
Sep 20, 2025 1318 Views
Abstract
The genome-wide screen Tn-seq (van Opijnen et al., 2009) is very valuable tools to identify bacterial genes with a conditionally essential function, for instance genes involved in bacterial virulence. These techniques are based on the generation of a random mutant library, which is grown in a control of challenge situation (Figure 1). The advantage of using a mariner transposon for the generation of a random transposon mutant library is its insertion into TA sites, which makes the insertion in the genome highly random. In addition, an MmeI restriction site can be introduced in the inverted repeat of the transposon, without affecting the recognition by HimarC9 transposase.
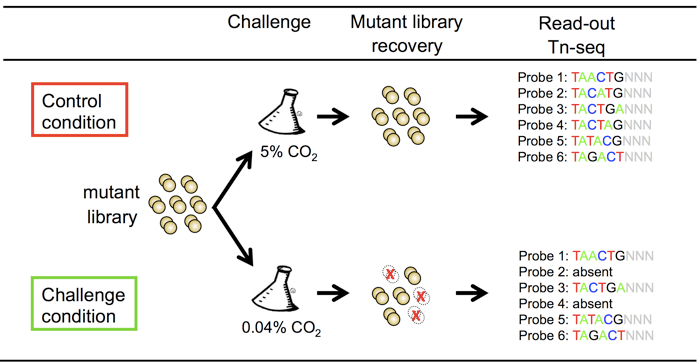
Figure 1. Schematic representation of the non-typeable Haemophilus influenzae tn-seq mutant library screen for survival and growth in environmental air
Materials and Reagents
- 1 U/μl Calf Intestinal Alkaline Phoshatase (CIAP) (New England Biolabs, catalog number: M0290S )
- Chloroform: isoamyl alcohol
- Phenol: chloroform: isoamayl alcohol
- Milli-Q water
- 10 mM dNTP mix (New England Biolabs, catalog number: N0447S )
- 1 mM dNTP mix
- Absolute ethanol
- 70 % Ethanol
- 10 mg/ml Glycogen
- 2 U/μl MmeI restriction enzyme (New England Biolabs, catalog number: R0637S )
- 10x NEBuffer 4
- 32 mM S-denosylmethionine
- 3 M NaAc (pH 5.3)
- 5 M NaCl
- 2 U/μl Phusion DNA polymerase (New England Biolabs, catalog number: M0530S )
- 5x Phusion HF buffer
- 10 U/μl T4 DNA ligase (New England Biolabs, catalog number: M0202S )
- 20 U/μl T4 DNA ligase
- 10x T4 DNA ligase buffer
- 2.5 U/μl T4 DNA polymerase (New England Biolabs, catalog number: M0203S )
- 10x T4 DNA polymerase buffer
- T4 polynucleotide kinase (3' phosphatase minus) (New England Biolabs, catalog number: M0236S )
- 100x TE buffer
- 1 M NaOH
- 50 % Glycerol
- 1 mM DTT
- 5 M NaCl
- 1 M MgCl2
- 10 mg/ml BSA
- 5 U/ml E.coli DNA ligase (New England Biolabs, catalog number: M0205S )
- 10x E.coli DNA ligase buffer
- 1 M Hepes (pH 7.9)
- HimarC9 transposase
- M-IV medium (Herriott et al., 1970)
- 1 mg/ml Hemin (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: H9039 )
- 10 mg/ml Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: N7004 )
- Brain heart infusion medium (BHI) (BD Biosciences, catalog number: 237500 )
- Supplemented BHI, BHI medium containing 10 μg/ml Hemin and 2 μg/ml NAD
- Bacto-agar (BD Biosciences, catalog number: 212030 )
- Supplemented BHI plates, sBHI containing 1.5% bacto agar
- PBS
- 100 mg/ml RNase A (Roche Diagnostics, catalog number: 10109142001 )
- Qiagen Genomic-tip 20/G columns (QIAGEN, catalog number: 10223 )
- Qiagen Genomic DNA buffer set (QIAGEN, catalog number: 19060 )
- Minelute Reaction Cleanup Kit (QIAGEN, catalog number: 28204 )
- Qubit dsDNA BR assay (Life technologies, catalog number: Q32850 )
- Acceptor DNA
Any type of DNA can serve as acceptor for in vitro mariner transposition. The most common types of acceptor DNA are: Chromosomal DNA of the target strain (High quality DNA is required, preferably isolated with Qiagen Genomic Tip columns) or PCR products of target genes or regions. - Donor DNA
Any type of DNA that carries a mariner transposon with MmeI restriction site in the inverted repeat can serve as donor for transposon in the in vitro mariner transposition reaction. Used pGSF8 plasmid, carrying transposon with spectinomycin resistance cassette, suitable for GAF and TnSeq (Langereis et al., 2013). - Primers used for sequence adapters ligation and PCR amplification (see Appendixes)
Equipment
- Pipet tips: 0.5-10 μl, 2-20 μl, 20-200 μl 100-1000 μl
- 15 cm dishes
- Heating block for incubations ranging from 16 °C and 75 °C (Grant QBD2)
- Microcentrifuge for 1.5 ml tubes (Eppendorf, model: 5417R )
- Centrifuge for 50 ml tubes (Eppendorf, model: 5810 )
- T100 thermal cycler (Bio-Rad Laboratories)
- Nanodrop spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Nanodrop, model: ND1000 )
- Incubator with 5% CO2 (BINDER GmbH, model: CB 150 )
- Qubit Fluorometer (Life Technologies)
- Bioanalyser (Agilent Technologies)
Procedure
This detailed protocol is divided into four sections:
Part I. Generation of mutant library
We provide a detailed protocol for the generation of a mutant library in non-typeable Haemophilus influenzae, but this can be used for all bacteria that are naturally competent.
Part II. Mutant library screen
As example, we provide a detailed protocol for the identification of non-typeable Haemophilus genes essential for survival in environmental air, as published before (Langereis et al., 2013).
Part III. Mutant library readout
Part IV. Data analysis
For data analysis, the web-based analysis software ESSENTIALS was used (Zomer et al., 2012). A detailed manual can be found on the website (http://bamics2.cmbi.ru.nl/websoftware/essentials/essentials_start.php).
Part I. Generation of mutant library
- Transposition reaction
- Prepare the 6x transposition buffer enough for 30 reactions fresh by combining
60 μl 50 % glycerol
0.6 μl 1 M DTT
7.5 μl Hepes (pH 7.9)
7.5 μl 10 mg/ml BSA
6.0 μl 5 M NaCl
3.0 μl 1 M MgCl2
15.4 μl sterile dH2O - Combine in a 1.5 ml tube
3.3 μl 6x Transposition Buffer
0.5-1.0 μg recipient DNA
0.5-1.0 μg donor for mariner transposon
1 μl recombinant Himar1 transposase
Sterile dH2O until Vtotal= 20 μl
Mix and incubate for about 4 h at 30 °C in a heating block. - Inactivate transposase for 10 min at 75 °C in a heating block.
- Add to inactivated transposition reaction
2 μl 3 M Sodium Acetate (pH ~5.3)
0.5 μl 20 mg/ml glycogen
50 μl 100% ethanol
Mix and place in -20 °C freezer for at least 30 min. - Centrifuge at maximum speed in a precooled (4 °C) microcentrifuge for 15 min.
- Remove supernatant with 1 ml pipet (do not touch the pellet).
Note: At this moment it is not necessary to carefully remove al liquid. - Add 250 μl of 70% ethanol (just add, do not try to resuspend the pellet).
- Centrifuge at maximum speed in a precooled (4 °C) microcentrifuge for 5 min.
- Carefully remove all supernatant with a 1 ml pipet (do not touch the pellet).
(Optional: Centrifuge in a microcentrifuge for a few seconds to collect the remainder of the supernatant at the bottom of the tube and carefully remove all supernatant with a 200 μl pipet.) - Dry the pellet on air (pellets turns from opaque to white in ~30 min).
(Optional: Place the tubes in a heating block at 30 °C to speed up evaporation of liquid.) - Dissolve pellet in 15.8 μl sterile dH2O.
- Prepare the 6x transposition buffer enough for 30 reactions fresh by combining
- Repair of the transposition reaction
- Add to the dissolved pellet
2 μl 10x T4 DNA polymerase Reaction Buffer
0.2 μl 10 mg/ml BSA
1 μl 1 mM dNTP mix
1 μl 2.5 U/μl T4 DNA polymerase
Incubate for 30 min at 16 °C. - Inactivate polymerase for 10 min at 75 °C in a heating block.
- Add to inactivated polymerase reaction
2 μl 3 M Sodium acetate
0.5 μl 20 mg/ml glycogen
50 μl 100% ethanol
Mix and incubate in -20 °C freezer for at least 30 min. - Centrifuge at maximum speed in a precooled (4 °C) microcentrifuge for 15 min.
- Remove supernatant with 1 ml pipet (do not touch the pellet).
Note: At this moment it is not necessary to carefully remove al liquid. - Add 250 µl of 70% ethanol.
- Centrifuge at maximum speed in a precooled (4 °C) microcentrifuge for 5 min.
- Carefully remove all supernatant with a 1 ml pipet (do not touch the pellet).
(Optional: Centrifuge in a microcentrifuge for a few seconds to collect the remainder of the supernatant at the bottom of the tube and carefully remove all supernatant with a 200 μl pipet.) - Dry the pellet on air (pellets turns from opaque to bright white in ~30 min).
(Optional: place the tubes in a heating block at 30 °C to speed up evaporation of liquid) - Dissolve pellet in 17.8 µl sterile dH2O.
- Add to the dissolved pellet
2 μl 10x E.coli DNA ligase Reaction Buffer
0.2 μl E.coli DNA ligase (5 U/µl)
Incubate overnight at 16 °C. - Store mutagenized DNA at -20 °C.
- Add to the dissolved pellet
- Transformation
- Grow 10 ml non-typeable Haemophilus influenzae (NTHi) in BHI medium containing 10 μg/ml hemin and 2 μg/ml NAD shaking with 225 rpm at 37 °C to an OD620 of 0.3.
- Centrifuge the bacteria 10 min with 3,000 x g and resuspend in 10 ml PBS.
- Centrifuge the bacteria 10 min with 3,000 x g and resuspend in 10 ml M-IV medium and incubate 100 min shaking with 100 rpm at 37 °C.
- Centrifuge the bacteria 10 min with 3,000 x g and resuspend in 1 ml M-IV medium and transfer to a 1.5 ml tube.
- Add 1-5 μg mutagenized DNA and incubate 60 min with 100 rpm at 37 °C.
- Plate 1 to 100 μl per sBHI plate for over night growth at 37 °C + 5% CO2.
- Collect the colonies by adding 5 ml PBS + 15% glycerol on the plates and store 1 ml aliquots at -80 °C.
Note: The number of colonies (transposon mutants) is dependent on the transformation efficiency of the NTHi strain used in this experiment. It is recommended to use a highly competent NTHi strain in order to obtain large mutant libraries. Alternatively, multiple transformations can be pooled to obtain sufficient transposon mutants, typically 10-20-fold the number of genes in the genome.
Part II. Mutant library screen
The mutant library can be used in any control and stress condition. As proof of principle, we have used growth in air enriched with 5% CO2 (control condition) or ambient air with 0.04% CO2 (stress condition). To do so, the mutant library was constructed with 5% CO2 enriched M-IV medium (M-IV medium incubated at least 2 h at 5% CO2 in an open 50 ml tube) without shaking to prevent loss of mutants while making the mutant library (generation mutant library steps 27-28).
- Thaw 1 ml aliquot of the NTHi mutant library at RT.
- Centrifuge 2 min at 10,000 x g in microcentrifuge.
- Remove the medium containing glycerol and resuspend the bacteria in 1 ml sBHI medium.
- Grow the mutant library in 5 ml sBHI medium enriched with 5% CO2 (incubate BHI medium overnight in the incubator + 5% CO2 and add hemin and NAD fresh before use) without shaking to OD620 = 0.5 and store three 1 ml aliquots with 15% glycerol at -80 °C. (Start culture)
- Dilute the start culture 1:100 in 5 ml 5% enriched sBHI medium (control) or sBHI medium (stress) and grow to OD620 = 0.5 with 5% CO2 (control) or ambient air (stress) at 37 °C and store three 1 ml aliquots with 15% glycerol at -80 °C for storage and start culture for next round. (Round 1)
- Dilute the first round culture 1:100 in 5 ml 5% enriched sBHI medium (control) or sBHI medium (stress) and grow to OD620 = 0.5 with 5% CO2 (control) or ambient air (stress) at 37 °C and store three 1 ml aliquots with 15% glycerol at -80 °C for storage and start culture for next round. (Round 2)
- Dilute the second round culture 1:100 in 5 ml 5% enriched sBHI medium (control) or sBHI medium (stress) and grow to OD620 = 0.5 with 5% CO2 (control) or ambient air (stress) at 37 °C and store three 1 ml aliquots with 15% glycerol at -80 °C for storage. (Round 3)
- Thaw the challenged mutant library at RT, centrifuge 3 min 10.000 x g and resuspend the bacteria in 1 ml buffer B1 supplemented with 2 μl RNase A solution (100 mg/ml).
Part III. Mutant library readout
- Mutant library chromosomal DNA isolation and digestion
- Thaw the challenged mutant library at RT, centrifuge 3 min 10,000 x g and resuspend the bacteria in 1 ml buffer B1 supplemented with 2 μl RNase A solution (100 mg/ml).
- Isolate the chromosomal DNA from the challenged mutant libraries with Qiagen Genomic Tip columns.
- Add 20 μl lysozyme (100 mg/ml) and 45 μl proteinase K (10 mg/ml) and incubate 30 min at 37 °C.
- Add 350 μl buffer B2 and incubate 30 min at 50 °C.
- Place a Qiagen genomic tip 20/G column on a 15 ml tube and the column with 2 ml buffer QBT.
- Vortex the sample and apply it to the equilibrated column.
- Wash the column 3x with 1 ml buffer QC.
- Replace the 15 ml tube and elute the DNA with 2x 1 ml buffer QF.
- Transfer 3x 650 μl buffer to a 1.5 ml tube, add 455 μl RT isopropanol and centrifuge immediately 15 min. with max. speed at 4 °C.
- Remove the isopropanol and wash with 1 ml cold 70% ethanol. Vortex briefly and centrifuge 10 min. with max. speed at 4 °C.
- Remove the ethanol and wash a second time with 1 ml cold 70% ethanol. Vortex briefly and centrifuge 10 min. with max. speed at 4 °C.
- Remove the ethanol and let the pellet dry. Do not completely dry the pellet.
- Resuspend the DNA pellet in 100 µl TE.
(Optional: Incubate at 50 °C to dissolve the DNA pellet.)
- Prepare reaction mixture in 1.5 ml microfuge tube
2 μg chromosomal DNA of mutant library
5 μl 2 U/μl MmeI (=10 U)
20 μl 10x NEBuffer 4
0.3 μl 32 mM S-adenosylmethionine
Vtotal with dH2O= 200 μl
Incubate at 37 °C, >4 h. - Add 1 μl 1 U/μl CIAP and mix (=1 U) and incubate at 50 °C, 30 min.
- Add 200 μl phenol:chloroform:isoamayl alcohol and vortex 10 sec.
- Centrifuge max speed, 5 min at RT.
- Transfer upper layer (~200 μl) to new 1.5 ml microfuge tube with 200 μl chloroform: isoamyl alcohol and vortex 10 sec.
- Centrifuge max speed, 5 min at RT.
- Transfer upper layer (~200 μl) to new 1.5 ml microfuge tube.
- Add to the tube
20 μl 3 M Sodium Acetate
0.5 μl 20 mg/ml glycogen
500 μl 100% ethanol
Mix and incubate in -20 °C freezer for at least 30 min. - Centrifuge at maximum speed in a precooled (4 °C) microcentrifuge for 15 min.
- Remove supernatant with 1 ml pipet (do not touch the pellet).
Note: At this moment it is not necessary to carefully remove al liquid. - Add 500 µl of 70% ethanol.
- Centrifuge at maximum speed in a precooled (4 °C) microcentrifuge for 5 min.
- Carefully remove all supernatant with a 1 ml pipet (do not touch the pellet).
(Optional: Centrifuge in a microcentrifuge for a few seconds to collect the remainder of the supernatant at the bottom of the tube and carefully remove all supernatant with a 200 μl pipet.) - Dry the pellet on air (pellets turns from opaque to bright white in ~30 min).
(Optional: Place the tubes in a heating block at 30 °C to speed up evaporation of liquid.) - Dissolve pellet in 20 μl dH2O.
- Measure the DNA concentration.
- Adapter annealing
For each adapter, a F- and R-primer must be annealed (see primers listed in the appendix). A total of 12 adapters are listed in the appendix, but the number needed for the experiment (e.g. 4 or 8) can be annealed in parallel in separate tubes.- For primer annealing, prepare mix in 1.5 ml microfuge tube
5 μl 1 nmol/μl F primer
5 μl 1 nmol/μl R primer
0.5 μl 100x TE
0.5 μl 5 M NaCl
39 μl dH2O
Incubate for 10 min at 95 °C in heating block. - Remove metal tube holder from heating block and allow to cool slowly on bench to T< 30 °C.
- Store samples at -20 °C until further use (annealed adapters can be stored > 1 year).
- For 5'-phosphorylation of the annealed adapters, prepare mix in 1.5 ml microfuge tube
2 μl annealed adapter (100 pmol/μl)
2 μl 10x T4 DNA ligase buffer
0.5 μl 10 U/μl T4 polynucleotide kinase (3' phosphatase minus)
15.5 μl dH2O - Incubate for 5 min at 37 °C.
- Incubate 10 min at 70 °C in a heat block.
- Remove metal tube holder from heating block and allow to cool slowly on bench to T< 30 °C.
- For primer annealing, prepare mix in 1.5 ml microfuge tube
- Adapter ligation and PCR amplification
- MmeI restriction fragments and annealed adapters were ligated in the following reaction mixture
100 ng dephosphorylated MmeI restriction fragments
0.2 μl (10 pmol/μl) freshly phosphorylated annealed adapter
2 μl 10x T4 DNA ligase buffer
0.2 μl (10 U/μl) T4 DNA ligase
Vtotal with dH2O= 20 μl
Incubate for over night at 16 °C. - Ligated adapter and restriction fragments were PCR amplified in the following reaction mixture
26 μl dH2O
10 μl 5x Phusion HF buffer
1 μl 10 mM dNTP mix
5 μl (4 pmol/μl) PBGSF23 primer
5 μl (4 pmol/μl) PBGSF31 primer
2.5 μl ligation mixture
0.5 μl Phusion DNA polymerase
Incubate reaction according to the following PCR program
72 °C - 1 min
98 °C - 30 sec
98 °C - 10 sec |
57 °C - 30 sec | 25x
72 °C - 10 sec |
72 °C - 5 min - Check 2 μl of the PCR reaction on a 2.5 % agarose gel with a 100 bp ladder.
Note: PCR product should be a single band of ~125 bp. - Cleanup PCR reaction with Minelute Reaction Cleanup Kit.
- Mix 50 μl PCR reaction with 50 μl dH2O.
- Add 300 μl ERC buffer.
- Apply to MinElute column in 2 ml tube; centrifuge 1 min at 18,000 rpm.
- Discard flow-through, reuse 2 ml tube.
- Add 750 μl buffer PE; centrifuge 1 min at 18,000 rpm.
- Discard flow-through, reuse 2 ml tube.
- Centrifuge 1 min at maximum speed to completely dry membrane.
- Place MinElute column in RNase-free 1.5 ml tube.
- Pipet 10 μl dH2O on center of the column membrane; wait 1 min.
- Centrifuge 1 min at maximum speed.
- Mix 50 μl PCR reaction with 50 μl dH2O.
- Measure DNA concentration with Nanodrop using d H2O as blank.
- Combine equimolar amounts of differently barcoded DNA probes in one tube.
- For quality control, perform a Qubit DNA concentration measurement and a bioanalyser run.
- 9 fmol of DNA probe was loaded on a Genome Analyzer II (Illumina) for sequence analysis according to the manufacturer's protocols, using a Genomic DNA Sequencing Primer (Illumina) and 36 sequencing cycles.
For further information about Illumina sequencing see Zomer et al. (2012).
- MmeI restriction fragments and annealed adapters were ligated in the following reaction mixture
Part. IV. Data analysis
Data analysis is in detail described in Langereis et al. (2013).
- Generate FASTQ files with 35 bp sequences.
Note: The first nucleotide of the Genome Analyzer II (Illumina) 36-bp sequence reads often has a poor quality and is therefore omitted. - Generate a config file as Table 1 below.
Table 1. Example for config file used for data analysislink barcode transposon sample type library sample format compression http://bamicsb.cmbi.ru.nl/tnseq/co2_Hinfluenza/s_1_export.txt TCACG ACAGGTTGGATGAT target lib1 export none http://bamicsb.cmbi.ru.nl/tnseq/co2_Hinfluenza/s_1_export.txt GATGT ACAGGTTGGATGAT control lib1 export none http://bamicsb.cmbi.ru.nl/tnseq/co2_Hinfluenza/s_1_export.txt TAGGC ACAGGTTGGATGAT target lib1 export none http://bamicsb.cmbi.ru.nl/tnseq/co2_Hinfluenza/s_2_export.txt GACCA ACAGGTTGGATGAT control lib1 export none http://bamicsb.cmbi.ru.nl/tnseq/co2_Hinfluenza/s_2_export.txt GATGT ACAGGTTGGATGAT target lib1 export none http://bamicsb.cmbi.ru.nl/tnseq/co2_Hinfluenza/s_2_export.txt TCACG ACAGGTTGGATGAT control lib1 export none http://bamicsb.cmbi.ru.nl/tnseq/co2_Hinfluenza/s_2_export.txt GACCA ACAGGTTGGATGAT target lib1 export none http://bamicsb.cmbi.ru.nl/tnseq/co2_Hinfluenza/s_2_export.txt TAGGC ACAGGTTGGATGAT control lib1 export none - Choose the finished genome or upload a genbank file for the pathogen used in the screen.
- Upload the config .txt file.
- Press next.
- Analysis is performed with the following parameters (see Figure 2).
- Select TA for selected for mariner transposon mutant libraries.
- Select 30,000 for “library size”.
- Select yes for “perform repeat filtering”.
- Select 2 for “barcode mismatch”.
- Select 17 for “genomic sequence remaining of read”.
- Select bol for “barcode side”.
- Select eol for “transposon inverted repeat side”.
- Select 14 for “minimal sequence match”.
- Select 1(=forward) for “strand to align”.
- Select truncated.ptt for “3’ truncated genes for matching insertion site”.
- Select yes for “remove genomic position bias”.
- Select TMM for “normalization”.
- Select qCML for “paired analysis”.
- Select tagwise for “modeling of variance”.
- Select 10 for “amount of smoothing”.
- Select BH for “p-value adjustment method”.
- Select corrected for “p-value”.
- Select 20 for “minimal number of reads”.
- Select yes for “create ZIP archive”.
- Press proceed
Note: Analysis can take up to a few hours. - Unzip the created zip file and the file gene_alloutputmerged.tsv contains the data analysis for conditionally essential genes.
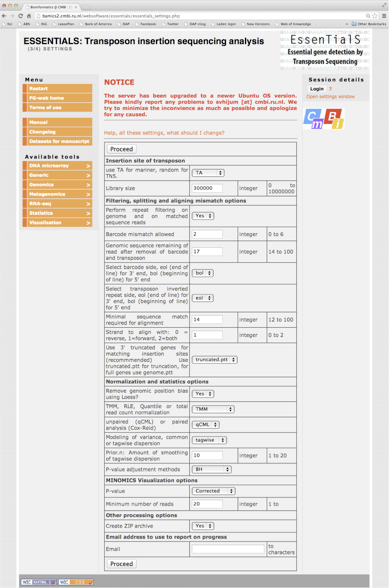
Figure 2. Screenshot of the analysis parameters on the ESSENTIALS website
Acknowledgments
This protocol is adapted from a previously published paper: Langereis et al. (2013).
References
- Langereis, J. D., Zomer, A., Stunnenberg, H. G., Burghout, P. and Hermans, P. W. (2013). Nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae carbonic anhydrase is important for environmental and intracellular survival. J Bacteriol 195(12): 2737-2746.
- Herriott, R. M., Meyer, E. M. and Vogt, M. (1970). Defined nongrowth media for stage II development of competence in Haemophilus influenzae. J Bacteriol 101(2): 517-524.
- Illumina sequencing technology. http://res.illumina.com/documents/products/techspotlights/techspotlight_sequencing.pdf.
- van Opijnen, T., Bodi, K. L. and Camilli, A. (2009). Tn-seq: high-throughput parallel sequencing for fitness and genetic interaction studies in microorganisms. Nat Methods 6(10): 767-772.
- Zomer, A., Burghout, P., Bootsma, H. J., Hermans, P. W. and van Hijum, S. A. (2012). ESSENTIALS: software for rapid analysis of high throughput transposon insertion sequencing data. PLoS One 7(8): e43012.
Appendix
Table 2. Primers used for tn-seq analysis*
*All primers were PAGE purified; P, phosphorylated; Barcodes are based on Illumina TruSeq TechnologyCharacteristics sequence (5'-3') Adapter F primer with ATCACG barcode TTCCCTACACGACGCTCTTCCGATCTATCACGNN A R primer with ATCACG barcode P-CGTGATAGATCGGAAGAGCGTCGTGTAGGGAAAGAGT-P F primer with CGATGT barcode TTCCCTACACGACGCTCTTCCGATCTCGATGTNN B R primer with CGATGT barcode P-ACATCGAGATCGGAAGAGCGTCGTGTAGGGAAAGAGT-P F primer with TTAGGC barcode TTCCCTACACGACGCTCTTCCGATCTTTAGGCNN C R primer with TTAGGC barcode TTCCCTACACGACGCTCTTCCGATCTTGACCANN F primer with TGACCA barcode TTCCCTACACGACGCTCTTCCGATCTTGACCANN D R primer with TGACCA barcode P-TGGTCAAGATCGGAAGAGCGTCGTGTAGGGAAAGAGT-P F primer with ACAGTG barcode TTCCCTACACGACGCTCTTCCGATCTACAGTGNN E R primer with ACAGTG barcode P-CACTGTAGATCGGAAGAGCGTCGTGTAGGGAAAGAGT-P F primer with GCCAAT barcode TTCCCTACACGACGCTCTTCCGATCTGCCAATNN F R primer with GCCAAT barcode P-ATTGGCAGATCGGAAGAGCGTCGTGTAGGGAAAGAGT-P F primer with CAGATC barcode TTCCCTACACGACGCTCTTCCGATCTCAGATCNN G R primer with CAGATC barcode P-GATCTGAGATCGGAAGAGCGTCGTGTAGGGAAAGAGT-P F primer with ACTTGA barcode TTCCCTACACGACGCTCTTCCGATCTACTTGANN H R primer with ACTTGA barcode P-TCAAGTAGATCGGAAGAGCGTCGTGTAGGGAAAGAGT-P F primer with GATCAG barcode TTCCCTACACGACGCTCTTCCGATCTGATCAGNN I R primer with GATCAG barcode P-CTGATCAGATCGGAAGAGCGTCGTGTAGGGAAAGAGT-P F primer with TAGCTT barcode TTCCCTACACGACGCTCTTCCGATCTTAGCTTNN J R primer with TAGCTT barcode P-AAGCTAAGATCGGAAGAGCGTCGTGTAGGGAAAGAGT-P F primer with GGCTAC barcode TTCCCTACACGACGCTCTTCCGATCTGGCTACNN K R primer with GGCTAC barcode P-GTAGCCAGATCGGAAGAGCGTCGTGTAGGGAAAGAGT-P F primer with CTTGTA barcode TTCCCTACACGACGCTCTTCCGATCTCTTGTANN L R primer with CTTGTA barcode P-TACAAGAGATCGGAAGAGCGTCGTGTAGGGAAAGAGT-P Amplification primer 1 CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAAGACCGGGGACTTATCATCCAACCTGT Amplification primer 2 AATGATACGGCGACCACCGAGATCTACACTCTTTCCCTACACGACGCTCTTCCGATCT
Article Information
Copyright
© 2014 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Langereis, J. D. (2014). Generation and Screening of a Non-typeable Haemophilus influenzae Tn-seq Mutant Library . Bio-protocol 4(5): e1065. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1065.
Category
Microbiology > Microbial genetics > Mutagenesis
Molecular Biology > DNA > Mutagenesis
Systems Biology > Genomics > Transposons
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link









