- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Phosphoinositides Coated Beads Binding Assay
Published: Vol 4, Iss 3, Feb 5, 2014 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1039 Views: 12765
Reviewed by: Lin FangFanglian He

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols
Protein-lipid Interaction Analysis by Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR)
Olga Lucia Baron and David Pauron
Sep 20, 2014 14551 Views
Contemporaneous Measurement of Outer and Inner Membrane Permeability in Gram-negative Bacteria
Bo Ma [...] Zheng Hou
Mar 5, 2020 7010 Views

A Fluorescence Dequenching-based Liposome Leakage Assay to Measure Membrane Permeabilization by Pore-forming Proteins
Javier Aguilera [...] Jianjun Sun
May 20, 2021 7108 Views
Abstract
The PIs coated beads assay or “PIP-Beads” developed by Echelon Biosciences (Salt Lake City, USA) is a quick assay to recognize which PIs are able to bind to a given protein domain, in a quantitative way. It is much faster and cheaper than liposomes and more reproducible than PIP-strip assays. The “PIP-Beads” assay is a biochemical assay that basically involves an incubation of a purified protein or protein domain with the appropriate PI-coated set of beads. After washing, drying and resuspending the samples, they can be easily analyzed by SDS-PAGE separation. Phosphoinositides (PIs) have been characterized as important determinants of cell membrane domains, such as the apical and basolateral domains in epithelial polarized cells (Martin-Belmonte and Mostov, 2007), controlling membrane trafficking (Szentpetery et al., 2010) or determining the presynaptic or postsynaptic terminal in neurons, among other functions (Di Paolo and De Camilli, 2006). These phosphoinositides enriched membranes bring the proteomic machinery together, confers to these membrane their different identities and functions. This protein-PIs interaction in many cases involves direct binding of specific protein membrane domains with certain PIs. Some of these domains are characterized such as PH domains from phospholipase-C- or synaptotagmin-like C2 domains (Galvez-Santisteban et al., 2012), while some of them are not. To determine which PI is binding to a given protein domain, it is important to have a quick and efficient assay. The liposome binding assays are very good to establish the kinetic properties of binding, but they are expensive and permit only to test a few PIs per experiment. On the other hand, PIP-strip (phosphatidil-inositol-phosphate) based analysis is easy and fast, however the PIs are presented in a flat surface and the reproducibility is sometimes limited.
Materials and Reagents
- PIP-Beads (Echelon) with the corresponding phosphoinositide of interest. Echelon provides a wide range of PI and other phospholipid coated beads on demand, including a sample pack that has a wide range of PIP-coated beads (P-B00S).
- 2 µg of purified GST-tagged protein per tube of beads and GST alone for control
The protein can be produced and purified by standard methods of GST-tagged protein purification by glutathione-sepharose beads. For the present assay, it is recommended to elute the protein from glutathione-sepharose beads and quantify it before use. Moreover, it is important to use high concentrations of protein, in order to use the smallest possible volume. - HEPES
- Lgepal CA630
- SDS
- Glycerol
- Tris-HCl
- β-mercaptoethanol
- Bromophenol blue
- Wash/binding buffer (see Recipes)
- 2x Reducing Laemmli Sample Buffer (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Refrigerated centrifuge
- Oscillatory or gyratory shaker
- Aspiration pump
- Needles 0.7 x 30 mm
- 1.5 ml Tubes
Procedure
- Before starting
a.Prepare or thaw the purified GST-protein.
b.Pre-cool the centrifuge.
c.Prepare the wash/binding buffer.
d.Make aspiration tips by cutting the tip of a needle with pliers or a similar tool (Figure 1). This will minimize the needle diameter.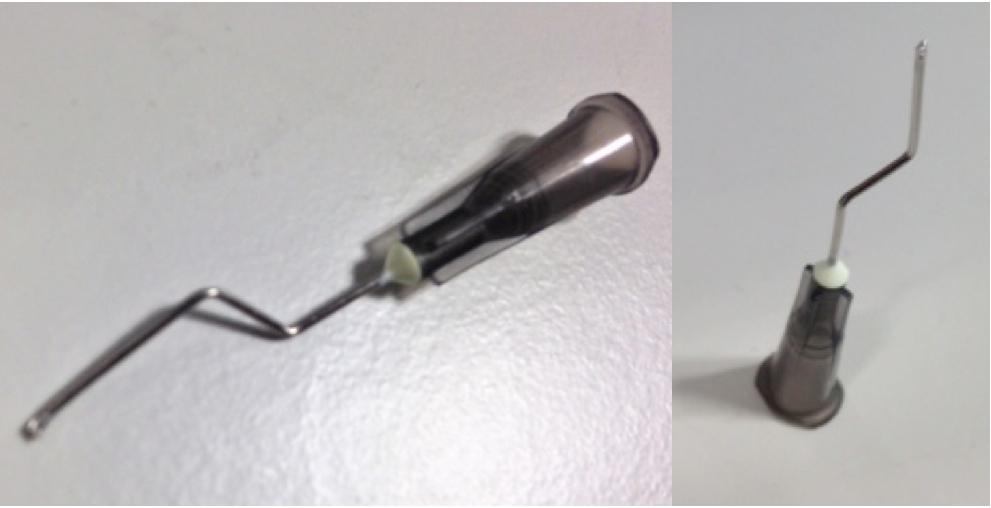
Figure 1. Aspiration tips - Use 50 µl of PI-beads per protein. Echelon provide beads suspended in buffer 50/50.
- Briefly wash three times the beads with 500 μl of precooled wash/binding buffer at 300 x g, 30 sec.
- Centrifuge the beads at 300 x g, 4 °C.
- Add 1 ml of wash/binding buffer to each tube with PI-beads.
- Add 2 µg of the interest GST-tagged protein to the PI-beads.
- Incubate the GST-tagged protein or protein domains with the beads rotating for 2 h at room temperature. For some protein domains longer incubation time or overnight 4 °C incubation may be required, depending on the affinity of the selected domain for the phosphoinositide.
- Wash the beads by pelleting them by centrifugation (300-400 x g at 4 °C). Then add 1 ml of wash buffer and resuspend the beads. Invert the tube 5 times and centrifuge at 4 °C, 300-400 x g. Aspirate carefully the supernatant, without touching the beads with the tip of the needle. Repeat this process 5 times.
- After last wash, dry the beads by aspiration and immediately add 100 μl of 2x Laemli buffer.
- Boil the sample at 95 °C for 5-10 min.
- The sample now can be kept at -20 °C upon analysis in SDS-PAGE.
- Centrifuge the samples 5 min at 27,000 x g before loading in SDS-PAGE gel. This will pellet the beads.
- The binding can be analyzed by western-blot, detecting the interest protein or domain by anti-GST antibody. GST control alone should not produce any kind of binding.
Recipes
- Wash/binding buffer
10 mM HEPES (pH 7.4)
150 mM NaCl
0.25 % Igepal CA630 - 2x Reducing* Laemmli Sample Buffer
4% SDS
20% Glycerol
120 mM Tris-HCl (pH 6.8)
5% β-mercaptoethanol
0.2% Bromophenol blue
*It is important that the buffer is Reducing and fresh, because the reducing agent together with the boiling will be necessary for eluting the protein from the phosphoinositides beads.
Acknowledgments
This protocol has been adapted from Galvez-Santisteban et al. (2012).
References
- Di Paolo, G. and De Camilli, P. (2006). Phosphoinositides in cell regulation and membrane dynamics. Nature 443(7112): 651-657.
- Galvez-Santisteban, M., Rodriguez-Fraticelli, A. E., Bryant, D. M., Vergarajauregui, S., Yasuda, T., Banon-Rodriguez, I., Bernascone, I., Datta, A., Spivak, N., Young, K., Slim, C. L., Brakeman, P. R., Fukuda, M., Mostov, K. E. and Martin-Belmonte, F. (2012). Synaptotagmin-like proteins control the formation of a single apical membrane domain in epithelial cells. Nat Cell Biol 14(8): 838-849.
- Martin-Belmonte, F. and Mostov, K. (2007). Phosphoinositides control epithelial development. Cell Cycle 6(16): 1957-1961.
- Szentpetery, Z., Varnai, P. and Balla, T. (2010). Acute manipulation of Golgi phosphoinositides to assess their importance in cellular trafficking and signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107(18): 8225-8230.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2014 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Gálvez-Santisteban, M., Rodriguez-Fraticelli, A. E. and Martin-Belmonte, F. (2014). Phosphoinositides Coated Beads Binding Assay. Bio-protocol 4(3): e1039. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1039.
Category
Biochemistry > Lipid > Lipid-protein interaction
Biochemistry > Protein > Interaction > Protein-lipid interaction
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link









