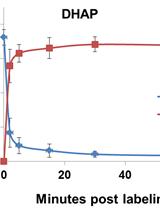
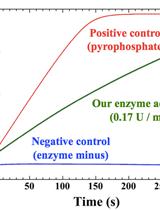
Measurement of Nucleotide Triphosphate Sugar Transferase Activity via Generation of Pyrophosphate
Nucleotide triphosphate (NTP) transferases (EC. 2. 7. 7. X) transfer a nucleoside monophosphate moiety from NTP to another substrate. NTP sugar transferases form a large member of the NTP transferase. There are many variations for the substrate combination of the NTP sugar transferases. It is important to measure the precise enzymatic activity of such NTP sugar transferases by a simple and efficient method. In our method, we measure pyrophosphate as a byproduct of nucleotide diphosphate (NDP)-sugar generation using the pyrophosphate assay kit. The kit reagents include two enzymes that convert pyrophosphate to phosphate, and then phosphorolyze chromogenic substrate to allow color development at 360 nm (see details below). Thus, the NDP-sugar formation can be simply traced as production of pyrophosphate, which is monitored by absorbance at 360 nm. This method is reliable and versatile for measurements of various pyrophosphate-producing enzymes that include NTP sugar transferases.[Principle and overview] NTP transferases catalyze the reversible reaction as follows: NTP + sugar-1P NDP-sugar + PPi The enzyme reaction can be monitored as generation of inorganic pyrophosphate (PPi). The EnzChek Pyrophosphate Assay kit (Molecular Probes, Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA) includes two enzymes and sufficient materials for color development to quantitate pyrophosphate. The inorganic pyrophosphatase (component E in the kit) degrades pyrophosphate into phosphate. Purine nucleoside phosphorylase (PNP, component B) utilizes phosphate to cleave the colorgenic substrate 2-amino-6-mercapto-7-methylpurine ribonucleoside (MESG, component A) into ribose-1-phosphate and 2-amino-6-mercapto-7-methylpurine. The product 2-amino-6-mercapto-7-methylpurine has the absorption maximum at 360 nm. The component C is the dilution solution that includes minimal MgCl2 sufficient for the inorganic pyrophosphatase. Thus, NTP transferase activity can be monitored at 360 nm as generation of a byproduct pyrophosphate. Typically, the nucleotidyl sugar transferase reactions have been measured by High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) (Kawano et al., 2014). There are several advantages and disadvantages in HPLC method and our enzymatic method (O: advantage, X: disadvantage).{HPLC method}O) Can measure the reaction in both directions (NDP-sugar formation and degradation)O) Can measure with a small amount of the sample protein X) Can not follow the real-time reactionX) The peaks of substrates and products must be separated in the chromatogram{Pyrophosphate assay method}O) Can observe the reaction in real-timeO) Easy to use many kinds of substrates because of the simple detection at 360 nmO) Can be used in other pyrophosphate or phosphate generating reactions such as adenylate cyclase, diguanylate cyclase ( Enomoto et al., 2014), and DNA polymeraseX) Can not measure the pyrophosphate-consuming direction of the reversible reaction of NDP-sugar pyrophosphorylase. Km and kcat for NDP-sugar and pyrophosphate are not obtained by the pyrophosphate assay method but by HPLC method.X) Need certain amount of the experimental protein. The maximum activity that the kit reagents allow corresponds theoretically to the rate of color development for the positive control is 2 x 10-2 U in our case. The instruction states the minimum detection of 5 x 10-5 U. Of course, the minimum activity we can measure may depend on the background activity due to contaminants in the substrates or in the sample preparation.