- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Past Issue in 2017
Volume: 7, Issue: 21
Biochemistry
Preparation of the Partially Methylated Alditol Acetates Derived from CS Tetrasaccharides Containing Galactose for the Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry Analysis
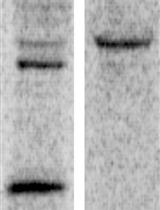
Monitoring the Targeting of Cathepsin D to the Lysosome by Metabolic Labeling and Pulse-chase Analysis
Cancer Biology
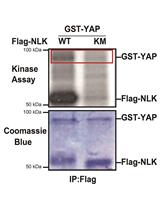
In vitro NLK Kinase Assay
Xenograft Mouse Model of Human Uveal Melanoma
Cell Biology
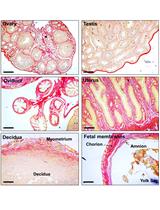
Histochemical Staining of Collagen and Identification of Its Subtypes by Picrosirius Red Dye in Mouse Reproductive Tissues
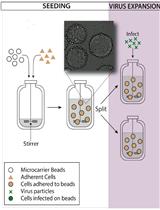
A Bioreactor Method to Generate High-titer, Genetically Stable, Clinical-isolate Human Cytomegalovirus
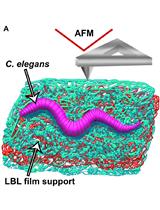
Nematode Epicuticle Visualisation by PeakForce Tapping Atomic Force Microscopy
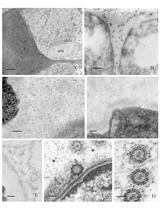
Immunogold Localization of Molecular Constituents Associated with Basal Bodies, Flagella, and Extracellular Matrices in Male Gametes of Land Plants
Immunology
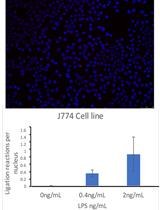
Proximal Ligation Assay (PLA) on Lung Tissue and Cultured Macrophages to Demonstrate Protein-protein Interaction
Microbiology
Isolation of Rice Stripe Virus Preparation from Viruliferous Small Brown Planthoppers and Mechanic Inoculation on Rice
Neuroscience
Isolation, Culture and Differentiation of Adult Hippocampal Precursor Cells
Assessment of Aversion of Acute Pain Stimulus through Conditioned Place Aversion
Sensitive Estimation of Flavor Preferences in STFP Using Cumulative Time Profiles
Stem Cell
Isolation of Primary Human Skeletal Muscle Cells