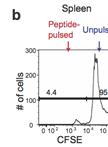
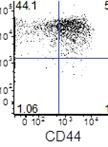
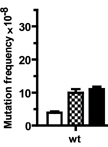
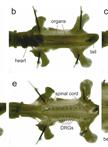
Phagolysosomal Trafficking Assay
Phagolysosomal trafficking is an important innate defense pathway that clears microbes by delivering them to lysosomes, the degradative compartment of the cell. Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb), the causative agent of tuberculosis, subverts this host defense mechanism by arresting maturation of the phagosome. The ability of Mtb to arrest its delivery to the lysosome can be demonstrated by the prolonged co-localization of bacteria containing phagosomes/vacuole with early phagosomal markers [such as, Ras- related proteins in the brain 5 (Rab5) and Transferrin receptor (TfR)], and a failure to acquire late phagosomal and lysosomal markers (such as Rab7 and LAMP1) (Deretic and Fratti, 1999, Mehra et al., 2013). Here, a protocol is outlined for infection of macrophages with mycobacterial species like pathogenic Mtb, vaccine strain Mycobacterium bovis- bacillus Calmatte- Guérin (BCG) and rapidly dividing non-pathogenic Mycobacterium smegmatis (Msmeg), followed by indirect-immunofluorescence microscopy to visualize host vacuolar markers. Thereafter, automated quantification of degree of co-localization between mycobacteria and host vacuolar markers like TfR and LAMP1 is done by processing the binary images of bacteria using mathematical tools. This results in quantification of the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of these host markers directly around the bacteria/bacterial clusters with increased sensitivity relative to when done manually. By manipulating host or pathogen, this assay can be used to evaluate host or bacterial determinants of intracellular trafficking. The basic method can be applied to studying trafficking of other bacteria or particles like beads, although the kinetics of infection and phagosome maturation will depend upon the phagocytic cargo. The mathematical analysis tools are available in many standard imaging analysis programs. However, any adaption for similar analysis should be confirmed by the individual user with their imaging and analysis platform.