- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Coculture between hMADS and Mouse Adult CM
Published: Vol 4, Iss 14, Jul 20, 2014 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1178 Views: 10791
Reviewed by: Anonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Spheroid Sheets: A Scalable Platform for Producing Tissue Membrane Constructs
Quang Bach Le [...] Deepak Choudhury
Nov 20, 2025 1536 Views

A Protocol to Induce Brown and Beige Adipocyte Differentiation From Murine and Human Adipose-Derived SVF
Rohit Raj Yadav [...] Narendra Verma
Dec 5, 2025 1642 Views

Optimization of Adipogenic Differentiation Protocol for Murine and Human Cell Culture Models
Junwan Fan [...] Wenyan He
Jan 20, 2026 211 Views
Abstract
Heart failure occurring after acute myocardial infarction (MI) is among the main causes of death in western countries. Cell therapies, particularly those based on mesenchymal stem cells (MSC), represent one of the most promising approaches to repair damaged heart tissues. Several reports have provided evidences that injection of mesenchymal stem cells improved heart function following myocardial infarction (Shake et al., 2002; Zimmet and Hare, 2005; Zeng et al., 2007). Nevertheless, the mechanism(s) by which MSC exert their therapeutic action is far from being understood, and further knowledges in this field are required especially to optimize efficiency of current cardiac cell therapies. To assess the regenerative mechanisms developed by MSC in vitro, we developed the method described above which is expected to mimic the micro-environment typical of an infarcted heart. This method consists in a species mismatch coculture between mouse terminally differentiated cardiomyocytes in a distressed state and human Multipotent Adipose Derived Stem cells (hMADS cells) used herein as an MSC model.
Materials and Reagents
- hMADS cells were isolated as described previously (Rodriguez et al., 2005)
- Perfusion Buffer stock solution (sPB)
- Liberase blendzyme TM (Roche Diagnostics, catalog number: 05401119001 )
- Trypsin (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T4549 )
- Calcium chloride
- Annexin V/7AAD staining (BD Biosciences, catalog number: 559763 )
- 18α-glycyrrhetinic acid (18α-GA) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G-8503 )
- M Latrunculin A (Life Technologies, catalog number: L12370 )
- Nocodazole (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M-1404 )
- Sodium chloride (NaCl) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S9625 )
- Potassium chloride (KCl) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P4504 )
- Potassium phosphate monobasic (KH2PO4) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P5379 )
- Sodium phosphate dibasic (Na2HPO4) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S0876 )
- Magnesium sulfate heptahydrate (MgSO4.7H2O) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M9397 )
- Sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S5761 )
- Potassium bicarbonate (KHCO3) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P9144 )
- 1 M HEPES buffer solution (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M3375 )
- Taurine (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T0625 )
- Phenol Red (last) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P5530 )
- 5.5 mM glucose (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G7528 )
- 0.25 mg/ml liberase blendzyme (Roche Diagnostics, catalog number: 1988417 )
- Trypsin (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T4549)
- 10% newborn calf serum (Life Technologies, Gibco®, catalog number: 16010167 )
- 5% bovine calf serum (BCS) (HyClone, catalog number: SH30073 )
- Pentobarbital sodium (CEVA, CIP number: 6742145 )
- Heparin choay (sanofi-aventis, CIP number: 3048450 )
- 1x perfusion buffer stock solution (see Recipes)
- 2,3-Butanedione monoxime (BDM) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: B0753 ) (see Recipes)
- Perfusion buffer (pH 7.46) (PB) (see Recipes)
- Digestion buffer (see Recipes)
- Stopping buffer 1 (see Recipes)
- Stopping buffer 2 (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Langendorff apparatus (see below)
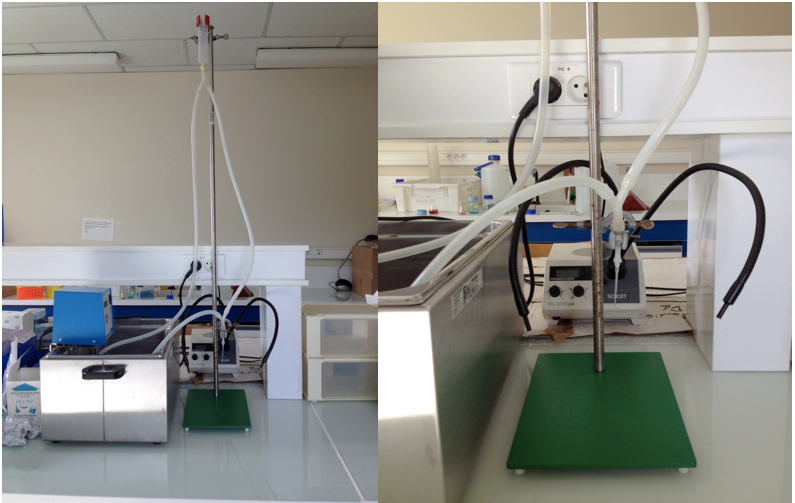
Figure 1. Langendorff apparatus - Water bath at 37 °C
- Surgical silk 4.0
- Petri dishes (Dutscher Scientific, catalog number: 628103 )
- Surgical instruments
- Disposable transfer pipets (VWR International, catalog number: 612-1681 )
- Falcon 15 ml propylene conical tubes (Dutscher Scientific, catalog number: 352095 )
Procedure
- Cardiomyocytes isolation
Ventricular cardiomyocytes were obtained from 2 to 5 months old male C57BL/6J mice (Janvier) according to the AfCS Procedure Protocols PP00000125 by O’Connell T, Ni Y.- Perfusion buffer, digestion buffer, stopping buffers (1 and 2) must be prepared daily.
- Perfusion buffer and digestion buffer must be warmed to 37 °C prior to use.
- Prepare the Langendroff perfusion apparatus. The circulating water bath is set so that the outflow from the tip of the cannula is 37 °C. The perfusion system is rinsed with 100 ml of purified water then with the perfusion buffer for at least 5 min and air bubbles are eliminated.
- 2-5 months old male mice were anesthetized with a solution of pentobarbital (60 mg/kg) and received heparin (200 UI/kg).
- Heart was excised and perfused on a Langendorff apparatus with calcium-free oxygenated (95% O2, 5% CO2) perfusion buffer at 37 °C.
- Then, heart was perfused for few minutes with the digestion buffer, the same calcium-free perfusion buffer supplemented with 0.25 mg/ml of liberase blendzyme TM, 0.14 mg/ml of trypsin and 12.5 μM of calcium chloride.
- Heart was removed, placed in a dish containing stop buffer 1 and further diced into small pieces using small scissors. Auricles and aorta were removed. Cellular dissociation was achieved by gentle mechanical agitation in stopping buffer 1.
- Cell suspension was transferred to a 15 ml polypropylene conical tube. The plate was rinsed with 2.5 ml of room temperature stopping buffer 1. This washing solution was then added to the cell suspension to reach a final volume of 5 ml. Stop buffer solution 1 contains serum to inactivate proteases. The final calf serum concentration is 5%, and the final calcium concentration is 12.5 µM.
- Cardiomyocytes were sedimented by gravity for 8-10 min in the 15 ml tubes at 37 °C.
For each tube, the supernatant was eliminated after sedimentation and the pellet was resuspended in 5 ml of stop buffer 2 added to increasing concentration of Ca2+.
5 ml of SB2 + 50 µl 10 mM Ca2+ (112 µM)
5 ml of SB2 + 100 µl 10 mM Ca2+ (212 µM)
5 ml of SB2 + 25 µl 100 mM Ca2+ (500 µM)
5 ml of SB2 + 50 µl 100 mM Ca2+ (1 mM) - The viability of freshly isolated CM was assessed by flow cytometry analysis following Annexin V/7AAD staining.
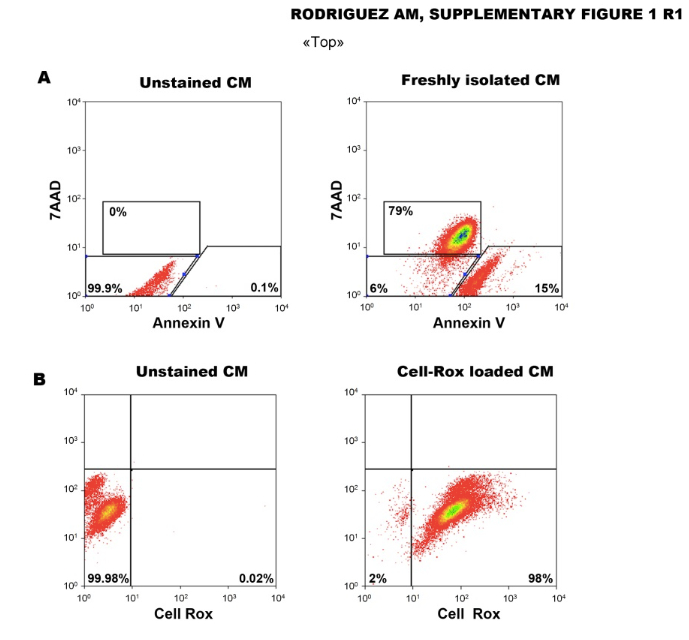
Figure 2. Suffering state of freshly isolated mouse CM (Figeac et al., 2014)
- Perfusion buffer, digestion buffer, stopping buffers (1 and 2) must be prepared daily.
- Coculture
Notes:- Freshly isolated mouse cardiomyocytes were cocultured with mesenchymal stem cells in different conditions depending on the parameter to assess.
- Although most of our experiments were performed with hMADS cells, some of them were done with hMSC from bone marrow generous gift from EFS, Créteil (Acquistapace, et al., 2011).
- To assess cardiomyocyte reprogramming process, cocultures were placed in DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS, Gentamycine (1/500) and Fungizone (1/100) in a 1:1 ratio, each cell type seeded at 3,500 cells per square centimeter.
- To prevent physical contact between the two cell types, cell-culture inserts containing a polycarbonate membrane with different pore sizes (from 0.4 µm up to 3 µm pore size) were used.
Note: We use a 1 µm pore size insert which allows the diffusion of soluble factors, exosomes and large microparticules as apoptotic bodies to demonstrate that these cell-to cell communication pathways were not involved in the paracrine alteration of mesenchymal stem cells through coculture. We also used 0.4 µm pore size which allows the diffusion of soluble factors and small exosomes but impedes the transfer of microvesicules and apoptotic bodies to confirm that cell-to cell communication through soluble soluble factors and exosomes did not affect stem cell phenotype and the generation of hybrid cardiac progenitor cells. - To measure soluble factors released by MSC during the coculture, each of the two cell types was seeded at 105 cells/ml (ratio 1:1) in a growth medium, containing low amount of fetal calf serum, namely, DMEM supplemented with 0.8% FBS, Gentamycine (1/500) and Fungizone (1/100).
- As control for these experiments, hMADS and adult cardiomyocytes were seeded at 105 cells/ml of DMEM supplemented with 10% and 0.8% FBS, according the experiments considered. We used 10% FBS concentration to perform experiments on the characterization of cell fusion processes and the phenotype of resulting hybrid cells. We used 0.8% FBS concentration to study secretome changes induced by coculture in order to decrease the risk of contamination by the soluble factors contained in the serum.
- To determine the communication pathways involved in the paracrine activation of hMADS cells, we performed coculture experiments in presence of several pharmacological compounds. Fresh cocultures were performed in 0.8% FBS DMEM medium during 24 h in presence of 100 mM 18α-glycyrrhetinic acid to inhibit gap junction and 2.5 x 10-8 M Latrunculin A or 5 x 10-8 M Nocodazole, to inhibit tunneling nanotube formation.
- Freshly isolated mouse cardiomyocytes were cocultured with mesenchymal stem cells in different conditions depending on the parameter to assess.
Representative data
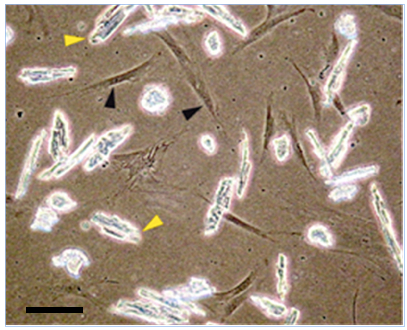
Figure 3. Coculture between hMADS cells (black arrowhead) and mouse adult cardiomyocytes (yellow arrowhead) at day 0. Scale bar, 30 µm (Acquistapace et al., 2011)
Recipes
- 1x perfusion buffer stock solution (AfCS Solution Protocols, protocol ID: PS00000452 from Kachura M)
113 mM sodium chloride (NaCl)
4.7 mM potassium chloride (KCl)
0.6 mM potassium phosphate monobasic (KH2PO4)
0.6 mM sodium phosphate dibasic (Na2HPO4)
1.2 mM magnesium sulfate heptahydrate (MgSO4.7H2O)
12 mM sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3)
10 mM potassium bicarbonate (KHCO3)
10 mM HEPES buffer solution 1 M
30 mM taurine
0.032 mM Phenol Red (last)
Add all components to 900 ml purified water in a 2 L beaker
Stir until all components are thoroughly dissolved
Transfer to a 1 L graduated cylinder and adjust final volume to 1 L with purified water
Prewash a 0.22 µm filter unit with 10 ml of purified water
Sterilize the solution
Stored at 4 °C - 2,3-Butanedione monoxime (BDM) (AfCS Solution Protocols, protocol ID: PS00000438)
500 mM 2,3-Butanedione monoxime
Weigh BDM and add to 30 ml purified water in a 100 ml beaker
Stir until solution is thoroughly dissolved
Transfer solution to a 50 ml graduated cylinder and adjust final volume to 50 ml with purified water
Prewash a 0.2 µm filter with 10 ml purified water
Sterilize the solution by filtering through the prewashed filter
Stored at 4 °C - Perfusion buffer (PB) (pH 7.46) (AfCS Solution Protocols, protocol ID: PS00000451 by Kachura M)
1x stock perfusion buffer; 0.98x (AfCS Solution Protocols, protocol ID: PS00000452)
500 mM, 10 mM 2,3-Butanedione monoxime (BDM)
5.5 mM glucose
Weigh glucose and add to 400 ml of stock perfusion buffer in a 1 L beaker
Add 10 ml of BDM to the beaker and stir until all components are thoroughly dissolved
Transfer solution to a 500 ml graduated cylinder and adjust final volume to 500 ml with stock perfusion buffer
Cover with parafilm and mix by inversion
Prewash a 0.22 µm 500 ml filter unit with 10 ml purified water
Sterilize the solution by filtering through the prewashed filter unit
Final pH is 7.46 after filtration - Digestion buffer (AfCS Solution Protocols, protocol ID: PS00000447)
1x perfusion buffer (pH 7.46)
0.25 mg/ml liberase blendzyme
0.14 mg/ml trypsin
12.5 µM calcium chloride (CaCl2, 100 mM; AfCS Solution Protocols, protocol ID: PS00000441)
Weigh liberase blendzyme and add to 30 ml of perfusion buffer in a 100 ml beaker
Measure and add trypsin and 100 mM CaCl2 to the beaker
Stir until all components are thoroughly dissolved
Adjust final volume to 50 ml with perfusion buffer in a graduated cylinder
Cover with parafilm and mix by inversion
Prewash a 0.2 µm filter attached to a 60 ml syringe with 10 ml purified water
Sterilize the solution by filtering through the prewashed filter - Stopping buffer 1 (AfCS Solution Protocols, protocol ID: PS00000449)
1x perfusion buffer (pH 7.46) (AfCS Solution Protocols, protocol ID: PS00000451)
10% newborn calf serum
12.5 µM calcium chloride (CaCl2) 10 mM (AfCS Solution Protocols, protocol ID: PS00000440)
Pipette 1 ml of NCS and 12.5 µl of CaCl2 into a 10 ml graduated cylinder
Adjust final volume to 10 ml with perfusion buffer
Cover with parafilm and mix by inversion
Prewash a 50 ml tube filter with 10 ml purified water
Sterilize the solution by filtering through the prewashed filter - Stopping buffer 2 (AfCS Solution Protocols, protocol ID: PS00000450)
1x perfusion buffer (pH 7.46) (AfCS Solution Protocols, protocol ID: PS00000451)
5% bovine calf serum (BCS)
Calcium chloride (CaCl2) 10 mM (AfCS Solution Protocols, protocol ID: PS00000440) 12.5 µM
Pipette 1.5 ml of BCS and 37.5 µl of CaCl2 into a 50 ml graduated cylinder
Adjust final volume to 30 ml with perfusion buffer
Cover with parafilm and mix by inversion
Prewash a 0.2 µM filter attached to a 35 ml syringe with 10 ml purified water
Sterilize the solution by filtering through the prewashed filter
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for the cardiomyocyte extraction protocol (AfCS Procedure Protocol PP00000125 by O’Connell T, Ni Y) that we have adapted and modified for the coculture protocol. This protocol has been adapted from two previously published papers (Figeac et al., 2014; Acquistapace et al., 2011). This work was supported by funding from French National Institute of Health and Medical Research (INSERM) and Association pour la Recherche et l’Etude des Maladies Cardiovasculaires (AREMCAR).
References
- Acquistapace, A., Bru, T., Lesault, P. F., Figeac, F., Coudert, A. E., Le Coz, O., Christov, C., Baudin, X., Auber, F. and Yiou, R. (2011). Human mesenchymal stem cells reprogram adult cardiomyocytes toward progenitor‐like state through partial cell fusion and mitochondria transfer. Stem Cells 29(5): 812-824.
- Figeac, F., Lesault, P. F., Le Coz, O., Damy, T., Souktani, R., Trebeau, C., Schmitt, A., Ribot, J., Mounier, R., Guguin, A., Manier, C., Surenaud, M., Hittinger, L., Dubois-Rande, J. L. and Rodriguez, A. M. (2014). Nanotubular crosstalk with distressed cardiomyocytes stimulates the paracrine repair function of mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells 32(1): 216-230.
- Rodriguez, A. M., Pisani, D., Dechesne, C. A., Turc-Carel, C., Kurzenne, J. Y., Wdziekonski, B., Villageois, A., Bagnis, C., Breittmayer, J. P., Groux, H., Ailhaud, G. and Dani, C. (2005). Transplantation of a multipotent cell population from human adipose tissue induces dystrophin expression in the immunocompetent mdx mouse. J Exp Med 201(9): 1397-1405.
- Shake, J. G., Gruber, P. J., Baumgartner, W. A., Senechal, G., Meyers, J., Redmond, J. M., Pittenger, M. F. and Martin, B. J. (2002). Mesenchymal stem cell implantation in a swine myocardial infarct model: engraftment and functional effects. Ann Thorac Surg 73(6): 1919-1925.
- Zeng, L., Hu, Q., Wang, X., Mansoor, A., Lee, J., Feygin, J., Zhang, G., Suntharalingam, P., Boozer, S., Mhashilkar, A., Panetta, C. J., Swingen, C., Deans, R., From, A. H., Bache, R. J., Verfaillie, C. M. and Zhang, J. (2007). Bioenergetic and functional consequences of bone marrow-derived multipotent progenitor cell transplantation in hearts with postinfarction left ventricular remodeling. Circulation 115(14): 1866-1875.
- Zimmet, J. M. and Hare, J. M. (2005). Emerging role for bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells in myocardial regenerative therapy. Basic Res Cardiol 100(6): 471-481.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2014 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Figeac, F., Acquistapace, A., Coz, O. L., Lesault, P. F. and Rodriguez, A. (2014). Coculture between hMADS and Mouse Adult CM. Bio-protocol 4(14): e1178. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1178.
Category
Stem Cell > Adult stem cell > Mesenchymal stem cell
Stem Cell > Adult stem cell > Maintenance and differentiation
Cell Biology > Cell isolation and culture > Cell differentiation
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link













