- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Isolation and Culture of Bone Marrow-derived Mast Cells
Published: Vol 4, Iss 4, Feb 20, 2014 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1053 Views: 23198
Reviewed by: Anonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols
Isolation and Culture of Peritoneal Cell-derived Mast Cells
Krisztina V. Vukman [...] Sandra M. O’Neill
Feb 20, 2014 16870 Views
Abstract
The generation of mast cells for in vitro studies comes from a variety of sources including mast cell lines (MC/9) (McCurdy et al., 2001), bone marrow-derived mast cells (BMMCs) (Supajatura et al., 2001), skin-derived mast cells (FSMCs) (Matsushima et al., 2004), peritoneal-derived mast cells (PMCs) (Hochdorfer et al., 2011) and peritoneal cell-derived cultured mast cells (PCMCs) (Vukman et al., 2012). BMMCs are generally used for in vitro studies because of the high yield of mast cells generated and also because they can be generated from knockout and transgenic mice making this a good source to examine specific factors important for mast cell function. Due to the large yield of cells generated they are the cells of choice for reconstitution studies in mast cell knockout mice (Sur et al., 2007). Furthermore, they are more responsive to both allergic and non-allergic stimuli when compared to mast cell lines. The major disadvantage of BMMCs is that they are not fully matured when compared to mast cells generated or obtained from other sources. For example, compared to PCMCs [see the protocol “Isolation and Culture of Peritoneal Cell-derived Mast Cells” (Vukman et al., 2014)], BMMCs express a restricted range of TLRs and cytokines when stimulated with TLR ligands (Mrabet-Dahbi et al., 2009). The different sources of mast cells can display phenotypical and functional differences and therefore it is important that when designing an experiment the correct cellular source is obtained. Here, we describe a protocol for the isolation and culture of murine mast cells from mouse bone marrow.
Keywords: Mast cellsMaterials and Reagents
- C57BL/6 mice or mouse model of choice (Harlan Laboratories, catalog number: 057 ; Charles River Laboratories International, catalog number: BLCSIFE49D )
- Industrial methylated spirit (IMS) (Lennox Laboratory Supplies, catalog number: CRTS10330716 )
- WEHI-3 conditioned medium generated from WEHI-3 cell line (ATCC, catalog number: TIB68 )
- Sterile phosphate buffered saline (PBS) (Life Technologies, Gibco®, catalog number: 14190 )
- IL-3 (BioLegend, catalog number: 432101 )
- IMDM with L-glutamine (Life Technologies, Gibco®, catalog number: 12440 )
- Fetal calf serum (FCS) (Life Technologies, Gibco®, catalog number: 10270 )
- Penicillin/streptomycin (Life Technologies, Gibco®, catalog number: 15140 )
- Mercapto-ethanol (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M3148 )
- Trypan blue stain (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T8154 )
- Complete IMDM (see Recipes)
- Growth factors (see Recipes)
- Kimura dye (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Sterile forceps
- Sterile scissors
- Sterile pipette
- Syringe (10 ml)
- Needle (19-, 21- and 27-gauge)
- Falcon tube (50 ml)
- Cell scraper (SARSTEDT AG, catalog number: 83.183 0)
- Filtropur S 0.45 filter (SARSTEDT AG, catalog number: 83.1826 )
- Petri dishes (100 x 20 mm)
- PD100 petri dish
- Water bath
- Centrifuge
- T75 Cell culture flask (SARSTEDT AG, catalog number: 83.1813.502 )
- T175 Cell culture flask (SARSTEDT AG, catalog number: 83.1812.502 )
- Haemocytometer
- Safety cabinet
Procedure
Note: All procedures are performed in a sterile environment in a class II safety cabinet.
- Preparing WEHI-3 conditioned medium
- Thaw cells from stock (which is stored in liquid nitrogen) by incubating cells in a water bath at 37 °C for 2 min.
- Resuspend cells in 37 °C complete IMDM as quick as possible. Final cell number has to be 2 x 105 cells/ml and culture cells in T75 tissue culture flask at 37 °C, 5% CO2.
- Passages: Transfer medium from tissue culture flask into a 50 ml Falcon tube.
- Scrape cells using sterile cell scraper.
- Transfer scraped cells into the same 50 ml Falcon tube.
- Count cells, the concentration has to be > 6 x 105 cell/ml.
- Centrifuge cells at 300 x g for 5 min.
- Transfer supernatant into new Falcon tube.
- Resuspend cells in fresh complete IMDM (2 x 105 cell/ml).
- Plate cells into new flasks (T75/T175).
- Centrifuge the supernatant again at 600 x g for 15 min.
- Transfer and filter supernatant into new Falcon tube.
- Take 0.5 ml for measurement of IL-3 concentrations by commercial ELISA. The concentration should range between 10 to 100 ng/ml and a minimum of 10 ng/ml should be used.
- Freeze supernatants at -20 °C.
- WEHI-3 conditioned medium can be harvested every 3-4 days following the steps A3-14. The cell number should not be over 2 x 106.
- Thaw cells from stock (which is stored in liquid nitrogen) by incubating cells in a water bath at 37 °C for 2 min.
- Isolation and culture of BMMCs
Day 0 [Passage (P) 1]- Kill mouse by cervical dislocation.
- Spray mouse thoroughly with 70% alcohol (or IMS) and lay down on 70% alcohol soaked paper.
- Two sets of sterile tweezers and scissors are used, one for the outer skin of the mouse and the other for the removal of legs (tibia and femur).
- Make a small incision below the sternum of the mouse and cut the skin away from the front around the back to make a complete circle. Peel the fur away completely from the lower half of the mouse leaving the legs exposed.
- Use the second pair of scissors and tweezers. Holding the tail with the index and middle finger and the leg of interest between the ring finger and thumb, cut the muscle away from the hind leg around the hip in a straight cutting manner so as to make the hip-joint amenable for cutting.
- Cut the hip-joint to free the leg from the body of the mouse. Be careful not to cut and hence expose the bone marrow of the femur. Repeat this with the second leg of the mouse.
- Cut the ankle of each leg to remove the feet, and discard them.
- Place legs in 50 ml tubes on ice partially filled with IMDM until next step.
- Place legs onto one half of a PD100 petri dish and remove residual muscle, fat and connective tissue using forceps and scissors.
- Cut the knee joint to separate the femur and tibia.
- Use fresh pair of forceps and scissors to cut each bone in turn at either end to expose the bone marrow.
- Flush the bone marrow onto the dish using a 10 ml syringe filled with ice cold media with a 27-gauge needle. Repeat this for all bones.
- Use a 19-gauge needle to break up and suspend the bone marrow by pipetting.
- Transfer the bone marrow suspension in to a 50 ml tube and centrifuged at 300 x g for 10 min.
- Discard the supernatant and resuspend cells in culture medium (IMDM with 30% WEHI-3 conditioned medium; 20 ml medium/mouse) and transfer suspension into tissue-treated cell culture flask (T75).
- Culture cells at 37 °C, 5% CO2.
- Transfer cell suspension into a 50 ml tube (avoid taking adherent cells!). Pellet the cells by centrifugation (300 x g, 10 min, 4 °C), discard supernatant. Loosen pellet by flicking the tube and resuspend cells in 20 ml fresh culture medium and transfer cell suspension into a new tissue-treated cell culture flask (T75).
- Repeat procedure as on day 5.
- Transfer cell suspension into a new big tissue treated cell culture flask (T175), (avoid taking over adherent cells!) and add 20 ml fresh culture medium.
- Same procedure as on day 5 but use a big (T175) culture flask.
- Transfer 20 ml of cell suspension into a 50 ml tube. Pellet the cells by centrifugation (300 x g, 10 min, 4 °C). Discard supernatant. Loosen pellet by flicking the tube and resuspend cells in 20 ml fresh culture medium and transfer cell suspension back into the cell culture flask.
- When cells are 4 weeks of age (P9) count cells and determine purity of mast cells via Kimura stain or FACS-analysis. If the cells are > 95% pure, they can be used for experiments (Figure 1). If the purity is less, they have to be cultured another week.
Note: Do not exceed a cell density of 2.5 x 106.
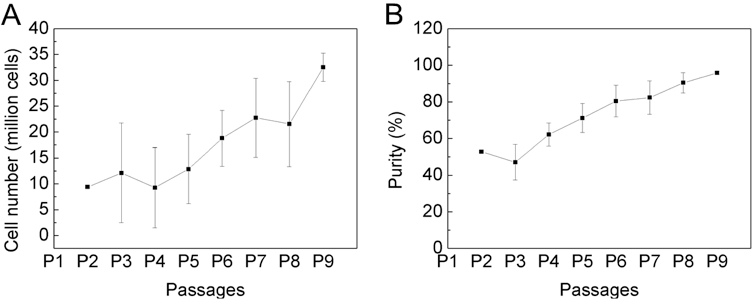
Figure 1. The purity of bone marrow-derived cultured mast cells is over 95% after 4 weeks of cultivation. Bone marrow cells from C57BL/6 mouse were cultured for 4 weeks in IMDM (with 10% FCS, 100 U/ml penicillin/streptomycin and 50 μM 2-mercaptoethanol) in the presence of 30% WEHI-3 conditioned medium. Cell number (A) and purity (B) was determined by every passage, twice a week with trypan blue and Kimura staining. Data are presented as the mean ± SD of nine independent experiments.
- Kill mouse by cervical dislocation.
Recipes
- Complete IMDM
IMDM (500 ml)
10% FCS (50 ml per 450 ml of IMDM)
5 ml Penicillin (100 U/ml)/Streptomycin (100 μg/ml)
1 M 2-mercaptoethanol (add 25 μl to 500 ml for 50 μM final concentration)
- Growth factors (add to IMDM prior to use)
30% WEHI-3 conditioned medium
- Kimura dye
Toluidine blue solution (50 ml) (0.5 mg/ml Toluidine blue, 18 g/l NaCl and 22% ethanol)
Saturated saponin (2.27 ml) (4 mg/ml saponin in ethanol)
NaH2PO4 solution (22.7 ml) (60 mM)
Acknowledgments
The protocol described here was adapted from Sur et al. (2007) and Vukman et al. (2012).
References
- Hochdorfer, T., Kuhny, M., Zorn, C. N., Hendriks, R. W., Vanhaesebroeck, B., Bohnacker, T., Krystal, G. and Huber, M. (2011). Activation of the PI3K pathway increases TLR-induced TNF-alpha and IL-6 but reduces IL-1beta production in mast cells. Cell Signal 23(5): 866-875.
- Matsushima, H., Yamada, N., Matsue, H. and Shimada, S. (2004). TLR3-, TLR7-, and TLR9-mediated production of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines from murine connective tissue type skin-derived mast cells but not from bone marrow-derived mast cells. J Immunol 173(1): 531-541.
- McCurdy, J. D., Lin, T. J. and Marshall, J. S. (2001). Toll-like receptor 4-mediated activation of murine mast cells. J Leukoc Biol 70(6): 977-984.
- Mrabet-Dahbi, S., Metz, M., Dudeck, A., Zuberbier, T. and Maurer, M. (2009). Murine mast cells secrete a unique profile of cytokines and prostaglandins in response to distinct TLR2 ligands. Exp Dermatol 18(5): 437-444.
- Supajatura, V., Ushio, H., Nakao, A., Okumura, K., Ra, C. and Ogawa, H. (2001). Protective roles of mast cells against enterobacterial infection are mediated by Toll-like receptor 4. J Immunol 167(4): 2250-2256.
- Sur, R., Cavender, D. and Malaviya, R. (2007). Different approaches to study mast cell functions. Int Immunopharmacol 7(5): 555-567.
- Vukman, K. V., Adams, P. N., Metz, M., Maurer, M. and O'Neill, S. M. (2013). Fasciola hepatica tegumental coat impairs mast cells' ability to drive Th1 immune responses. J Immunol 190(6): 2873-2879.
- Vukman, K. V., Metz, M., Maurer, M. and O'Neill, S. M. (2014). Isolation and culture of peritoneal cell-derived mast cells. Bio-protocol 4(4): e1052.
- Vukman, K. V., Visnovitz, T., Adams, P. N., Metz, M., Maurer, M. and O'Neill, S. M. (2012). Mast cells cultured from IL-3-treated mice show impaired responses to bacterial antigen stimulation. Inflamm Res 61(1): 79-85.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2014 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Vukman, K. V., Metz, M., Maurer, M. and O’Neill, S. M. (2014). Isolation and Culture of Bone Marrow-derived Mast Cells. Bio-protocol 4(4): e1053. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1053.
Category
Immunology > Immune cell isolation > Mast cell
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link









