- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Aldicarb-induced Paralysis Assay to Determine Defects in Synaptic Transmission in Caenorhabditis elegans
Published: Vol 7, Iss 14, Jul 20, 2017 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2400 Views: 9945
Reviewed by: Neelanjan BoseLU HANManish Chamoli

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Evaluation of Burkholderia cepacia Complex Bacteria Pathogenicity Using Caenorhabditis elegans
Pietro Tedesco [...] Donatella de Pascale
Oct 20, 2016 7697 Views

Artificial Optogenetic TRN Stimulation of C. elegans
Ithai Rabinowitch [...] Jihong Bai
Oct 20, 2016 8621 Views

Aerotaxis Assay in Caenorhabditis elegans to Study Behavioral Plasticity
Qiaochu Li [...] Karl Emanuel Busch
Aug 20, 2022 2252 Views
Abstract
Aldicarb treatment causes an accumulation of acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft of the neuromuscular junction, resulting in sustained muscle activation and eventually paralysis. Aldicarb-induced paralysis assay is an easy and fast method to determine whether synaptic transmission of a C. elegans mutant of interest is altered. This assay is based on the correlation of the rate of neurotransmitter release with the rate of paralysis. In this protocol, we describe a method for simultaneously assessing the aldicarb sensitivity of animals with different genotypes.
Keywords: AldicarbBackground
Synaptic transmission is initiated by arrival of action potential at presynaptic terminals, which in turn results in the release of neurotransmitters. The released neurotransmitters bind to and activate postsynaptic receptors (Sudhof, 2013). C. elegans locomotion is controlled by acetylcholine-releasing excitatory motor neurons and GABA (γ-aminobutyric acid)-releasing-inhibitory motor neurons (Richmond and Jorgensen, 1999; Zhen and Samuel, 2015). Acetylcholine released from cholinergic motor neurons activates acetylcholine receptors on the muscle membrane, leading to muscle excitation and contraction. Acetylcholinesterase breaks down acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft and thus terminates neurotransmission. Aldicarb is an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. In the presence of aldicarb, acetylcholine continues to accumulate, causing persistent muscle contraction and eventual paralysis. Mutant animals with decreased levels of synaptic transmission are resistant to the paralyzing effect of aldicarb because acetylcholine more slowly accumulates in the synaptic cleft of these animals than that of wild type animals. Conversely, mutant animals with increased levels of synaptic transmission, and as a result, a faster accumulation of acetylcholine, are more sensitive to the paralyzing effect of aldicarb than wild-type animals (Rand, 2007). Thus, by comparing the time-course of aldicarb-induced paralysis, it is possible to infer the relative efficiency of synaptic transmission. However, it is necessary to note that this assay does not necessarily demonstrate that abnormal aldicarb sensitivity is a result of a presynaptic defect. For example, a defect in post-synaptic acetylcholine receptor function may also result in resistance to aldicarb (Loria et al., 2004). Thus, the aldicarb-induced paralysis assay should be considered as the first step in investigating the involvement of synaptic transmission, and further corroborated by other means, such as electrophysiological analysis (Richmond, 2006).
Materials and Reagents
- 60 mm Petri dish (Genesee Scientific, catalog number: 32-105G )
- 90% platinum, 10% iridium wire (Tritech Research, catalog number: PT-9010 )
- Copper rings (PlumbMaster, catalog number: 17668 )
- E. coli OP50 (University of Minnesota, Caenorhabditis Genetic Center)
- Aldicarb (ChemService, catalog number: N-11044 )
- Ethanol (Ethyl alcohol, 190 proof, ACS-USP grade) (PHARMCO-AAPER, catalog number: 111000190 )
- Cholesterol (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: C3045 )
- Calcium chloride dihydrate (CaCl2·2H2O) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: C3306 )
- Magnesium sulfate (MgSO4) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M7506 )
- Potassium phosphate, monobasic (KH2PO4) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P5379 )
- Potassium phosphate, dibasic (K2HPO4) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P8281 )
- Sodium chloride (NaCl) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S7653 )
- Bacto-agar (BD, BactoTM, catalog number: 214040 )
- Bacto-peptone (BD, BactoTM, catalog number: 211820 )
- 100 mM aldicarb stock solution (see Recipes)
- 5 mg/ml cholesterol (see Recipes)
- 1 M CaCl2 stock solution (see Recipes)
- 1 M MgSO4 stock solution (see Recipes)
- 1 M KPO4, pH 6.0 stock solution (see Recipes)
- Nematode growth medium (NGM) agar plates (see Recipes)
- Nematode growth medium (NGM) agar plate containing aldicarb (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Forceps
- Rotator
- Autoclave
- 2 L flask
- Magnetic stir bar
- Microscope (Leica Microsystems, model: Leica MZ6 ) with KL 200 LED light source (Leica Microsystems, model: KL 200 LED )
Software
- GraphPad Prism 6.0, RRID:SCR_002798
Procedure
- For the routine maintenance of worms, see Stiernagle, T. Maintenance of C. elegans (Stiernagle, 2006).
- Prepare NGM agar plates containing 1 mM aldicarb (see Recipes) at least one day before the assay and store at 4 °C until use. Regular NGM agar plates for the routine maintenance should be seeded with OP50 E. coli and be available before the assay.
- Pick 30-40 L4 stage wild-type N2 and mutants of interest onto separate NGM plates seeded with OP50 E. coli (but not containing aldicarb), and culture them at 20 °C for 20 to 24 h.
- Use forceps to pick up a copper ring and dip into 70% ethanol. Flame the copper ring for a few seconds and immediately place it on the aldicarb-containing NGM agar plate. The copper ring will be lightly embedded in the agar surface of the plate (Figure 1). This will corral worms inside the ring. Place 3 copper rings on each assay plate and add 10 μl of OP50 E. coli (OD600 = 1.2) at the center of the ring. Bacteria help keep the worms around the center of the ring. Let the plates dry for 30 min. Three genotypes can be assayed on the same plate.
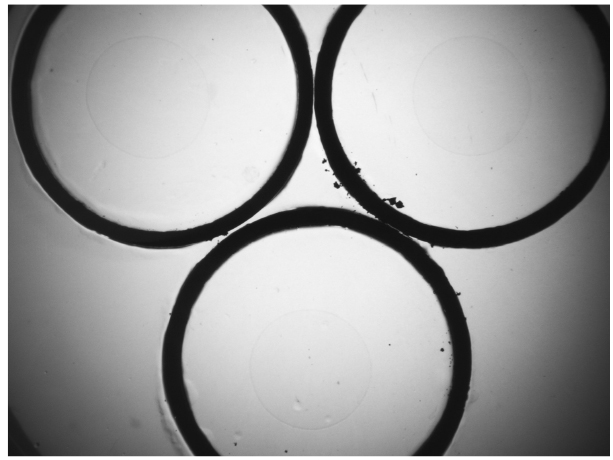
Figure 1. A representative image of a copper ring embedded agar plate. Three copper rings are placed on a 60 mm NGM agar plate, and 10 μl of OP50 is added at the center of the ring. - Transfer 20-30 worms of each genotype from step 3 to the center of each ring. Record the number of worms placed in each ring. Stagger worm transfer every 2-3 min so that all 3 genotypes are examined within a 10-min interval.
- Observe the worms in a 10-min interval. If there are worms not moving, then gently prod their heads with a platinum wire until they move (Videos 1 and 2). If they fail to move their head in response to even harsh touch, then remove them from the plate and record. Continue until no worm is left. Make sure that all of the worms are accounted for throughout the assay.Video 1. A video recording of responses of worms with different genotypes in the presence of aldicarb. The video (120 frames) was recorded for 4 min after 50 min incubation on an aldicarb plate. * indicates the paralyzed worms. WT: wild-type animals, slo-1: slo-1(eg142lf), mutant: an uncharacterized mutant.Video 2. A video recording shows paralyzed worms that do not respond to harsh touch
Data analysis
- Software: Prism 6.0
- Use ‘Survival analysis’ function to plot the survival graph (Figure 2). At least 20 worms of each genotype are used per assay. Repeat the assay two more times on different days (total 3 trials) and report the summary of the statistics as shown in Tables 1A and 1B.
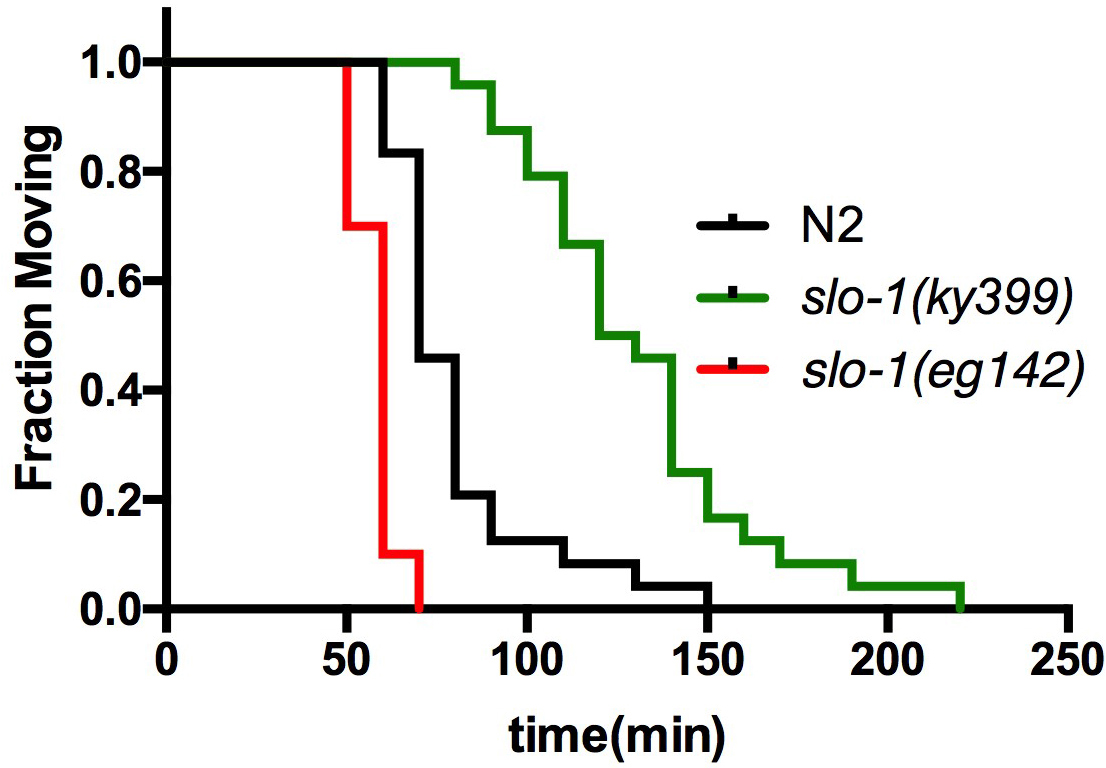
Figure 2. Survival curve for aldicarb-induced paralysis assay. Wild-type, slo-1(ky399 gain-of-function) and slo-1(eg142 loss-of-function) mutant animals were simultaneously tested for aldicarb sensitivity in a copper ring-embedded assay plate (adapted from Oh et al., 2017).
Table 1A. Median survival time of C. elegans exposed to aldicarb (Median survival unit is minutes. The number in parenthesis is sample number)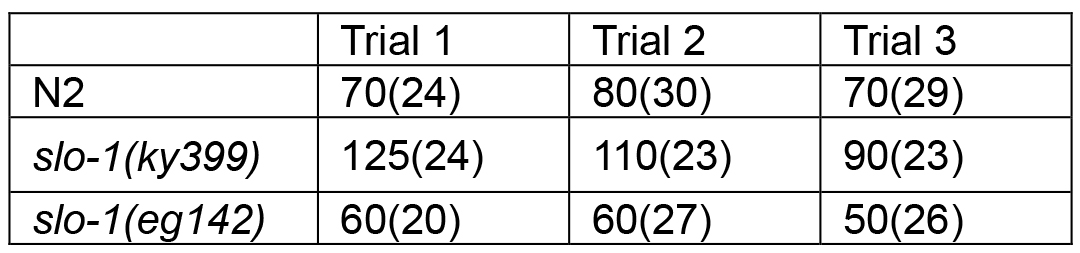
Table 1B. P values of Log-rank test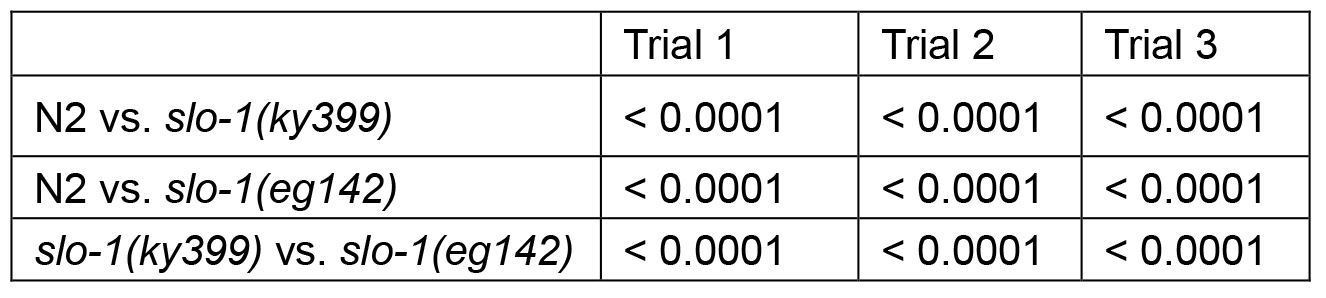
- Statistical analysis: The log-rank test is used to analyze the data. Prism software returns overall curve comparison results. However, pair-wise comparisons can be performed to compare 2 specific groups. Statistically significant P-values need to be adjusted for multiple comparisons if more than 2 pair-wise comparisons are performed. A Bonferroni corrected threshold is used to determine statistically significant P-values (http://www.graphpad.com/guides/prism/6/statistics/index.htm?survival_curves.htm). In this example, 3 comparisons, N2 vs. slo-1(ky399), N2 vs. slo-1(eg142), and slo-1(ky399) vs. slo-1(eg142), are performed and P-values for each comparison is obtained. If threshold for statistical significance is set at a P-value of 0.05, then any P-value that is less than the corrected threshold, i.e., 0.05 divided by 3, is considered statistically significant in this example.
Notes
- As per standard scientific procedure, the experimenter should be blinded to the genotypes of the test worms. Ideally a colleague should place the worms (procedure step 5) and label the worms to prevent the experimenter from identifying the genotypes. For mutants with obvious phenotypes, an additional mutant with a similar phenotype, which is unrelated to the study of interest, may be added.
- The resolution of differential sensitivity can be changed by varying the concentration of aldicarb. For example, mutants that have higher rates of neurotransmission than wild type worms may be better distinguishable at a lower concentration of aldicarb (e.g., 0.5 mM), which increases the time for the worms to get paralyzed.
Recipes
- 100 mM aldicarb stock solution
Dissolve 100 mg of aldicarb in 5.25 ml of 70% ethanol at room temperature
Store at 4 °C
Note: We have stored the stock up to 2 weeks and have not tried longer storage. - 5 mg/ml cholesterol
Add 250 mg of cholesterol in 50 ml of 95 % ethanol and mix by rotating on a rotator at room temperature. It takes a few hours to dissolve. Store at room temperature - 1 M CaCl2 stock solution
Dissolve 14.7 g of CaCl2·2H2O in 100 ml ddH2O and autoclave for 30 min at 121 °C. Store at room temperature - 1 M MgSO4 stock solution
Dissolve 12.04 g of MgSO4 in 100 ml ddH2O and autoclave for 30 min at 121 °C. Store at room temperature - 1 M KPO4, pH 6.0 stock solution
Make 500 ml of 1 M KH2PO4 (monobasic) and 250 ml of 1 M K2HPO4 (dibasic) solution. While measuring pH of 1 M KH2PO4 (pH is below 5), add and stir 1 M K2HPO4 slowly until pH reaches 6.0. It will take less than 250 ml of K2HPO4 to reach pH 6.0. Aliquot the solution and autoclave for 30 min at 121 °C. Store at room temperature - Nematode growth medium (NGM) agar plate
- Add 3 g of NaCl, 16 g of Bacto-agar, and 2.5 g of Bacto-peptone in a 1 L of ddH2O in a 2 L flask with magnetic stir bar
- Autoclave for 30 min at 121 °C
- Let the NGM agar cool to 55 to 60 °C while stirring on a stirrer, Add 1 ml of 5 mg/ml cholesterol, 1 ml of 1 M CaCl2, 1 ml of 1 M MgSO4, and 25 ml of 1 M KPO4, pH 6.0 while stirring
- Dispense 10 ml per 60 mm Petri dish and let them solidify without perturbation
- Nematode growth medium (NGM) agar plate containing aldicarb
- For aldicarb-containing NGM plates, add aldicarb solution to a desired final concentration along with cholesterol, CaCl2, MgSO4, and 1 M KPO4, pH 6.0 when NGM agar medium is cooled to 55 to 60 °C
- For 1 mM aldicarb, add 1 ml of 100 mM aldicarb for 100 ml of NGM. Pour 10 ml per 60 mm Petri dish and let them dry for at least 1 day. Plates can be stored at 4 °C
Note: We have used plates stored at 4 °C for up to 2 weeks without any issue.
Acknowledgments
The protocol has been adapted from Oh et al. (2017), eLife 6: e24733. This work was supported, in part, by a grant from the National Institute of Health.
References
- Loria, P. M., Hodgkin, J. and Hobert, O. (2004). A conserved postsynaptic transmembrane protein affecting neuromuscular signaling in Caenorhabditis elegans. J Neurosci 24(9): 2191-2201.
- Oh, K. H., Haney, J. J., Wang, X., Chuang, C. F., Richmond, J. E. and Kim, H. (2017). ERG-28 controls BK channel trafficking in the ER to regulate synaptic function and alcohol response in C. elegans. Elife 6.
- Rand, J. B. (2007). Acetylcholine. WormBook 30: 1-21.
- Richmond, J. E. (2006). Electrophysiological recordings from the neuromuscular junction of C. elegans. WormBook 6: 1-8.
- Richmond, J. E. and Jorgensen, E. M. (1999). One GABA and two acetylcholine receptors function at the C. elegans neuromuscular junction. Nat Neurosci 2(9): 791-797.
- Stiernagle, T. (2006). Maintenance of C. elegans. WormBook 11: 1-11.
- Sudhof, T. C. (2013). Neurotransmitter release: the last millisecond in the life of a synaptic vesicle. Neuron 80(3): 675-690.
- Zhen, M. and Samuel, A. D. (2015). C. elegans locomotion: small circuits, complex functions. Curr Opin Neurobiol 33: 117-126.
Article Information
Copyright
Oh and Kim. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY 4.0).
How to cite
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Oh, K. H. and Kim, H. (2017). Aldicarb-induced Paralysis Assay to Determine Defects in Synaptic Transmission in Caenorhabditis elegans. Bio-protocol 7(14): e2400. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2400.
- Oh, K. H., Haney, J. J., Wang, X., Chuang, C. F., Richmond, J. E. and Kim, H. (2017). ERG-28 controls BK channel trafficking in the ER to regulate synaptic function and alcohol response in C. elegans. Elife 6.
Category
Neuroscience > Behavioral neuroscience > Animal model > Other
Neuroscience > Cellular mechanisms > Intracellular signalling
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link










