- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Measurement of Resting Energy Metabolism in Mice Using Oxymax Open Circuit Indirect Calorimeter
Published: Vol 5, Iss 18, Sep 20, 2015 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1602 Views: 11773
Reviewed by: Xuecai GeAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Quantification of Macrophage Cellular Ferrous Iron (Fe2+) Content using a Highly Specific Fluorescent Probe in a Plate-Reader
Philipp Grubwieser [...] Christa Pfeifhofer-Obermair
Feb 5, 2024 2226 Views

In-Gel Activity Assay of Mammalian Mitochondrial and Cytosolic Aconitases, Surrogate Markers of Compartment-Specific Oxidative Stress and Iron Status
Wing-Hang Tong and Tracey A. Rouault
Dec 5, 2024 2208 Views

Reliable and Sensitive Detection of Carbonylated Proteins by Oxime Blot
Filip Luka Mikulić [...] Mladen Merćep
Aug 5, 2025 1242 Views
Abstract
Indirect calorimeter is a powerful tool to monitor resting energy metabolism through the measurement of oxygen (O2) consumption and carbon dioxide (CO2) production. From the measurement of VO2 and VCO2, the respiratory exchange ratio (RER) can be calculated to assess energy fuel utilization and energy expenditure (Evan et al., 2012). Previously, indirect calorimeter has been widely used in metabolic disease research in mice to reveal the potential roles of specific genes or treatments in regulating energy metabolism (for example: Bi et al., 2014; Feng et al., 2014). Here, we described a protocol to evaluate the resting energy metabolism of C57BL/6 mice during dark and light cycles using the Oxymax Open Circuit indirect calorimeter.
Keywords: Brown adipose tissueMaterials and Reagents
- Adult mice (C57BL/6 male mice at 3-month old were used for data acquisition in this protocol, but male or female mice of other genetic backgrounds or strains, at different ages can be used)
- Food (normal chow diet or high fat diet) and water (ad lib)
- Compressed gas mixture with the components of 4,929 PPM CO2, 20.47% O2 and Balance N2
Equipment
- Oxymax Open Circuit Indirect Calorimeter (Columbus Instruments, model: Open Circuit Indirect Calorimeter) (Figure 1)
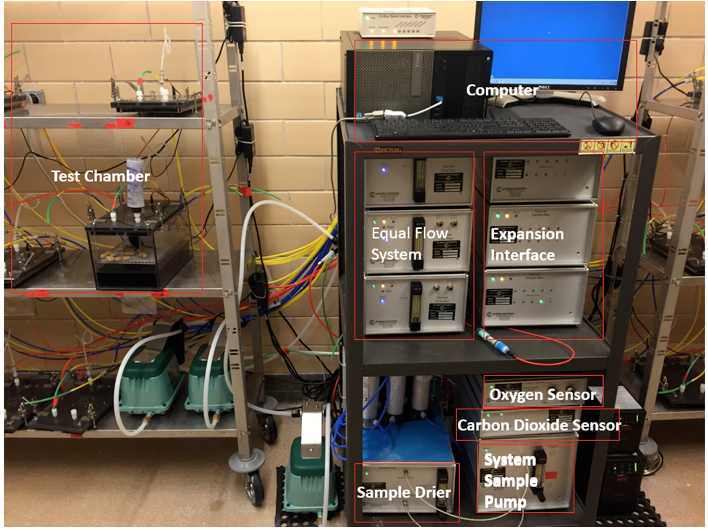

Figure 1. Open circuit indirect calorimeter components - Computer with software provided by the manufacture (Columbus Instruments, model: Oxymax v4.91 )
Procedure
- Turn on the Oxymax instrument and computer, allowing the system to warm up for 2 h;
- Start the Oxymax v4.91 program;
- Perform CO2 calibration;
- Select calibration in the program, turn on the gas tank and set it to 5-10 psi;
- Press the CO2 button in “calibration” window (Figure 2a). Gain should be close to 1 after calibration (Figure 2b);
- Select calibration in the program, turn on the gas tank and set it to 5-10 psi;
- Perform O2 calibration;
- Press the O2 button in “calibration” window (Figure 2a);
- Desired O2 level is listed in the first prompt window (Figure 2d). Use the fine and coarse knobs (Figure 2c) to adjust the O2 level to desired level;
- Turn off the gas tank after finishing the O2 calibration.
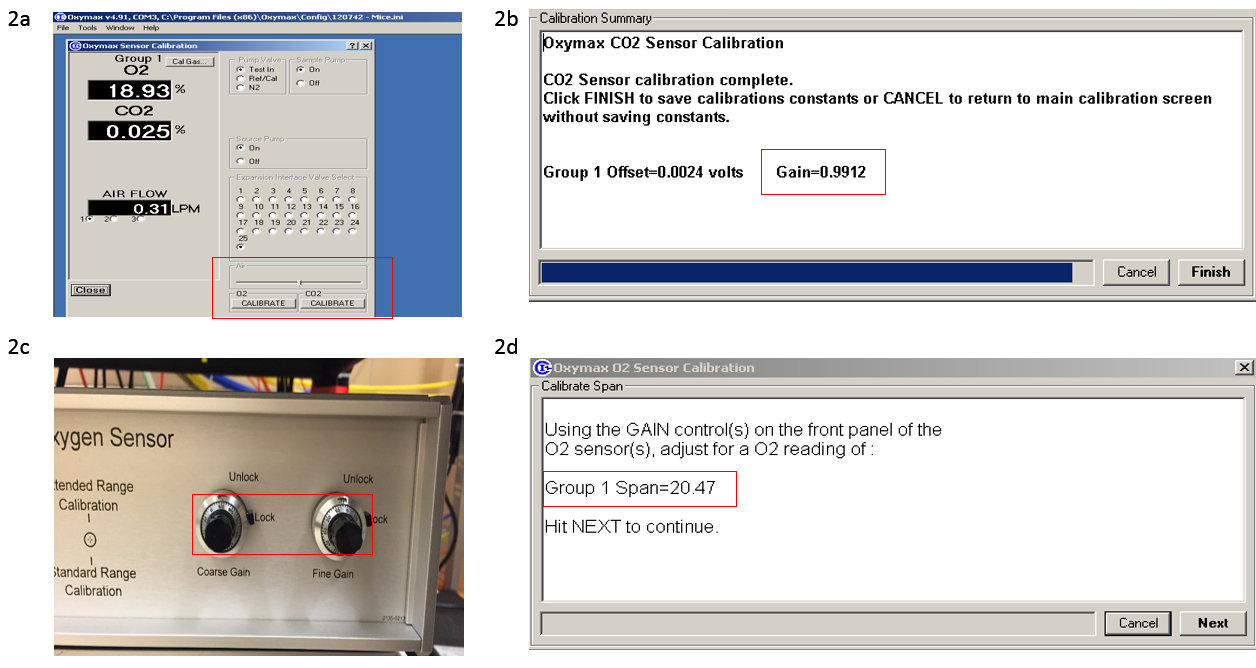
Figure 2. CO2 and O2 calibration
- Press the O2 button in “calibration” window (Figure 2a);
- Setup a new experiment, choose the chambers to be used, input the Identification number and weight of mice to be measured (Figure 3), only one mouse is allowed per chamber;
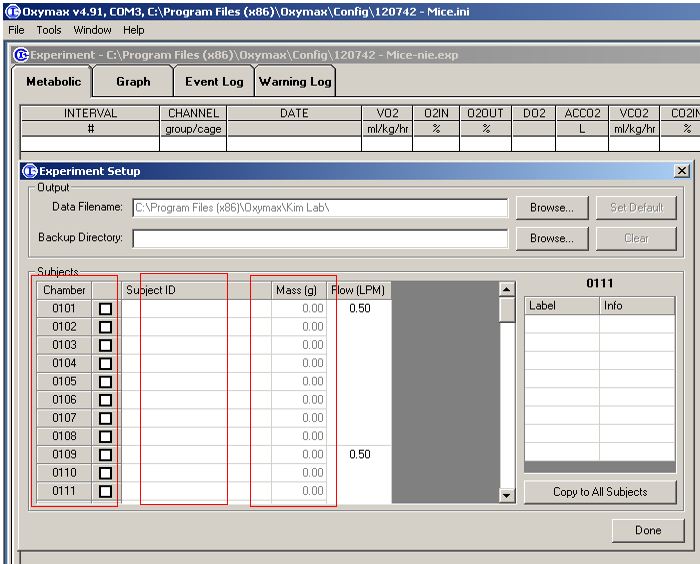
Figure 3. Input of mouse information - Setup the measurement schedule including number of Intervals, time of cage settle, cage measure, reference settle, reference measure, and reference method (Figure 4).
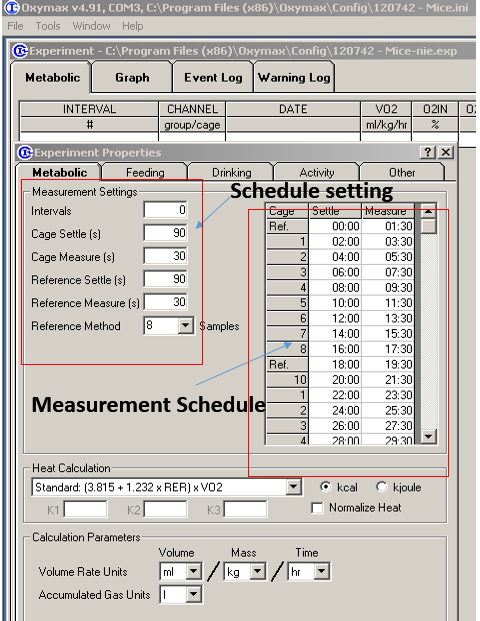
Figure 4. Setup schedule for measurement. “0” for intervals means the experiment will run indefinitely until stopped by the user. “8” for reference methods means the experiment will measure the reference air after every 8 subjects. - Place the mice in the corresponding calorimetric chambers, standard cages are used (Figure 5);
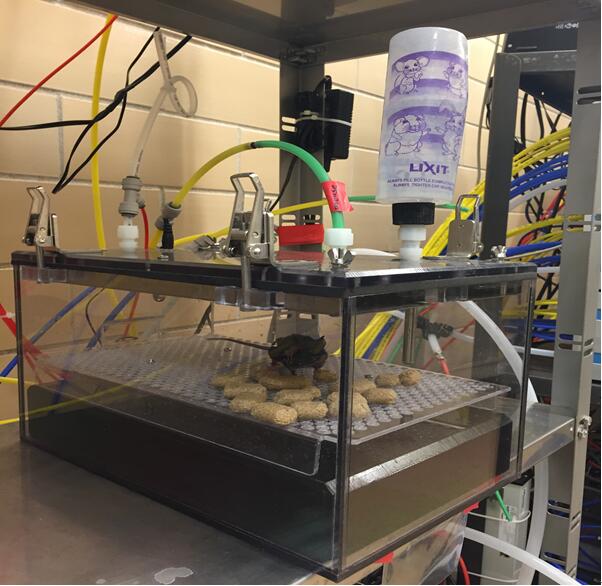

Figure 5. Test chamber for mice (standard cage) - Fill the cage with sufficient food and water for a period of 24 h. Ensure that food and water are available ad libitum (Figure 5);
- Check if there is any leakage in the system with software as follows:
Open Tools → Select Sample Pump from Oxymax utility → Ensure Test in Valve open and N2 and Ref Air/Cal Valve closed → Turn Sample Pump ON → Select the chamber to be tested in Expansion Interface Disconnect drier input tubing from tested chamber → put the finger over it, If there is no system leaks, the ball on the front of the system sample pump will drop to 0; If not, check all air fittings to assure an air-tight connection and test it again (Figure 6).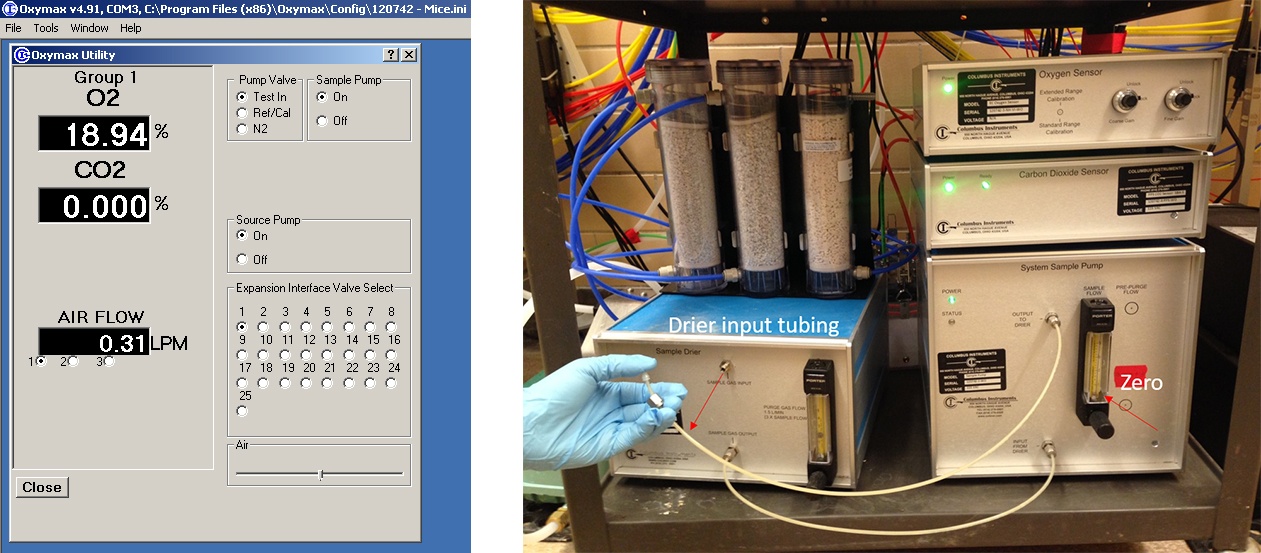
Figure 6. Gas leakage check - Run the experiment for 24 h and export the data in Excel file format, which include the data listed as below:
- O2 consumption = (VO2 input) – (VO2 output), ml/kg/h;
- CO2 production = (VCO2 output) – (VCO2) input, ml/kg/h;
- Respiratory exchange ratio (RER) = VCO2/VO2 Ratio;
- Energy Expenditure (Heat production) = calorific value (Cv ) x VO2 =(3.815 + 1.232 x RER) x VO2, cal/h;
- O2 consumption = (VO2 input) – (VO2 output), ml/kg/h;
- Close the experiment and return the mice to their home cages;
- Turn off the system and clean the calorimetry with water and appropriate disinfectant.
Representative data
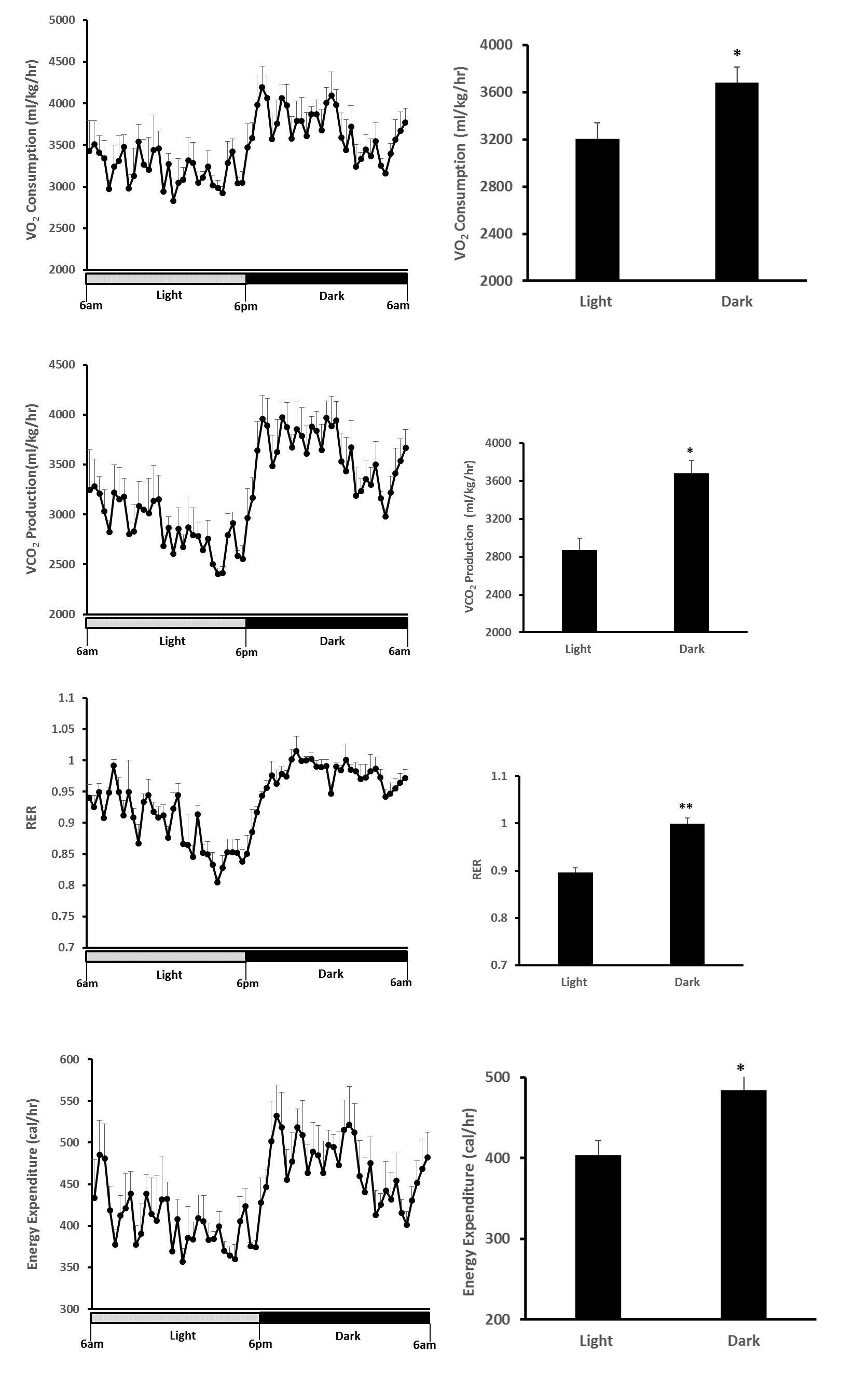
Figure 7. O2 consumption, CO2 production, RER and Energy Expenditure of 3-month old C57BL6 mice during light and dark cycle. The daily rhythms of metabolic parameters were recorded under a 12 h-light (open bar) and 12 h-dark cycle (black bar) (Left). Data were presented as Means ± SE (n = 5) during light and dark cycle (right). *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01 analyzed by the Student’s t-test (comparison of mean values between the light and dark cycles).
Notes
- Begin data collection of mice after 1-day of acclimation in the metabolic chambers;
- Install the Oxymax system under a constant environmental temperature (22 °C) and 12 h light (6 am-6 pm), 12 h dark cycle (6 pm-6 am);
- VO2 and VCO2 were increased by approximately 15% and 28% in dark cycle, respectively;
- RER was increased from 0.90 (light cycle) to 0.99 (dark cycle), suggesting a shift in macronutrient source from a mix of fat + carbohydrates to predominant carbohydrates in the dark cycle (the VCO2/VO2 ratio of fatty acid oxidation is 0.7 and carbohydrates oxidation is 1.0);
- Energy expenditure was 20% greater in dark than light cycle, with the most active phase of mice being between 7 pm-12 pm;
- Indirect calorimetry is a versatile system to investigate alternations of metabolic rate under different conditions. For example:
- To compare metabolic homeostasis and energy expenditure in wild type and mutant mice fed with normal chow diet or high-fat-diet;
- To investigate changes in metabolic rate with aging, a potential indicator of improved health status.
- Oxymax open circuit indirect calorimeter can also be incorporated with other chamber systems, such as activity, body mass, feeding, drinking, food access control, running wheel, urine collection, sleep detection, body core temperature and heart rate to fulfill different experimental designs.
- To compare metabolic homeostasis and energy expenditure in wild type and mutant mice fed with normal chow diet or high-fat-diet;
References
- Bi, P., Shan, T., Liu, W., Yue, F., Yang, X., Liang, X. R., Wang, J., Li, J., Carlesso, N., Liu, X. and Kuang, S. (2014). Inhibition of Notch signaling promotes browning of white adipose tissue and ameliorates obesity. Nat Med 20(8): 911-918.
- Even, P. C. and Nadkarni, N. A. (2012). Indirect calorimetry in laboratory mice and rats: principles, practical considerations, interpretation and perspectives. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 303(5): R459-476.
- Feng, B., Jiao, P., Helou, Y., Li, Y., He, Q., Walters, M. S., Salomon, A. and Xu, H. (2014). Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase 3 (MKP-3)-deficient mice are resistant to diet-induced obesity. Diabetes 63(9): 2924-2934.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2015 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Nie, Y., Gavin, T. P. and Kuang, S. (2015). Measurement of Resting Energy Metabolism in Mice Using Oxymax Open Circuit Indirect Calorimeter. Bio-protocol 5(18): e1602. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1602.
Category
Cell Biology > Cell metabolism > Other compound
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link










