- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Physicochemical Quantification of Abscisic Acid Levels in Plant Tissues with an Added Internal Standard by Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography
Published: Vol 5, Iss 18, Sep 20, 2015 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1599 Views: 13774
Reviewed by: Marisa RosaSara Posé Sriema L. Walawage

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Evaluation of Root pH Change Through Gel Containing pH-sensitive Indicator Bromocresol Purple
Aparecida L. Silva [...] Daniel S. Moura
Apr 5, 2018 10019 Views

Quantification of Salicylic Acid (SA) and SA-glucosides in Arabidopsis thaliana
Valérie Allasia [...] Harald Keller
May 20, 2018 13142 Views

Extraction and Quantification of Plant Hormones and RNA from Pea Axillary Buds
Da Cao [...] Christine A. Beveridge
Oct 5, 2022 2968 Views
Abstract
The phytohormone abscisic acid (ABA) is critical for a range of plant responses to the environment, most importantly in closing the stomata of seed plants during drought (Mittelheuser and Van Steveninck 1969; Brodribb et al. 2014). The high precision quantification of this hormone by physicochemical methods is a relatively simple process, essential for studies that aim to investigate the role or action of this hormone in plants. Outlined here is a method for the extraction, purification and quantification of ABA levels in plant tissues. This method involves methanolic extraction of ABA from homogenised tissue. Purification of ABA is then undertaken by a simple etheric partitioning method. A focus is placed on determining ABA levels in leaves; however this method is suitable for all tissue types, including plant solutes such as xylem sap, seeds (both dry and green) and large samples of tissue such as root systems.
Keywords: Plant hormonesMaterials and Reagents
- Methanol (Merck Schuchardt OHG, catalog number: 603-001-00-X )
- 2, 6-di-tert-butyl-4-methylphenol (BHT) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: B1378 )
- Liquid nitrogen (optional for manual homogenization method only)
- Labelled or deuterated ABA (such as 13C labelled, [2H6] ABA or other form with any number of deuterium atoms) (e.g. OlChemIm Ltd, catalog numbers: 03 2721-03 2723 ; catalog numbers: 35671-08-0 )
- Acetic acid (Analytical grade, any supplier)
- Diethyl ether (Analytical grade, any supplier)
- Acetonitrile (for UPLC-MS) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 271004 )
- Aluminium foil
- 50 ml conical centrifuge tube (Greiner Bio-One GmbH, catalog number: 210261 )
- 0.5 ml Eppendorf tubes (any brand will suffice)
- 2 ml screw-cap tubes (Scientific Specialities, catalog number: 2330-00 ) with tethered screw tube caps (Scientific Specialities, catalog number: 2002-59 ) (optional for very small samples or samples that require long-distance freight)
- Whatman no. 1 filter paper (optional for large samples only)
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf tubes (any brand will suffice)
- Centrifuge for 2 ml Eppendorf tubes
- Filtered glass 150 mm Pasteur pipettes (Poulten & Graf GmbH, model: D810 )
- Rubber nipple for Pasteur pipette
- 10-100 µl pipette (any brand will suffice)
- 100-1,000 µl pipette (any brand will suffice)
- 5 ml pipette and tips (any brand will suffice)
- 80% methanol in water (v/v) (see Recipes)
- 2% acetic acid (v/v) (see Recipes)
- 80% methanol in water (v/v) with added butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) (see Recipes)
- 80% methanol in water (v/v) (see Recipes)
- 2% acetic acid (v/v) (see Recipes)
- 5% methanol, 94% water and 1 % acetic acid (v/v) (see Recipes)
- 1% acetic acid (v/v) (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Balance (±0.001 g)
- Scholander pressure chamber (e.g. PMS Instrument Company, model: 600 ) (optional for specialised experiments or quantification of ABA from xylem sap)
- Stainless steel beads 7 mm (QIAGEN, catalog number: 69989 / 69990 ) (optional for very small samples only)
- Modelling clay or Blu-tak (Bostik) (optional for very small samples only)
- Glass beaker (variable size) (optional for large samples)
- General purpose 21 cm scissors
- Tissue homogeniser [either modified Ba-mix® or Physcotron (Microtec Co., model: NS-7 )]
- Cell lysis machine (e.g. QIAGEN, model: TissueLyser II ) (optional for very small samples only)
- Conventional Ba-mix® or similar hand-held blender (optional for large samples only)
- Ceramic mortar and pestle (optional for manual homogenization method only)
- Büchner funnel (optional for large samples only)
- Vacuum flask (optional for large samples only)
- Vacuum sample concentrator (or rotary evaporator with 100 ml round bottom flask, optional for large samples)
- Fume hood
- Heating block that can contain 0.5 ml Eppendorf tubes (gentle stream of nitrogen gas, passing through a low flow regulator, tubing and funnelled through a standard 100 µl pipette tip, if desired) (e.g. Ratek Instruments, model: DBH10DP )
- A LCGC Certified Clear Glass 12 x 32 mm Screw Neck Vial, with Cap and PTFE/silicone Septum , 2 ml Volume, 100 /pkg [(Waters, catalog number: 186000272C ), Insert 150 µl with preinstalled plastic spring (Waters, catalog number: WAT094171 )]
- Aerosol barrier pipette tips for both µl pipettes (these are important to prevent sample contamination of the pipette which can compromise future samples. They can be made by inserting a small amount of cotton wool into the barrel end of the pipette tip.) (any brand will suffice)
- Ultra-performance liquid chromatograph and multiple reaction-monitoring tandem mass spectrometer [Water Acquity H-series UPLC coupled to a Waters Xervo triple quadrupole mass spectrometer, containing a Waters Acquity UPLC BEH C18 column (2.1 mm x 100 mm x 1.7 µm particles)]
Software
- Waters MassLynx and TargetLynx software
Procedure
- For leaf samples: A 50 ml conical centrifuge tube should be pre-labelled and stabilised on the weighing platform of a ±0.001 g balance by being placed in a glass beaker. Approximately 0.05-0.5 g of leaf tissue (as required or necessary, depending on the amount of tissue available for the species) was harvested, weighed on the balance into the conical centrifuge tube. Tissue collected should reflect the experiment undertaken, but for most experiments the newest, fully expanded leaf is preferable.
Note for step 1: It is important that the balance, beaker and labelled conical centrifuge tube are tared prior to sampling to save inadvertent and unnecessary exposure of tissue to desiccation in the air post excision. Generally 0.05-0.1 g of tissue is more than adequate, however much lower weights of tissue can be measured, for example 0.01 g of epidermal tissue with high resolution (McAdam and Brodribb, 2015). When determining the amount of tissue to be harvested, consideration of the expected level of ABA in the tissue (drought stressed plants will have a high abundance of ABA and thus less tissue maybe required), the amount of secondary metabolites, resins or mucilage in the species of interest (less tissue maybe better in species with an abundance of either or all of these compounds e.g. conifers). In large angiosperm leaves, a sample from the middle of the leaf, or region of interest, is all that is required; for imbricate conifers, twigs suffice; in general petioles and stems though, should be avoided when sampling for foliar ABA. See Figure 1.
For xylem sap samples: Tissue for which ABA analysis is required should be enclosed in a Scholander pressure chamber and an over pressure of 0.4 MPa applied to the sample, the first drop should be discarded due to contamination from cytosolic contents after which the sap can be collected into an 0.5 ml Eppendorf tube, continue from step 6. See Figure 2.
For very small samples (less than 0.05 g) of species with very soft leaves/tissue (e.g. angiosperm herbs, some ferns and Selaginella species or leaf epidermis) or samples of green seeds: Tissue can be harvested and weighed (±0.001 g) into 2 ml screw-cap tubes containing a stainless steel bead that has been pre-labelled, stabilised on the weighing platform of the balance in a small piece of modelling clay or Blu-Tack and tared prior to harvesting.
For very large samples (e.g. whole root systems or entire large leaves, samples > 0.7 g): Tissue can be harvested and weighed (±0.001 g) into a glass beaker of appropriate size, pre-labelled and tared on the balance prior to harvesting.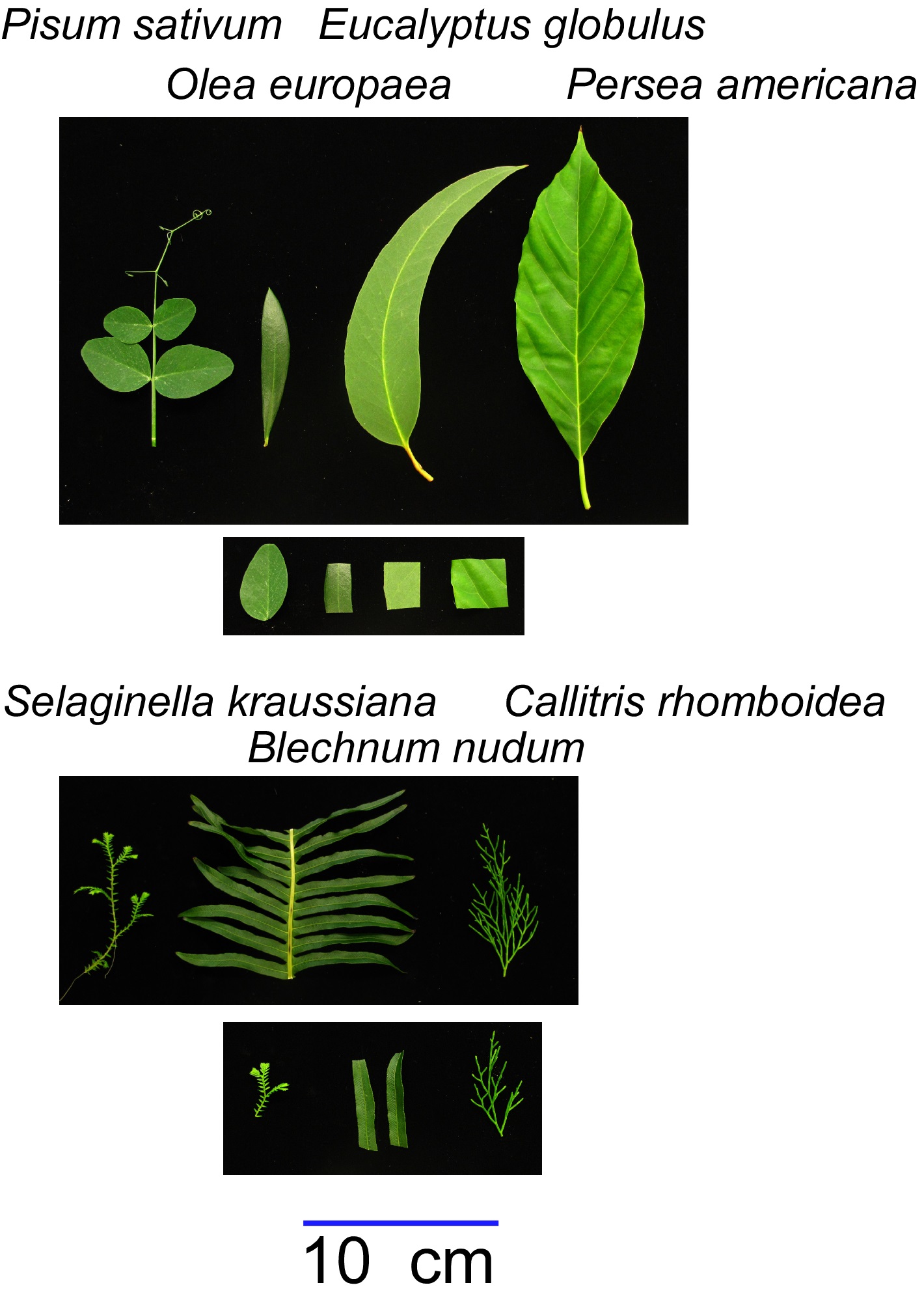
Figure 1. Representative leaves of angiosperms (top panel) and a lycophyte, fern and conifer (bottom panel) with an example of the tissue taken to quantify ABA from each (shown in the images immediately below). Note that a leaflet of Pisum sativum can be used, while a section of leaf from Olea europaea, Eucalyptus globulus and Persea americana are used. Similarly in Selaginella kraussiana a small section of stem with leaves, pieces of pinnules of the fern Blechnum nudum and small branch of the conifer Callitris rhomboidea can be used.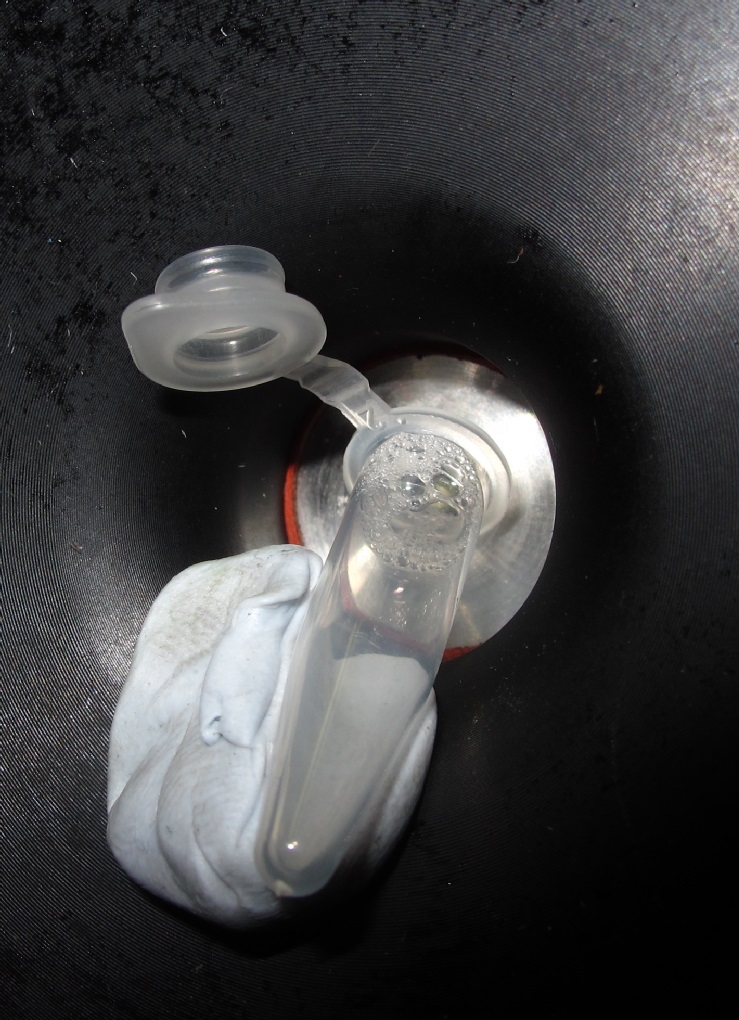
Figure 2. An example of xylem sap being collected from a sample enclosed in a Scholander pressure chamber. The collection tube can be held in place with Blu-Tack or modeller’s clay. - For leaf samples: The sample was then chopped into smaller pieces using scissors and covered in approximately 8-10 ml of cold (-20 °C) 80% methanol in water with added BHT (see Figure 3 for an example of the extent to which samples should be chopped at this stage).
For samples in 2 ml screw-cap tubes the sample should just be covered in approximately 1.5 ml of cold 80% methanol in water with added BHT (see Figure 4 for an example of tissue enclosed in 2 ml screw-cap tubes at this stage).
For very large samples: The sample was chopped into smaller pieces using scissors and covered with cold 80% methanol in water with added BHT.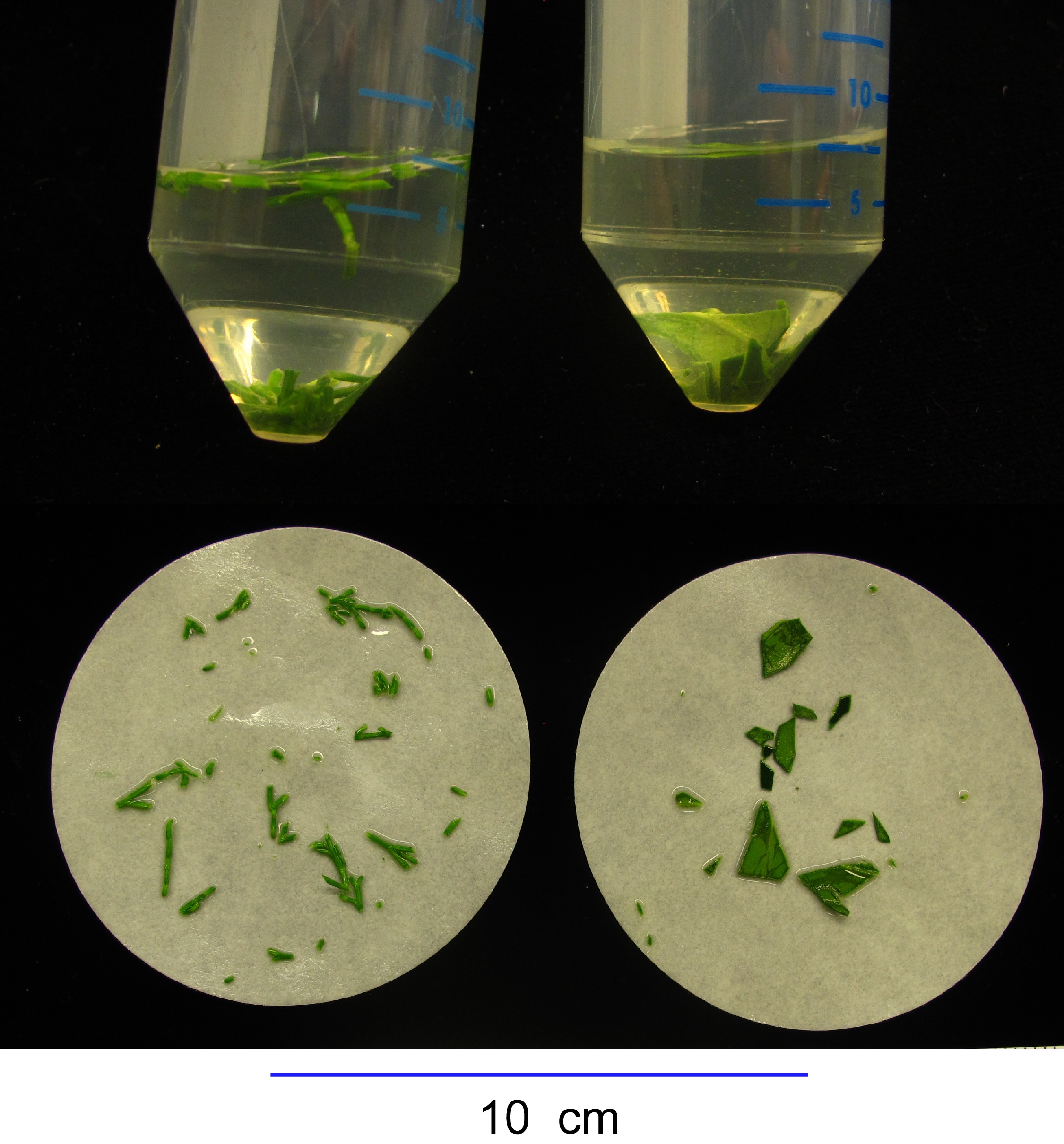
Figure 3. An example of the extent to which samples of the conifer Callitris rhomboidea (right) and angiosperm Olea europaea (left) should be chopped immediately prior to covering with cold 80% methanol in water with added BHT. The same samples (not to scale) are shown both in 50 ml conical centrifuge tubes covered with cold 80% methanol in water with added BHT (top) and on filter paper (bottom) (not to scale). Scale bar for filter paper images is shown below.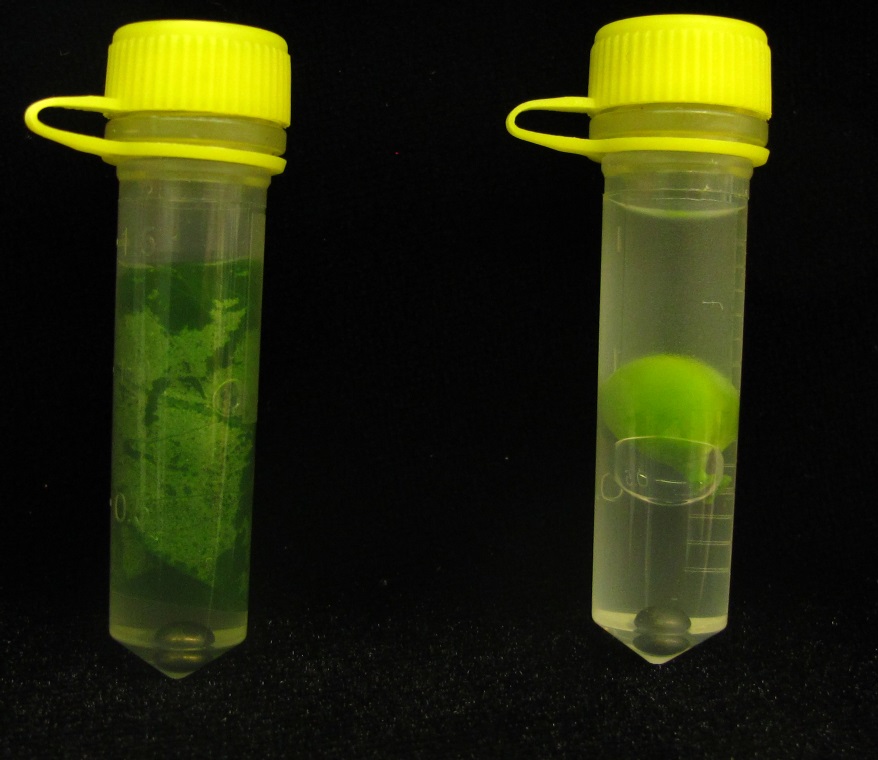
Figure 4. Leaflet tissue of the angiosperm Pisum sativum (left) (taken from Figure 1) and a green seed of Pisum sativum (right) enclosed in 2 ml screw-top tubes and covered in cold 80% methanol with added BHT. Note the stainless steel bead that has already been added to the tube at the bottom, and the correct tethering of the tube (a step critical for successful long-distance freight). - Samples were then stored at -20 °C overnight to ensure that all biochemical processes in the tissue were deactivated.
Notes for steps 1-3: As ABA levels in the leaves of angiosperms can increase rapidly on exposure to dry air or dehydration (McAdam and Brodribb, 2015) it is critical that as little time as possible is taken from harvesting tissue to covering the sample in cold 80% methanol in water with added BHT. It is especially important to prevent the samples from being exposed to the open air or sunlight after excision [as isomerisation of ABA can rapidly take place (Brabham and Biggs, 1981)], so wrapping tissue in damp paper towelling, then aluminium foil, and enclosing wrapped tissue in a plastic zip-lock bag and placing in a dark box is critical if any number of samples are being collected at the same time. So long as leaves do not desiccate, leaf water potential can be quantified using a Scholander pressure chamber. For this samples must be wrapped in damp paper towelling, aluminium foil and bagged to avoid desiccation. The Scholander pressure chamber should also contain damp paper towelling. If these steps are adhered to prior to weighing the sample for ABA analysis, the quantification of ABA will not be adversely affected (Brodribb et al., 2014). Gradual increases and decreases in pressure should, however, always be applied to the tissue with care being taken to avoid over pressurisation, for correct use see ‘Pressure Chamber’ PrometheusWiki http://prometheuswiki.publish.csiro.au/tiki-pagehistory.php?page=Pressure%20chamber&preview=14.
Notes for step 3 regarding samples collected remotely: For samples collected where access to a freezer is not immediately available, after weighing, samples can be stored on ice in the dark until such time as a freezer is available. Provided that the tissue has been placed at -20 °C overnight, it is then possible to transport samples at room temperature (in the dark) so long as all of the samples in an experiment are exposed to the same conditions prior to step 5.
Notes for step 3 regarding samples requiring long-distance freight: For samples that are collected a substantial distance from the laboratory where purification, extraction and quantification will take place, requiring long-distance freight for transport, tissue should be collected, briskly chopped and weighed into screw-cap tubes similar to that described for very small samples, but without the stainless steel beads. Samples should be covered in cold 80% methanol in water with added BHT and stored at -20 °C overnight. It is then possible to transport these samples by air freight. Care must be taken to ensure that the lids of the screw-cap tubes are correctly sealed to avoid loss of sample due to changes in pressure (see Figure 4). Standard (non-screw-capped) Eppendorf tubes should never be used for samples that will be transported by long-distance freight. - For leaf samples: Tissue was homogenized using a Physcotron [or modified Ba-mix® (Figure 5)]. Care should be taken when rinsing the homogenizer to not increase the volume of the sample excessively (i.e. the volume should below 20 ml, ideally 10 ml, for increased accuracy), for this 80% methanol in water (v/v) at room temperature should be used. See Figure 6 for an example of the extent of homogenization expected for the tissue shown in Figure 3 after using a Physcotron.
For very small samples in screw-cap tubes containing a stainless steel bead: Tissue was homogenized using a cell lysis machine run until samples are ground well (approximately 2 min). See Figure 7.
For samples in screw-cap tubes that have been transported by long-distance freight: tissue and solutes should be transferred to 50 ml conical centrifuge tubes and homogenised using a Physcotron (or modified Ba-mix®). It is important to thoroughly rinse the tubes using 80% methanol in water.
For very large samples in a beaker: Tissue was homogenized using a conventional un-modified Ba-mix® or other hand-held blender of appropriate size for the beaker. Care should be taken to rinse the Ba-mix® after homogenization with 80% methanol in water (v/v) into the sample.
Special note for step 4: In the absence of all other means of tissue homogenization, samples can be harvested as described in step 1, wrapped in aluminium foil and immersed in liquid nitrogen. Samples can then be stored at -70 °C until homogenization is required. Homogenization of such samples can be undertaken using a mortar and pestle, pre-cooled by filling mortar with liquid nitrogen and which should be allowed to evaporate. Tissue should be initially broken gently with the pestle then, before defrosting, ground to a fine powder in a small volume of liquid nitrogen. All of this powder should be then briskly transferred while cold to a 50 ml conical centrifuge tube, weighed (as described in step 1) and covered in cold 80% methanol in water with added BHT, it is especially important to ensure that this is done briskly so as to not allow de-frosting of the sample, more liquid nitrogen should be added if this is occurring. Special care should be taken when working with liquid nitrogen.
Following homogenization proceed immediately to step 5.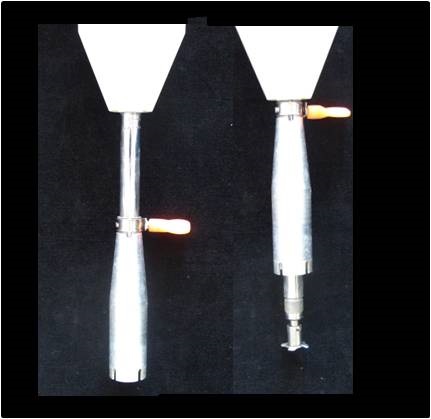
Figure 5. Modified Ba-Mix® for homogenizing plant tissues in a 50 ml centrifuge tube. Note the movable aluminium sleave, the right-hand image shows the sleave fully raised exposing the modified blade. The blade of this Ba-Mix® spins at high speed and, if the sleeve is moved up and down while homogenizing, the sample is forced through the spinning blade and is macerated. It is important that the tissue is forced passed the blade by adjusting the height of the sleeve relative to the blade.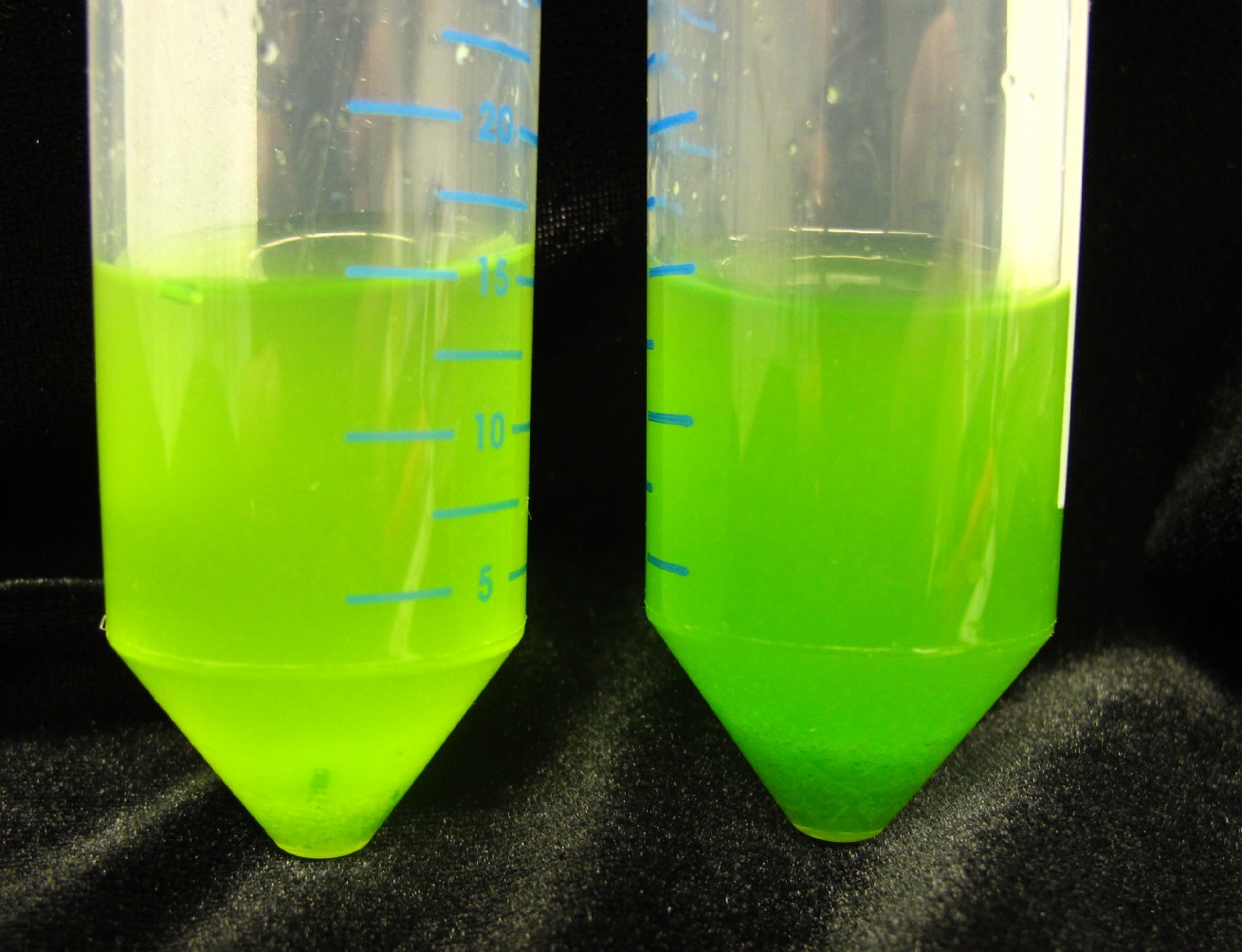
Figure 6. An example of the degree of homogenization after the use of a Physcotron on the samples of the conifer Callitris rhomboidea (left) and angiosperm Olea europaea (right) shown in Figure 4. Note the increase in liquid from rinsing the homogenizer in 80% methanol in water after use.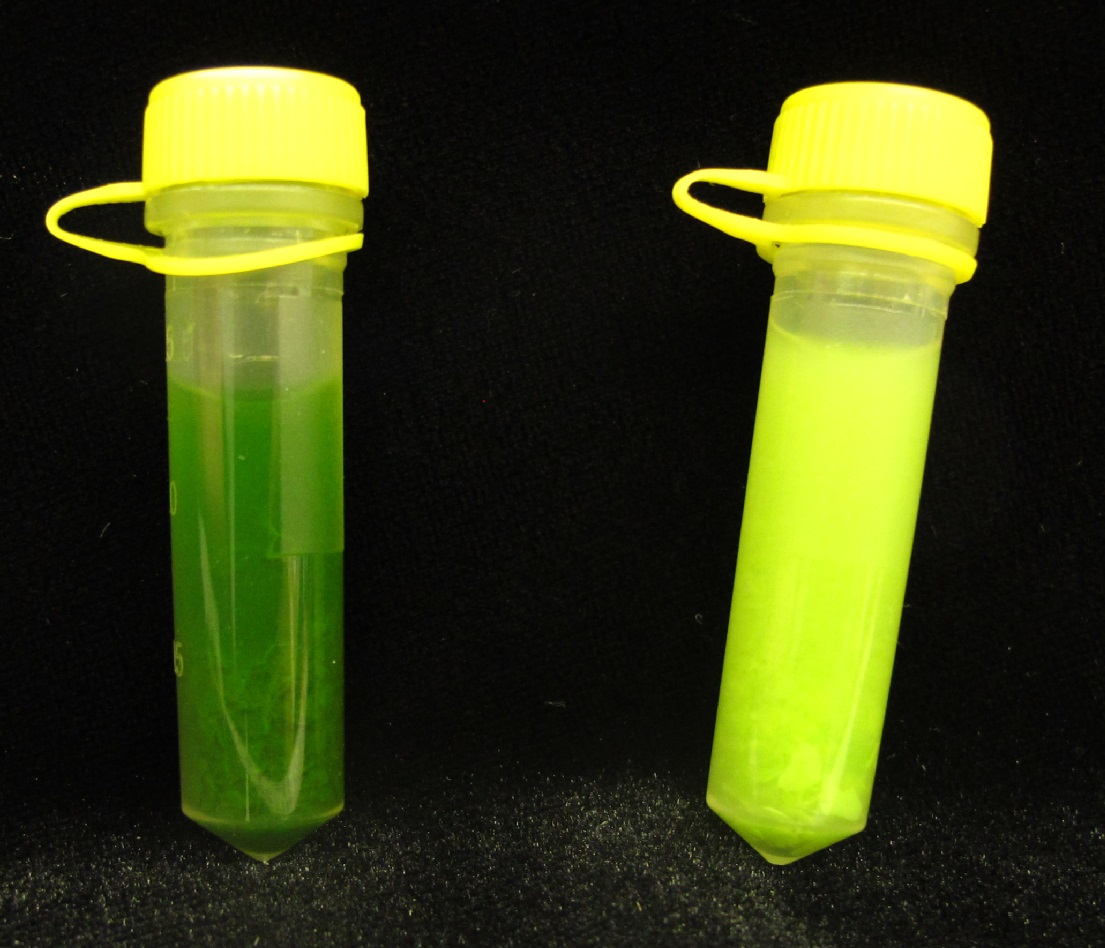
Figure 7. An example of the homogenization obtained after the use of cell lysis machine and stainless steel bead on the leaflet and green seed samples shown in Figure 4. Note that this method is only effective for soft, herbaceous leaves or green seeds. - To each sample, 15 ng of deuterated [2H6] ABA (or similar) was added.
- ABA was then extracted from the homogenized tissue by passive diffusion into the 80% methanol in water with added BHT by incubating at 4 °C, overnight.
Note for step 6: After this step samples can be stored for extended periods of time, in the dark at any temperature (although preferably at -20 °C). - For all samples in a 50 ml conical centrifuge tube: An aliquot of 5 ml was taken from each sample, being careful not to disturb the settled pellet of homogenized tissue in the tube.
For very small samples in 2 ml screw-cap tubes: Tubes were centrifuged for 5 min at 13,000 x g and a 1 ml aliquot was taken from each sample, being careful not to disturb the pellet.
For very large samples: Samples were vacuum filtrated through a Büchner funnel and Whatman no 1 filter paper. An aliquot of at least 50% of this filtrate was taken from each sample. - The aliquot was dried under vacuum at no more than 30 °C.
Note on step 8: For 5 ml of sample drying times using a sample concentrator normal take 5 h, 1 ml of sample for very small samples approximately 1 h, large volumes from very large samples can be dried using a rotary evaporator and normally take approximately 15 to 30 min, depending on the volume. - ABA was then resuspended in 500 µl of 2% acetic acid in water (v/v) by pipetting and transferred to a 1.5 ml Eppendorf tube.
- 300 µl of diethyl ether was added to each tube and the tube was inverted vigorously a number of times to ensure the partitioning of ABA into the ether phase. Steps using diethyl ether should be undertaken in a fumehood. If inversion results in emulsion, a brief centrifugation (1 min at 13,000 x g) will result in the separation of the two distinct phases.
- Using a glass Pasture pipette, the diethyl ether phase (top phase) was collected and placed into a 500 µl Eppendorf tube. See Figure 8 for differentiating the diethyl ether layer.

Figure 8. The visual differentiation of the diethyl ether phase containing ABA above the 2% acetic acid in water phase is apparent. Holding tubes at a slight angle, as depicted, greatly aids the differentiation of these layers for ease of pipetting. - Steps 10 and 11 were repeated, with the second diethyl ether phase pooled with the first.
Note for steps 11 and 12: Care should be taken to avoid collecting any of the 2% acetic acid in water layer when collecting the diethyl ether phase. - Samples in diethyl ether were then dried to completeness on a heating block at 40 °C (to decrease drying times samples can be dried under a nitrogen stream).
- After drying, ABA was resuspended in 150 µl of 5% methanol in 2% acetic acid in water (v/v) (this volume can be reduced according to the expected level of ABA in the sample; samples with lower levels of ABA may need to be resuspended in only 50 µl).
- Tubes were then centrifuged at the maximum speed for a bench-top centrifuge at room temperature for 3 min, to ensure that any particulate matter form a pellet (i.e. 13,000 x g).
- 50 µl from each sample was taken, avoiding any pelleted particulate matter, and placed into an appropriate autosampling vial for UPLC-MS analysis.
Note for step 16: samples should be covered in aluminium foil to protect from sunlight. - Detailed UPLC-MS analysis methods can be found in McAdam and Brodribb (2012).
Briefly the method is was as follows:
Solvents used were 1% acetic acid (v/v) in water (A) and acetonitrile (B), a flow rate 0.35 ml/min was used with a gradient of 80% A: 20% B to 5% A: 95% B at 5 min, equilibrated to starting conditions for 3 min. Column temperature was 45 °C and injection volume 40 µl. The mass spectrometer was operated in negative ion electrospray mode. Needle and cone voltages were 2.7 kV and 32 V respectively. Selected reaction monitoring was used to detect endogenous ABA and [2H6]ABA. The ion source and desolvation temperature were 130 °C and 450 °C respectively. The desolvation gas and cone gas was nitrogen at flow rates of 950 L/h and 50 L/h respectively. Tandem MS transitions monitored for ABA were mass to charge ratios (m/z) 263.2 to 153.1, 204.2 and 219.2, for [2H6]ABA the transitions were 269.2 to 159.1, 207.2 and 225.2. Collision energies for m/z 263.2 to 153.1 and 204.2 were 18 V, for m/z 263.2 to 219.2 was 16 V, this was similar for the corresponding deuterium-labelled channels. Dwell time was 50 ms for each channel. Data were analysed using the Waters MassLynx and TargetLynx software. Only the m/z 263.2 to 153.1 and corresponding deuterium-labelled channels were used for quantification. - To quantify ABA levels in the sample (in terms of fresh weight) the following formula was used:
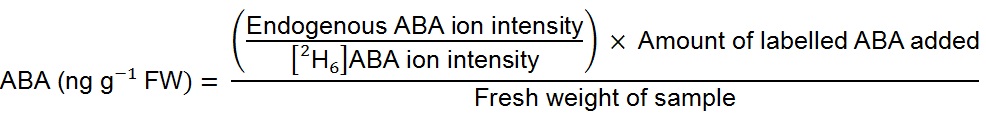
Example A: A 0.0783 g leaf sample of the fern Blechnum nudum (shown in Figure 1) was harvested and prepared as described above for leaf samples. The resulting chromatogram from the UPLC-MS of this sample is depicted in Figure 9. As 15 ng of labelled [2H6]-ABA was added to the sample during preparation the level of endogenous ABA in the sample was calculated as follows: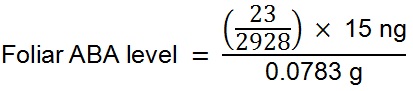
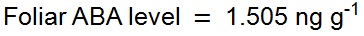
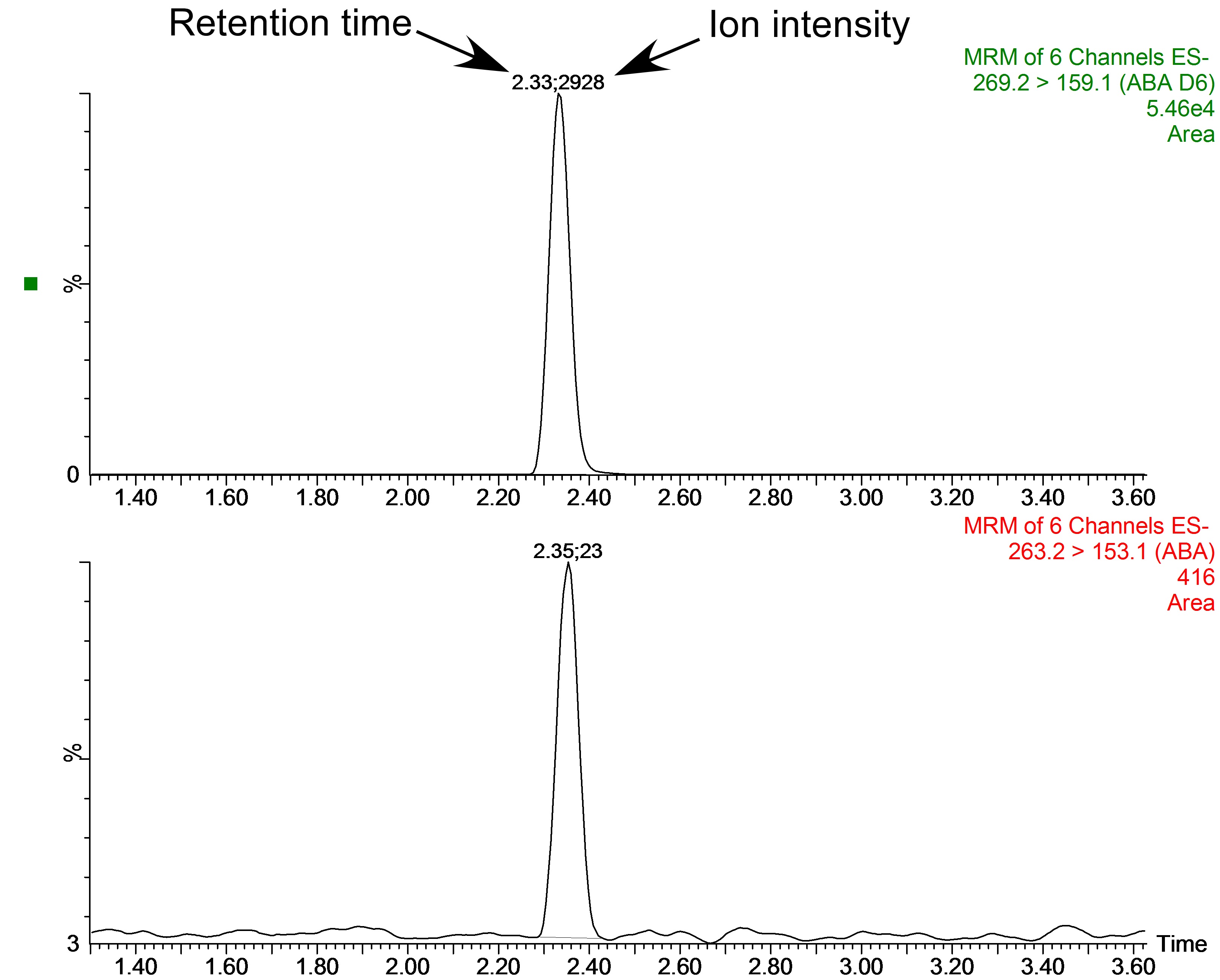
Figure 9. An example raw chromatogram output from the UPLC-MS analysis of a leaf sample from the fern Blechnum nudum showing the peaks of [2H6]ABA (top) and endogenous ABA (bottom). Above the peaks are shown the retention time (left, this is also depicted as the x-axis of the graph) and ion intensity (right, shown as relative ion intensity on the y-axis).
Example B: Unstressed foliar ABA levels vary depending on the species. Table 1 provides mean foliar ABA levels from a range of unstressed species.
Table 1. Mean foliar ABA levels in unstressed individuals from across the diversity of vascular land plantsSpecies Family Mean unstressed foliar ABA level (ng g-1 FW) Reference Selaginella kraussiana Selaginellaceae 11.4 ±1.4 McAdam and Brodribb, 2012 Blechnum nudum Blechnaceae 1.505 Example A Callitris rhomboidea Cupressaceae 402 ±60 Brodribb and McAdam, 2013 Pinus radiata Pinaceae 104 ±10 Brodribb and McAdam, 2013 Quercus robur Fagaceae 17.5 ±1.3 McAdam and Brodribb, 2015 Pisum sativum Fabaceae 3.85 ±1.1 McAdam and Brodribb, 2015
Recipes
- 80% methanol in water (v/v) (1 L)
Combine 200 ml of dH2O with 800 ml of methanol
Stored at room temperature in glassware, provided it is not allowed to evaporate, this reagent can be used indefinitely. - 2% acetic acid (v/v) (100 ml)
Combine 2 ml of glacial acetic acid with 98 ml of dH2O
Stored at room temperature in glassware this reagent can be used indefinitely - 80% methanol in water (v/v) with added butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) (1 L)
Dissolve 250 mg of BHT in an aliquot of methanol
Add remaining methanol (total methanol, including dissolving aliquot, should be 800 ml)
Add 200 ml of dH2O
Store and use at -20 °C
This reagent can be used directly from the stock, it should be stored in glassware and once mixed, provided it is not allowed to evaporate can be used indefinitely. - 80% methanol in water (v/v) (1 L)
Combine 200 ml of dH2O with 800 ml of methanol
Stored at room temperature in glassware, provided it is not allowed to evaporate, this reagent can be used indefinitely. - 2% acetic acid (v/v) (100 ml)
Combine 2 ml of glacial acetic acid with 98 ml of dH2O
Stored at room temperature in glassware this reagent can be used indefinitely - 5% methanol, 94% water and 1 % acetic acid (v/v) (100 ml)
Combine 5 ml of methanol, 94 ml of dH2O and 1 ml of glacial acetic acid
Stored at room temperature in glassware, provided it is not allowed to evaporate, this reagent can be used indefinitely. - 1% acetic acid (v/v) (100 ml)
Combine 1 ml of glacial acetic acid with 99 ml of dH2O
Stored at room temperature in glassware this reagent can be used indefinitely
Acknowledgments
This protocol was adapted from previously published studies McAdam and Brodribb (2012) and McAdam and Brodribb (2014) and was performed by McAdam and Brodribb (2015). This work was supported by Australian Research Council grants. Thanks must go to John Ross for invaluable advice on improving methods of sample preparation over many years and the Central Science Laboratory, University of Tasmania for undertaking UPLC-MS analyses and method development.
References
- Brabham, D. E. and Biggs, R. H. (1981). Cis-trans photoisomerization of abscisic acid. Photochem Photobiol 34: 33-37.
- Brodribb, T. J. and McAdam, S. A. (2013). Abscisic acid mediates a divergence in the drought response of two conifers. Plant Physiol 162(3): 1370-1377.
- Brodribb, T. J., McAdam, S. A., Jordan, G. J. and Martins, S. C. (2014). Conifer species adapt to low-rainfall climates by following one of two divergent pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111(40): 14489-14493.
- McAdam, S. A. and Brodribb, T. J. (2012). Fern and lycophyte guard cells do not respond to endogenous abscisic acid. Plant Cell 24(4): 1510-1521.
- McAdam, S. A. and Brodribb, T. J. (2014). Separating active and passive influences on stomatal control of transpiration. Plant Physiol 164(4): 1578-1586.
- McAdam, S. A. and Brodribb, T. J. (2015). The evolution of mechanisms driving the stomatal response to vapor pressure deficit. Plant Physiol 167(3): 833-843.
- Mittelheuser, C. J. and Van Steveninck, R. F. M. (1969). Stomatal closure and inhibition of transpiration induced by (RS)-abscisic acid. Nature 221:281-282.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2015 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- McAdam, S. A. M. (2015). Physicochemical Quantification of Abscisic Acid Levels in Plant Tissues with an Added Internal Standard by Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography. Bio-protocol 5(18): e1599. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1599.
- McAdam, S. A. and Brodribb, T. J. (2014). Separating active and passive influences on stomatal control of transpiration. Plant Physiol 164(4): 1578-1586.
Category
Plant Science > Plant biochemistry > Plant hormone
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link










