- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Measurement of Net High-affinity Urea Uptake in Maize Plants
Published: Vol 5, Iss 11, Jun 5, 2015 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1490 Views: 9339
Reviewed by: Samik BhattacharyaSriema L. WalawageAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Visualization of Nitric Oxide, Measurement of Nitrosothiols Content, Activity of NOS and NR in Wheat Seedlings
Sandeep B. Adavi [...] Shailendra K. Jha
Oct 20, 2019 6354 Views

A Quick Method to Quantify Iron in Arabidopsis Seedlings
Chandan Kumar Gautam [...] Wolfgang Schmidt
Mar 5, 2022 3931 Views

CAPS-Based SNP Genotyping for Nitrogen-Response Phenotypes in Maize Hybrids
Jannis Jacobs [...] Peter K. Lundquist
Dec 20, 2025 550 Views
Abstract
Despite its extensive use as a nitrogen fertilizer, the role of urea as a directly accessible nitrogen source for crop plants is still poorly understood. So far, the physiological and molecular aspects of urea acquisition have been investigated only in a few plant species highlighting the importance of a urea transporter in roots, DUR3 (Kojima et al., 2007; Wang et al., 2012; Zanin et al., 2014a). Regarding maize plants, a crop that needs a large amount of urea fertilizer, the capability to take up urea via an inducible and high-affinity transport system has been recently characterized (Zanin et al., 2014a; Zanin et al., 2014b). Here, we described a small-scale protocol suitable for the measurement of urea net high-affinity uptake in roots of intact maize plants.
Keywords: TransportMaterials and Reagents
- Maize seeds (Zea mays L., cv. PR33T56, Pioneer Hi-bred Italia S.p.A., Parma, Italy)
- Potassium hydroxide (KOH) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 60370 )
- Calcium sulphate (CaSO4) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 12090 )
- Urea [CO(NH2)2] (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 15604 )
- Diacetylmonoxime [CH3C(=NOH)COCH3] (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 31550 )
- Thiosemicarbazide (NH2CSNHNH2) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 89050 )
- Sulphuric acid (H2SO4) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 320501 )
- Ortho-phosphoric acid (H3PO4) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: W290017 )
- Ferric chloride hexahydrate (FeCl3) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 12319 )
- Sterile deionized water
- KCl (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P9541 )
- CaSO4 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 12090 )
- MgSO4 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 746452 )
- KH2PO4 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P9791 )
- NaFe-EDTA (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 03650 )
- H3BO3 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: B7901 )
- MnSO4 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 221287 )
- ZnSO4 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: Z1001 )
- CuSO4 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: C3036 )
- Na2MoO4 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M1651 )
- Nutrient solution (see Recipes)
- Urea solution stock (see Recipes)
- Mixed colour reagent (see Recipes)
- Mixed acid reagent (see Recipes)
- Colour development reagent (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Growth chamber and hydroponic growing system (including plastic net, plastic pots)
- pH meter (Jenway, model: 3510 )
- Plastic box (15 x 10 cm; H 4 cm; Figure 1A, alternatively you can use the bottom of the pipette tips, Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P5161 )
- 0.2 ml 96-well plate (AB ANALITICA Advanced Biomedicine, catalog number: B50601 ; Figure 1B)
- Clear 96-well microplate with flat bottoms (STARLAB, catalog number: S1837-9600 ; Figure 1C)
- Sealing tapes, optically clear (SARSTEDT AG, catalog number: 95.1994 )
- Thermocycler (Eppendorf, model: Mastercycler® personal )
- Orbital shaker (Janke & Kunkel IKA-Labortechnik, model: KS 501D )
- Spectrophotometric multiwell plate reader (TECAN, model: GENios Microplate Reader )
- Timer
- Pipettes (Eppendorf, model: 0.5-10 μl, 20-200 μl, 100-1,000 μl, Eppendorf Reference® 2 ) and tips
- 1.5 ml plastic tubes (Eppendorf, catalog number: 0030 125.150 )
- Absorbent paper (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: Z270849 )
Figure 1. Plastic equipment. A. plastic box; B. 0.2 ml 96-well plate; C. Clear 96-well microplate.
Procedure
- Maize growth conditions
- Germinate maize seeds on a plastic net placed at the surface of an aerated 0.5 mM CaSO4 solution in a growth chamber at 25 °C in the dark.
- After 3 days, transfer the seedlings into an aerated hydroponic system containing 0.5 mM CaSO4 under controlled climatic conditions: day/night photoperiod, 16/8 h; light intensity, 220 µmol m-2s-1; temperature (day/night) 25/20 °C; relative humidity 70 to 80%.
- After 2 days (5-day-old) plants were transferred for 4 hours in a N-free nutrient solution containing (µM): KCl 5; CaSO4 500; MgSO4 100; KH2PO4 175; NaFe-EDTA 20; H3BO3 2.5; MnSO4 0.2; ZnSO4 0.2; CuSO4 0.05; Na2MoO4 0.05. N is supplied in form of 1 mM CO(NH2)2 (urea-treated plants); or as control, plants are exposed to a N-free nutrient solution (control-plants). The pH of solution is adjusted to pH 6.0 with potassium hydroxide (KOH).
- Germinate maize seeds on a plastic net placed at the surface of an aerated 0.5 mM CaSO4 solution in a growth chamber at 25 °C in the dark.
- Root uptake of urea and collection of samples
- Gently remove intact plants (six urea-treated plants and six control plants) from hydroponic system and rinse plant roots for 10 sec in 500 ml of calcium sulphate solution (500 µM CaSO4), repeat this step twice (Figure 2A).
- On an absorbent paper, absorb the excess of calcium sulphate solution from maize plants taking care to not damage roots (Figure 2B).
- For each measurement, fill three plastic boxes with 40 ml of urea solution (8 ml of 1 mM urea solution stock and 32 ml of 500 µM calcium sulphate, final urea concentration 200 µM) and place the boxes on the orbital shaker (speed 90 rpm).
- Set the timer to count up 10 min.
- In each plastic box, place two intact plants submerging the roots in the urea solution (avoid to submerge the seed of the plants). Starting the timer (T = 0 min), collect 60 µl of the urea solution in a 96-well plate (Figure 2C-E).
- Net uptake is measured as urea depletion from the solution per unit of time, removing samples of solution (60 µl) for urea determination every 2 min for 10 min, span time during which uptake had a linear trend. Thus, continue to collect the urea solution from each plastic box every two minutes from the start point, at T = 2, 4, 6, 8 and 10 min.
- At the end of the harvesting time, turn off the orbital shaker. In each plastic box, cut and dry roots on absorbent paper; then weigh the maize roots of two plants (Figure 2F).
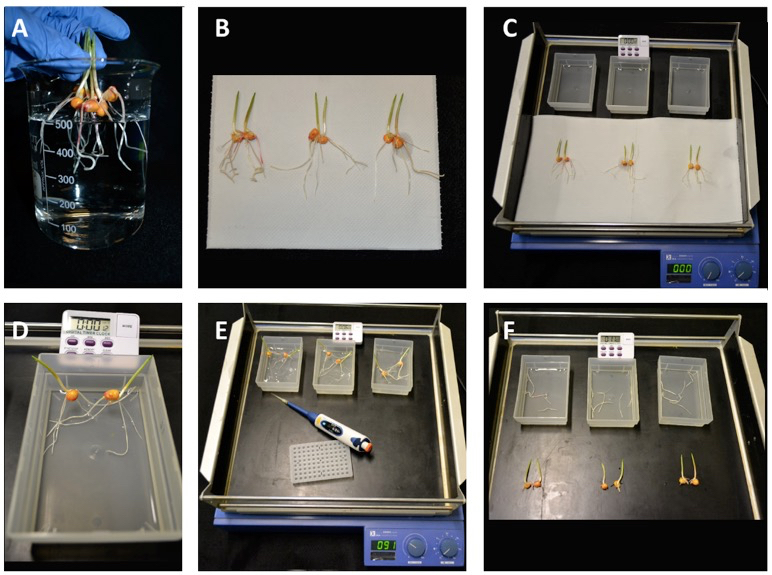
Figure 2. Procedures to collect the samples. A. Rinse the maize roots; B. dry maize roots on absorbent paper; C. Prepare plants on an orbital shaker; D. Two plants of maize are transferred in each plastic box, with roots submerged in the urea solution; E. during the experimental time span of 10 min, collect 60 µl of urea solution every two minutes; F. at the end of the experiment, cut and weight the roots.
- Gently remove intact plants (six urea-treated plants and six control plants) from hydroponic system and rinse plant roots for 10 sec in 500 ml of calcium sulphate solution (500 µM CaSO4), repeat this step twice (Figure 2A).
- Urea standards
- In 1.5 ml plastic tubes, dilute 1 mM urea solution stock as indicated in Table 1 to create the standard curve.
Table 1. Urea standardsUrea solution stock
(1 mM)Calcium sulphate
(500 µM)Final urea concentration 0 µl 1000 µl 0 µM 100 µl 900 µl 100 µM 120 µl 880 µl 120 µM 140 µl 860 µl 140 µM 160 µl 840 µl 160 µM 180 µl 820 µl 180 µM 200 µl 800 µl 200 µM 250 µl 750 µl 250 µM - Transfer 60 µl of the standards into separate wells of the 96-well plate.
- In 1.5 ml plastic tubes, dilute 1 mM urea solution stock as indicated in Table 1 to create the standard curve.
- Urea determination by assay colorimetric reaction
- Prepare fresh the colour development reagent by mixing 25 ml of mixed acid reagent with 25 ml of mixed colour reagent.
- Add 120 µl of colour development reagent to each well of 96-well plate containing the samples or the standards.
- Seal the plate with a sealing tape.
- Incubate for 15 min at 99 °C (lid temperature: 105 °C) in a thermocycler.
- Cool the samples for 5 min on ice.
- Remove the sealing tape from the plate and transfer 160 µl of all samples in a clear 96-well microplate with flat bottoms.
Note: To avoid to loss material, de-pressurize the wells with a needle before removing the sealing tape from the plate. - Measure the absorbance at 540 nm using a microtiter plate reader (Figure 3).
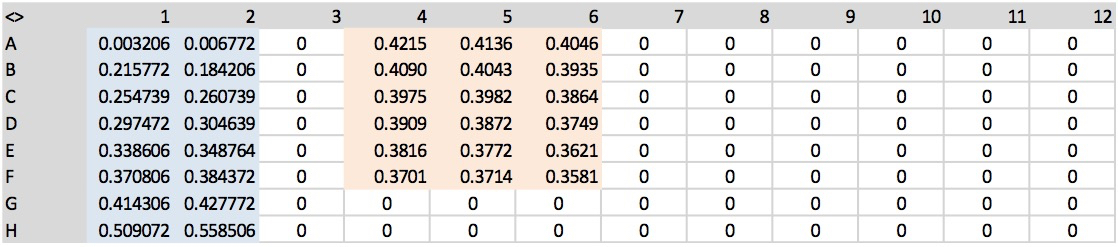
Figure 3. An example of output data from a microtiter plate reader at 540 nm. In blue and red are highlighted standards and samples, respectively. - The capacity of maize roots to take up urea was determined measuring urea depletion from the solution during the time span of 10 minutes. Net-uptake rates of urea were expressed as µmol urea/g root fresh weight (FW)/h. An example of calculation is provided in Supplemental file 1.
- Prepare fresh the colour development reagent by mixing 25 ml of mixed acid reagent with 25 ml of mixed colour reagent.
Notes
After the harvesting, it is possible to freeze the samples at -20 °C and in the following day proceed the samples.
The urea was determined by diacetylmonoxime and thiosemicarbazide colorimetric assay modified from Killingsbaeck (1975) and Mérigout et al. (2008). In order to analyze a great numbers of samples, the colorimetric reaction was performed using 96-well microplates and the volumes of reagents were optimized. Kojima et al. (2007) used the same colorimetric reaction to determined urea accumulation in Arabidopsis tissues. The authors pointed out that the ureides allantoin, ornithine, arginine, and uric acid, did not interfere with urea determinations, although other ureides were not tested.
Recipes
- Nutrient solution
KCl 5 µM
CaSO4 500 µM
MgSO4 100 µM
KH2PO4 175 µM
NaFe-EDTA 20 µM
H3BO3 2.5 µM
MnSO4 0.2 µM
ZnSO4 0.2 µM
CuSO4 0.05 µM
Na2MoO4 0.05 µM - Urea solution stock
1 mM urea
500 µM calcium sulphate - Mixed colour reagent
7% (v/v) 0.2 M diacetylmonoxime
7% (v/v) 0.05 M thiosemicarbazide - Mixed acid reagent
20% (v/v) sulphuric acid
9% (v/v) ortho-phosphoric acid
0.06% (v/v) 74 mM ferric chloride hexahydrate - Colour development reagent
50% (v/v) mixed colour reagent
50% (v/v) mixed acid reagent
Acknowledgments
The procedures for the root-uptake measurements were adapted from previous studies on nitrate uptake (Rizzardo et al., 2012). The work was supported by a grant from the Italian autonomous region of Friuli Venezia Giulia and the Italian Ministry of University and Research.
References
- Kojima, S., Bohner, A., Gassert, B., Yuan, L. and von Wiren, N. (2007). AtDUR3 represents the major transporter for high-affinity urea transport across the plasma membrane of nitrogen-deficient Arabidopsis roots. Plant J 52(1): 30-40.
- Merigout, P., Lelandais, M., Bitton, F., Renou, J. P., Briand, X., Meyer, C. and Daniel-Vedele, F. (2008). Physiological and transcriptomic aspects of urea uptake and assimilation in Arabidopsis plants. Plant Physiol 147(3): 1225-1238.
- Rizzardo, C., Tomasi, N., Monte, R., Varanini, Z., Nocito, F. F., Cesco, S. and Pinton, R. (2012). Cadmium inhibits the induction of high-affinity nitrate uptake in maize (Zea mays L.) roots. Planta 236(6): 1701-1712.
- Wang, W. H., Kohler, B., Cao, F. Q., Liu, G. W., Gong, Y. Y., Sheng, S., Song, Q. C., Cheng, X. Y., Garnett, T., Okamoto, M., Qin, R., Mueller-Roeber, B., Tester, M. and Liu, L. H. (2012). Rice DUR3 mediates high-affinity urea transport and plays an effective role in improvement of urea acquisition and utilization when expressed in Arabidopsis. New Phytol 193(2): 432-444.
- Zanin, L., Tomasi, N., Wirdnam, C., Meier, S., Komarova, N. Y., Mimmo, T., Cesco, S., Rentsch, D. and Pinton, R. (2014a). Isolation and functional characterization of a high affinity urea transporter from roots of Zea mays. BMC Plant Biol 14: 222.
- Zanin, L., Zamboni, A., Monte, R., Tomasi, N., Varanini, Z., Cesco, S. and Pinton, R. (2015). Transcriptomic analysis highlights reciprocal interactions of urea and nitrate for nitrogen acquisition by maize roots. Plant Cell Physiol 56(3): 532-548.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2015 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Zanin, L., Tomasi, N. and Pinton, R. (2015). Measurement of Net High-affinity Urea Uptake in Maize Plants. Bio-protocol 5(11): e1490. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1490.
Category
Plant Science > Plant physiology > Nutrition
Plant Science > Plant metabolism > Nitrogen
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link










