- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Extraction and Quantification of Poly P, Poly P Analysis by Urea-PAGE
Published: Vol 4, Iss 9, May 5, 2014 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1113 Views: 10241
Reviewed by: Anonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols
Extraction and Quantification of Polyphosphate in the Budding Yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae
David Canadell [...] Joaquín Ariño
Jul 20, 2016 12369 Views

Determination of Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) Content in Cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 Using Acid Hydrolysis Followed by High-performance Liquid Chromatography
Janine Kaewbai-ngam [...] Tanakarn Monshupanee
Aug 20, 2023 1825 Views

An HPLC-based Assay to Study the Activity of Cyclic Diadenosine Monophosphate (C-di-AMP) Synthase DisA from Mycobacterium smegmatis
Avisek Mahapa [...] Dipankar Chatterji
Dec 20, 2024 1790 Views
Abstract
Inorganic polyphosphate (poly P) molecules, linear chains containing hundreds of orthophosphate (Pi) residues linked by high-energy phosphoanhydride bonds are abundant in every cell in nature. These molecules are widely distributed among bacteria, including key pathogens, and eukaryotes, poly P is present in organelles, including nuclei, mitochondria, and vesicles.
Remarkable properties of this molecule as a polyanion have been discovered and have made it suited for a crucial role in the emergence of cells on earth. Poly P is essential for bacterial responses to stresses and starvation, motility, quorum sensing, biofilm formation, and virulence and essential for survival. Polymers of different lengths are present in different locations and have different roles in the cell.
Materials and Reagents
- [γ-32P] ATP, [32P] (Amersham Biosciences)
- Poly P (types 15 and 75) (apyrase, and common chemicals) (Sigma-Aldrich)
- Poly P35, Poly P50, Poly P300, and Poly P750
- Polyphosphatase (PPX) isolated from yeast
- Polyphosphate kinase (PPK) isolated from Escherichia coli (E. coli) (EcPPK)
- Tris-HCl (pH 8.0)
- Ammonium sulfate
- Toluidine blue
- 25% methanol
- 5% glycerol
- 5x sample buffer (see Recipes)
- THK buffer (see Recipes)
- Elution buffer (see Recipes)
- Aacrylamide solution (see Recipes)
Equipment
- DE81 disk
- Monolight 2010 (Analytical Luminescence Laboratory)
- Topcount (Packard Instruments)
- Microfuge (14,000 rpm or 16,000 x g)
- Phosphorimager (Molecular Dynamics) (conventional)
- Kodak X-Omat AR film
Procedure
Note: This protocol can be suitable for any kind of extract. The amount of sample for poly P quantification depends on the total amount of poly P in the sample and the right dilution should be determined experimentally.
- Extraction and quantification
- Acid-soluble and salt-soluble poly P fractions were extracted at 4 °C with 0.5 N HClO4 and a saturated solution of NaClO4 in 1 N HClO4, respectively.
- The remaining biomass was treated with 0.5 N HClO4 for 30 min at 90 °C, and the level of the acid-insoluble poly P fraction was measured as the amount of released Pi (Vagabov et al., 2000).
- Nucleotides were removed from the acid-soluble fraction by adsorption to Norit A charcoal (Ault-Riche et al., 1998).
- The levels of poly P in the acid-soluble and salt-soluble poly P fractions were calculated as a difference in the P amount before and after hydrolysis of samples in the presence of 1 N HCl for 10 min at 100 °C (labile phosphorus).
- The DE81 filter paper treatment was used in parallel to estimate the amount of poly P (Rao et al., 1998).
- An aliquot of the cell lysate (20 μl) was loaded onto a DE81 disk (1.3 cm diameter) and set on a paper towel for 2 to 5 min to dry.
- Each disk was washed three times by shaking in 10 ml of THK buffer.
- Partially air-dried disks were then placed in a 0.5-ml Eppendorf tube without the cap and with a tiny hole at the bottom; the tube with disk was then placed inside a 1.5-ml Eppendorf tube.
- Poly P was eluted with 50 μl of elution buffer by soaking the disk in the buffer for 10 min at room temperature and then centrifuging the tubes for 5 sec at 14,000 rpm in a microfuge; elution with 50 μl of buffer was repeated three times.
- To the combined 200 μl of eluate was added 2 μl of poly P, type P65 (20 μg), and 6 μl of a 15% Norit suspension in water.
- The suspension was mixed and centrifuged for 5 min at 14,000 rpm in a microfuge.
- The supernatant was transferred to a fresh Eppendorf tube and the pellet was washed twice with 400 μl of 10 mM Tris-HCl buffer (pH 8.0).
- The supernatants were pooled to yield a total volume of 1.0 ml, which constituted the purified poly P extract.
- Protein levels were determined using bovine serum albumin as a standard.
- To estimate total Poly P levels we used the method of Ault-Riché (Ault-Riche et al., 1998; Rao et al., 1998), in which the enzyme assay is performed with purified PPK from E. coli (Ec-PPK); in the presence of ADP and poly P, ATP is generated and measured using a luminescence assay as described in (Ault-Riche and Kornberg, 1999).
- Poly P assay
- 0.1 ml reaction mixture
50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.4)
40 mM ammonium sulfate
4 mM MgCl2
5 μM ADP
24,000 U of Ec-PPK (pure enzyme)
Incubated at 37 °C for 40 min and then at 90 °C for 2 min. - The reaction mixture was diluted 1:100 in 100 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0) - 4 mM EDTA, of which 0.1 ml was added to 0.1 ml of luciferase reaction mixture.
- Luminescence was measured by using a luminometer (Monolight 2010 or Topcount).
- A standard curve for ATP (0, 0.55, 1.1, 1.65, and 3.3 pmol) in 100 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0) - 4 mM EDTA was used for comparison.
- Concentration of poly P is given in terms of Pi residues. [32P] poly P values are based on specific radioactivity and susceptibility to hydrolysis with PPX.
- 0.1 ml reaction mixture
- Poly P analysis by urea-PAGE
- Urea-polyacrylamide gels were prepared by mixing:
10.51 g of urea
3.75 ml of acrylamide solution
2.5 ml of 0.9 M Tris borate (pH 8.3)
27 mM EDTA, to a final volume of 25 ml
Ammonium persulfate (15 μg) and TEMED (25 μl) - The gel was poured (14 x 23 x 0.75 mm) and allowed to polymerize.
- Gels of other strengths were made with appropriate volumes of the stock acrylamide solution. The gel was pre-electrophoresed at 300 V for 1 h.
- Poly P was mixed with 0.25 volume of 5x sample buffer and loaded on the gel.
- Electrophoresis was at 300 V until the dye was 7 to 8 cm from the top of the gel.
- Gels were stained with:
0.05% toluidine blue in 25% methanol and 5% glycerol for 20 min followed by destaining in the same solvent without toluidine blue. - Gels containing radioactivity were analyzed on a Phosphorimager and autoradiography on Kodak X-Omat AR film (Kumble and Kornberg, 1995).
- For determination of chain lengths, marker poly P of various sizes was electrophoresed along with the samples and the markers localized by toluidine blue staining (Figure 1).
- Centimeters migrated versus chain length was plotted, the mobility of the sample was measured, and its chain length was determined by extrapolating from the plot.
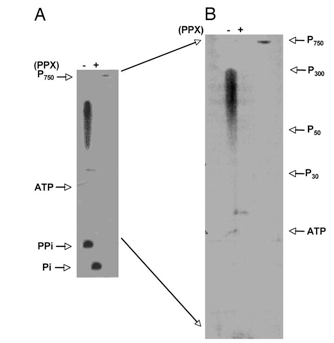
Figure 1. Poly P products of DdPPK1. Poly P synthesis with 40 ng of DdPPK1 was carried out with [γ-32P] ATP under the optimal conditions for 30 min. Products were purified, treated with exopolyphosphatase (PPX) (as described in Materials and Reagents) and separated by 20% PAGE containing 7 M urea, and visualized by PhosphorImager. P750 is a purified product of EcPPK1, which has a chain length of ≈ 750 residues. P300, P50, and P30 indicate the position of poly P with different chain lengths. PPi, pyrophosphate. (A) Poly P products before (−) and after (+) PPX-treatment. (B) The region between poly P750 and PPi from gel A is magnified to highlight the chain lengths of poly P. (Zhang et al., 2007)
- Urea-polyacrylamide gels were prepared by mixing:
Notes
The poly P analysis in Synechococcus is just like extracting poly P from E. coli. Preparation of a cell lysate by sonication, Synechococcus has a lot of poly P, so, prepare 1/10 and 1/100 dilutions and follow step A4 above. This is true as well for any other prokaryotes with high poly P content.
Recipes
- 5x sample buffer
50% sucrose
0.125% bromophenol blue
450 mM Tris borate at pH 8.3
13.5 mM EDTA - THK buffer
10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0)
100 mM KCl
5 mM KPO4 (pH 8.0) - Elution buffer
10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0)
500 mM KCl - Aacrylamide solution
38 g of acrylamide and 2 g of bisacrylamide dissolved in deionized water to a final volume of 100 ml
Acknowledgments
This protocol is adapted from Ault-Riche et al. (1998); Ault-Riche et al. (1999); Rao et al. (1998); and Zhang et al. (2007).
References
- Ault-Riche, D. and Kornberg, A. (1999). Definitive enzymatic assays in polyphosphate analysis. Prog Mol Subcell Biol 23: 241-252.
- Ault-Riche, D., Fraley, C. D., Tzeng, C. M. and Kornberg, A. (1998). Novel assay reveals multiple pathways regulating stress-induced accumulations of inorganic polyphosphate in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 180(7): 1841-1847.
- Kumble, K. D. and Kornberg, A. (1995). Inorganic polyphosphate in mammalian cells and tissues. J Biol Chem 270(11): 5818-5822.
- Rao, N. N., Liu, S. and Kornberg, A. (1998). Inorganic polyphosphate in Escherichia coli: the phosphate regulon and the stringent response. J Bacteriol 180(8): 2186-2193.
- Vagabov, V. M., Trilisenko, L. V. and Kulaev, I. S. (2000). Dependence of inorganic polyphosphate chain length on the orthophosphate content in the culture medium of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochemistry (Mosc) 65(3): 349-354.
- Zhang, H., Gomez-Garcia, M. R., Shi, X., Rao, N. N. and Kornberg, A. (2007). Polyphosphate kinase 1, a conserved bacterial enzyme, in a eukaryote, Dictyostelium discoideum, with a role in cytokinesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104(42): 16486-16491.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2014 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Garcia, M. R. G. (2014). Extraction and Quantification of Poly P, Poly P Analysis by Urea-PAGE. Bio-protocol 4(9): e1113. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1113.
Category
Microbiology > Microbial biochemistry > Other compound
Biochemistry > Other compound > Ion > Phosphate
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link









