- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Reverse Zymmogram Analysis for the Detection of Protease Inhibitor Activity
反向酶谱分析测定蛋白酶抑制剂活性
(*contributed equally to this work) 发布: 2013年08月20日第3卷第16期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.856 浏览次数: 12234
评审: Tie Liu
Abstract
This protocol describes a gel-based procedure to detect protease inhibitor activity. In this method gelatin is used as a substrate for proteolysis and is copolymerized within the polyacrylamide matrix. Protein extracts are fractioned by SDS-PAGE and then the gel is treated with the protease of interest, which degrades gelatin, except in the areas where inhibitory activity is present. Inhibition of protease activity appears as colored bands against a clear background after staining with Coomassie Brilliant Blue (Figure 1). The effectiveness of the assay is dependent on the capacity of the protease inhibitor to refold after SDS-PAGE fractionation. Alternatively, it can be performed using native (PAGE) gels. Although the protocol presented here has been standardized to test for subtilisin inhibitory activity, it can easily be adapted to test other proteases and protease inhibitors.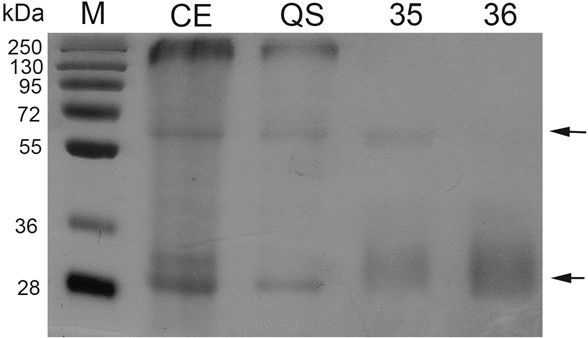
Figure 1. Protease inhibitor activity by zymogram analysis of different purified fractions and a protein crude extract. Zymogram was performed after SDS-PAGE. One microgram of protein was loaded to each lane. CE: Crude extract; QS: Fraction from anion exchange chromatography (Q-sepharose); Fractions 35-36: Obtained after a size exclusion chromatography (Superdex 200). M: Molecular markers. Arrows indicate inhibition activity.
Materials and Reagents
- Protein extract or purified protein (1-5 μg)
- Aprotinin (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A-3886 )
- Subtilisin (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P-5380 )
- 30% Acrylamide stock (29:1 acrylamide:bisacrylamide) (Bio-Rad Laboratories)
- TEMED (Sigma-Aldrich)
- Ammonium persulfate (Bio-Rad Laboratories)
- SDS (Bio-Rad Laboratories)
- Tris base (Sigma-Aldrich)
- Gelatin (Sigma-Aldrich)
- Bromophenol Blue (Sigma-Aldrich)
- β-mercaptoethanol (Sigma-Aldrich)
- Glycine (Sigma-Aldrich)
- EDTA (JT Baker)
- Glycerol (JT Baker)
- Pre-stain Protein Standard (Bio-Rad Laboratories)
- Coomassie blue G250 (Sigma-Aldrich)
- Ethanol (JT Baker)
- Phosphoric acid (Sigma-Aldrich)
- Triton X-100 (Sigma-Aldrich)
- Separating gel buffer (8x) (see Recipes)
- Stacking gel buffer (4x) (see Recipes)
- Gelatin-SDS-PAGE Separating gel (see Recipes)
- Stacking gel (see Recipes)
- Sample loading buffer (see Recipes)
- Laemmli Reservoir buffer (see Recipes)
- Stain solution (4 L) (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Protein mini gel cassettes (Bio-Rad Laboratories)
- Power supply
- Orbital shaker
- Incubator
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2013 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Bernal, L., García-Campusano, F., Nájera, E. and Cruz-García, F. (2013). Reverse Zymmogram Analysis for the Detection of Protease Inhibitor Activity. Bio-protocol 3(16): e856. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.856.
- Jimenez-Duran, K., McClure, B., Garcia-Campusano, F., Rodriguez-Sotres, R., Cisneros, J., Busot, G. and Cruz-Garcia, F. (2013). NaStEP: a proteinase inhibitor essential to self-incompatibility and a positive regulator of HT-B stability in Nicotiana alata pollen tubes. Plant Physiol 161(1): 97-107.
分类
植物科学 > 植物生物化学 > 蛋白质 > 活性
生物化学 > 蛋白质 > 电泳
生物化学 > 蛋白质 > 修饰
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link