- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Preparation of Candida albicans Biofilms Using an in vivo Rat Central Venous Catheter Model
使用体内大鼠中心静脉导管制备白色念珠菌生物膜
发布: 2013年07月20日第3卷第14期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.823 浏览次数: 9567
评审: Fanglian He
Abstract
In vivo biofilms grown on medical devices are necessary to understand the interactions of the fungal biofilm and the host environment in which it is most commonly found. This protocol describes a way to grow Candida albicans biofilms on the interior lumen of central venous catheters surgically implanted into rats, which mimics quite well the clinical cases of biofilms found on human central venous catheters. These infected catheters can then be studied via a multitude of different experiments, including cell counting by plating, imaging the catheters under light or electron microscopy, or comparing the relative content of in vivo biofilms to in vitro biofilms and planktonic cultures. These biofilms also provide enough high quality RNA for transcriptional profiling.
Keywords: Candida (念珠菌)Materials and Reagents
- 350 g Specific-pathogen-free male Sprague-Dawley rats (Harlan)
- Plate containing grown Candida albicans colonies
- Ethylene oxide
- 4 way Large Bore (lipid resistant) Stopcock (Baxter, catalog number: 2C62047 )
- Xylazine (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: X1126 )
- Ketamine (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: K2753 )
- Bacitracin (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: B0125 )
- Bacto-peptone (BD Biosciences, catalog number: 211677 )
- Bacto-yeast extract (BD Biosciences, catalog number: 212750 )
- Betadine (SWIFT, catalog number: 159935 )
- Difco agar (BD Biosciences, catalog number: 214530 )
- Difco dextrose (BD Biosciences, catalog number: 215530 )
- Heparin 1,000 U/ml (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: H3393 )
- Intramedic PE 160 polyethylene tubing (BD Biosciences, catalog number: 427430 )
- Needle holder (World Precision Instruments, catalog number: 14109 )
- Silk braided sutures (size 2-0) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 14-516-130 )
- Size med rat jacket (Braintress Scientific, catalog number: RJ-M )
- Sodium chloride (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: S671-3 )
- Sterile surgical draping materials (autoclaved hospital towels)
- Surgical button attached to wire rat tether (Instech Solomon, catalog number: LW95S )
- Uridine (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: U3750 )
- Xylazine/ketamine anesthetic (see Recipes)
- YPD + uridine media (see Recipes)
- Heparinized saline (see Recipes)
- 0.85% saline solution (see Recipes)
- YPD + uridine plates (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Iris scissors (Braintree Scientific, catalog number: SC128 )
- Metzenbaum scissors (Braintree Scientific, catalog number: SC126 )
- Micro scissors (Braintree Scientific, catalog number: SC152 )
- Hartman Mosquito-Hemostatic forceps (World Precision Instruments, catalog number: 15920 )
- Adson forceps (Braintree Scientific, catalog number: FC028 )
- Micro-Tissue forceps (Braintree Scientific, catalog number: FC145 , FC146 , FC147 )
- Scalpels (Bladex, catalog number: 22-080-087 )
- 35 mm Surgical staples and associated stapler (Ethicon Endo-Surgery, catalog number: TR35B )
- Animal Care Facilities
- Gas sterilization chamber
- Hemocytometer
- Shaking incubator with adjustable temperatures and speeds
- Vein scissors
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2013 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Taff, H. T., Marchillo, K. and Andes, D. R. (2013). Preparation of Candida albicans Biofilms Using an in vivo Rat Central Venous Catheter Model . Bio-protocol 3(14): e823. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.823.
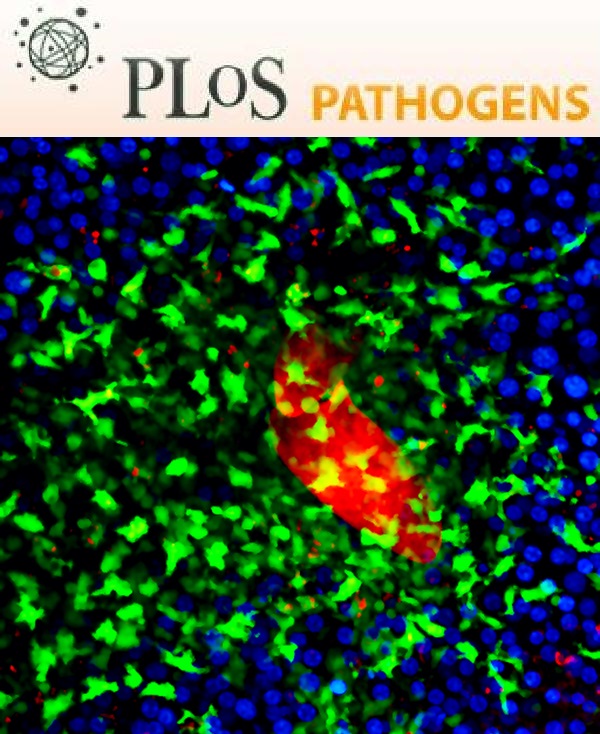
- Taff, H. T., Nett, J. E., Zarnowski, R., Ross, K. M., Sanchez, H., Cain, M. T., Hamaker, J., Mitchell, A. P. and Andes, D. R. (2012). A Candida biofilm-induced pathway for matrix glucan delivery: implications for drug resistance. PLoS Pathog 8(8): e1002848.
分类
微生物学 > 微生物生物膜 > 生物膜培养
微生物学 > 微生物-宿主相互作用 > 体内实验模型 > 哺乳动物
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link