- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Nuclei Isolation Methods on Frozen Clotted Blood Samples
发布: 2026年01月20日第16卷第2期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.5573 浏览次数: 17
评审: Joyce ChiuKarthik Amudhala HemanthakumarAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
It is common practice for laboratories to discard clotted blood or freeze it for future DNA extraction after extracting serum from a serum-separating tube. If freezing for DNA extraction, the blood clot is not usually cryopreserved, which leads to cell membrane fragility. In this protocol, we describe steps to isolate high-quality nuclei from leukocytes derived from whole blood samples frozen without a cryoprotective medium. Nuclei isolated from this protocol were able to undergo ATAC (assay for transposase-accessible chromatin) sequencing to obtain chromatin accessibility data. We successfully characterized and isolated B cells and T cells from leukocytes isolated from previously frozen blood clot using Miltenyi’s gentleMACS Octo Dissociator coupled with flow sorting. Nuclei showed round, intact nuclear envelopes suitable for downstream applications, including bulk sequencing of nuclei or single-cell nuclei sequencing. We validated this protocol by performing bulk ATAC-seq.
Key features
• This protocol is compatible with previously collected blood that has been frozen.
• Previous cryopreservation of the samples is not required for this protocol.
• This protocol enables flow sorting of non-viable leukocytes for a more precise cell population for bulk sequencing experiments.
Keywords: Nuclei dissociationGraphical overview
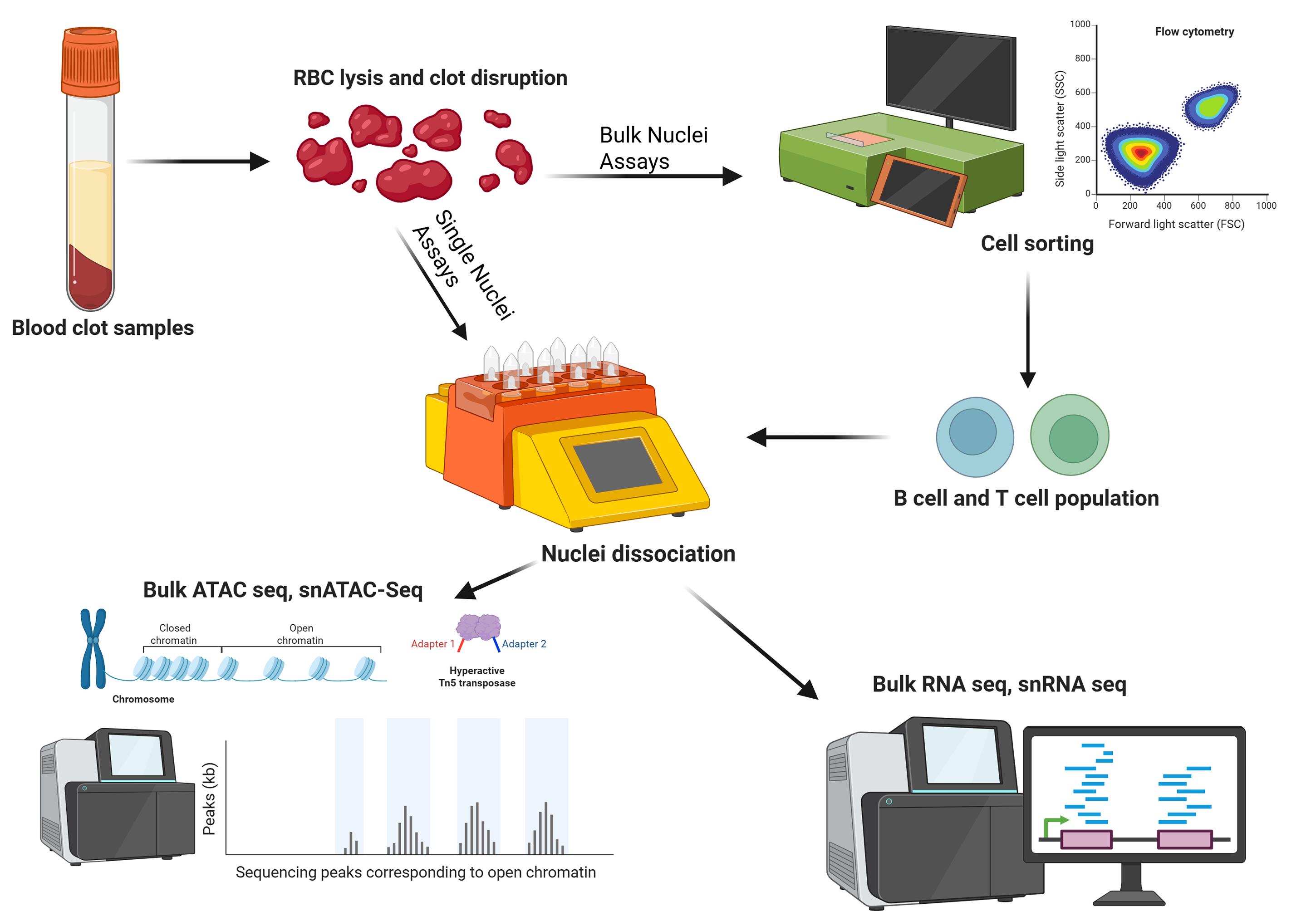
Background
Biobanks are an essential tool in human disease research. Blood samples are ubiquitous in biobanks due to their versatility and ease of collection in clinical settings [1]. Technological advancements in biomedical research continue to elucidate the molecular mechanisms of diseases. However, many biobanks in existence predated these technologies [2–4]; samples are often collected with unspecific future assays in mind, and optimal preservation methods were not always known at the time of collection, especially for samples collected prior to newer technical advances. Blood samples kept in -80 °C freezers without cryoprotectants lose cellular integrity but often have some viable nucleic acids that can be extracted. One common strategy is to extract all the nucleic acids from the entire sample to perform DNA or RNA sequencing [5,6]. While this is useful, all epigenetic modifications are stripped from the DNA, effectively shutting out epigenetic studies from historical samples. Obtaining total mRNA is also challenging with these samples due to high endogenous RNase activity from cell lysis that occurs during freezing without cryoprotectants [7]. The ability to extract nuclei from these samples enables researchers to obtain more data for disease mechanisms with genetic components.
Nuclei-based assays are becoming more popular in the study of molecular mechanisms [8]. Researchers are increasingly investigating variable genetic expression related to diseases by integrating multiple datasets for a more holistic, multiomics approach. The assay for transposase-accessible chromatin using sequencing (ATAC sequencing) is a useful method for mapping chromatin accessibility. Bulk ATAC sequencing and single-nuclei ATAC sequencing both require good-quality nuclei as input, as opposed to whole cells [9–11]. Nuclei can also serve as input for nuclear RNA sequencing and single-nuclei RNA sequencing [12–14]. Even though nuclei sequencing ignores mRNA present in the cytoplasm, important transcriptomic data can still be gathered from samples that are difficult to dissociate into a single-cell suspension or samples with compromised cell membranes.
Here, we describe a protocol to extract nuclei from leukocytes from frozen blood samples. This protocol is useful for applications where blood samples were previously frozen without any cryopreservation or PBMC isolation. It is compatible with fresh blood clot samples in a serum-separating tube, which is incompatible with Ficoll gradient due to the clotting factor present [15]. Additionally, we show that the leukocyte extraction protocol is gentle on fragile cells, allowing cell sorting to be done by flow cytometry prior to nuclei extraction. This enables bulk sequencing assays from a purified population of nuclei, which may be more cost-effective than single-nuclei assays. The flexibility of this protocol makes it adaptable to both frozen and fresh clotted blood, and can help researchers gather valuable data from older, previously banked samples that may still have intact nuclei and mostly intact cell membranes. Flow sorting is successful despite the non-viability of the cells after leukocyte extraction.
This protocol has been validated using frozen blood clot, including flow cytometry and bulk ATAC-seq. Performing flow cytometry steps is only necessary if bulk sequencing is the end goal to isolate nuclei from a homogeneous population. This part of the protocol can be omitted if the endpoint experiment is a single-nuclei assay. We have reliably isolated >700,000 nuclei from one tube of frozen blood clot that was left from an 8.5 mL serum-separating tube after serum was extracted. The volume of blood clot typically left behind is approximately 3 mL. This protocol has also been successfully conducted on fresh clotted blood by adjusting lysis times and running the 4C_Nuclei_1 dissociation protocol twice on a gentleMACS Octo Dissociator. It may be possible to apply this protocol to frozen unclotted blood in EDTA or sodium heparin blood tubes to eliminate the Ficoll gradient step; however, we did not verify these sample types. Miltenyi Biotec product sheets were used as a reference for sections C and D [16,17], but optimization was done for this specific sample type.
Materials and reagents
Biological materials
1. Frozen blood clot
2. Fresh blood clot (optional)
Reagents
1. Bovine serum albumin (BSA) (MilliporeSigma, catalog number: 12660910GM)
2. Flow cytometry antibodies (only applicable if flow sorting)
a. FITC CD3 antibody (Miltenyi Biotec, catalog number: 130-113-700)
b. PE CD19 antibody (Miltenyi Biotec, catalog number: 130-114-172)
c. VioBlue CD11B (Miltenyi Biotec, catalog number: 130-110-616)
d. APC CD11C (Miltenyi Biotec, catalog number: 130-114-110)
e. Other antibodies (optional): Add other suitable antibodies to tailor the cell population of interest
3. Compensation beads (Invitrogen, catalog number: 01-2222-41)
4. Anti-nucleus microbeads (Miltenyi Biotec, catalog number: 130-132-997)
5. RNase inhibitor (Applied Biosystems, catalog number: N8080119)
6. Ethanol 200 proof (Decon, catalog number: 2701)
7. Puregene RBC lysis solution (Qiagen, catalog number: 158106)
8. EDTA (Lonza, catalog number: 51201)
9. Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) (Gibco, catalog number: 10010023)
10. Nuclei extraction buffer (Miltenyi Biotec, catalog number: 130-128-024)
11. Trypan Blue solution, 0.4% (Gibco, catalog number: 15250061)
Solutions
1. 1% BSA (see Recipes)
2. MACS buffer (see Recipes)
3. Lysis buffer (see Recipes)
4. Nuclei separation buffer (see Recipes)
5. Resuspension buffer (see Recipes)
Recipes
Note: All total volumes are per sample.
1. 1% BSA
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| BSA | n/a | 10 mg |
| PBS | n/a | Bring final volume to 1 mL |
2. MACS buffer
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| 1× PBS | n/a | 9.96 mL |
| BSA | 10 mg/mL | 100 mg |
| 0.5 M EDTA | 2 mM | 40 μL |
| Total | n/a | 10 mL |
3. Lysis buffer
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| RNase inhibitor | 0.2 U/μL | 40 μL |
| Nuclei extraction buffer | n/a | 3.96 mL |
| Total | n/a | 4 mL |
4. Nuclei separation buffer
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| RNase inhibitor* | 0.2 U/μL | 80 μL* |
| 1% BSA | 0.04% | 320 μL |
| Nuclei extraction buffer | 14% | 1.12 mL |
| PBS | n/a | 6.56 mL or 6.48 mL* |
| Total | n/a | 8 mL |
*Add RNase inhibitor to this buffer if RNA sequencing is desired as a downstream application.
Adjust PBS volume as necessary.
5. Resuspension buffer
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| RNase inhibitor | 0.2 U/μL | 15 μL |
| 1% BSA | 0.1% | 1.5 μL |
| PBS | n/a | 1483.5 μL |
| Total | n/a | 1.5 mL |
Laboratory supplies
1. Serum-separating tube 8.5 mL (BD Vacutainer, catalog number: 0268396)
2. Serological pipettes 5 mL (Fisherbrand, catalog number: 1367811D)
3. Serological pipettes 10 mL (Fisherbrand, catalog number: 1367811E)
4. Serological pipettes 25 mL (Fisherbrand, catalog number: 1367811)
5. TipOne RPT filter tips P1000 (USA Scientific, catalog number: 1182-1830)
6. TipOne RPT filter tips P200 (USA Scientific, catalog number: 1180-8810)
7. TipOne RPT filter tips P20 (USA Scientific, catalog number: 1180-1810)
8. TipOne RPT filter tips P10 (USA Scientific, catalog number: 1182-3810)
9. Kimwipes (KimClark, catalog number: 066-66A)
10. LS columns (Miltenyi Biotec, catalog number: 130-042-401)
11. QuadroMACS separator (Miltenyi Biotec, catalog number: 30-090-976)
12. gentleMACS C tubes (Miltenyi Biotec, catalog number: 130-093-237)
13. MTCTM Bio Screw Cap MacroTubes® 5 mL (MTC Bio, catalog number: MTCC2545)
14. 15 mL conical tubes (Nunc, catalog number: 12-656-269)
15. 50 mL conical tubes (Nunc, catalog number: 12-565-271)
16. Microcentrifuge tubes (Thermo Fisher, catalog number: 3541)
17. Cryovials (Genesee Scientific, catalog number: 24-202P) (only for optional freezing of leukocyte aliquots)
18. MACS SmartStrainers 70 μm (Miltenyi Biotec, catalog number: 130-098-462)
19. MACS SmartStrainers 30 μm (Miltenyi Biotec, catalog number: 130-098-458)
20. 5 mL Polyprene round-bottom tube (Falcon, catalog number: 352063) (only for flow sorting with drop-based cell sorters such as Sony MA900)
21. HighSpeed MACSQuant Tyto cartridge (Miltenyi Biotec, catalog number: 130-121-549) (only required if using Miltenyi MACSQuant Tyto Cell Sorter)
Equipment
1. Water bath
2. Centrifuge with cooling capability that accommodates 15 and 50 mL conical tubes (Beckman Coulter Allegra X-30 or equivalent)
3. Microcentrifuge with cooling capability (SorvallTM LegendTM Micro 17R Microcentrifuge, catalog number: 75002440 or equivalent)
4. Vortexer
5. Rocker (Benchmark Scientific, catalog number: BR2000 or equivalent)
6. Serological pipette controller (Eppendorf, catalog number: 4430000018 or equivalent)
7. Micropipettes (Eppendorf, catalog number: 2231001168 or equivalent)
8. gentleMACS Octo Dissociator (Miltenyi Biotec, catalog number: 130-095-937)
9. gentleMACS Octo Coolers (Miltenyi Biotec, catalog number: 130-130-533)
10. MACS MultiStand (Miltenyi Biotec, catalog number: 130-042-303)
11. Cell Sorter
Note: This protocol has been verified using both the Miltenyi MACSQuant Tyto Cell Sorter and the Sony MA900 Multi Application Cell Sorter.
Software and datasets
1. Adobe PDF (version 2025.001.20997)
2. Photoviewer (for microscopy image viewing)
Note: All gentleMACS Octo dissociator programs used in this protocol were pre-programed into the device. We did not modify any programs. The Multi_A_01 protocol used on the gentleMACS Octo Dissociator takes 36 s in total duration, with 268 total rounds per run. The 4C_nuclei_1 takes 5 min and 15 s in total duration, with 2415 total rounds per run. Both devices used for flow cytometry export results as PDF.
Procedure
文章信息
稿件历史记录
提交日期: Oct 31, 2025
接收日期: Dec 10, 2025
在线发布日期: Dec 29, 2025
出版日期: Jan 20, 2026
版权信息
© 2026 The Author(s); This is an open access article under the CC BY license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
如何引用
Cuevas, M., Jones, K. and Miller, N. H. (2026). Nuclei Isolation Methods on Frozen Clotted Blood Samples. Bio-protocol 16(2): e5573. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.5573.
分类
分子生物学
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link








