- EN - English
- CN - 中文
PhosphoLIMBO: An Easy and Efficient Protocol to Separate and Analyze Phospholipids by HPTLC From Plant Material
PhosphoLIMBO:一种基于HPTLC的植物材料磷脂分离与分析简便高效方法
(*contributed equally to this work) 发布: 2025年09月05日第15卷第17期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.5434 浏览次数: 1331
评审: Nona FarbehiAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
Phospholipids are major structural and regulatory elements of biological membranes and are involved in many different cellular and physiological processes. In this protocol, we provide an easy, cost-effective, and efficient method to obtain an overview of the phospholipid composition using high-performance thin layer chromatography (HPTLC). While the currently known phospholipid separation methods based on HPTLC display co-migration of certain lipid classes, the method we describe here allows the separation of all phospholipid classes, including anionic phospholipids in plant samples. This protocol combines elements of the classical Vitiello and Touchstone solvent systems to optimize phospholipid separation in a scaled pattern. Here, we provide a full characterization of this method, including statistical analyses of the retention factor of each phospholipid to show the robustness of the method and its efficiency in separating all phospholipid classes of a biological sample.
Key features
• Analysis of phospholipid composition through an easy, fast, robust, and cost-effective HPTLC method.
• Separation of anionic phospholipids from the other phospholipid species.
• Full overview of all phospholipids categories, including anionic phospholipids.
• Qualitative and quantitative approach.
Keywords: Plant biology (植物生物学)Graphical overview
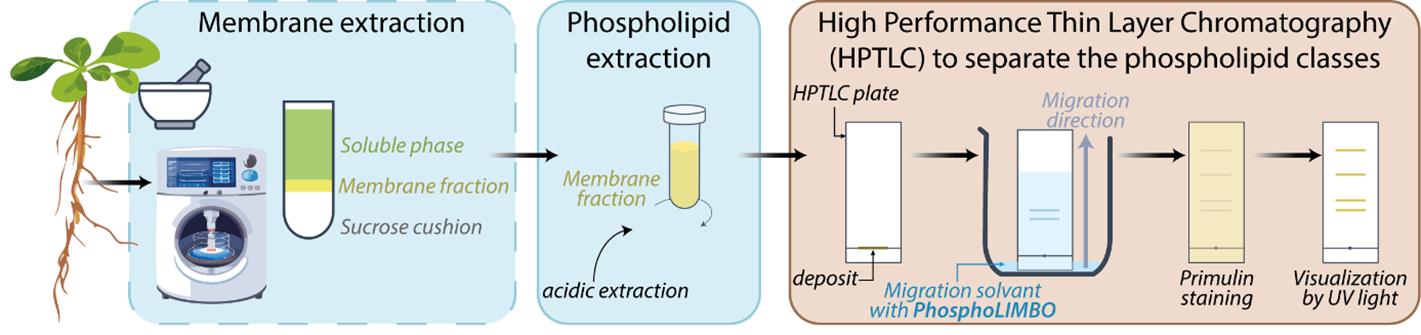
Background
Lipids are major molecular and cellular actors due to the structural properties they confer to cellular membranes and their functional roles in, but not limited to, cell signaling, intracellular trafficking, cell division, cell growth, and differentiation [1]. Lipids are classified into different classes according to their chemical structure, of which three main classes are predominant: glycerolipids, sphingolipids, and sterols. Glycerolipids are the most abundant class of lipids in plants and comprise diacylglycerol (DAG), triacylglycerols (TAG), glycolipids such as galactolipids [e.g., monogalactosyldiacylglycerol (MGDG), digalactosyldiacylglycerol (DGDG), and the sulpholipid sulfoquinovosyl diacylglycerol (SQDG)], and phosphoglycerides, commonly named phospholipids. Depending on the nature of the hydrophilic group attached to the phosphate, phospholipids are ranked into different categories: neutral, as phosphatidylglycerol (PG), phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) and phosphatidylcholine (PC), or anionic phospholipids, as phosphatidic acid (PA), phosphatidylserine (PS), and phosphadylinositol (PI) and its phosphate derivatives phosphatidylinositol-phosphate (PIPs) and phosphatidylinositol-biphosphate (PIP2) [2]. PC is the most abundant phospholipid [around 20% in the plant plasma membrane (PM)]. At the PM, anionic phospholipids are less prominent, with PI and PS each representing around 5%, and PIPs and PIP2 representing less than 1% [3]. Glycerolipids have been shown to be involved in a wide range of physiological processes in plants. Glycolipids are important for photosynthesis, early plant development before photosynthesis establishes (lipid droplets in seeds), and resistance to environmental stresses such as phosphate starvation [4,5]. Phospholipids are important structural elements of the membranes; anionic phospholipids, despite their low abundance, have been shown to be crucial lipids to cell signaling, polar trafficking, autophagy, cell division, and cell–cell communication [1,6–10]. Thus, the detection and quantification of glycerolipids, including glycolipids, phospholipids, and anionic phospholipids, is crucial in lipid research.
Protocols for the detection and quantification of glycerolipids by liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry (LC–MS/MS) have been deployed previously [11,12]. However, the accessibility of LC–MS/MS equipment and the expertise required to run and interpret mass-spectrometry results might be a bottleneck. High-performance thin layer chromatography (HPTLC) allows the separation of phospholipids from a lipid extract. HPTLC is an accessible, fast, and cost-effective method. A widely used method to detect phosphoglycerolipids is based on the radioactive element 32Pi to maximize sensitivity, allowing quantification of anionic phospholipids [13]. Radioactive-free methods exist and are commonly based on Vitiello and Touchstone protocols [14,15]. However, these methods have some limitations. PA/PG are not separated using the Vitiello solvent mix, while PE/PI are not separated using the Touchstone method. In the same way, in yeast, the solvent mix classically used cannot separate PI/PS [16,17]. The same issue was reported in murine skin melanoma cells [18]. In addition, in all these methods, PIPs and PIP2 are stuck close to the deposit line and are not mobilized during migration [14,15]. In this protocol, we optimize a solvent mix that we called PhosphoLIMBO (for PhosphoLIpid Migration Best Optimization and in reference to the limbo dance, where the goal is to pass under a scale). This protocol enables the separation in a scaled pattern of all species of glycerolipids extracted from a microsomal fraction of Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings. Our method is based on a combination of several published protocols [14,15], is radioactive-free, easy, and cost-effective to implement, and has already been successfully used in several publications [3,19].
Materials and reagents
Biological materials
1. Columbia-0 (Col-0) seeds (NASC, catalog number: CS1093)
Reagents
1. Bleach (Manutan, catalog number: LJ26659A)
2. Murashige and Skoog powder (Duchefa Biochemie, catalog number: M0222.0050)
3. HEPES (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: H4034-500G)
4. Potassium hydroxide (KOH) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P5958-500G)
5. Sucrose (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 84100-1KG)
6. Magnesium chloride (MgCl2) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 208337-100G)
7. Dithiothreitol (Euromedex, catalog number: EU0006-D)
8. Polyvinylpyrrolidone (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P2307-100G)
9. Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF) (Roche, catalog number: 10837091001)
10. Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D8418-250ML)
11. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: ED4SS-1KG)
12. Cocktail protease inhibitor (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P9599-5ML)
13. Chloroform (Fisher Chemical, catalog number: C/4960/17)
14. Methanol (Fisher Chemical, catalog number: M/4062/17)
15. Hydrochloric acid (HCl) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 320331-2.5L)
16. 2-Propanol (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 33539-2.5L-M)
17. Potassium chloride (KCl) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P9333-500G)
18. Methyl acetate (Acros Organics, catalog number: 181380025)
19. Triethylamine (Acros Organics, catalog number: 157910010)
20. HPTLC Silica gel 60 F254 20 × 10 cm (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 1.05642.0001)
21. Sodium chloride (NaCl) (Euromedex, catalog number: 1112-A)
22. Potassium phosphate monobasique (KH2PO4) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P5655-500G)
23. Di-sodium hydrogen phosphate (Na2HPO4) (Euromedex, catalog number: 1309)
24. Brain phosphatidylinositol-4,5-biphosphate (PI4,5P2) (Avanti polar lipid, catalog number: 850155P)
25. 18:1 phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate (PI4P) (Avanti polar lipid, catalog number: 850151P)
26. 18:1 phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate (PI3P) (Avanti polar lipid, catalog number: 850150P)
27. Soybean phosphatidylinositol (PI) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 79401)
28. Soybean phosphatidylserine (PS) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P0474)
29. Egg yolk phosphatidylcholine (PC) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P3556)
30. Egg yolk phosphatidic acid (PA) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P9511)
31. Egg yolk phosphatidyl ethanolamine (PE) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P6386)
32. Egg yolk lecithin phosphatidyl glycerol (PG) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P8318)
33. β-Sitosterol (Avanti polar lipid, catalog number: 700095P)
34. Plant MGDG (Avanti polar lipid, catalog number: 840523)
35. Plant DGDG (Avanti polar lipid, catalog number: 840524)
36. 20:0 MG (NU-CHEK PREP, catalog number: M-174)
37. 18:1 DG (Avanti polar lipid, catalog number: 800811)
38. 1,3-Dioleoyl-2-palmitoylglycerol (TG) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D1657)
39. MilliQ water (H2O) (sterile and non sterile)
40. Acetone (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 32201-2.5L-M)
41. Primulin (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 206865-5G)
Solutions
1. HEPES solution (see Recipes)
2. 2 M MgCl2 (see Recipes)
3. 1 M Dithiothreitol (see Recipes)
4. Membrane extraction buffer (see Recipes)
5. PMSF solution (see Recipes)
6. 38% sucrose solution (see Recipes)
7. Membrane resuspension buffer (see Recipes)
8. 0.25% KCl (see Recipes)
9. 2 M HCl (see Recipes)
10. 1 M HCl (see Recipes)
11. 0.01 M HCl (see Recipes)
12. Phospholipid extraction “Kill” mix (see Recipes)
13. Phospholipid wash mix (see Recipes)
14. 10× PBS (see Recipes)
15. Migration solvent mix, PhosphoLIMBO (see Recipes)
16. Primulin solution (see Recipes)
Recipes
Note: For safety reasons, we recommend using solvents under an extractor hood and wearing personal protective equipment: gloves, lab coat, and safety goggles. When using acids such as HCl, always add the acid to the water with the same safety measures as for solvents.
1. HEPES solution
| Reagent | Final concentration | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| HEPES | 50 mM | 12 g |
| H2O | n/a | 1,000 mL |
Adjust pH to 7.5 with KOH.
Note: Can be stored at 4 °C for a few months.
2. 2 M MgCl2
| Reagent | Final concentration | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| MgCl2 | 2 M | 9.52 g |
| H2O | n/a | 50 mL |
Note: The MgCl2 powder must be added very cautiously inside glass containers (due to exothermic reaction in water).
3. 1 M Dithiothreitol
| Reagent | Final concentration | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Dithiothreitol | 1 M | 7.712 g |
| H2O | n/a | 50 mL |
Note: Can be stored at -20 °C for a few months.
4. Membrane extraction buffer
| Reagent | Final concentration | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Sucrose | 0.45 M | 77 g |
| MgCl2 | 5 mM | 1.25 mL (from 2 M stock solution) |
| Dithiothreitol | 1 mM | 500 μL (from 1 M stock solution) |
| Polyvinylpyrrolidone | 0.5 g/100 mL | 2.5 g |
| HEPES (50 mM, pH 7.5) | n/a | 500 mL |
Note: Can be stored at -20 °C for a few months.
5. PMSF solution
| Reagent | Final concentration | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| PMSF | 100 mM | 0.174 g |
| DMSO | n/a | 10 mL |
PMSF 1 mM needs to be prepared freshly in the membrane extraction buffer.
Note: Can be stored at -20 °C for a few months.
6. 38% sucrose solution
| Reagent | Final concentration | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Sucrose | 38 g/100 mL | 38 g |
| HEPES (50 mM, pH 7.5) | n/a | 100 mL |
Note: Can be stored at -20 °C for a few months.
7. Membrane resuspension buffer
| Reagent | Final concentration | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Sucrose | 0.25 M | 0.34 g |
| MgCl2 (2 M) | 1.5 mM | 3 μL |
| EDTA (0.5 M, pH8) | 0.2 mM | 1.6 μL |
| NaCl (5 M) | 150 mM | 120 μL |
| HEPES (50 mM, pH 7.5) | n/a | 4 mL |
| PMSF | 1 mM | 40 μL |
| Cocktail Protease Inhibitor | 1 mL/100 mL | 40 μL |
Note: PMSF and cocktail protease inhibitor must be added at the last moment and kept on ice.
8. 0.25% KCl
| Reagent | % solution | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| KCl | 0.25% | 0.25 g |
| Water | n/a | 100 mL |
9. 2 M HCl
| Reagent | Final concentration | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| HCl (37% fumant) | 2 M | 9.86 mL |
| Water | n/a | 30.14 mL |
10. 1 M HCl
| Reagent | Final concentration | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| HCl (2 M) | 1 M | 25 mL |
| Water | n/a | 50 mL |
11. 0.01 M HCl
| Reagent | Final concentration | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| HCl (1 M) | 0.01 M | 500 μL |
| Water | n/a | 50 mL |
12. Phospholipid extraction “Kill” mix
| Reagent | % solution | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Methanol | 64.57% | 484 mL |
| Chloroform | 32.29% | 242 mL |
| HCl (1 M) | 3.14% | 24 mL |
| Total | n/a | 750 mL |
Shake vigorously by hand.
13. Phospholipid wash mix
| Reagent | % solution | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Methanol | 26.66% | 12 mL |
| Chloroform | 53.34% | 24 mL |
| HCl (0.01 M) | 20% | 9 mL |
| Total | n/a | 45 mL |
Shake vigorously by hand. Let the solution stabilize for a few minutes in a two-phase solution.
14. 10× PBS
| Reagent | Final concentration | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Na2HPO4·2H2O | 2.05 g/L | 2.05 g |
| KH2PO4 | 240 mg/L | 0.24 g |
| NaCl | 800 mg/L | 0.8 g |
| KCl | 200 mg/L | 0.2 g |
| Water | n/a | 1,000 mL |
Adjust pH at 7.4. Shake vigorously by hand.
Note: Can be stored at room temperature on the bench.
15. Migration solvent mix, PhosphoLIMBO
| Reagent | Final concentration | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Chloroform | 30.3% | 5 mL |
| Methanol | 10.4% | 1.7 mL |
| 2-propanol | 24.2% | 4. mL |
| KCl (0.25%) | 7.9% | 1.3 mL |
| Methyl acetate | 24.2% | 4 mL |
| Triethylamine | 3% | 0.5 mL |
Note: We recommend preparing it freshly.
16. Primulin solution
| Reagent | Final concentration | Amount |
| Primulin | 0.1 g/L | 20 mg |
| Acetone | 50% | 100 mL |
| PBS (10×) | 1× | 20 mL |
| Water | n/a | 80 mL |
Shake vigorously by hand and let it sit for some minutes on the bench.
Note: We recommend preparing it freshly.
Laboratory supplies
1. Microtube SafeSeal 1.5 mL (Sarstedt, catalog number: 72.706.400)
2. Microtube SafeSeal, 2 mL, PP, Biosphere® plus (Sarstedt, catalog number: 72.695.200)
3. Falcon 50 (Sarstedt, catalog number: 62.547.254)
4. Falcon 15 (Sarstedt, catalog number: 62.554.502)
5. Erlenmeyer flask Duran® with baffles, GL 45, with 4 baffles, with membrane cap and PP pouring ring (Duran, catalog number: WD21283445)
6. Mortar HaldenwangerTM L 55/3/GLASIERT (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 10053504)
7. Pestle HaldenwangerTM L 56/00/RAUH (Fischer Scientific, catalog number: 10405011)
8. Short stem funnel (Duran, catalog number: DWK213514103-10EA)
9. Gauze Miracloth (Millipore, catalog number: 475855)
10. 2 mL HPLC vials (Agilent, catalog number: 5182-0714)
11. Pasteur glass pipette (FisherbrandTM, catalog number: 11566963)
12. CAMAG® twin trough chamber for 20 × 10 cm plates, with stainless steel lid (CAMAG, catalog number: 022.5254)
13. FLACON 50 mL SVL 25 (Pyrex, catalog number: 203924)
14. Glass recipient (large enough to hold the plate) (Pyrex, catalog number: 234B000)
Equipment
1. Autoclave PBI Stematic III (GEMINI, catalog number: 05523)
2. Table shaker (Infors HT, Orbitron)
3. Balances (Sartorius)
4. Scientific Industries SITM Vortex-GenieTM 2 (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 15547335)
5. Centrifuge for Falcon50 (Beckman Coulter, Allegra21R)
6. Centrifuge for Eppendorfs (Eppendorf®, Centrifuge 5425 G, catalog number: EP5405000760-1EA)
7. Ultracentrifuge (Thermo ScientificTM, SorvallTM WX+, catalog number: 15362177)
8. Ultracentrifuge rotors for 12 mL tubes (Thermo Scientific™, Rotor swing-out TH-641, catalog number: 12161690)
9. Dosage syringe 100 μL for Linomat (CAMAG, catalog number: 695.0014)
10. Semi-automatic sample dispenser (CAMAG, Linomat 5, catalog number: 022.7808)
11. ChemiDoc MP imaging system (Bio-Rad, model: ChemiDocTM XRS, catalog number: 1708265)
Software and datasets
1. VisionCATs software (version 2.5, September 2019)
2. Image LabTM software (version 5.1, February 2014)
3. FIJI, Image J (version 1.53t, August 2022)
Procedure
文章信息
稿件历史记录
提交日期: May 13, 2025
接收日期: Jul 30, 2025
在线发布日期: Aug 11, 2025
出版日期: Sep 5, 2025
版权信息
© 2025 The Author(s); This is an open access article under the CC BY license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
如何引用
Fougère, L., Moreau, H., Mirande-Bret, C., Fouillen, L. and Boutté, Y. (2025). PhosphoLIMBO: An Easy and Efficient Protocol to Separate and Analyze Phospholipids by HPTLC From Plant Material. Bio-protocol 15(17): e5434. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.5434.
分类
植物科学 > 植物生物化学 > 脂质
生物化学 > 脂质 > 膜脂
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link