- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Production of Homogeneous, Functional Zinc-Finger Arrays in High Yield With Two Chromatographic Steps
两步层析高效制备均一且具功能性的锌指蛋白阵列
(§Technical contact: liangjch@stanford.edu) 发布: 2025年08月20日第15卷第16期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.5420 浏览次数: 1468
评审: Navnita DuttaAnonymous reviewer(s)

相关实验方案
Cluster FLISA——用于比较不同细胞系蛋白表达效率及蛋白亚基聚集状态的方法
Sabrina Brockmöller and Lara Maria Molitor
2025年11月05日 1204 阅读

适用于 LC–MS/MS 蛋白质组学分析的大体积细胞培养上清分泌组样品制备方法优化
Basil Baby Mattamana [...] Peter Allen Faull
2025年12月20日 1208 阅读
Abstract
Zinc-finger (ZF) arrays are compact, sequence-specific polynucleotide-binding domains, which have been used to target the delivery of diverse effector domains, enabling applications such as gene identification, localization, regulation, and editing. To facilitate in vitro applications of ZF arrays, we have developed a general method for their expression and purification. Here, we describe a protocol involving two chromatographic steps that yields homogeneous and functional ZF arrays in milligram quantities.
Key features
• A general method for expressing and purifying C2H2 ZF arrays in E. coli, compatible with both natural and artificial ZFs.
• The His-SUMO tag improves ZF-array solubility, eliminating the need for denaturation and refolding steps.
• Simple, two-step purification yields milligram-scale ZF arrays suitable for downstream applications.
Keywords: Zinc fingers (锌指蛋白)Graphical overview
Background
Zinc-finger (ZF) proteins—initially identified in Xenopus laevis transcription factor IIIA [1]—are DNA-binding domains found in the most prevalent family of transcription factors in metazoans [2–4]. ZFs adopt a variety of structural motifs, among which the most abundant and well-studied is that of the C2H2 family, which comprises between 28 and 30 amino acids, including two cysteine and two histidine residues that tetrahedrally coordinate the central zinc ion [5,6]. The “recognition helix” of the resulting ββα fold projects into the major groove of DNA, forming hydrogen bonds with three consecutive base pairs [7,8]. The recognition of extended sequences is made possible by the assembly of ZFs in tandem to form polydactyl arrays [6,9–14]. Because the specificity of each finger is affected by its neighbors [9], the development of polydactyl arrays has posed considerable challenges. Recently, these challenges have been mitigated by the advent of deep-learning methods, enabling the design of ZF arrays targeting arbitrary DNA sequences [15].
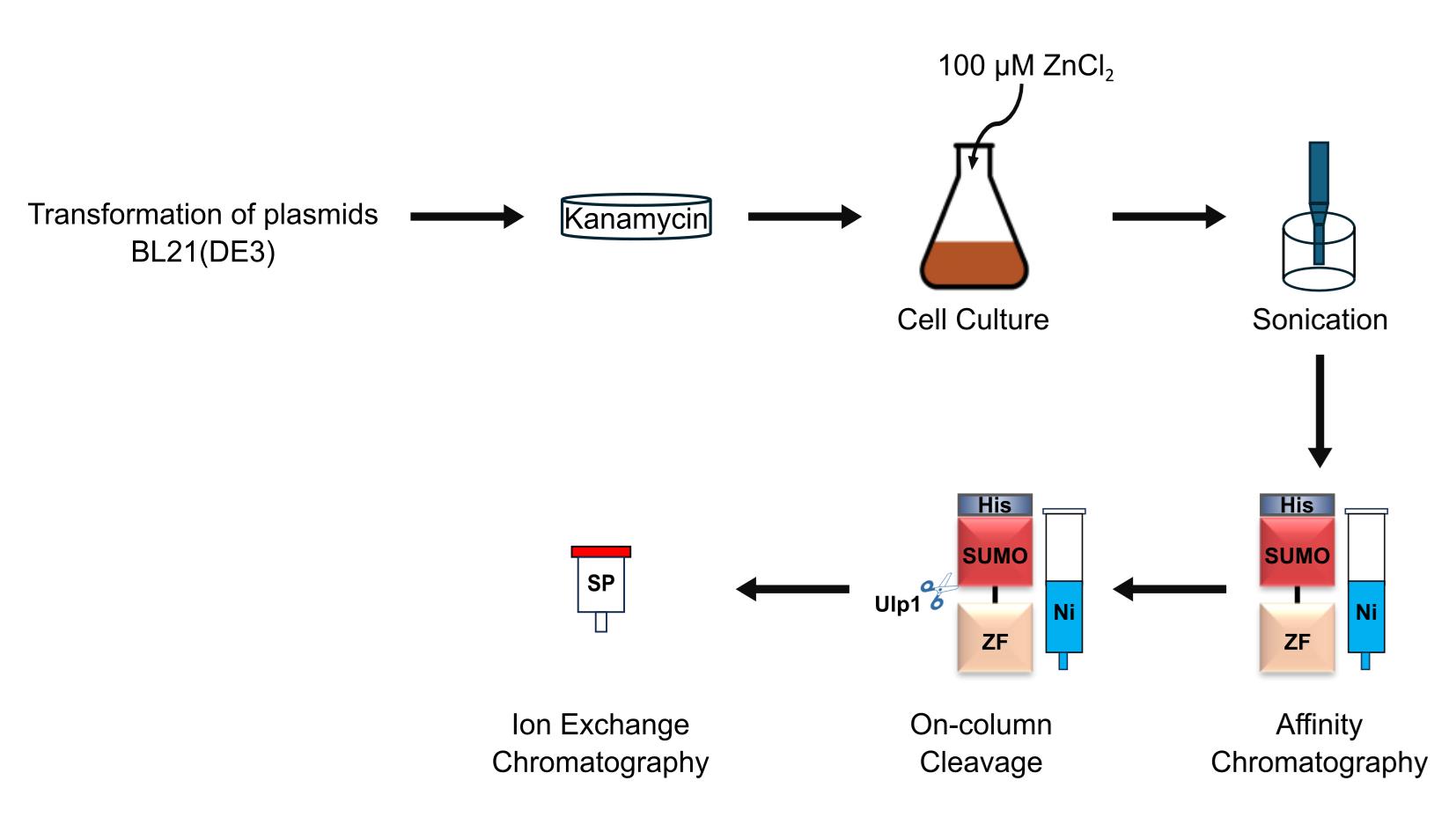
ZF arrays are commonly expressed directly in target cells by the introduction of transgenic expression constructs [16–20]. An alternative approach, involving purified ZF arrays, has demonstrated certain advantages, such as greater efficiencies and lower off-target rates in gene editing by ZF nucleases [21]. However, the production of ZF arrays in suitable amounts and purity for exogenous delivery has been hitherto challenging, as there has been a need to optimize the expression and purification procedures for each new ZF array [22–30]. Existing strategies include the use of an affinity tag—polyhistidine (His-tag) [22–24], glutathione S-transferase (GST) [25,26], or maltose-binding protein (MBP) [27,28]—and the exploitation of biochemical properties of ZFs, such as their coordination to zinc ions or their specific binding to DNA sequences [29,30]. To avoid the requirement of tailoring procedures to each unique ZF array, we developed a simple and general method, based on the His-SUMO tag, for the expression and purification of functional ZF arrays in milligram quantities [31]. We present the procedure here in full detail.
Materials and reagents
A. Expression of ZF arrays in E. coli BL21 (DE3)
1. pET-28a-SUMO-ZF plasmids (Genewiz)
2. QIAprep® Spin Miniprep kit (QIAGEN, catalog number: 27104)
3. BL21 (DE3) competent E. coli (New England Biolabs, catalog number: C2527H)
4. Tryptone (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: BP14212)
5. Yeast extract (USBiological, catalog number: Y2008)
6. Kanamycin sulfate (Teknova, catalog number: K2150)
7. Agar (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: A360-500)
8. Sodium chloride (NaCl) (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: BP358-212)
9. Zinc chloride (ZnCl2) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: Z0152)
10. Isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) (GOLDBIO, catalog number: I2481C100)
B. Purification of ZF arrays in E. coli BL21 (DE3)
1. Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P7626-250MG)
2. Benzamidine hydrochloride monohydrate (GOLDBIO, catalog number: B-050-500)
3. Pepstatin A (GOLDBIO, catalog number: P-020-100)
4. Leupeptin hemisulfate (GOLDBIO, catalog number: L-010-100)
5. Absolute ethanol (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: BP2818-4)
6. Ni-NTA Superflow (QIAGEN, catalog number: 1018611)
7. PierceTM Bradford Plus Protein Assay Reagent (Thermo Scientific, catalog number: 23238)
8. HiTrapTM SP HP column (Cytiva, catalog number: 17115101)
9. Tris base (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: BP1521)
10. Hydrochloric acid (HCl) ~37% (Thermo Scientific, catalog number: LC149501)
11. Imidazole (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 56750-500g)
12. 2-Mercaptoethanol (MP, catalog number: 190242)
13. L-Arginine (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 11009-100G)
14. Coomassie Brilliant Blue R-250 Dye (Thermo Scientific, catalog number: 20278)
15. 2-Propanol (J.T. Baker, catalog number: 9084-01)
16. Acetic acid (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: A38SI-212)
17. NuPAGETM Bis-Tris Mini Protein Gels, 4%–12%, 1.0–1.5 mm (Invitrogen, catalog number: NP0321BOX)
18. 2-(N-Morpholino)ethanesulfonic acid (MES) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M3671)
19. Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) (Invitrogen, catalog number: 15525-017)
20. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: BP120-1)
21. Precision Plus ProteinTM Dual Color Standards (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 1610374)
22. Ulp1 (home-made, Addgene plasmid #229224) or commercial SUMO Protease (Invitrogen, catalog number: 12588-018)
Solutions
1. LB medium (see Recipes)
2. LB agar (see Recipes)
3. Kanamycin stock (1,000×) (see Recipes)
4. ZnCl2 stock (0.1 M) (see Recipes)
5. IPTG stock (1 M) (see Recipes)
6. PMSF stock (100×) (see Recipes)
7. Protease inhibitor cocktail stock (200×) (see Recipes)
8. Imidazole stock, pH 7.5 (5 M) (see Recipes)
9. L-Arginine stock (1M) (see Recipes)
10. NaCl stock (5 M) (see Recipes)
11. Tris-HCl, pH 7.5 (1 M) (see Recipes)
12. Coomassie Brilliant Blue R-250 staining solution (see Recipes)
13. Lysis buffer (see Recipes)
14. Wash buffer (see Recipes)
15. Cleavage buffer A (see Recipes)
16. Cleavage buffer B (see Recipes)
17. Stock buffer (see Recipes)
18. 20× MES SDS running buffer (see Recipes)
Recipes
1. LB medium
| Reagent | Final concentration | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Tryptone | 10 g/L | 10 g |
| Yeast extract | 5 g/L | 5 g |
| Sodium chloride | 10 g/L | 10 g |
| Double-distilled water (ddH2O) | N/A | Up to 1 L |
Autoclave the LB medium and store at room temperature.
2. LB agar plates
| Reagent | Final concentration | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Tryptone | 10 g/L | 10 g |
| Yeast extract | 5 g/L | 5 g |
| Sodium chloride | 10 g/L | 10 g |
| Agar | 15 g/L | 15 g |
| ddH2O | N/A | Up to 1 L |
Autoclave the prepared LB Agar. Allow it to cool to approximately 50 °C, then add antibiotics, mix thoroughly, and pour plates immediately. Store the prepared LB agar plates inverted at 4 °C.
3. Kanamycin stock (1,000×)
| Reagent | Final concentration | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Kanamycin sulfate | 50 mg/mL | 2.5 g |
| ddH2O | N/A | Up to 50 mL |
Sterilize the solution by passing it through a 0.22 μm polyethersulfone filter and store at -20 °C.
4. ZnCl2 stock (0.1 M)
| Reagent | Final concentration | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Zinc chloride | 0.1 M | 13.628 g |
| ddH2O | N/A | Up to 1 L |
If the powder does not dissolve completely after stirring, add a few drops of concentrated HCl (~37%) while stirring to facilitate dissolution. Sterilize the solution by passing it through a 0.22 μm polyethersulfone filter and store at room temperature.
5. IPTG stock (1 M)
| Reagent | Final concentration | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| IPTG | 1 M | 11.915 g |
| ddH2O | N/A | Up to 50 mL |
Sterilize the solution by passing through a 0.22 μm polyethersulfone filter and store at -20 °C.
6. PMSF stock (100×)
| Reagent | Final concentration | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| PMSF | 100 mM | 1.7419 g |
| Absolute ethanol | N/A | Up to 100 mL |
Store at -20 °C.
7. Protease inhibitor cocktail stock (200×)
| Reagent | Final concentration | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Benzamidine hydrochloride monohydrate | 0.4 M | 3.1322 g |
| Pepstatin A | 0.4 mM | 13.7178 mg |
| Leupeptin hemisulfate | 0.12 mM | 2.8536 mg |
| Absolute ethanol | N/A | Up to 50 mL |
Store at -20 °C.
8. Imidazole stock, pH 7.5 (5 M)
| Reagent | Final concentration | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Imidazole | 5 M | 340.4 g |
| HCl | N/A | Adjust pH to 7.5 |
| ddH2O | N/A | Up to 1 L |
Wrap the bottle with aluminum foil to protect from light and store at room temperature.
9. L-Arginine stock (1 M)
| Reagent | Final concentration | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| L-Arginine | 1 M | 174.2 g |
| HCl | N/A | Adjust pH to 7.5 |
| ddH2O | N/A | Up to 1 L |
Store at room temperature.
10. NaCl stock (5 M)
| Reagent | Final concentration | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Sodium chloride | 5 M | 292.2 g |
| ddH2O | N/A | Up to 1 L |
Store at room temperature.
11. Tris-HCl, pH 7.5 (1 M)
| Reagent | Final concentration | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Tris base | 1 M | 121.14 g |
| HCl | N/A | Adjust pH to 7.5 |
| ddH2O | N/A | Up to 1 L |
Store at room temperature.
12. Coomassie Brilliant Blue R-250 staining solution
| Reagent | Final concentration | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Coomassie Brilliant Blue R-250 Dye | 1 g/L | 1 g |
| 2-Propanol | N/A | 250 mL |
| Acetic acid | N/A | 100 mL |
| ddH2O | N/A | Up to 1 L |
Mix completely and store at room temperature.
13. Lysis buffer
| Reagent | Final concentration | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Tris-HCl, pH 7.5 (1 M) | 20 mM | 20 mL |
| NaCl stock (5 M) | 2 M | 400 mL |
| Imidazole stock, pH 7.5 (5 M) | 10 mM | 2 mL |
| ZnCl2 stock (0.1 M) | 100 μM | 1 mL |
| ddH2O | N/A | Up to 1 L |
Store at 4 °C.
14. Wash buffer
| Reagent | Final concentration | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Tris-HCl, pH 7.5 (1 M) | 20 mM | 20 mL |
| NaCl stock (5 M) | 500 mM | 100 mL |
| Imidazole stock, pH 7.5 (5 M) | 60 mM | 12 mL |
| ZnCl2 stock (0.1 M) | 100 μM | 1 mL |
| ddH2O | N/A | Up to 1 L |
Store at 4 °C.
15. Cleavage buffer A
| Reagent | Final concentration | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Tris-HCl, pH 7.5 (1 M) | 20 mM | 20 mL |
| NaCl stock (5 M) | 100 mM | 20 mL |
| ZnCl2 stock (0.1 M) | 100 μM | 1 mL |
| L-Arginine stock (1M) | 100 mM | 100 mL |
| 2-Mercaptoethanol | 5 mM | 340 μL |
| ddH2O | N/A | Up to 1 L |
Prepare the solution freshly before use and store at 4 °C.
16. Cleavage buffer B
| Reagent | Final concentration | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Tris-HCl, pH 7.5 (1 M) | 20 mM | 20 mL |
| NaCl stock (5 M) | 1 M | 200 mL |
| ZnCl2 stock (0.1 M) | 100 μM | 1 mL |
| L-Arginine stock (1 M) | 100 mM | 100 mL |
| 2-Mercaptoethanol | 5 mM | 340 μL |
| ddH2O | N/A | Up to 1 L |
Prepare the solution freshly before use and store at 4 °C.
17. Stock buffer
| Reagent | Final concentration | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Tris-HCl, pH 7.5 (1 M) | 20 mM | 20 mL |
| NaCl stock (5 M) | 100 mM | 20 mL |
| ZnCl2 stock (0.1 M) | 100 μM | 1 mL |
| L-Arginine stock (1 M) | 100 mM | 100 mL |
| ddH2O | N/A | Up to 1 L |
Store at 4 °C.
18. 20× MES SDS running buffer
| Reagent | Final concentration | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| MES | 1 M | 97.6 g |
| Tris base | 1 M | 60.6 g |
| SDS | 69.3 mM | 10 g |
| EDTA | 20.5 mM | 3.8 g |
| ddH2O | N/A | Up to 500 mL |
Store at room temperature. The pH of 1× MES SDS running buffer should be 7.3.
Laboratory supplies
1. Thermo Scientific NalgeneTM Rapid-FlowTM sterile disposable bottle-top filters with PES, CN, SFCA or Nylon membranes (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 09-741-07)
2. Petri dish, untreated, UltraCruz® (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, catalog number: sc-516726)
3. FalconTM 50 mL high-clarity conical centrifuge tubes (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 14-432-22)
4. Pyrex® narrow-mouth graduated Erlenmeyer flask (Millipore, catalog number: CLS498050-12EA)
5. Borosilicate glass narrow-mouth Erlenmeyer flasks, 3,000 mL (United Scientific, catalog number: FG4980-3000)
6. Econo-Pac® chromatography columns (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 7321010)
7. Amicon® Ultra centrifugal filter, 3 kDa MWCO (Millipore, catalog number: UFC9003)
Equipment
1. FisherbrandTM IsotempTM general purpose deluxe water baths (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: FSGPD02)
2. Digital incubator (VWR, model: 1525)
3. Refrigerated centrifuge (Eppendorf, model: 5810R)
4. Refrigerated incubator shaker (New Brunswick Scientific, model: Innova 4430)
5. Sonicator (QSONICA, model: Q500)
6. SorvallTM LYNX 6000 superspeed centrifuge (Thermo Scientific, catalog number: 75006591)
7. Roto-Torque® heavy duty rotator (Cole-Parmer, model: 7637)
8. Econo pump (Bio-Rad, model: EP-1)
9. ÄKTA pureTM micro (Cytiva, catalog number: 29302479)
10. XCell SureLockTM Mini-Cell (Invitrogen, catalog number: EI0001)
11. ChemiDocTM MP imaging system (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 12003154)
12. NanoDropTM 2000c Spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific, catalog number: ND-2000C)
13. FiberliteTM F9-6 × 1000 LEX fixed angle rotor for LYNX 6000 superspeed centrifuge (Thermo Scientific, catalog number: 096-061075)
14. FiberliteTM F21-8 × 50y fixed angle rotor with auto-lock for LYNX 4000 and 6000 superspeed centrifuges (Thermo Scientific, catalog number: 096-084275)
Software and datasets
1. UnicornTM 7 for ÄKTA purifier (GE Healthcare, https://www.cytivalifesciences.com/en/us/shop/chromatography/software/unicorn-7)
Procedure
文章信息
稿件历史记录
提交日期: May 12, 2025
接收日期: Jun 27, 2025
在线发布日期: Aug 1, 2025
出版日期: Aug 20, 2025
版权信息
© 2025 The Author(s); This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/).
如何引用
Liang, J., Azubel, M., Wang, G., Nie, Y., Kornberg, R. D., Beel, A. J. and Matteï, P. J. (2025). Production of Homogeneous, Functional Zinc-Finger Arrays in High Yield With Two Chromatographic Steps. Bio-protocol 15(16): e5420. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.5420.
分类
生物化学 > 蛋白质 > 分离和纯化
生物化学 > 蛋白质 > 表达
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link