- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Direct Activity Measurement of Heterotrimeric Gi Proteins and Gq Protein By Effector Pulldown
通过效应蛋白下拉法直接测定异源三聚体Gi蛋白与Gq蛋白的活性
发布: 2025年08月05日第15卷第15期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.5406 浏览次数: 2072
评审: Jibin SadasivanAnonymous reviewer(s)

相关实验方案
基于蛋白筛选策略从合成文库中分离抗原特异性纳米抗体:结合 MACS 的酵母展示筛选与 FLI-TRAP 方法
Apisitt Thaiprayoon [...] Dujduan Waraho-Zhmayev
2026年01月20日 410 阅读
Abstract
Studying G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) activation of heterotrimeric G proteins is crucial for understanding diverse physiological processes and developing novel therapeutics. Traditional methods to assay GPCR activation of G proteins, including assays of second messengers and biosensors, involve complex or indirect procedures. However, second messengers like cAMP and calcium are not direct readouts of GPCR activity due to signaling crosstalk, while biosensors can have undesired consequences due to structural alteration caused by fluorescent protein insertion. Here, we present a streamlined protocol employing GST-tagged bait proteins and epitope-embedded Gα subunits to achieve direct monitoring of Gα activity within cells. This method involves purification of GST-tagged bait constructs from bacteria and subsequent direct interaction studies with GluGlu-tagged Gα proteins expressed in any human cells of interest by including GST-tagged bait proteins in the cell lysis buffer. The approach enables sensitive detection of activated Gα within cells following extracellular stimulation. Advantages of this protocol include high sensitivity, enhanced monitoring of GPCR signaling dynamics under physiologically relevant conditions with minimum alteration in Gα, and the ability to distinguish between highly homologous isoforms within the same Gα family.
Key features
• Improved analysis of GPCR-Gα signaling: Establishes a novel effector pulldown method to monitor Gα activation within cells.
• Endogenous GPCR activity measurement with increased sensitivity: Enables assays of endogenous physiological GPCR activities with improved sensitivity by increasing sample sizes.
• Epitope Incorporation without affecting functions: Uses epitope tag sequence with a few amino acid substitutions functioning like wild-type proteins, adaptable for any endogenous Gα assay if suitable antibodies are available.
• Isoform distinction: Distinguishes Gα isoforms by using embedded epitope.
Keywords: GPCR (GPCR)Graphical overview
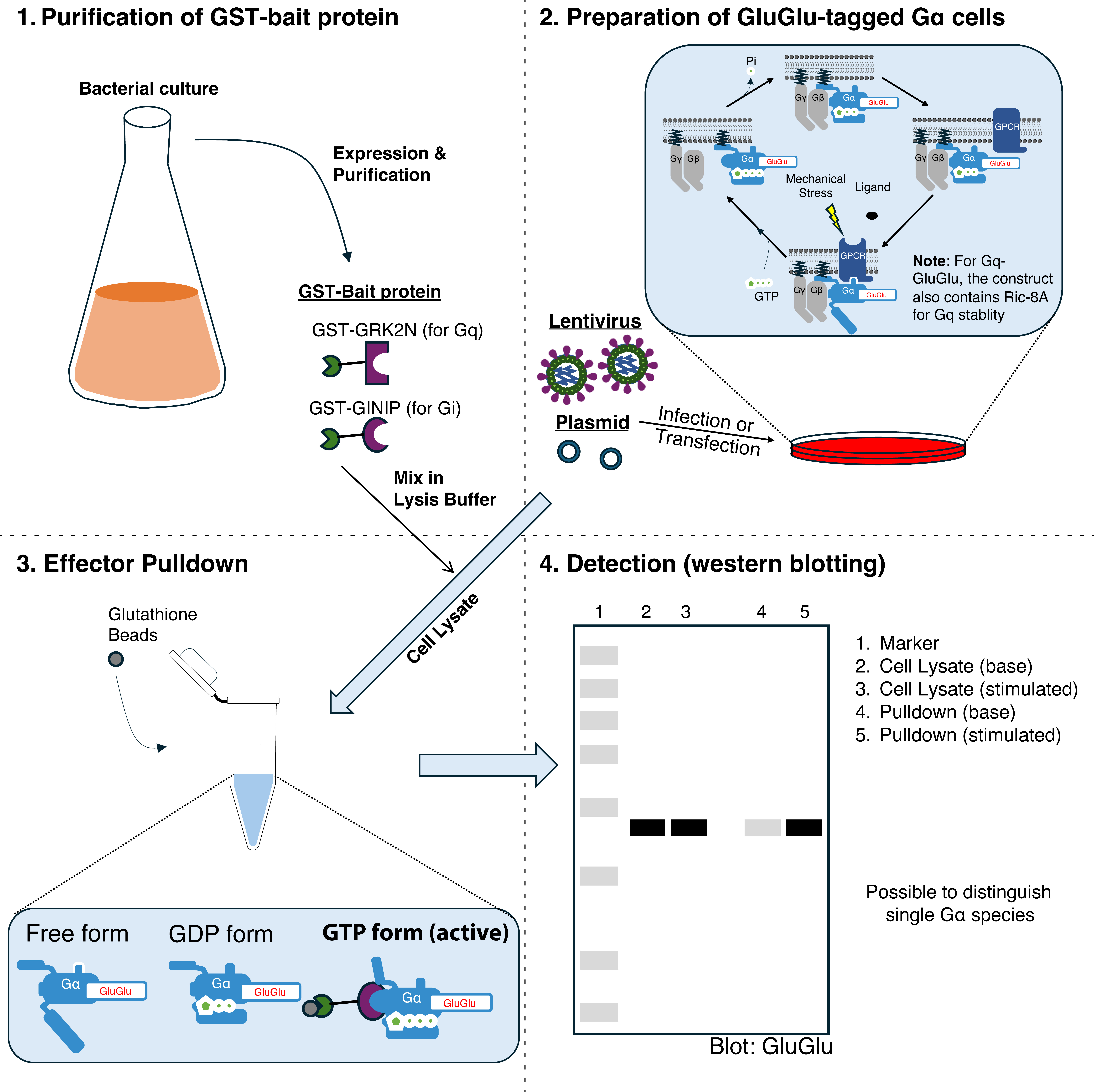
Four major steps in the effector pull-down assay to measure Gα activity within cells. (1) Purification of GST-bait protein, (2) preparation of GluGlu-tagged Gα cells, (3) effector pulldown, and (4) detection by western blotting.
Background
G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) comprise a large family of membrane proteins that mediate responses to a vast range of extracellular signals. These include neurotransmitters, hormones, metabolites, and photons [1,2]. Consequently, they are essential for many physiological processes, and their dysregulation frequently leads to human diseases. Conversely, GPCRs are the targets of 30%–40% of all FDA-approved drugs.
GPCRs transduce extracellular stimuli through activation of heterotrimeric Gα proteins [2,3], although previous studies demonstrated that they can also initiate signaling through coupling to β-arrestins. The critical event in Gα protein activation is the exchange of guanosine diphosphate (GDP) with guanosine triphosphate (GTP), which is catalyzed by the guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) activity of activated GPCRs [1]. GTP loading induces dissociation of Gα from Gβγ, both of which then activate various downstream effectors. Humans possess four major Gα protein families (Gi, Gq/11, Gs, and G12/13), each of which activates specific effectors [1]. Gα protein signaling is terminated by their intrinsic GTPase activity, which then allows reassembly of the heterotrimeric Gα-Gβγ complex. Additionally, signaling is regulated by multiple associated proteins that modulate Gα GTPase activity or conformation [4]. For instance, some Gq family proteins require chaperone proteins such as Ric-8A for their proper function [5].
Developing tools to monitor G-protein activity with high sensitivity is crucial to elucidate the complex signaling processes during GPCR to Gα activation and their feedback regulation. Measuring downstream effectors, such as cAMP and calcium, as proxies for Gα protein activation has significant caveats since their responses are not generally equivalent to GPCR-Gα signaling due to pathway crosstalk and subsequent signal amplification or suppression. Alternatively, multiple biosensors have been developed for monitoring the dissociation of Gα and Gβγ subunits [6–8]. However, these biosensors require the expression of multiple genetic components as well as significant structural alteration in Gα by embedding relatively large fluorescent proteins or luciferase, which have potentially undesired consequences. Additionally, Gα isoforms (even in the same Gα family) can specifically couple to distinct receptors [9] and regulate specific physiological processes, which biosensors do not readily distinguish.
To address these challenges, we employed pull-down assays to directly detect Gα proteins in their activated state. To enhance sensitivity and allow isoform-specific detection, we expressed Gα subunits with inserted GluGlu epitope tags (Figure 1). These Gα mutants are tagged by mutation of a short stretch of amino acids to create GluGlu epitopes, without perturbing function [10,11]. Historically, GTPase effector pulldowns were developed to detect small GTPase activation [12]. It was previously reported that GINIP binds specifically to active, GTP-bound Gi [13], while the N-terminal region of GRK2 binds specifically to active Gq [14]. Consequently, we found these GluGlu-tagged Gα mutants selectively bind to GINIP or GRK2 N-terminal region when they are in the activated GTP-bound state.
Using this assay, we successfully monitored unique G protein activation by endogenous GPCRs, with the additional advantage of increasing sensitivity by collecting large lysate volumes. Refining these methodologies as described here in detail will provide more precise insights into GPCR signaling and their roles in health and disease.

Figure 1. GluGlu-tag embedded Gα protein sequence. Red highlights a GluGlu epitope sequence. GluGlu epitope is derived from a 314–319 amino acid sequence of the middle T antigen of mouse polyoma virus [15]. Sequences are obtained from Tanaka et al. [16].
Materials and reagents
Biological materials
1. One ShotTM Stbl3TM chemically competent E. coli (Invitrogen, catalog number: C737303)
2. BL21(DE3) competent cells (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: EC0114)
3. Lenti-XTM 293T cell line (Takara, catalog number: 632180)
4. HUVECs (human umbilical vein endothelial cells) (Yale Vascular Biology & Therapeutics Program, catalog number: T75SC-1)
Reagents
1. Constructs expressing GST-tagged GINIP protein (kind gift from Dr. Mozlich) [13]
2. Constructs expressing GST-tagged GRK2 N-terminal domain (Tanaka et al., Dr. Schwartz lab; File S1)
3. Constructs expressing GluGlu-epitope inserted human Gi1 protein (Tanaka et al., Dr. Schwartz lab; File S1)
4. Constructs expressing GluGlu-epitope inserted human Gi2 protein (Tanaka et al., Dr. Schwartz lab; File S1)
5. Constructs expressing GluGlu-epitope inserted human Gi3 protein (Tanaka et al., Dr. Schwartz lab; File S1)
6. Constructs expressing GluGlu-epitope inserted human Gq protein and Ric8A protein (Tanaka et al., Dr. Schwartz lab; File S1)
7. Constructs expressing GluGlu-epitope inserted human Gi1 Q204L protein (Tanaka et al., Dr. Schwartz lab; File S1)
8. Constructs expressing GluGlu-epitope inserted human Gi2 Q205L protein (Tanaka et al., Dr. Schwartz lab; File S1)
9. Constructs expressing GluGlu-epitope inserted human Gi3 Q204L protein (Tanaka et al., Dr. Schwartz lab; File S1)
10. Constructs expressing GluGlu-epitope inserted human Gq Q209L protein (Tanaka et al., Dr. Schwartz lab; File S1)
11. pcDNA5/FRT-HA-hM3D(Gq) (Addgene, catalog number: 45547)
12. pcDNA5/FRT-HA-hM4D(Gi) (Addgene, catalog number: 45548)
13. Lentivirus packaging plasmid (psPAX2) (Addgene, catalog number: 12260)
14. Lentivirus envelope plasmid (pMD2.G) (Addgene, catalog number: 12259)
15. Ampicillin sodium salt (Sigma, catalog number: A0166-25G)
16. LB medium (capsules) (MP Biomedicals, catalog number: 3002021)
17. BactoTM agar (BD, catalog number: 214010)
18. BactoTM yeast extract (Gibco, catalog number: 212750)
19. BactoTM tryptone (Gibco, catalog number: 211705)
20. Glycerol (Sigma, catalog number: G7893)
21. Sodium chloride (NaCl) (J.T. Baker, catalog number: 3624-05)
22. IPTG (isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside) (AmericanBio, catalog number: 18501800)
23. KH2PO4 (J.T. Baker, catalog number: 3246-05)
24. K2HPO4 (J.T. Baker, catalog number: 3252-01)
25. Trizma® base (Sigma, catalog number: T6066)
26. Hydrogen chloride (HCl) (Sigma, catalog number: H1758-500ML)
27. Triton X-100 (AmericanBio, catalog number: AB02025)
28. Dithiothreitol (DTT) (Sigma, catalog number: D9779)
29. Lysozyme from chicken egg white (Sigma, catalog number: L6876-10G)
30. cOmpleteTM, mini, EDTA-free protease inhibitor cocktail (Sigma, catalog number: 11836170001)
31. HaltTM protease and phosphatase inhibitor cocktail (100×) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 78440)
32. Glutathione Sepharose 4B (Millipore/Sigma, catalog number: 17-0756-01)
33. Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) (J.T. Baker, catalog number: 3115-05)
34. L-Glutathione reduced (Sigma, catalog number: G6529-1G)
35. Bio-Rad Protein Assay Dye Reagent Concentrate (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 5000006)
36. DMEM, high glucose, pyruvate (Gibco, catalog number: 11995073)
37. Fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Phoenix-Scientific, catalog number: PS-100-02-500)
38. Penicillin/Streptomycin (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 15140163)
39. Trypsin-EDTA 0.25% (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 25200114)
40. Opti-MEMTM I reduced serum medium (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 31985088)
41. LipofectamineTM 2000 transfection reagent (Invitrogen, catalog number: 11668-019)
42. Clozapine N-oxide (Tocris Bioscience, catalog number: 4936)
43. Bovine plasma (Pel-Freez, catalog number: 37140-1)
44. Gelatin Sepharose 4B (Amersham, catalog number: 17-0956-01)
45. Fibronectin bovine protein, plasma (ThermoFisher, catalog number: 33010018)
46. Sodium acetate (J.T. Baker, catalog number: 3470-01)
47. Acetic acid, glacial (Millipore, catalog number: AX0073-9)
48. PMSF (MilliporeSigma, catalog number: 10837091001)
49. 0.5 M EDTA pH 8.0 (Invitrogen, catalog number: AM9262)
50. CAPS (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: BP321-100)
51. Urea (Sigma, catalog number: U5378-1KG)
52. M199 media (Invitrogen, catalog number: 11150-059)
53. Bovine hypothalamus (Pel-Freez, catalog number: 57117-2)
54. Streptomycin sulfate (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 11860038)
55. Endothelial cell growth supplement (Yale Vascular Biology & Therapeutics Program, ECGS)
56. Heparin sodium salt from porcine intestinal mucosa (Sigma, catalog number: H3149)
57. Hexadimethrine bromide (Polybrene) (Sigma, catalog number: H9268-5G)
58. GibcoTM PBS, pH 7.4 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 10-010-031)
59. 10× TBS (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 1706435)
60. 10× Tris/Glycine/SDS (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 1610772)
61. 10× Tris/Glycine (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 1610734)
62. Tween 20 (Sigma, catalog number: P9416)
63. Sodium dodecyl sulfate (AmericanBio, catalog number: AB01920)
64. 2-Mercaptoethanol (Sigma, catalog number: M3148)
65. Bromophenol blue (Sigma, catalog number: B0126-25G)
66. Ammonium persulfate (Sigma, catalog number: 911127-100G)
67. 30% Acrylamide/Bis Solution 37.5:1 (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 1610158)
68. TEMED (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 1610801)
69. Non-fat dry milk Omniblok (AmericanBio, catalog number: AB10109)
70. GLU-GLU monoclonal antibody (BioLegend, catalog number: MMS-115R)
71. GST antibody (Cell Signaling, catalog number: 2625)
72. Tubulin antibody (Invitrogen, catalog number: 62204)
73. Actin antibody (Santa Cruz, catalog number: sc-8432)
74. Reblot Plus Strong antibody stripping solution (10×) (Millipore, catalog number: 2504)
Solutions
1. Terrific broth (see Recipes)
2. Bacteria lysis buffer (see Recipes)
3. Glutathione beads wash buffer (see Recipes)
4. Glutathione S transferase elution buffer (see Recipes)
5. Lenti-X 293T cell culturing medium (see Recipes)
6. Cell lysis buffer (see Recipes)
7. 2× SDS buffer (see Recipes)
8. (Optional) Fibronectin (1 mg/mL) from frozen bovine plasma (see Recipes)
Recipes
1. Terrific broth
Combine 3.6 g of tryptone, 7.2 g of yeast extract, and 1.2 mL of glycerol in a glass flask. Add water to reach a total volume of 270 mL and then sterilize the mixture by autoclaving. Separately dissolve 0.231 g of KH2PO4 (final concentration 0.017 M) and 1.254 g of K2HPO4 (final concentration 0.072 M) in water up to 30 mL. Filter this solution through a 0.45 μm filter, mix it with the autoclaved broth, and adjust the volume to 300 mL.
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
| Tryptone | 3.6 g | |
| Yeast extract | 7.2 g | |
| Glycerol | 1.2 mL | |
| Water | 270 mL | |
| Autoclave the solution above | ||
| KH2PO4 | 0.017 M | 0.231 g |
| K2HPO4 | 0.072 M | 1.254 g |
| Water | 30 mL | |
| Filter 30 mL of phosphate solution through a 0.45 μm filter and add it to the autoclaved broth | ||
| Total | 300 mL | |
2. Bacteria lysis buffer
Prepare this buffer fresh each time for optimal effectiveness. Mix 400 μL of 1 M Tris-HCl (pH 7.5) (final 10 mM), 1.2 mL of 5 M NaCl (final 150 mM), 400 μL of Triton X-100 (final 1%), 200 μL of 1 M DTT (5 mM), 40 mg of Lysozyme (1 mg/mL), and protease inhibitor in distilled water using 50 mL conical tubes (40 mL in two tubes). Adjust the solution to 40 mL with distilled water. Mix everything well and keep the buffer on ice until use.
Note: Avoid EDTA since it interferes with heterotrimeric G protein function.
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| 1 M Tris-HCl (pH 7.5) | 10 mM | 400 μL × 2 |
| 5 M NaCl | 150 mM | 1.2 mL × 2 |
| Triton X-100 | 1% | 400 μL × 2 |
| 1 M DTT | 5 mM | 200 μL × 2 |
| Lysozyme | 1 mg/mL | 40 mg × 2 |
| Protease inhibitor | 1 capsule per 10 mL | |
| Water | Up to 40 mL × 2 |
3. Glutathione beads wash buffer
Prepare this buffer fresh each time for optimal effectiveness. Mix 400 μL of 1 M Tris-HCl (pH 7.5) (final 10 mM), 1.2 mL of 5 M NaCl (final 150 mM), 400 μL of Triton X-100 (final 1%), and 200 μL of 1 M DTT (5 mM) in distilled water using 50 mL conical tubes (40 mL in two tubes). Adjust the solution to 40 mL with distilled water. Mix everything well and store the buffer on ice until use. Add protease and phosphatase inhibitor prior to usage.
Note: Avoid EDTA since it interferes with heterotrimeric G protein function.
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| 1 M Tris-HCl (pH 7.5) | 10 mM | 400 μL × 2 |
| 5 M NaCl | 150 mM | 1.2 mL × 2 |
| Triton X-100 | 1% | 400 μL × 2 |
| 1 M DTT | 5 mM | 200 μL × 2 |
| Water | Up to 40 mL × 2 |
4. Glutathione S transferase elution buffer
Mix 2 mL of 1 M Tris-HCl (pH 7.5) (final 10 mM), 6 mL of 5 M NaCl (final 150 mM), 2 mL of Triton X-100 (final 1%), and 1 mL of 1 M DTT (5 mM) in distilled water using a 200 mL glass bottle. Adjust the solution to 50 mL with distilled water. Mix everything well and adjust the pH to 7.2 using 10 N NaOH. Make up the final volume with distilled water to 200 mL. Store at 4 °C until use. Add protease and phosphatase inhibitor just before use.
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
| 1 M Tris-HCl (pH 7.5) | 10 mM | 2 mL |
| 5 M NaCl | 150 mM | 6 mL |
| Triton X-100 | 1% | 2 mL |
| 1 M DTT | 5 mM | 1 mL |
| Glutathione | 50 mM | 3.07 g |
| 10 N NaOH | To pH 7.2 | |
| Water | Up to 200 mL | |
| Store at 4 °C and aliquot in 10 mL before use | ||
| Protease and phosphatase inhibitor | 1× | 100 μL |
5. Lenti-X 293T cell culturing medium
Remove 55 mL from the DMEM bottle to make the total volume 500 mL. Pour in 50 mL of FBS and 5 mL of penicillin/streptomycin. Mix gently to combine everything.
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| DMEM | 445 mL | |
| FBS | 10% | 50 mL |
| Penicillin/Streptomycin | 5 mL | |
| Total | 500 mL |
6. Cell lysis buffer
Prepare this buffer fresh each time for optimal effectiveness. Mix 100 μL of 1 M Tris-HCl (pH 7.5) (final 10 mM), 300 μL of 5 M NaCl (final 150 mM), 100 μL of Triton X-100 (final 1%), 50 μL of 1 M DTT (5 mM), and protease and phosphatase inhibitor in distilled water in 15 mL conical tubes. Add 20 μg of GST-GINIP protein for Gi assay or 20 μg of GST-GRK2 N-terminal domain for Gq assay. Adjust the solution to 10 mL with distilled water. Mix everything well and store on ice until use.
Note: Avoid EDTA since it interferes with heterotrimeric G protein function.
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| 1 M Tris-HCl (pH 7.5) | 10 mM | 100 μL |
| 5 M NaCl | 150 mM | 300 μL |
| Triton X-100 | 1% | 100 μL |
| 1 M DTT | 5 mM | 50 μL |
| GST-bait protein (GINIP for Gi, GRK2 N for Gq) | 2 μg/mL | 1 aliquot (20 μg) |
| Protease and phosphatase inhibitor | ||
| Water | Up to 10 mL |
7. 2× SDS buffer
Mix 3 mL of 1 M Tris-HCl (pH 6.8), 5 mL of glycerol, 10 mL of 10% SDS, and 2 mL of beta-mercaptoethanol. Take a small pinch of bromophenol blue in 1.5 mL tubes and add distilled water to make a suspension. Take water-saturated bromophenol blue into the mixture. Adjust the total volume to 20 mL using distilled water.
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| 1 M Tris-HCl (pH 6.8) | 0.12 M | 3 mL |
| Glycerol | 20% | 5 mL |
| 10% SDS | 4% | 10 mL |
| Beta-mercaptoethanol | 2.5 mL | |
| Water-saturated bromophenol blue | 2 mL | |
| Water | Up to 25 mL |
8. (Optional) Fibronectin (1 mg/mL) from frozen bovine plasma
Prepare a gelatin Sepharose 4B column by pouring 25 mL of resin into a column, and wash sequentially with cleaning buffers (cleaning buffer #1: 16× of column volume, and cleaning buffer #2: 16× of column volume) without allowing it to dry. Fresh frozen bovine plasma is then thawed, volume-measured, treated with 1 mM PMSF, and centrifuged at 20,000× g to remove precipitates. The supernatant is carefully loaded onto the prepared column without disturbing the column bed.
The column undergoes subsequent washes (12 column volumes of column wash buffer #1, 4 column volumes of column wash buffer #2, and 2 column volumes of column wash buffer #1); then, elute fibronectin with 50 mL of elution buffer. Collect the eluate in 1.5 mL fractions and measure optical density at 280 nm to determine fibronectin concentration, combining peak fractions from an O.D. starting at 0.7. Dialyze overnight at 4 °C in dialysis buffer, with a change of buffer the next morning with additional incubation for 3 h. Measure the optical density again, dilute the fibronectin to 1 mg/mL (OD280 of 1.3 equals 1 mg/mL of fibronectin), aliquot, freeze in liquid nitrogen, and store at -80 °C.
8.1. Cleaning buffer #1 (200 mL)
| Reagent | Final concentration | Volume |
|---|---|---|
| 1 M Tris-HCl (pH 8.5) | 100 mM | 20 mL |
| 5 M NaCl | 500 mM | 20 mL |
| Water | Up to 200 mL |
8.2. Cleaning buffer #2 (200 mL)
| Reagent | Final concentration | Volume |
|---|---|---|
| Sodium acetate | 100 mM | |
| 5 M NaCl | 500 mM | 20 mL |
| Acetic acid | Adjusting to pH 4.5 | |
| Water | Up to 200 mL |
8.3. Column wash buffer #1 (1 L)
| Reagent | Final concentration | Volume |
|---|---|---|
| PBS | 1× | Up to 1 L |
| 1 M PMSF | 1 mM | 1 mL |
| 0.5 M EDTA | 2 mM | 4 mL |
8.4. Column wash buffer #2 (1 L)
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| PBS | 1× | Up to 1 L |
| 1 M PMSF | 1 mM | 1 mL |
| NaCl | 1 M | 58.44 g |
| 0.5 M EDTA | 2 mM | 4 mL |
8.5. Dialysis buffer (4 L)
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| CAPS | 10 mM | 8.85 g |
| 1 M PMSF | 1 mM | 4 mL |
| 5 M NaCl | 0.15 M | 120 mL |
| 0.5 M EDTA | 2 mM | 8 mL |
| 10 N NaOH | Adjust to pH 11.0 | |
| Water | Up to 4 L |
8.6. Elution buffer (100 mL)
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| Dialysis buffer | 1× | Up to 100 mL |
| Urea | 4M | 24 g |
Note: Commercially available fibronectin (e.g., ThermoFisher, catalog number: 33010018) can also be used.
Laboratory supplies
1. 14 mL round-bottom high-clarity PP test tube (BD, Falcon, catalog number: 352059)
2. 15 mL conical tube (Corning, catalog number: 430791)
3. 50 mL conical tube (Corning, catalog number: 430828)
4. 10 cm bacteriological Petri dish (Corning, catalog number: 351029)
5. ZebaTM spin desalting columns, 7 K MWCO, 10 mL (Thermo Fisher, catalog number: 89893)
6. Corning® 100 mm TC-treated culture dish (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 08-772-22)
7. 25 mL pipettes (Greiner, catalog number: 760160)
8. 10 mL pipettes (Greiner, catalog number: 607180)
9. 5 mL pipettes (Greiner catalog number: 606180)
10. TipOne® RPT pipette tip refills (1,250 μL) (USA Scientific, catalog number: 1161-1720)
11. TipOne® 200 μL natural pipette tips in racks (USA Scientific, catalog number: 1111-0840)
12. TipOne® filter tips 10 μL (USA Scientific, catalog number: 1121-3810)
13. FisherbrandTM Premium microcentrifuge tubes, 1.5 mL (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 05-408-129)
14. Tube Posi-Click 1.7 mL natural graduated (labForce, catalog number: 1149K01)
15. 0.45 μm MillexTM-HP filter unit (sterile) (Millipore, catalog number: SLHP033RS)
16. 10 mL syringes (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 14-823-2A)
17. Nitrocellulose membrane (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 10484059)
18. Filter paper
Equipment
1. pH meter (METTLER TOLEDO, model: SevenDirect SD20)
2. Scales (METTLER TOLEDO, model: ML802T and XSR105)
3. Magnetic stirrer (Corning, model: PC351)
4. Laboratory centrifuge with rotors for 15 and 50 mL conical tubes (Beckman Coulter, model: Avanti JXN-26)
5. Autoclave (Steris, model: AMSCO 250LS)
6. Forced-air incubator (for bacteria plates) (Yamato, model: IC400)
7. Bacterial incubator shaker (New Brunswick, model: Innova 44/44R or Innova 4000)
8. Sonic dismembrator (Fisher Scientific, model: Model 500)
9. Laboratory centrifuge with rotors for 1.5 mL microcentrifuge tubes (Thermo Scientific, model: SorvallTM LegendTM Micro 21 Microcentrifuge)
10. Cell incubator (SANYO, model: MCO-19AIC)
11. Biological safety cabinet (LabGard, model: NU-425-600)
12. Chemiluminescence imaging system (Syngene, G:BOX, model: Chemi-XX9)
13. Racks
14. Liquid nitrogen (N2) tank
15. Freezer (-80 °C)
16. Freezer (-20 ° C)
17. Refrigerator (4°C)
Software and datasets
1. GeneSys (Syngene, Version 1.8.12.0, Database Version 2.2)
2. ImageJ/Fiji
3. Microsoft Excel
4. GraphPad Prism
Procedure
文章信息
稿件历史记录
提交日期: Apr 7, 2025
接收日期: Jun 12, 2025
在线发布日期: Jul 22, 2025
出版日期: Aug 5, 2025
版权信息
© 2025 The Author(s); This is an open access article under the CC BY license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
如何引用
Tanaka, K. and Schwartz, M. A. (2025). Direct Activity Measurement of Heterotrimeric Gi Proteins and Gq Protein By Effector Pulldown. Bio-protocol 15(15): e5406. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.5406.
分类
生物化学 > 蛋白质 > 相互作用 > 蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用
细胞生物学 > 基于细胞的分析方法 > 蛋白互作
细胞生物学 > 细胞信号传导 > 胞内信号传导
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link