- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Assessment of SREBP Activation Using a Microsomal Vesicle Budding Assay
基于微粒体囊泡出芽实验的SREBP活化评估
发布: 2024年12月20日第14卷第24期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.5139 浏览次数: 1539
评审: Philipp A.M. SchmidpeterShailesh KumarMaria Falzone

相关实验方案
哺乳动物线粒体和胞质顺乌头酸酶的凝胶内活性测定——分区特异性氧化应激与铁状态的替代标志物
Wing-Hang Tong and Tracey A. Rouault
2024年12月05日 2199 阅读
Abstract
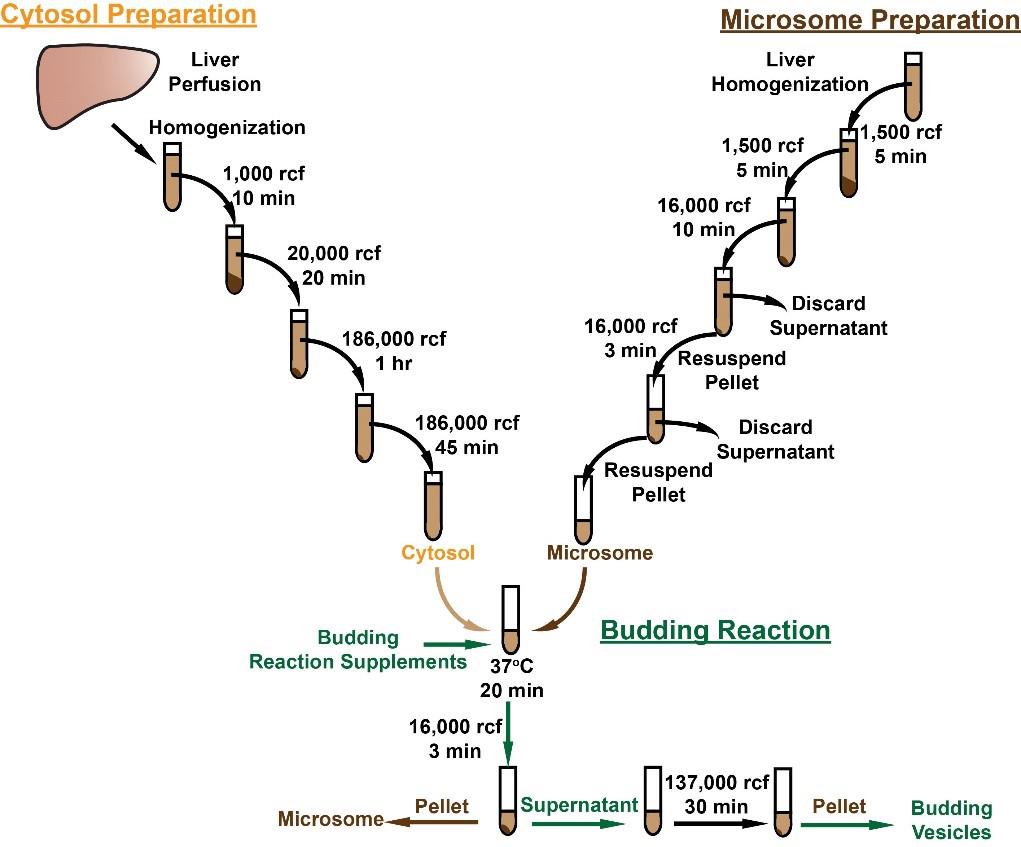
Sterol regulatory element binding proteins (SREBPs) are transcription factors that reside in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane as inactive precursors. To be active, SREBPs are translocated to the Golgi where the transcriptionally active N-terminus is cleaved and released to the nucleus to regulate gene expression. Nuclear SREBP levels can be determined by immunoblot analysis; however, this method can only determine the steady-state levels of nuclear SREBPs and does not capture the actual status of activation. The vesicle budding assay provides an alternative way to quantify the activation of SREBPs by monitoring the initiation of SREBP translocation from the ER to the Golgi through vesicles. Microsomal membranes isolated from the liver are incubated in a reaction buffer containing the necessary components to facilitate vesicle formation. Microsomal membranes and vesicles are isolated and SREBPs are quantified in each by immunoblot analysis. The amount of SREBPs found in the budded vesicles provides an assessment of the SREBP activation in the liver.
Key features
• This protocol describes a method to isolate budding vesicles from liver ER membranes
• The in vitro budding assay can be applied to investigate the movement of proteins from the ER to the Golgi
• This protocol was developed based on the procedures described previously with cultured cells [1–3]
Keywords: Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) (内质网)Graphical overview
Background
The transport of proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) to the Golgi complex is required for additional protein modifications and/or protein secretion. Small transport vesicles that bud from mammalian ER and fuse to Golgi were reported in the late 1980s [4] and further characterized thereafter [2,3,5]. Sterol regulatory element binding proteins (SREBPs) are a family of membrane-bound transcription factors that regulate the expression of genes involved in cholesterol and fatty acid homeostasis [6–8], which utilize small vesicles for transport from the ER to the Golgi for activation [1]. Newly synthesized SREBP proteins are embedded in the ER membrane, forming a complex with SREBP cleavage activating protein (SCAP), a protein that serves as a sterol sensor and escort protein. The process of SREBP activation requires the membrane-bound SREBP/SCAP complex to move from the ER to Golgi, where two proteases reside, which cleave and free the transcriptionally active N-terminal portion of SREBPs from the membrane. The N-terminal SREBPs then enter the nucleus and regulate the transcription of downstream genes [8].
Immunoblot analysis is routinely used to evaluate the degree of SREBP activation. The molecular weight of the cleaved mature/nuclear form of SREBPs is ~68 kD, while the molecular weight of the membrane-bound precursor SREBP is ~125 kD. By quantifying the amount of cleaved nuclear SREBPs, an estimation of SREBP activation can be achieved. However, nuclear SREBP levels represent a steady-state measurement of the combined results of both protein activation and degradation. In a recent study, we developed a new method to determine SREBP activation by measuring the full-length SREBPs in budding vesicles of mouse liver. Although the in vitro budding reaction might have the limitation of not reflecting the in vivo status, this method measures the initiation of SREBP transportation from the ER to Golgi for cleavage activation. Compared to measuring the cleaved nuclear form SREBPs, evaluation of SREBP activation by measuring the SREBPs in the budding vesicles eliminates the potential effects of degradation of nuclear SREBPs.
Materials and reagents
Biological materials
Note: The general microsomal budding assay is not dependent on the animal or diet used.
Human SREBP-1c transgenic rat
High carbohydrate diet (MP Biomedicals, catalog number: 960238)
HEPES (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: H3375)
D-Sorbitol (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S6021)
Potassium acetate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P1190)
Magnesium acetate tetrahydrate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M5661)
0.5 M EGTA-KOH, pH 8.0 (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 50-997-744)
1 M Tris-Cl, pH 6.8 (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 50-843-263)
Dithiothreitol (DTT) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D9779)
Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 75746)
Bromophenol blue (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: B0126)
Glycerol (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G5516)
Trizma base (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T1503)
Protease inhibitor cocktail (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P8340)
0.9% Sodium chloride irrigation (Saline) (Baxter, catalog number: BX-2F7124)
Isoflurane (Piramal Critical Care, catalog number: 33794-013-25)
Creatine phosphate (Millipore Sigma, catalog number: 10621714001)
ATP (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G6419)
GTP (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G8877)
Creatine kinase (Millipore Sigma, catalog number: 10127566001)
Anti-HA antibody (Cell Signaling, catalog number: 3724)
Anti-Calnexin antibody (Enzo, catalog number: ADI-SPA-860-F)
Anti-ERGIC-53 antibody (Abcam, catalog number: ab125006)
Goat anti-rabbit IgG, F(ab’)2 (Jackson Immuno, catalog number: 115-035-072)
PierceTM BCA Protein Assay kit (Thermo Fisher, catalog number: A65453)
SuperSignal West Pico chemiluminescent substrate (Thermo Fisher, catalog number: 23225)
Buffer 1 (see Recipes)
Buffer 2 (see Recipes)
5× SDS-loading buffer (see Recipes)
20× budding reaction supplement (see Recipes)
Recipes
pH values of buffers are all adjusted at room temperature.
Buffer 1
Reagent Final concentration Quantity or Volume 1 M HEPES-KOH, pH 7.2 10 mM 500 μL 2 M Sorbitol 250 mM 6.25 mL 1 M KOAc 10 mM 500 µL 1 M Mg(OAc)2 1.5 mM 75 µL Total n/a Adjust pH to 7.2 with KOH, then add H2O to 50 mL Can be stored at 4 °C for up to two months.
Buffer 2
Reagent Final concentration Volume 1 M HEPES-KOH, pH 7.2 50 mM 2.5 mL 2 M Sorbitol 250 mM 6.25 mL 1 M KOAc 70 mM 3.5 mL 1 M Mg(OAc)2 2.5 mM 125 µL 0.5 M EGTA-KOH, pH 8.0 5 mM 500 µL Total n/a Adjust pH to 7.2 with KOH, then add H2O to 50 mL Can be stored at 4 °C for up to two months.
5× SDS-loading buffer
Reagent Final concentration Volume SDS 15% 15 g Bromophenol blue 0.02% 20 mg Glycerol 25% 25 mL 1 M Tris-Cl, pH 6.8 0.15 M 15 mL Total n/a Add H2O to 100 mL Add 62.5 μL of β-mercaptoethanol for each 500 μL of loading buffer freshly before use.
20× budding reaction supplement
The following reagents should be freshly prepared individually. Prepare the 20× budding reaction supplement by mixing equal volumes of each reagent immediately before carrying out the budding reaction.
Note: The molecular weight or specific activity of each reagent will be different depending on the source and lot number of the reagents. The quantity needs to be calculated based on the information from the vendor.
Reagent 20× concentration Quantity Final volume in H2O Creatine phosphate 200 mM 26.2 mg 100 µL ATP 30 mM 6.61 mg 100 µL GTP 10 mM 2.09 mg 100 µL Creatine kinase 80 U/mL 1 mg 10 mL
Laboratory supplies
18 G catheter (BD, catalog number: 382644)
Protein LoBind tubes (Eppendorf, catalog number: 022431081)
Polycarbonate centrifuge tubes (for AT3 rotor) (Beckman Coulter, catalog number: 343776)
Polycarbonate centrifuge tubes (for AT6 rotor) (Beckman Coulter, catalog number: 362305)
Equipment
Tabletop centrifuge (Eppendorf, model: Centrifuge 5424)
37 °C incubator (ThermoMixer, Eppendorf, model: F1.5 was used in this experiment)
Ultracentrifuge (Thermo Scientific, model: Sorvall MX120)
S100-AT6 fixed angle rotor (Thermo Scientific, catalog number: 45588)
S120-AT3 fixed angle rotor (Thermo Scientific, catalog number: 45584)
Peristaltic pump (Amersham Biosciences, model: Pump P-1)
Dounce tissue homogenizer-2 mL (DWK life sciences, catalog number: 885300-002)
Dounce tissue homogenizer-7 mL (DWK life sciences, catalog number: 885300-007)
Procedure
文章信息
稿件历史记录
提交日期: Sep 18, 2024
接收日期: Oct 21, 2024
在线发布日期: Nov 4, 2024
出版日期: Dec 20, 2024
版权信息
© 2024 The Author(s); This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/).
如何引用
Xia, M., Edwards, T. and Rong, S. (2024). Assessment of SREBP Activation Using a Microsomal Vesicle Budding Assay. Bio-protocol 14(24): e5139. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.5139.
分类
分子生物学 > 蛋白质 > 活性
细胞生物学 > 基于细胞的分析方法 > 蛋白成熟
细胞与分子生物学
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link