- EN - English
- CN - 中文
A Simple Staining Method Using Pyronin Y for Laser Scanning Confocal Microscopy to Evaluate Gelatin Cryogels
利用Pyronin Y的简单染色方法评估明胶冷冻凝胶的激光扫描共聚焦显微镜技术
发布: 2024年11月20日第14卷第22期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.5115 浏览次数: 1898
评审: Hélène LégerHsih-Yin TanAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
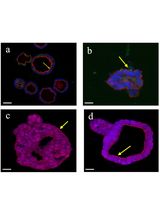
This study explores the novel application of pyronin Y for fluorescently labeling extracellular matrices (ECMs) and gelatin cryogels, providing a simple and reliable method for laser scanning confocal microscopy. Pyronin Y exhibited remarkable staining ability of the porous structures of gelatin cryogels, indicating its potential as a reliable tool for evaluating such biomaterials. Confocal imaging of pyronin Y–stained cryogels produced high signal-to-noise ratio images suitable for quantifying pores using Fiji/Image J. Importantly, pyronin Y enabled effective dual-color imaging of cryogel-labeled mesenchymal stem cells, expanding its utility beyond traditional RNA assays. Traditional staining methods like Mason’s trichrome and Sirius Red have limitations in cryogel applications. Pyronin Y emerges as a powerful alternative due to its water solubility, minimal toxicity, and stability. Our results demonstrate pyronin Y’s ability to specifically stain gelatin cryogel's porous structures, surpassing its weak staining of ECMs in 2D. Confocal imaging revealed enduring staining even under rigorous scanning, with no notable photobleaching observed. Furthermore, pyronin Y's combination with Alexa Fluor 647 for dual-color imaging showed promising results, validating its versatility in fluorescence microscopy. In conclusion, this study establishes pyronin Y as a cost-effective and rapid option for fluorescent staining of gelatin cryogels. Its simplicity, efficacy, and compatibility with confocal microscopy make it a valuable tool for characterizing and evaluating gelatin-based biomaterials, contributing significantly to the field of cryogel imaging. The study opens new avenues for dual-color imaging in biomaterial research and tissue engineering, advancing our understanding of cellular interactions within scaffolds.
Key features
• Fluorescent staining of gelatin-based cryogels with an inexpensive yet less time-consuming protocol.
• Pyronin Y staining is suitable for dual-color confocal imaging by combining with far-red fluorophores (such as Alexa Fluor 647).
• The method is conducted routinely.
Keywords: Pyronin Y (Pyronin Y)Graphical overview
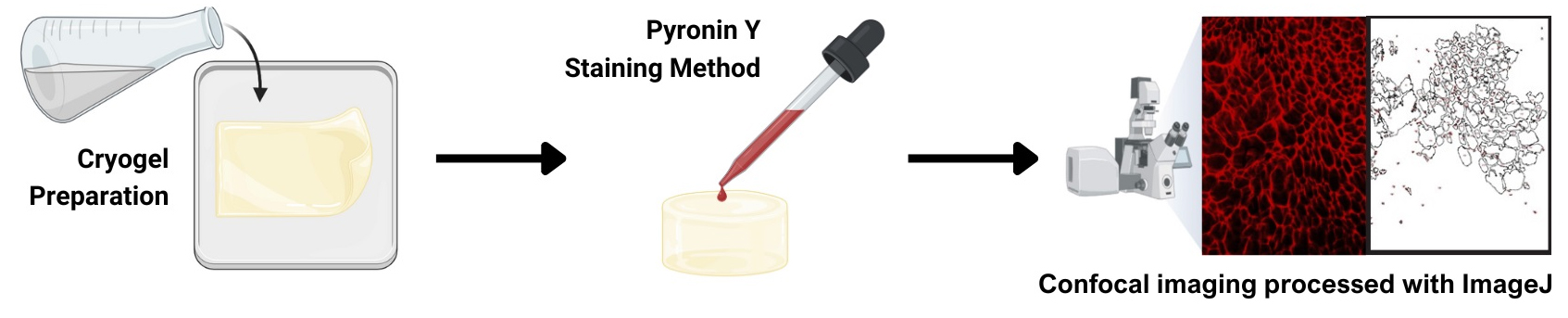
Gelatin cryogel staining using pyronin Y
Background
In this study, we report the novel application of pyronin Y dye in cryogel imaging combined with confocal microscopy, focusing on the detailed visualization of the cryogel’s porous structure. To our knowledge, this is the first protocol demonstrating a very fast yet reliable fluorescent staining of gelatin-based cryogels. We also show its compatibility with dual-color imaging.
The lack of a straightforward, rapid, and reliable fluorescent labeling method for cryogels is one obstacle in the field. Traditional methods like Mason’s trichrome for collagen [1] and the anionic dye, Sirius Red, for polarized microscopy [2] have limitations in cryogel applications. Mason’s trichrome staining is optimized to stain collagen fibers of tissue sections, not biomaterials [3]. While immunofluorescent staining of cryogels is possible using anti-gelatin antibodies, it is cost-prohibitive and not used for cryogels. Covalent conjugation of fluorescent dyes to gelatin is effective in visualizing the architecture of gelatin-based cryogels [4]; however, it is time-consuming.
Initially, we evaluated the dye’s potential for staining extracellular matrix (ECM)-coated glass surfaces in 2D cultures and discovered that pyronin Y can specifically stain 3D porous structures. Traditionally, pyronin Y has been a staple in RNA analysis [5–7]. Cryogels are unique porous scaffolds formed at sub-zero temperatures (around -20 °C) through a freeze-thaw process resulting in the formation of a porous network of polymer strands, post-thawing, due to the sublimation of ice crystals [8,9]. The interconnected porosity of cryogels allows efficient diffusion of nutrients and oxygen, rendering them advantageous for a variety of applications in tissue engineering, including superior cell growth [10].
Pyronin Y (C17H19CIN2O) features a dimethylamino group [N(CH3)2] and a xanthene-3-iminium group, which render the dye its cationic nature and distinctive red fluorescence. Additionally, pyronin Y is water-soluble and therefore easy to apply to various biological applications. Furthermore, it is considered to be safe for use in biological research, due to its relatively low toxicity. Lastly, pyronin Y is a stable dye that can be stored for extended periods without significant degradation or loss of fluorescence intensity. Past studies [5,7,11] have demonstrated pyronin Y’s efficacy in RNA analysis, owing to its ability to emit fluorescent light upon binding to RNA through ionic interactions. Thus, pyronin Y is established as a crucial component in a variety of RNA-based assays, such as in situ hybridization, [11], flow cytometry [5], and real-time RNA imaging [7]. However, no studies explored pyronin Y's potential for the imaging of ECMs, as shown here.
The properties of pyronin Y, such as its vivid red fluorescence, positive charge, water solubility, minimal toxicity, and chemical stability, render it a highly adaptable dye for the analysis of various extracellular matrices. Gelatin, which primarily constitutes heterogeneous peptides, is a predominantly negatively charged protein in alkaline pH [10]. This protocol explores the efficacy of pyronin Y in staining gelatin-based cryogels.
Materials and reagents
Biological materials
StemProTM BM mesenchymal stem cell (Gibco, Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: A15652)
Note: Other mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) may be used, such as those isolated from the umbilical cord [12] or from other sources.
Reagents
Pyronin Y (Alfa Aesar, Brand, catalog number: J61068, lot F18Z037), stable at room temperature
Glutaraldehyde 25% solution (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G6257); once opened, you may store it in a refrigerator, tightly sealing the container
Sodium borohydride (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 452882)
Sodium carbonate (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: S64-500) (any equivalent or higher quality of the same chemicals should work fine)
Hydrochloric acid (for pH adjustment) (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: A1445-500) (any equivalent or higher quality of the same chemicals should work fine)
16% paraformaldehyde (Electron Microscopic Sciences, catalog number: 15700); once opened, you may store it in a refrigerator, tightly sealing the container
Triton X-100 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T8787)
Fish skin gelatin (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G7041)
Alexa Fluor 647 phalloidin (Invitrogen, Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: A22287)
Dulbecco’s modified Eagle medium (Gibco, Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 11995), store at 4 °C
Fetal bovine serum (premium) (Gibco, Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: A5670701)
Dulbecco’s phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) without calcium and magnesium (Gibco, Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 14190144)
Solutions
Gelatin cryogel solution (see Recipes)
0.1 M sodium bicarbonate buffer (see Recipes)
Pyronin Y solution (see Recipes)
4% Paraformaldehyde solution (see Recipes)
0.5% Triton X-100 solution (see Recipes)
Recipes
Gelatin cryogel solution
Reagent Final concentration Amount (per 1.5 mm thick gel) Gelatin (8.6%) 4.3% 3,000 μL Glutaraldehyde (25%) * 0.3% 72 μL H2O n/a 2,928 μL Total n/a 6,000 μL *Add after mixing other parts.
0.1 M sodium carbonate buffer (pH 9.2)
Reagent Final concentration Amount Sodium carbonate 0.1 M 10.6 g (when anhydrous is used) HCl n/a (add dropwise to adjust the pH) Total with H2O n/a 1,000 mL Pyronin Y solution
Reagent Final concentration Amount Pyronin Y 1 mg/mL 1 mg ddH2O n/a 1 mL Total n/a 1 mL It is highly recommended to spin briefly (~30 s) at 10,000× g to remove any insoluble pyronin Y particles after dissolving the pyronin Y powder.
4% paraformaldehyde solution
Reagent Final concentration Amount 16% paraformaldehyde solution 4% 2.5 mL PBS n/a 7.5 mL Total n/a 10 mL You can downscale the volume.
0.1% Triton X-100 solution
Reagent Final concentration Amount Triton X-100 0.1% 10 μL PBS n/a 9,990 μL Total n/a 10 mL You can downscale the volume. It will be fast to dissolve Triton X-100 by using a magnetic stirrer bar in a small beaker. Alternatively, making a 10% Triton X-100 stock solution helps this process. If a 10% stock solution is used, the volume of Triton X-100 should be 100 μL.
Laboratory supplies
1.5 mL or 2.0 mL microcentrifuge tubes
Micropipette (P200 and P1000)
1.5 mL tube rack
15 mL tubes
100 mm plastic Petri dishes or square dishes (e.g., Carolina Biological Supply, catalog number: 741470)
Gloves
Flat-tip forceps
35 mm glass bottom dishes (Mattek, catalog number: P35G-1.5-7-C)
Note: As long as the thickness is #1.5, any glass-bottom dishes for cellular imaging would be suitable.
1.5 mm spacer glass plates (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 1653312)
Short glass plates (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 1653308)
Mini-PROTEAN tetra cell casting stand & clamps (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 1658050)
Mini-PROTEAN casting stand gasket (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 1653305)
(alternative for 10/11) glass tube (the bottom has to be tightly sealed with a removable plug) or plastic disposable syringes (no needle required; the top has to be cut off)
Equipment
LSM 880 (Carl Zeiss)
20× objective lens; a high numerical aperture, longer working distance objective lens is strongly recommended, such as Plan-Apochromat 20×/N.A. = 0.8 M27 (Carl Zeiss, catalog number: 420650-9901-000)
-20 °C freezer (Thermo Fisher Scientific)
UV crosslinker (such as Spectronics Corporation, catalog number: XL-1000) or a cell culture hood equipped with a UV lamp
Software and datasets
Fiji/Image J (2.15.1), available without any cost
Microsoft Excel (no specific version as long as Office 2003 or newer versions are used)
Fluorescence Spectraviewer (Bio-Rad; https://www.bio-rad-antibodies.com/spectraviewer.html), available without any costs. Only required if you want to confirm the compatibility of your microscopic illumination settings.
Procedure
文章信息
稿件历史记录
提交日期: Jun 17, 2024
接收日期: Sep 23, 2024
在线发布日期: Oct 22, 2024
出版日期: Nov 20, 2024
版权信息
© 2024 The Author(s); This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/).
如何引用
Reece, B., Bahar, E. V., Pereira, A. C., Witek, L. and Kita, K. (2024). A Simple Staining Method Using Pyronin Y for Laser Scanning Confocal Microscopy to Evaluate Gelatin Cryogels. Bio-protocol 14(22): e5115. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.5115.
分类
生物工程 > 生物医学工程
细胞生物学 > 细胞分离和培养 > 3D细胞培养
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link