- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Measurement of the Activity of Wildtype and Disease-Causing ALPK1 Mutants in Transfected Cells With a 96-Well Format NF-κB/AP-1 Reporter Assay
96孔板NF-κB/AP-1报告基因检测转染细胞中野生型及致病性ALPK1突变体活性
发布: 2024年11月20日第14卷第22期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.5113 浏览次数: 1479
评审: Ralph Thomas BoettcherAlexandros C KokotosAnonymous reviewer(s)

相关实验方案
Cluster FLISA——用于比较不同细胞系蛋白表达效率及蛋白亚基聚集状态的方法
Sabrina Brockmöller and Lara Maria Molitor
2025年11月05日 1031 阅读
Abstract
Alpha-protein kinase 1 (ALPK1) is normally activated by bacterial ADP-heptose as part of the innate immune response, leading to the initiation of downstream signalling events that culminate in the activation of transcription factors such as NF-κB and AP-1. In contrast, disease-causing mutations in ALPK1 that cause ROSAH syndrome or spiradenoma allow ALPK1 to be activated in cells in the absence of bacterial infection (i.e., without ADP-heptose). This protocol describes a semi-quantitative reporter assay based on ALPK1 knockout HEK-Blue cells that measures the activity of transfected wildtype and disease-causing forms of ALPK1 by virtue of their ability to activate the transcription factors NF-κB and AP-1. These cells express a synthetic gene encoding alkaline phosphatase under the control of an NF-κB/AP-1-dependent promoter, and consequently, the activation of ALPK1 leads to the production of alkaline phosphatase, which is secreted into the culture media and can be measured colorimetrically at 645 nm after the addition of a detection reagent.
Key features
• Highly sensitive reporter assay allowing detection of low-level activity arising from ALPK1 mutants
• Optimised in 96-well plate format, requiring only 60,000 transfected ALPK1 KO HEK-Blue cells per well
• Rapid experimental design, taking only four days from start to finish
• Suitable for screening ALPK1 variants of unknown significance in an arrayed 96-well format
Keywords: ALPK1 (ALPK1)Background
Alpha-protein kinase 1 (ALPK1) is an atypical protein kinase that is activated allosterically by the binding of a bacterial nucleotide sugar, ADP-heptose, to its N-terminal ADP-heptose binding domain [1]. This enables ALPK1 to phosphorylate TIFA (TRAF-interacting protein with forkhead-associated domain) at Thr9, triggering its polymerization and the consequent activation of downstream signalling events that lead to activation of transcription factors such as NF-κB and AP-1 [1,2].
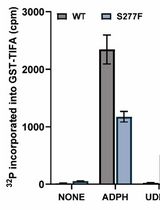
ROSAH syndrome (retinal dystrophy, optic nerve edema, splenomegaly, anhidrosis, and migraine headache) is an autosomal dominant genetic disorder caused by specific mutations in ALPK1 [3]. Most of the cases of ROSAH syndrome reported so far involve the mutation of Thr237 to Met, but cases have also been identified to be caused by the mutation of Tyr254 to Cys or Ser277 to Phe [4,5]. Thr237 directly interacts with ADP-heptose, whereas Tyr254 and Ser277 are outside of the ADP-heptose binding site itself but interact with each other through a hydrogen bond [5]. In contrast, ALPK1[Val1092Ala] is a driver mutation of a rare type of hair follicle tumour called spiradenoma, which can transform into an invariably fatal form known as spiradenocarcinoma [6].
The overexpression of these disease-causing ALPK1 mutants in ALPK1 knockout (KO) cells leads to the activation of NF-κB/AP-1-dependent gene transcription in the absence of ADP-heptose by a mechanism that is dependent on an intact ADP-heptose binding site [5,7]. This conundrum was resolved when it was found that these disease-causing ALPK1 mutants are activated by mammalian nucleotide sugars such as UDP-mannose and ADP-ribose, in addition to ADP-heptose [5,7]. In contrast, the normal form of ALPK1 is specifically activated by ADP-heptose.
This protocol outlines a cell-based assay designed to measure the activation of NF-κB and AP-1-dependent gene transcription by transfected ALPK1 mutants as utilised in previous studies on this topic [5,7]. The assay uses ALPK1 KO HEK-Blue cells, which express a synthetic gene encoding a secreted form of alkaline phosphatase under the control of an NF-κB/AP-1-dependent promoter. When these cells are transfected with plasmids encoding either wildtype or mutant forms of ALPK1, their ability to activate gene transcription in the presence or absence of ADP-heptose can be quantified by measuring the levels of alkaline phosphatase in the culture medium. This is achieved through a simple colorimetric assay where the absorbance is measured at 645 nm after the addition of a detection reagent, providing an efficient method for assessing ALPK1 activity. These reporter cells have been used previously to screen for activators or inhibitors of immune pathways [8], but here we expand their utility by showing their successful use to study variants of unknown significance.
The overexpression of ALPK1 mutants in this assay enables the detection of low-level activity, which can be difficult to observe when mutants are instead expressed under their endogenous promoter in immune cells and the resulting production of cytokines or chemokines is subsequently measured. Moreover, generating complex cell models such as these would be impractical for the screening of multiple ALPK1 variants of unknown significance at scale, but can be completed with minimal effort in four days using the protocol described here.
Materials and reagents
Biological materials
Cells should be cultured by incubation at 37 °C with 5% CO2 and tested regularly for mycoplasma using a MycoAlert Mycoplasma Detection Kit (Lonza, catalog number: LT07-318). The cells should be passaged once confluent at a ratio of 1:10 (v/v), and not used beyond 30 passages.
ALPK1 KO HEK-Blue cells (InvivoGen, #hkb-koalpk)
Reagents
The storage conditions for reagents are given in parentheses when not at room temperature. Commercial stock solutions are listed where possible, but many of these can also be prepared using standard methods.
ADP-heptose triethylammonium salt (InvivoGen, catalog number: tlrl-adph-l) (-80 °C)
Note: Resuspend 250 μg in 694 μL of PBS to generate a 0.5 mM stock. Aliquot and store at -80 °C.
Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) (Gibco, catalog number: 11960-085) (4 °C)
Heat-inactivated foetal bovine serum (FBS) (Labtech, catalog number: FB-1001/500) (-80 °C)
Note: FBS must be heat-inactivated to avoid high background alkaline phosphatase activity.
200 mM L-glutamine (Gibco, catalog number: 25030024) (-20 °C)
Penicillin-streptomycin 100× stock (Gibco, catalog number: 15140122) (-20 °C)
Opti-MEM I reduced serum medium (OptiMEM) (Gibco, catalog number: 31985062) (4 °C)
Lipofectamine 2000 (Thermo Fisher, catalog number: 11668019) (4 °C)
Trypan Blue solution (Gibco, catalog number: 11538886)
Quanti-BLUE solution 100× stock (InvivoGen, catalog number: rep-qbs) (-20 °C)
Note: Dilute the provided solutions together to 1× in water, prepare 20 mL aliquots, and store at -20 °C.
1 M magnesium chloride (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M8266)
Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) (Gibco, catalog number: 10010023) (4 °C)
Trypsin-EDTA solution (Gibco, catalog number: 25200056) (4 °C)
SDS sample buffer 4× stock (Millipore, catalog number: 70607) (4 °C)
Benzonase endonuclease (Millipore, catalog number: E1014) (-20 °C)
Complete EDTA-free protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche, catalog number: 11873580001) (4 °C)
Note: Dissolve a tablet in 1 ml of water to generate a 50× stock. Aliquot and store at -20 °C.
Antibodies
FLAG antibody (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: F3165), store at -20 °C
GAPDH (Cell Signalling Technology, catalog number: 2118), store at -20 °C
Plasmids
These plasmids encode WT and mutant forms of FLAG-ALPK1 under the control of a CMV promoter and are available to request via the MRC PPU Reagents and Services website (https://mrcppureagents.dundee.ac.uk). They were purified using NucleoBond Xtra Midi Endotoxin-Free kits (Macherey-Nagel, catalog number: 740420), resuspended to 0.5 mg/mL in endotoxin-free water and stored at -20 °C.
pcDNA5-FRT-TO-FLAG (empty vector, denoted “EV”) (catalog number: DU41457)
pcDNA5-FRT/TO-FLAG-ALPK1 (catalog number: DU65668)
pcDNA5-FRT-TO-FLAG-ALPK1[T237M] (catalog number: DU65723)
pcDNA5-FRT-TO-FLAG-ALPK1[Y254C] (catalog number: DU71685)
pcDNA5-FRT-TO-FLAG-ALPK1[S277F] (catalog number: DU71952)
pcDNA5-FRT-TO-FLAG-ALPK1[V1092A] (catalog number: DU65703)
pcDNA5-FRT-TO-FLAG-ALPK1[R150A] (catalog number: DU71740)
pcDNA5-FRT-TO-FLAG-ALPK1[R150A/T237M] (catalog number: DU71743)
pcDNA5-FRT-TO-FLAG-ALPK1[R150A/Y254C] (catalog number: DU71741)
pcDNA5-FRT-TO-FLAG-ALPK1[R150A/S277F] (catalog number: DU71954)
pcDNA5-FRT-TO-FLAG-ALPK1[R150A/V1092A] (catalog number: DU71742)
Solutions
Note: Storage conditions are given in parentheses.
Antibiotic-free culture media (4 °C) (see Recipes)
Culture media (4 °C) (see Recipes)
SDS lysis buffer (use immediately) (see Recipes)
Antibiotic-free culture media (1 bottle)
Reagent Final concentration Quantity to add DMEM Not applicable 500 mL FBS 10% (v/v) 50 mL 200 mM L-Glutamine 2 mM 5.6 mL Culture media (1 bottle)
Reagent Final concentration Quantity to add DMEM Not applicable 500 mL FBS 10% (v/v) 50 mL 200 mM L-Glutamine 2 mM 5.6 mL Penicillin-streptomycin 100× 1× 5.6 mL SDS lysis buffer (5 mL)
Reagent Final concentration Quantity to add SDS sample buffer 4× 1× 1.25 mL Benzonase endonuclease 0.2% (v/v) 10 μL 1 M magnesium chloride 1 mM 5 μL Protease inhibitor cocktail 50× 1× 100 μL Water Not applicable 3.635 mL
Laboratory supplies
Similar products can also be used, but those marked by an asterisk are highly recommended.
10 cm Nunc cell culture dishes (Thermo Fisher, catalog number: 150318)*
96-well Nunc cell culture plates (Thermo Fisher, catalog number: 167008)*
25 mL sterile reagent reservoir (Thermo Fisher, catalog number: 11405758)
Clear sealing tape for 96-well plates (Thermo Fisher, catalog number: 10105383)
50 mL conical centrifuge tubes (Greiner, catalog number: 227261)
15 mL conical centrifuge tubes (Greiner, catalog number: 188271)
Serological pipettes (Thermo Fisher, catalog number: 10710810)
Safe-Lock 1.5 mL microcentrifuge tubes (Eppendorf, catalog number: 30123611)
Cellometer counting chambers (Nexcelom, catalog number: 11522186)
Combitips advanced 0.5 mL (Eppendorf, catalog number: 30089421)
Equipment
Similar equipment from other suppliers can also be used instead of those listed below. Those that have been discontinued do not have a catalog number indicated.
Cellometer Auto 2000 (Nexcelom Bioscience)
Multipette M4 (Eppendorf, catalog number: 4982000012)
8-channel adaptor (Integra Biosciences, catalog number: 10023451)
8-channel pipettor 20–200 μL (VWR, catalog number: 89079-948)
Pipetman 4-Pipette Kit (Gilson, catalog number: F167360)
Stripettor Ultra pipet controller (Corning, catalog number: 4099)
CB150 cell culture incubator (Binder)
BioMAT 2-SF cell culture hood (Conditioned Air Solutions)
Allegra X-12 benchtop centrifuge (Beckman Coulter, catalog number: 392474)
QBT2 dry block heater (Grant)
Epoch plate reader (BioTek)
Procedure
文章信息
稿件历史记录
提交日期: Jul 25, 2024
接收日期: Sep 24, 2024
在线发布日期: Oct 15, 2024
出版日期: Nov 20, 2024
版权信息
© 2024 The Author(s); This is an open access article under the CC BY license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
如何引用
Snelling, T. (2024). Measurement of the Activity of Wildtype and Disease-Causing ALPK1 Mutants in Transfected Cells With a 96-Well Format NF-κB/AP-1 Reporter Assay. Bio-protocol 14(22): e5113. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.5113.
分类
生物化学 > 蛋白质 > 活性
细胞生物学 > 基于细胞的分析方法 > 蛋白合成
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
提问指南
+ 问题描述
写下详细的问题描述,包括所有有助于他人回答您问题的信息(例如实验过程、条件和相关图像等)。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link