- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Efficient Gene-Editing in Human Pluripotent Stem Cells Through Simplified Assembly of Adeno-Associated Viral (AAV) Donor Templates
通过简化腺相关病毒(AAV)供体模板组装高效编辑人多能干细胞基因
发布: 2024年11月05日第14卷第21期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.5097 浏览次数: 2872
评审: Rajesh RanjanGuanghui YangAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
Gene-edited human pluripotent stem cells provide attractive model systems to functionally interrogate the role of specific genetic variants in relevant cell types. However, the need to isolate and screen edited clones often remains a bottleneck, in particular when recombination rates are sub-optimal. Here, we present a protocol for flexible gene editing combining Cas9 ribonucleoprotein with donor templates delivered by adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors to yield high rates of homologous recombination. To streamline the workflow, we designed a modular system for one-step assembly of targeting vectors based on Golden Gate cloning and developed a rapid protocol for small-scale isolation of AAV virions of serotype DJ. High homology-directed repair (HDR) rates in human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs), ~70% in ACTB and ~30% in LMNB1, were achieved using this approach, also with short (300 bp) homology arms. The modular design of donor templates is flexible and allows for the generation of conditional and/or complex alleles. This protocol thus provides a flexible and efficient strategy workflow to rapidly generate gene-edited hPSC lines.
Key features
• Versatile approach combining AAV-DJ donors and CRISPR ribonucleoproteins, providing an efficient method for long and short edits, insertions, and deletions in human pluripotent stem cells
• One-step cloning method for rapid generation of customized AAV donor plasmids
• Simplified AAV purification pipeline for ready-to-infect virion preparations
Keywords: AAV purification (AAV纯化)Graphical overview
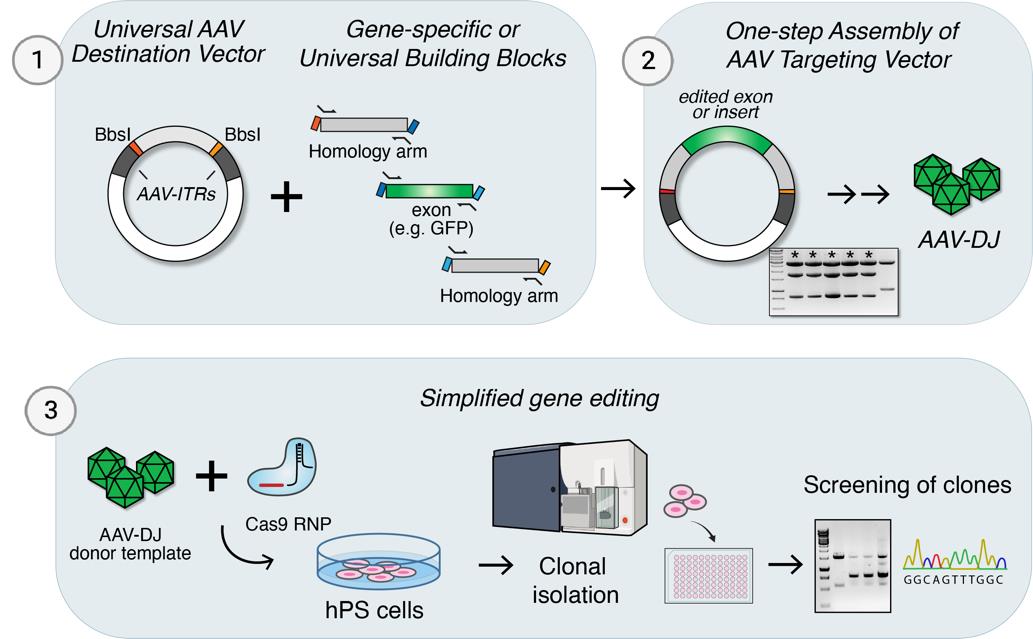
Background
The increasing availability of human genetic data offers unprecedented opportunities to understand, diagnose, and treat human diseases, but challenges remain in our ability to interpret the functional significance of specific genetic variants. At the same time, CRISPR/Cas-based gene-editing technologies have vastly simplified the means to introduce specific variants for functional interrogations [1–3]. Human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs), including human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) and human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs), are attractive model systems for such functional studies as they allow experimental manipulations in relevant human cell types [4,5]. Of particular importance, hPSCs allow disease modeling in cell types of the central nervous system, including neurons, astrocytes, and microglia [6], which are generally inaccessible from patients yet are highly relevant to study in the context of psychiatric and neuropsychiatric diseases such as autism and schizophrenia, which are both largely attributable to genetic variants that demand functional studies.
In a typical gene-editing experiment, Cas9 nuclease is introduced to a bulk of cells together with a gene-specific guide RNA (gRNA) and a repair template for homology-directed repair (HDR). This strategy provides a means for flexible and precise edits ranging from single-base-pair substitutions to large insertions. However, sub-optimal editing rates may require tedious screening of clones to obtain cells with the desired edit(s), in particular when bi-allelic edits are desired. Moreover, clonal isolation involves the inevitable risk of acquiring off-target differences between selected cells that may confound the interpretation of subsequent experiments [7], which necessitates validation in multiple clones or programmable strategies in which the same clone can give rise to both experimental and control conditions [8,9].
Recombinant adeno-associated viruses (AAVs) provide superior donor templates for HDR, especially when double-strand breaks (DSBs) are simultaneously introduced at targeted loci [10–12]. Previous studies have demonstrated high HDR rates in hPSCs when Cas9-induced DSBs were combined with AAV donors, reaching ~40%–90% without prior selection [13]. Multiple factors likely contribute to the superiority of AAV virions as vectors of HDR, including its single-stranded DNA genome and the nature of its flanking inverted terminal repeats (ITRs). Several AAV serotypes effectively transduce hPSCs, of which serotype 6 is commonly used [13,14]. AAV-DJ is a synthetic hybrid serotype with expanded tropism that provides comparable rates in hPSCs [13,15]. The use of AAV donor templates may thus overcome challenges related to limited targeting efficiencies. However, contrasting the off-the-shelf availability of Cas9 protein and synthetic sgRNAs, the multi-step cloning and production of AAV virions is time-consuming, which provides a barrier to this approach.
Here, we present a protocol for gene-editing of hPSCs that includes a system for one-step cloning of AAV targeting vectors by Golden Gate [16] assembly as well as a simplified protocol for rapid small-scale isolation of AAV virions. Combined with Cas9 ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complexes, this approach provides a highly efficient yet adaptable approach for gene editing in hPSCs, exemplified by large tag insertions, the generation of conditional alleles, as well as single base edits.
Materials and reagents
Biological materials
AAV-293 cells (Agilent, catalog number: 240073)
hESC H9, WA09 (WiCell, catalog number: WAe009-A)
One shot Stbl3 chemically competent E. coli (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: C737303)
AAV-GG plasmid vector (Addgene, # 213039)
AAV-packaging plasmids pHelper, pRC-DJ [15]
mTeSR Plus (STEMCELL, catalog number: 100-0276)
CloneR2 (STEMCELL, catalog number: 100-0691)
ReLeSR (STEMCELL, catalog number: 100-0483)
P3 Primary Cell 4D-Nucleofector Kit S (20 μL) (Lonza, catalog number: V4XP-3032)
DMEM, high glucose/GlutaMAX/pyruvate (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 31966047)
MEM, no glutamine, no phenol red (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 51200046)
Fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Merck, catalog number: F7524)
TrypLE Select enzyme, no phenol red (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 12563011)
DPBS without calcium and magnesium (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 14190250)
Bambanker freezing media (Techtum, catalog number: 23-BB01)
Matrigel hESC-qualified matrix (Corning, catalog number: 354277)
Accutase (STEMCELL, catalog number: 07920)
Thiazovivin (Cayman chemical, catalog number: 14245-5)
PrimeSTAR GXL DNA polymerase (Takara Clontech, catalog number: R050A)
Nuclease-free DEPC water, PCR grade (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: AM9937)
Alt-R S.p. HiFi Cas9 Nuclease V3, 500 μg (IDT, catalog number: 1081061)
Alt-R CRISPR-Cas9 crRNA, 2 nmol (IDT, custom design)
Alt-R CRISPR-Cas9 tracrRNA, 20 nmol (IDT, catalog number: 1072533)
BpiI FastDigest enzyme (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: FD1014)
T4 DNA ligase 2000 U/μL (NEB, catalog number: M0202T)
10× T4 DNA ligase buffer (NEB, catalog number: B0202S)
QIAEX II gel extraction kit (Qiagen, catalog number: 20021)
Plasmid Plus Midi Kit (Qiagen, catalog number: 12945)
DNEasy Blood and Tissue kit (50 st) (Qiagen, catalog number: 69504)
CaCl2 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S9888)
NaCl (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 223506)
KCl (Merck, catalog number: 4936.1000)
Na2HPO4 (Merck, catalog number: 1.06586.0500)
D-(+)-Glucose (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G7021)
HEPES (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: H3375)
MgCl2, (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M9272)
6-well culture plates (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 140675)
96-well culture plates (Corning, Falcon, catalog number: 353072)
1.5 mL Eppendorf tubes (VWR, catalog number: 89000-028)
15 mL centrifuge tubes (VWR, catalog number: 21008-216)
10 μL racked tips, low-retention sterile (VWR, catalog number: 10017-062)
200 μL racked tips, low-retention sterile (VWR, catalog number: 76322-150)
1000 μL low-retention tips (VWR, catalog number: 10017-090)
Nunc cell culture cryogenic tubes, 1 mL (500) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 377224PK)
PCR tubes and domed caps, strips of 8. (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: AB0266)
T25 EasYFlask, TC surface, filter cap (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 156367T25)
5 mL round-bottom polystyrene tubes (VWR, catalog number: 734-0445)
Amicon Ultra-4 centrifugal filter unit (Merck, catalog number: UFC810024)
35 μm cell strainer cap polystyrene tubes (Falcon, catalog number: 08-771-23)
Equipment
T100 Thermal Cycler (Bio-Rad, model: 1861096)
Microcentrifuge 5418R (Eppendorf, catalog number: 5401000010)
Benchtop refrigerated centrifuge 5430R (Eppendorf, catalog number: 022620601)
4D-Nucleofector X Unit (Lonza, catalog number: AAF-1003X)
NanoDrop 1000 UV/VIS Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: ND-1000)
FACS Aria™ Fusion Flow Cytometer (BD Biosciences, serial number: R656700J40005)
Software and datasets
CHOPCHOP [17] (version 3, http://chopchop.cbu.uib.no)
TIDE [18] (version 3.3.0; http://tide.nki.nl)
Sequence analysis software, e.g., Geneious Prime (version 2024.0.2, BioMatters, 2024-02-14)
Procedure
文章信息
稿件历史记录
提交日期: Jun 29, 2024
接收日期: Sep 6, 2024
在线发布日期: Sep 25, 2024
出版日期: Nov 5, 2024
版权信息
© 2024 The Author(s); This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/).
如何引用
de La Cruz, B. M., Mitra, S., He, B., Çelik, M., Kaminski, D., Smedler, E. and Sterky, F. H. (2024). Efficient Gene-Editing in Human Pluripotent Stem Cells Through Simplified Assembly of Adeno-Associated Viral (AAV) Donor Templates. Bio-protocol 14(21): e5097. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.5097.
分类
干细胞 > 多能干细胞 > 基于细胞的分析方法
分子生物学 > DNA > 基因表达
生物科学 > 生物技术 > CRISPR/Cas9
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link