- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Chromogranin B Purification for Condensate Formation and Client Partitioning Assays In Vitro
嗜铬蛋白B的纯化用于体外凝聚体形成及客户蛋白分配实验
发布: 2024年10月20日第14卷第20期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.5095 浏览次数: 1351
评审: Valérian DORMOYAnonymous reviewer(s)

相关实验方案

适用于 LC–MS/MS 蛋白质组学分析的大体积细胞培养上清分泌组样品制备方法优化
Basil Baby Mattamana [...] Peter Allen Faull
2025年12月20日 1210 阅读
Abstract
Chromogranin B and other members of the granin protein family form condensates that recruit clients like proinsulin. The condensation in the lumen of trans-Golgi network (TGN) is critical for the biogenesis of secretory granules. Here, we describe a protocol to purify the tagged version of chromogranin B close to its native form at the TGN, which can then be utilized for microscopy-based assays to monitor condensate formation in vitro and client partitioning depending on the material properties of chromogranin B assemblies.
Key features
• First instance of purification of full-length and tagged version of members of the chromogranin family of proteins.
• Allows purification of proteins with post-translational modifications that are acquired en route in the secretory pathway, thus closely resembling their native form at the TGN.
Keywords: Phase separation (相分离)Graphical overview
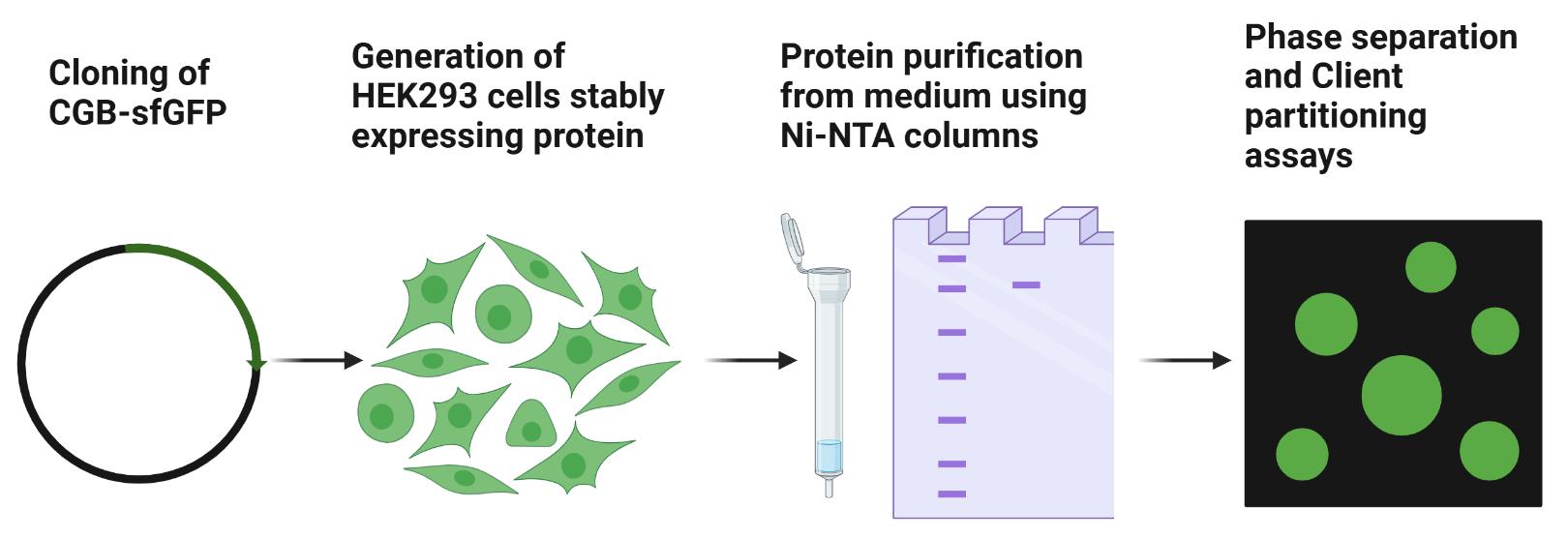
Background
Members of the chromogranin (CG) family of proteins are predominantly expressed in specialized secretory cells including the pancreatic beta cells and the cells of the neuroendocrine system. They play a critical role in driving secretory granule (SG) biogenesis [1–3]. Expression of either chromogranin A (CGA) and chromogranin B (CGB) or other granin proteins in non-specialized cells results in the formation of ectopic SG-like structures [2,4–6]. Experiments involving extracts or purified CGA, CGB, and secretogranin 2 (SCG2) from the adrenal or pituitary glands demonstrated aggregation of these proteins at an acidic pH (pH 5.2–5.5) and in presence of millimolar concentrations of calcium [6–10]. Since the pH used in previous studies is lower than that seen at the trans-Golgi network (TGN) and the calcium concentrations were much higher [10,11], the physiological significance of the aggregation in cargo sorting has remained elusive. Moreover, molecular mechanisms underlying higher-order assemblies of CGB and the impact of material properties of these assemblies on cargo sorting require further investigation.
We demonstrated that CGB forms condensates in milieu of the TGN, driven predominantly by the mildly acidic compartment of the TGN and independent of the requirement of divalent cations [12]. For this purpose, we developed a protocol using the PiggyBac transposon-based inducible mammalian expression system [13] to purify the superfolder GFP-tagged versions of CGB from the secreted medium. Moreover, by making different assemblies (condensates vs. aggregates) of CGB in the presence of calcium and zinc, respectively, we further demonstrate that the material properties of CGB assemblies drive client partitioning.
Materials and reagents
Materials
Plasmid for cloning human CGB gene (OriGene, RC201744L1)
RINS1 plasmid (Addgene, plasmid #107290)
2× Gibson master mix (NEB, catalog number: E2611)
Nhe1-HF (NEB, catalog number: R3131)
Not1-HF (NEB, catalog number: R3189)
Agarose (American Bio, catalog number: AB00972)
SYBR Safe DNA gel stain (Invitrogen, catalog number: S33102)
TAE Buffer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: B49)
PB-T-PAF, PB-RN, and PBase [13]
Water, molecular biology grade (Sigma, catalog number: W4502)
Qiagen Gel Extraction kit (Qiagen, catalog number: 28704)
Mini prep kit (Takara Bio, catalog number: 740588.50)
LB ampicillin plates (Recombinant Technologies)
HEK293 cells (ATCC, catalog number: CRL-1573)
Lipofectamine 2000 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 11668027)
DMEM high glucose (Gibco, catalog number: 11965092)
Fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Gibco, catalog number:16000044)
Penicillin-Streptomycin-Glutamine (100×) (Gibco, catalog number: 10378016)
OptiMEM (Gibco, catalog number: 51985034)
Puromycin dihydrochloride (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: J67236.XF)
G418 disulfate (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: J63871.AB)
cOmpleteTM His-Tag purification resin (Millipore Sigma, catalog number: 5893682001)
A23187 (Millipore Sigma, catalog number: C7522)
Doxycycline monohydrate (LKT Labs, catalog number: D5898)
Aprotinin (Millipore Sigma, catalog number: A6106)
Imidazole (Spectrum, catalog number: IM105)
0.45 µm cellulose acetate filtration unit (Corning, catalog number: 430768)
Amicon® Ultra centrifugal filter (Millipore Sigma, catalog number: UFC5030)
Amicon® Ultra-4 centrifugal filter (Millipore Sigma, catalog number: UFC800324)
AmiconTM Ultra-15 centrifugal filter units (Millipore Sigma, catalog number: UFC903024)
NaOH (Sigma, catalog number: 221465-500G)
Glycerol (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 02-002-937)
5 M NaCl solution (American Bio, catalog number: AB13198-01000)
Tris, 1 M Solution, pH 7.4 (American Bio, catalog number: AB14044-01000)
Sodium phosphate, dibasic, anhydrous (Na2HPO4) (J. T. Baker, catalog number: 3828-01)
Sodium phosphate, monobasic, monohydrate (NaH2PO4.H2O) (J. T. Baker, catalog number: 3818-01)
Cy3-labeled lysozyme (Lyz) (Nanocs, catalog number: LS1-S3-1)
Calcium chloride solution (Millipore Sigma, catalog number: 21115)
Zinc chloride (Sigma, catalog number: Z-4875)
1× DPBS (Gibco, catalog number: 14190250)
Chromatography columns (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 732-1010)
Glass-bottom imaging dishes (Cellvis, catalog number: D35-14-1.5-N)
250 mL filter system (Corning, catalog number: 430768)
PCR tubes (Thomas Scientific, catalog number: 1149K07)
1.5 mL microcentrifuge tubes (USA Scientific, catalog number: 1415-2500)
List of primers used for cloning of sfGFP and His tagged CGB using Gibson assembly (Table 1)
Table 1. List of primers
Primer name Sequence CGB_sfGFP_6XHis F1 FP ggcggccatcacaagtttgtacagctagcatgcagccaacgctgcttctcagcctc CGB_sfGFP_6XHis F1 RP caccggtggcgaccggtggatccaagcccctttggctgaatttctcagctatcttctgtagttcc CGB_sfGFP_6XHis F2 FP ggaactacagaagatagctgagaaattcagccaaaggggcttggatccaccggtcgccaccgg CGB_sfGFP_6XHis F2 RP ccagcacactggatcagttatctatgcggccgctcattagctgcccttgtacagctcgtccatgcc
Solutions
10× Na-P stock (see Recipes)
His-binding buffer (see Recipes)
Wash buffer (see Recipes)
Elution buffer (see Recipes)
Protein storage buffer (see Recipes)
Phase separation assay buffer (see Recipes)
NaOH solution for washing column (see Recipes)
Recipes
10× Na-P stock (500 mM, 500 mL)
33.1 g of Na2HPO4
2.4 g of NaH2PO4
pH 8.0
Store at 4°C
His-binding buffer (500 mL)
500 mM NaCl (14.61 g), 50 mM Na-P (50 mL stock) pH 6.8 (fresh)
Wash buffer
His-binding buffer with 10 mM imidazole: 150 mL of His-binding buffer + 0.1 g of imidazole (fresh).
Elution buffer
His-binding buffer with 250 mM imidazole: 10 mL of His-binding buffer + 0.17 g of imidazole (fresh).
Protein storage buffer (50 mL)
200 mM Tris-HCl (1 M Tris-HCl 10 mL), 500 mM NaCl (5 M NaCl 5 mL), 10% glycerol (5 mL), pH 6.8.
Store at 4 °C for a week if purifying more than one protein within a week.
Phase separation assay buffer (40 mL)
25 mM Tris-HCl (1 M Tris-HCl 1 mL), 150 mM NaCl (5 M NaCl 1.2 mL), 2.5% glycerol (1 mL), pH 6.1 (fresh).
NaOH solution for washing column
50 mL of 0.5 N NaOH (1 g)
Store at room temperature.
Equipment
Thermal cycler (Eppendorf, model: nexus eco)
Centrifuge (Eppendorf, model: 5425)
Centrifuge (Eppendorf, model: 5910 R)
Centrifuge (Thermo Scientific, model: Sorvall Legend Micro 21R)
S-4x Universal rotor
Zeiss LSM 880 Confocal with Airyscan (63×; 1.4 N.A. oil objective)
Nanodrop (Thermo Scientific, model: NANODROP ONEC)
Procedure
文章信息
稿件历史记录
提交日期: Apr 22, 2024
接收日期: Sep 1, 2024
在线发布日期: Sep 25, 2024
出版日期: Oct 20, 2024
版权信息
© 2024 The Author(s); This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/).
如何引用
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Parchure, A. and von Blume, J. (2024). Chromogranin B Purification for Condensate Formation and Client Partitioning Assays In Vitro. Bio-protocol 14(20): e5095. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.5095.
- Parchure, A., Tian, M., Stalder, D., Boyer, C. K., Bearrows, S. C., Rohli, K. E., Zhang, J., Rivera-Molina, F., Ramazanov, B. R., Mahata, S. K., et al. (2022). Liquid–liquid phase separation facilitates the biogenesis of secretory storage granules. J Cell Biol. 221(12): e202206132.
分类
生物化学 > 蛋白质 > 分离和纯化
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link