- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Imaging Assays to Detect DNA Damage in Trypanosome Parasites Using γH2A
利用γH2A成像检测锥虫寄生虫DNA损伤的分析方法
发布: 2024年07月05日第14卷第13期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.5026 浏览次数: 1814
评审: Marcelo S. da SilvaAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
Diseases caused by trypanosomatid parasites remain a significant unmet medical need for millions of people globally. Trypanosomatid parasites such as Trypanosoma cruzi and subspecies of Trypanosoma brucei cause Chagas disease and human African trypanosomiasis (HAT), respectively. Although efforts to find novel treatments have been successful for HAT, Chagas disease is still treated with decades-old therapies that suffer from long treatment durations and severe safety concerns. We recently described the identification and characterization of the cyanotriazole compound class that kills trypanosomes, in vitro and in vivo, by selective inhibition of the trypanosome nuclear topoisomerase II enzyme. To evaluate whether inhibition of the topoisomerase II enzyme led to parasite death due to lethal double-strand DNA breaks, we developed assays for detecting DNA damage in both intracellular amastigotes of T. cruzi and bloodstream-form T. brucei by using the canonical DNA damage marker γH2A. Herein, this article describes the protocols for detecting DNA damage using an immunofluorescence assessment of γH2A by microscopy in trypanosome parasites.
Key features
• Immunofluorescence-based assay to detect the γH2A response in T. brucei and T. cruzi parasites.
• Robust DNA damage pathway–based cellular assays to evaluate topoisomerase II poisons’ ability to cause DNA damage.
• A 384-well plate–based T. cruzi protocol allows high-resolution and high-throughput evaluation of compounds that cause DNA damage by measuring γH2A in intracellular parasites.
• This assay could be modifiable for evaluation of DNA damage responses in various intracellular and extracellular eukaryotic pathogens.
Keywords: DNA damage (DNA损伤)Background
Trypanosomatid parasites cause various medically important diseases including Chagas disease and human African trypanosomiasis, mainly affecting people living in Latin America and sub-Saharan Africa, respectively. Chagas disease is caused by the protozoan parasite Trypanosoma cruzi, which is transmitted to humans through the triatomine bug [1]. Human African trypanosomiasis (HAT) is caused by T. brucei gambiense and T. b. rhodesiense, which are transmitted through the bite of the tsetse fly [2]. Recent efforts have led to the discovery and development of fexinidazole as a novel oral treatment for HAT [3,4], whilst Chagas disease is still treated with nitroheterocyclics that have poor tolerability [1]. New efforts are needed to develop novel therapies to treat Chagas disease that are safer, efficacious, and have the potential for shortened treatment durations.
We described the identification and characterization of a novel cyanotriazole (CT) class of compounds showing promising parasiticidal activity in murine models of Chagas and HAT diseases [5]. Extensive mode of action studies showed that CTs act as trypanosome-specific topoisomerase II (Topo II) poisons. Topoisomerase II poisons act by stabilizing the enzyme in the Topo II-DNA complex after the topoisomerase II enzyme has cleaved the double-stranded DNA. The accumulation of these double-strand DNA breaks due to Topo II poisons ultimately results in cell death (Reviewed in Vann et al. [6]).
In eukaryotes, several DNA repair pathways are known to respond to DNA damage. One of the early responses to double-strand DNA breaks is a phosphorylation in the C-terminal region of histone H2A (H2AX in humans) to generate γH2A(X) [7]. In humans and non-human primates, this phosphorylation occurs on serine-139 of the conserved SQ motif. However, in T. brucei and T. cruzi, the phosphorylation occurs on threonine-130 and threonine-131, respectively. This phosphorylation is involved in signaling cascades to recruit DNA repair machinery to the site of damage. The H2A response can be detected with phospho-antibodies that recognize the specific γH2A-associated phosphorylation of histone H2A(X). Previous work by Glover and Horn identified this response in T. brucei [8], and the antibody was reported to be weakly cross-reactive against T. cruzi epimastigotes by western blot [9]; however, we were unsuccessful in detecting γH2A in T. cruzi using the T. brucei antibody in either epimastigotes or intracellular amastigotes by western blot or immunofluorescence microscopy. Therefore, we designed a new antibody to specifically detect γH2A in T. cruzi. This new antibody, specific for the T. cruzi epitope (Figure 1B), can detect T. cruzi γH2A in both western blots and immunofluorescence assays. Herein, we describe protocols for imaging-based γH2A assays for intracellular T. cruzi and bloodstream-form T. brucei.
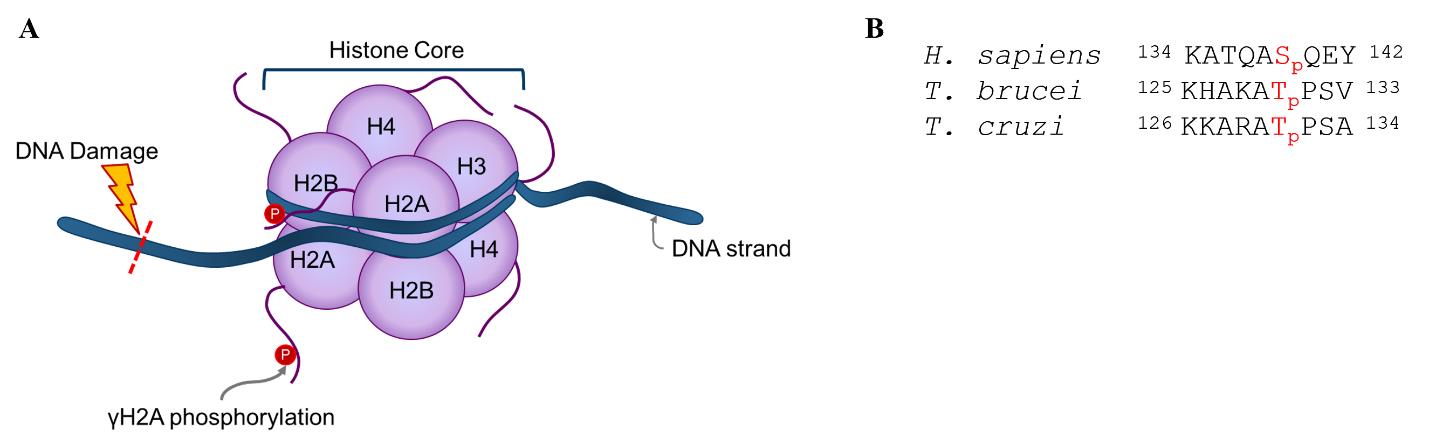
Figure 1. Overview of γH2A response to DNA damage. (A) Graphical representation of γH2A response to DNA damage. The graphic is not to scale. (B) Alignment of γH2A epitope between human (Homo sapiens), Trypanosoma brucei, and Trypanosoma cruzi. Sequences obtained from UniProt (P16104) [10] and TriTrypDB (Tb927.7.2820, TcCLB.508321.21) [11]. Numbering does not include initiator methionine.
Materials and reagents
Biological materials
Vero cells (ATCC CCL-81)
Trypanosoma cruzi CL Brener parasites expressing tdTomato (Tc) [12]
Bloodstream form (BSF) Trypanosoma brucei Plimmer and Bradford (ATCC PRA-382)
Reagents
RPMI 1640 (HyClone, catalog number: SH30027.02)
0.25% Trypsin-EDTA (Gibco, catalog number: 25200056)
Fibronectin powder (Corning, catalog number: 354008)
IMDM powder (Gibco, catalog number: 12200036)
Sodium bicarbonate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S5761)
Hypoxanthine (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: H9636)
Sodium hydroxide (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S8045)
Sodium pyruvate (100 mM) (Gibco, catalog number: 11360070)
Thymidine (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T1895)
L-cysteine (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: C7352)
Bathocuproine disulfonic acid (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 146625)
Beta-mercaptoethanol (Millipore-Sigma, catalog number: M6250)
Heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Gibco, catalog number: 10082147)
Penicillin-Streptomycin (Gibco, catalog number: 15070063)
Penicillin-Streptomycin-Glutamine (100×) (Gibco, catalog number: 10378016)
Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) (Gibco, catalog number: 20012027)
Paraformaldehyde 16% aqueous solution (Electron Microscopy Sciences, catalog number: 15710-S)
Triton X-100 (Sigma, catalog number: X100)
Tween-20 (Sigma, catalog number: P9416)
Bovine serum albumin (BSA) (Sigma, catalog number: A7906-500G)
Primary antibodies:
Rabbit anti-T. cruzi γH2A polyclonal antibody (custom-made by Thermo Fischer Scientific)
i. Epitope: KKARATpPSA
ii. Bleed 3, affinity purified
Rabbit anti-T. brucei γH2A polyclonal antibody (custom-made by Thermo Fischer Scientific)
i. Epitope: KHAKATpPSV
ii. Bleed 2, affinity purified
Secondary antibody: Goat anti-rabbit Alexa Fluor 488 (Abcam, catalog number: 150081)
Hoechst 33258 (Anaspec, catalog number: AS-83219)
VECTASHIELD Vibrance® antifade mounting medium with DAPI (Vector Laboratories, catalog number: H-1800-2)
Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D2650-100ML)
Phleomycin D1 (Zeocin) (Life Technologies, catalog number: R25001)
Compounds (as described in Rao et al. [5]):
GNF6702 (kinetoplastid proteasome inhibitor)
Benznidazole (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 419656)
CT0
CT1
CT3
Solutions
All solutions are stored at 4 °C. Solutions that are made fresh or need to be protected from light are indicated below each recipe.
RPMI complete medium (for Vero cells and T. cruzi parasites) (see Recipes)
8% fixative solution (see Recipes)
0.5% permeabilizing solution (see Recipes)
Blocking buffer 1 (see Recipes)
IFA wash buffer (see Recipes)
T. cruzi primary antibody solution (see Recipes)
T. cruzi secondary antibody solution (see Recipes)
Hoechst dye solution (see Recipes)
HMI-9 complete medium (for T. brucei) (see Recipes)
4% fixative solution (see Recipes)
0.25% permeabilizing solution (see Recipes)
Blocking buffer 2 (see Recipes)
T. brucei primary antibody solution (see Recipes)
T. brucei secondary antibody solution (see Recipes)
Recipes
RPMI complete medium (for Vero cells and T. cruzi parasites)
Reagent Final concentration Amount RPMI 1640 1× 1,000 mL FBS 9% 100 mL Penicillin-Streptomycin 0.9% 10 mL Total n/a 1,110 mL Filter medium through a 0.22 µm, low-protein binding filter.
8% fixative solution
Reagent Final concentration Amount 1× PBS - 15 mL Paraformaldehyde (16%) 8% 15 mL Total n/a 30 mL Make fresh on the day of the experiment.
0.5% permeabilizing solution
Reagent Final concentration Amount 1× PBS 1× 500 mL Triton X-100 0.5% 2.5 mL Total n/a 502.5 mL Blocking buffer 1 (for T. cruzi)
Reagent Final concentration Amount 1× PBS 1× 100 mL BSA 4% 4 g Tween-20 0.1% 0.1 mL Total n/a 100 mL IFA wash buffer
Reagent Final concentration Amount 1× PBS 1× 1,000 mL Tween-20 0.1% 1 mL Total n/a 1,000 mL T. cruzi primary antibody solution
Reagent Final concentration Amount Blocking buffer 1 1× 25 mL Primary antibody 1:250 0.1 mL Total n/a 25 mL Make fresh on the day of the experiment.
T. cruzi secondary antibody solution
Reagent Final concentration Amount Blocking buffer 1 1× 25 mL Secondary antibody 1:1,000 0.025 mL Total n/a 25 mL Make fresh on the day of the experiment, protect from light.
Hoechst dye solution
Reagent Final concentration Amount 1× PBS 1× 25 mL BSA 1% 0.25 g Hoechst 1:250 0.1 mL Total n/a 25 mL Make fresh on the day of the experiment, protect from light.
HMI-9 complete medium for T. brucei
Reagent Final concentration Amount Water n/a 730 mL IMDM powder 1× 1 packet Sodium bicarbonate 0.036 mM 3.02 g Hypoxanthine* 1.0 mM 0.136 g dissolved in 10 mL 0.1 M NaOH Sodium pyruvate 1.0 mM 10 mL Thymidine* 0.160 mM 0.039 g dissolved in 10 mL water L-cysteine* 1.0 mM 0.12 g dissolved in 10 mL water β-mercaptoethanol** 0.2 mM 14 µL diluted in 10 mL water Bathocuproine disulfonic acid* 0.050 mM 0.028 g dissolved in 10 mL water FBS 10% 100 mL Serum plus 10% 100 mL Penicillin-Streptomycin-Glutamine 1% 10 mL Total n/a 1,000 mL *Solid salts are dissolved in 10 mL of water (or 0.1 M NaOH) before adding to medium.
**β-mercaptoethanol is diluted in 10 mL of water before adding to medium. Combine ingredients and mix well. Filter medium through a 0.22 µm, low-protein binding filter.
4% fixative solution
Reagent Final concentration Amount 1× PBS - 12 mL Paraformaldehyde (16%) 4% 4 mL Total n/a 16 mL Make fresh on the day of the experiment.
0.25% permeabilizing solution
Reagent Final concentration Amount 1× PBS 1× 25 mL Triton X-100 0.25% 0.063 mL Total n/a 25 mL Blocking buffer 2 (for T. brucei)
Reagent Final concentration Amount 1× PBS 1× 100 mL BSA 3% 3 g Total n/a 100 mL T. brucei primary antibody solution
Reagent Final concentration Amount Blocking buffer 2 1× 25 mL Primary antibody 1:250 0.1 mL Total n/a 25 mL Make fresh on the day of the experiment.
T. brucei secondary antibody solution
Reagent Final concentration Amount Blocking buffer 2 1× 25 mL Secondary antibody 1:1,000 0.025 mL Total n/a 25 mL Make fresh on the day of the experiment, protect from light.
Laboratory supplies
384-well black, clear and flat-bottom microplates (Greiner, catalog number: 781097)
Tissue culture–treated cell culture flasks with vented caps in T-25, T-75, T-175 sizes (Corning, catalog numbers: 430639, 430641U, and 431306, respectively)
Micropipettes of various sizes and compatible tips (e.g., Rainin, catalog number 30456871)
Neubauer Improved hemocytometer (SKC, Inc. INCYTO C-ChipTM, catalog number: DHC-N015)
0.22 µm vacuum filter and storage bottle (Corning, catalog number: 431205)
15 mL and 50 mL conical tube (VWR, catalog numbers: 21008-216, 21008-242, respectively)
WypAll tissue wipes (WYPALL, catalog number: 34770)
24-well plate (Corning, catalog number: 3524)
1.7 mL microcentrifuge tube (Axygen, catalog number: MCT-175-C-S)
Poly-L-Lysine–coated coverslips, #1 thickness, 12 mm diameter (Corning, catalog number: 354085)
Parafilm (Amcor, catalog number: PM996)
Microscope slides (Propper, catalog number: 15400100)
Sharp-angled tweezers (Excelta, catalog number: 89411-808)
Blunt-end tweezers (Burkle, catalog number: 5386-0104)
KimTech Science KimWipes (Kimberley-Clark Professional, catalog number: 34120)
Immersion oil (Type F, Index = 1.518) (Nikon, catalog number: MXA22168)
Optional: Nalgene wash bottles (Thermo Fischer Scientific, catalog number: 2402-0500)
Optional: Benchtop vacuum aspirator
Equipment
Humidified incubator set at 37 °C, 5% CO2
NucleoCounter (ChemoMetec, NC-200) and counting cassettes: Via1-Cassette (ChemoMetec, model: 941-0012)
Microplate reagent dispenser (Thermo Fisher Scientific Multidrop) and cassettes:
Multidrop standard cassette (Thermo, catalog number: 24072670)
Multidrop small tube cassette (Thermo, catalog number: 24073295)
Benchtop light microscope with 20× (0.3 NA) objective (Zeiss, Primovert, catalog number: 491206-0005-000)
Microplate orbital shaker (Perkin Elmer DELFIA PlateShake, catalog number: 1296-004)
Plate sealer (Agilent PlateLoc Thermal Microplate Sealer)
Fluorescence microscope
ImageXpress Micro Confocal High-Content Imaging System (Molecular Devices)
Ti2-E epifluorescence microscope (Nikon)
Software and datasets
Nucleoview (ChemoMetec, version 1.2.0.0)
MetaXpress (Molecular Devices, LLC., version 6.7.0.211, 8 March 2021)
Prism v9.5.1 (GraphPad, January 26, 2023)
Excel (Microsoft, v2304, 25 April 2023)
NIS Elements AR (Nikon, version 5.20.02)
Procedure
文章信息
稿件历史记录
提交日期: Feb 21, 2024
接收日期: May 30, 2024
在线发布日期: Jun 24, 2024
出版日期: Jul 5, 2024
版权信息
© 2024 The Author(s); This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/).
如何引用
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Jumani, R. S., Thomas, B. and Rao, S. P. S. (2024). Imaging Assays to Detect DNA Damage in Trypanosome Parasites Using γH2A. Bio-protocol 14(13): e5026. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.5026.
Rao, S. P. S., Gould, M. K., Noeske, J., Saldivia, M., Jumani, R. S., Ng, P. S., René, O., Chen, Y. L., Kaiser, M., Ritchie, R., et al. (2023). Cyanotriazoles are selective topoisomerase II poisons that rapidly cure trypanosome infections. Science. 380(6652): 1349–1356.
分类
微生物学 > 微生物细胞生物学 > 细胞染色
细胞生物学 > 细胞成像 > 共聚焦显微镜
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link