- EN - English
- CN - 中文
CRISPR-Cas9 Protocol for Efficient Gene Knockout and Transgene-free Plant Generation
高效基因敲除和无转基因植物生成的CRISPR-Cas9方法
发布: 2024年06月05日第14卷第11期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.5012 浏览次数: 3407
评审: Noelia ForesiPooja VermaAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
Gene editing technologies have revolutionized plant molecular biology, providing powerful tools for precise gene manipulation for understanding function and enhancing or modifying agronomically relevant traits. Among these technologies, the CRISPR-Cas9 system has emerged as a versatile and widely accepted strategy for targeted gene manipulation. This protocol provides detailed, step-by-step instructions for implementing CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing in tomato plants, with a specific focus in generating knockout lines for a target gene. For that, the guide RNA should preferentially be designed within the first exon downstream and closer to the start codon. The edited plants obtained are free of transgene cassette for expression of the CRISPR-Cas9 machinery.
Key features
• Two sgRNAs employed.
• Takes 6–12 months to have an edited transgene-free plant.
• Setup in tomato.
Keywords: CRISPR-Cas9 (CRISPR-Cas9)Graphical overview
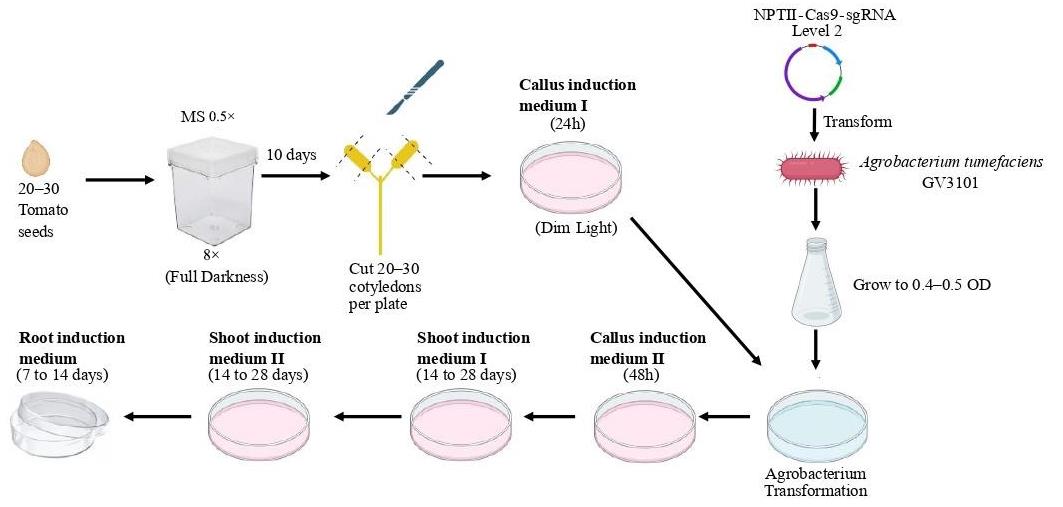
Agrobacterium-mediated transformation and plant regeneration in Solanum lycopersicum for gene editing by CRISPR-Cas9 method.
Background
Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) is an important model organism for crop improvement studies. CRISPR-Cas9 provides an effective tool for uncovering the function complexity of tomato genes. The main objective of this protocol is to establish a robust strategy for the production of knockout lines in tomato plants. Knockouts involve targeted disruption of a specific gene, resulting in loss of function. This specific variation allows researchers to examine the role of individual genes in a variety of biological processes, from development to environmental responses. It could also be used for plant genetic improvement. To achieve disruption of target genes, the CRISPR-Cas9 system utilizes small guide RNAs (sgRNAs) that direct the Cas9 endonuclease to specific genomic regions. In this system, sgRNAs have been carefully designed to target a region preferably within the first exon downstream of the ATG codon of the gene of interest. To improve efficiency, two sgRNAs are used in this protocol. The selection of sgRNAs is based on their specificity, avoiding off-targets, and ensuring efficiency. The protocol outlines a detailed workflow, including cloning of sgRNAs, assembly of expression cassettes in a vector, and Escherichia coli and Agrobacterium transformation. Then, we provide a detailed protocol for tomato transformation and screening of edited plants in order to generate homozygous edited plants free of transgene. We rely on works previously published by Nekrasov et al. [1] and Van Eck et al. [2], along with our own personal experience [3], to create a comprehensive and effective protocol for generating knock-out plants in tomato in 6–12 months. The protocol was used to demonstrate that phospholipase C2 knock-out tomato plants are more resistant to Botrytis cinerea than wild-type plants, with less ROS, an increase in jasmonic acid, and a reduction in salicylic acid–response marker genes [3].
Materials and reagents
Biological materials
Escherichia coli DH5α (Thermo Fisher, catalog number: EC0112)
Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum cv. MoneyMaker Cf-0) (in-house propagated)
Agrobacterium tumefaciens, strain: GV3101 (GoldBio, catalog number: CC-207-5x50)
pZG23C04 commercial vector (ZGene Biotech Inc, Taibei, Taiwan)
pICSL01009::AtU6p was a gift from Sophien Kamoun (Addgene plasmid #46968; http://n2t.net/addgene:46968; RRID: Addgene_46968)
pICH47751 was a gift from Sylvestre Marillonnet (Addgene plasmid #48002; http://n2t.net/addgene:48002; RRID: Addgene_48002)
pICH47761 was a gift from Sylvestre Marillonnet (Addgene plasmid #48003; http://n2t.net/addgene:48003; RRID: Addgene_48003)
pICSL11024 (pICH47732::NOSp-NPTII-OCST) was a gift from Jonathan D Jones (Addgene plasmid #51144; http://n2t.net/addgene:51144; RRID: Addgene_51144)
pICH47742::2x35S-5'UTR-hCas9(STOP)-NOST was a gift from Sophien Kamoun (Addgene plasmid #49771; http://n2t.net/addgene:49771; RRID: Addgene_49771)
pICH41780 was a gift from Sylvestre Marillonnet (Addgene plasmid #48019; http://n2t.net/addgene:48019; RRID: Addgene_48019)
pAGM4723 was a gift from Sylvestre Marillonnet (Addgene plasmid #48015; http://n2t.net/addgene:48015; RRID: Addgene_48015)
Reagents
Agar (Britania, catalog number: B010406)
Agarose (GenBiotech, catalog number: RU1010)
Ampicillin (Amp) (GenBiotech, catalog number: A-0104-5)
Acetosyringone (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D134406)
Bleach
BpiI (BbsI) (Thermo Scientific, catalog number: ER1011)
Buffer G (Thermo Scientific, catalog number: ER1011)
BsaI HF (New England BioLabs, catalog number: R3733S)
DNA Marker 100 bp (Inbio Highway, catalog number: K0177)
DNA Marker 100 bp (PBL, catalog number: MA0201)
DNA Marker Lambda/HindIII (Inbio Highway, catalog number: K0180)
Ethanol 96%
Plastic centrifuge tube, 15 and 50 mL (Henso Medical)
Gentamicin (GenBiotech, catalog number: G400-50)
HindIII (Promega, catalog number: R6041)
Buffer E (Promega, catalog number: R6041)
IPTG (GenBiotech, catalog number: I2481C5)
IAA (Merck, catalog number: 353)
Kanamycin (GenBiotech, catalog number: K0126-5)
Kinetin (Sigma, catalog number: K0753)
Kit dNTPS (Inbio Highway, catalog number: K1404)
Magenta boxes, W × L × H: 77 mm × 77 mm × 97 mm (V8505 MagentaTM vessel)
MS + Gamborg B5 vitamins (Duchefa-Biochemi, catalog number: P1278801)
NaCl (J.T. Baker, catalog number: 3624-i9)
PCR purification kit (Inbio Highway, catalog number: K1206)
Phytoagar (Sigma, catalog number: P8169)
Purification plasmid DNA kit (Qiagen, catalog number: 12123)
Rifampicin (GenBiotech, catalog number: R-120-1)
Sterile water
Sucrose (Cicarelli, catalog number: 841214)
Taq DNA polymerase (INBIO HIGHWAY, catalog number: K1007)
Taq DNA Buffer (INBIO HIGHWAY, catalog number: K1007)
MgCl2 (INBIO HIGHWAY, catalog number: K1007)
T4 ligase (Thermo Fisher, catalog number: EL0011)
T4 ligase buffer (Thermo Fisher, catalog number: EL0011)
Thiamine HCl (Sigma, catalog number: T-3902)
Timentin (GoloBio, catalog number: T-104-25)
Pipette tips (Henso Medical)
Tryptone (OXOID, catalog number: LP0042B)
X-Gal (GenBiotech, catalog number: I4281C5)
Yeast extract (OXOID, catalog number: LP0021)
2,4-D (Sigma, catalog number: D7299)
L trans-Zeatin (Golobio, catalog number: Z-105-50)
Eppendorf (Henso Medical)
Primers
Cas9_6F: 5' ACTAGCCTTGTGGCCCTACC 3'
Cas9_6R: 5' TCGATCTAGTAACATAGATGACACC 3'
RB_F1: 5' GGATAAACCTTTTCACGCCC 3'
Solutions
½ MS (see Recipes)
CIM I (see Recipes)
CIM II (see Recipes)
SIM I (see Recipes)
SIM II (see Recipes)
RIM (see Recipes)
LB (see Recipes)
Recipes
½ MS
2.15 g/L MS + Gamborg B5 vitamins
10 g/L sucrose
8 g/L agar
pH = 5.8
CIM I
4.3 g/L MS + Gamborg B5 vitamins
30 g/L sucrose
5.2 g/L Phytoagar
Sterilize and add 1 mg/L thiamine HCl, 1 mg/L 2,4-D, and 0.2 mg/L kinetin.
CIM II
4.3 g/L MS + Gamborg B5 vitamins
30 g/L sucrose
5.2 g/L Phytoagar
Sterilize and add 1 mg/L thiamine HCl, 1 mg/L 2,4-D, 0.2 mg/L Kinetin, and 200 μM acetosyringone
SIM I
4.3 g/L MS + Gamborg B5 vitamins
30 g/L sucrose
5.2 g/L Phytoagar
Sterilize and add 1 mg/L thiamine HCl, 2 mg/L trans-Zeatin, 100 mg/L kanamycin, and 250 mg/L timentin.
SIM II
4.3 g/L MS + Gamborg B5 vitamins
30 g/L sucrose
5.2 g/L Phytoagar
Sterilize and add 1 mg/L thiamine HCl, 1 mg/L trans-Zeatin, 100 mg/L kanamycin, 250 mg/L timentin, and 0.1 mg/L IAA.
RIM
4.3 g/L MS + Gamborg B5 vitamins
30 g/L sucrose
5.2 g/L Phytoagar
Sterilize and add 50 mg/L kanamycin, 250 mg/L timentin, and 1 mg/L IAA.
LB
10 g/L tryptone
5g/L NaCl
5g/L yeast extract
Laboratory supplies
Petri dishes (9 cm × 1.5 cm) (Biopetri)
Petri dishes (9 cm × 2.5 cm) (Biopetri)
Scalpel
Equipment
37 °C oven (SAN JOR, model: SE60A)
E. coli pulser transformation apparatus (Bio-Rad, model: 155103)
Heat dry bath (Benchmark, model: BSH1001-E)
Veriti 96-well thermal cycler (Applied Biosystems, model: 9902)
DNA electrophoresis apparatus (Bio-Rad, model: 55656)
Microcentrifuge Sorvall Legend Micro 17R (Thermo Fisher Scientific, model: 75002440)
30 °C oven (SAN JOR, model: SL300)
Orbital Shaker Thermo Forma (Thermo Fisher Scientific, model: 320REL)
PIPETMAN L Starter Kit, 4 Pipette Kit, P2L, P20L, P200L, P1000L (Gilson, model: F167370)
Cultivation room at 25 °C, photoperiod 16:8 h light/dark
Software and datasets
CRISPR2 (http://crispr.hzau.edu.cn/CRISPR2)
Cas-OFFinder (http://www.rgenome.net/cas-offinder/)
Solgenomics (https://solgenomics.net/)
Bioedit sequence alignment editor
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2024 The Author(s); This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/).
如何引用
Perk, E. A., Laxalt, A. M. and Cerrudo, I. (2024). CRISPR-Cas9 Protocol for Efficient Gene Knockout and Transgene-free Plant Generation. Bio-protocol 14(11): e5012. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.5012.
分类
植物科学 > 植物转化
植物科学 > 植物分子生物学 > DNA > DNA 重组
生物科学 > 生物技术 > CRISPR/Cas9
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link