- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Linearly Amplified Single-Stranded RNA-Derived Transcriptome Sequencing (LAST-seq)
线性扩增的单链RNA衍生转录组测序(LAST-seq)
发布: 2024年06月05日第14卷第11期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4998 浏览次数: 2148
评审: Alka MehraClara Morral Martinez
Abstract
Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) stands as a cutting-edge technology widely used in biological and biomedical research. Existing scRNA-seq methods rely on reverse transcription (RT) and second-strand synthesis (SSS) to convert RNA to cDNA before amplification. However, these methods often suffer from limited RT/SSS efficiency, which compromises the sensitivity of RNA detection. Here, we develop a new method, linearly amplified single-stranded RNA-derived transcriptome sequencing (LAST-seq), which directly amplifies the original single-stranded RNA without prior RT and SSS and offers high-sensitivity RNA detection and a low level of technical noise in single-cell transcriptome analysis. LAST-seq has been applied to quantify transcriptional bursting kinetics in human cells, advancing our understanding of chromatin organization’s role in regulating gene expression.
Key features
• An RNase H/DNA polymerase-based strategy to attach the T7 promoter to single-stranded RNA.
• T7 promoter mediated IVT on single stranded RNA template at single cell level.
Keywords: In vitro transcription (体外转录)Graphical overview
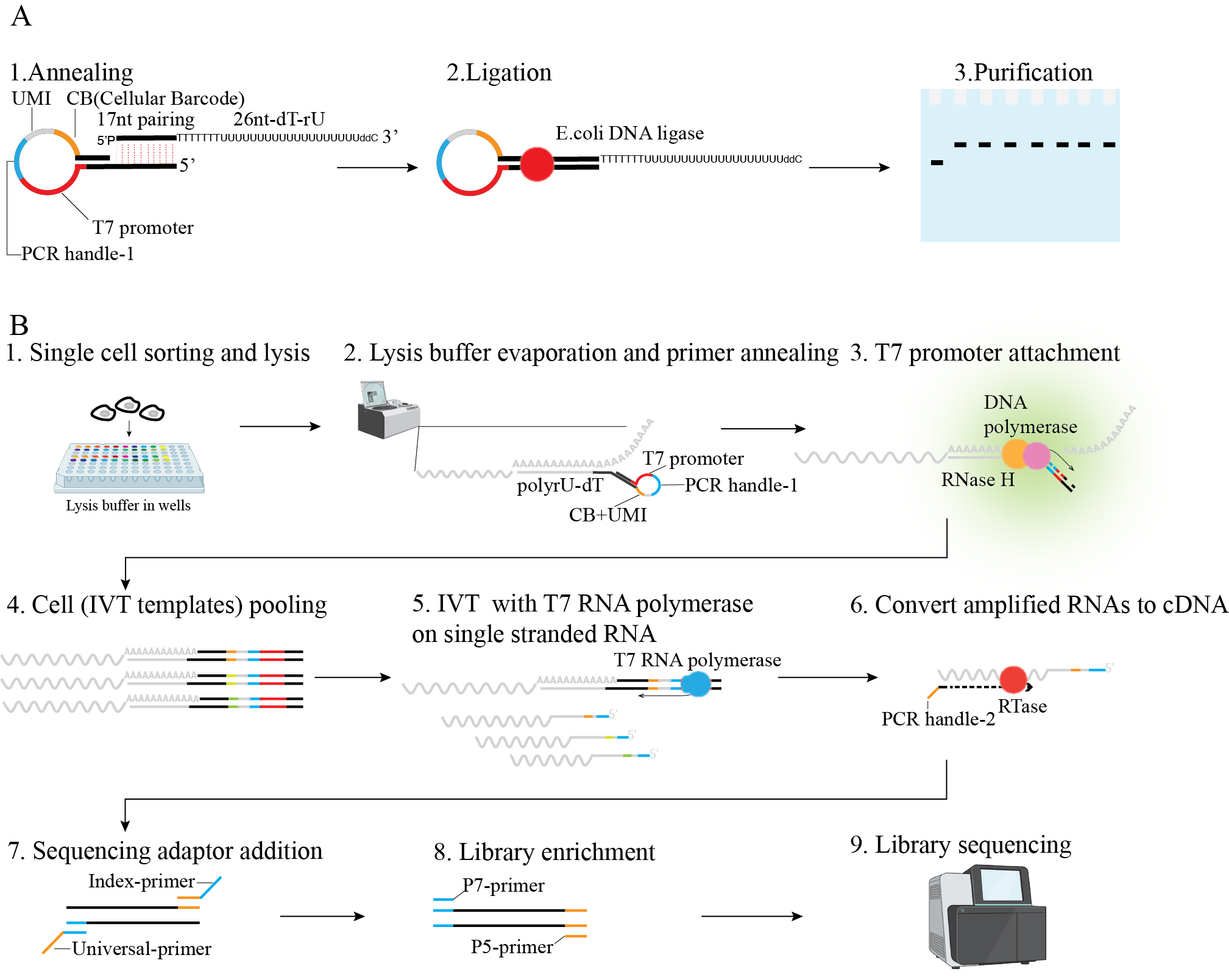
Figure 1. Scheme of linearly amplified single-stranded RNA-derived transcriptome sequencing (LAST-seq). A. LAST primer design and preparation. B. LAST-seq workflow.
Background
Single-cell transcriptome analyses have been fueled by the advancement in scRNA-seq methods. Recent technical progress has focused on enhancing digital counting through unique molecular identifiers (UMIs) [1–3], increasing cellular throughput while reducing the cost [4–10], optimizing individual protocol steps [1,2,11,12], and miniaturization [11,13,14].
Despite these improvements, the fundamental chemistry involving reverse transcription (RT) and second-strand synthesis (SSS) before single-stranded RNA amplification remains unchanged. While RT relies on reverse transcriptase, current scRNA-seq methods utilize various SSS strategies with limited efficiency, including terminal transferase [15,16] or template switching [1,5,6,9,11,12,17,18], to create cDNA priming sites for subsequent PCR, conversion from RNA/cDNA hybrid to double-stranded DNA by RNase H and DNA Pol for in vitro transcription [8,14,19], random annealing to the single-stranded cDNA for extension [2], and direct Tn5 tagmentation of the RNA/cDNA hybrid molecules [20]. As a result, the inherent limitations of RT/SSS efficiency in existing scRNA-seq methods compromise the single-molecule capture efficiency of the original RNA molecules in single cells, leading to reduced measurement accuracy and increased technical noise.
To address this challenge, we developed a novel scRNA-seq method, linearly amplified single-stranded RNA-derived transcriptome sequencing (LAST-seq). Unlike previous methods reliant on inefficient RT/SSS before RNA amplification, LAST-seq directly amplifies original ssRNA molecules in single cells in a linear fashion without prior RT/SSS. This approach achieves a high single-molecule capture efficiency and reduced technical noise compared with existing scRNA-seq methods [21]. Using LAST-seq, we characterized gene expression noise and transcriptional bursting kinetics and investigated the role of chromatin organization in regulating gene expression [21].
Materials and reagents
Reagents
E. coli DNA ligase (New England BioLabs, catalog number: M0205S)
10× TBE (Tris/boric acid/EDTA) buffer (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 1610770)
TEMED (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 1610800)
Ammonium persulfate (APS) (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 1610700)
40% Acrylamide/Bis Solution, 29:1 (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 1610146)
Urea (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 1610731)
Sodium acetate (NaOAc) (3 M) pH 5.5 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: AM9740)
NovexTM TBE-urea sample buffer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: LC6876)
Formamide (MilliporeSigma, catalog number: 11814320001)
Tris (1 M), pH 8.0 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: AM9855G)
GenEluteTM-LPA (MilliporeSigma, catalog number: 56575)
SYBRTM Gold nucleic acid gel stain (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: S11494)
Trypsin-EDTA (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 25200056)
DMEM (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 10564011)
Fetal bovine serum (MilliporeSigma, catalog number: F2442)
Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), 1× without calcium and magnesium (Corning, catalog number: 21-040-CV)
TritonTM X-100 (MilliporeSigma, catalog number: T8787)
SUPERase•InTM RNase inhibitor (Thermo Scientific, catalog number: AM2694)
Deoxynucleotide (dNTP) solution mix (New England BioLabs, catalog number: N0447S)
RNase H (New England BioLabs, catalog number: M0297S)
Klenow fragment (3'→5' exo-) (New England BioLabs, catalog number: M0212L)
Ribonucleotide solution mix (New England BioLabs, catalog number: N0466S)
T7 RNA polymerase (New England BioLabs, catalog number: M0658S)
DL-dithiothreitol solution (DTT) (MilliporeSigma, catalog number: 646563)
MgCl2 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: AM9530G)
RNA MagClean DX (Aline Bioscience, catalog number: C-1005-5/50)
Nuclease-free water (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: AM9937)
SuperScriptTM IV reverse transcriptase (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 18090050)
Q5® high-fidelity 2× Master Mix (New England BioLabs, catalog number: M0492S)
PCRClean DX (Aline Bioscience, catalog number: C-1003-5)
QubitTM dsDNA HS Assay Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: Q32854)
QubitTM assay tubes (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: Q32856)
Agilent High Sensitivity DNA kit (Agilent, catalog number: 5067-4626)
Oligos (Integrated DNA Technologies)
(Optional) High Output v2.5 reagent kit (Illumina, catalog number: 20024906)
Solutions
MIX solution for 10% TBE-Urea acrylamide gel (see Recipes)
Recipes
MIX solution for 10% TBE-Urea acrylamide gel
Components Volume 40% Acrylamide 29:1 125 mL Urea 210 g Formamide 100 mL 10× TBE 50 mL Nuclease-free water X Total 500 mL Note: The MIX can be stored at 4 °C for at least six months.
Laboratory supplies
Pipette tips (Neptune Scientific, model: S3)
AlumaSeal® CS films for cold storage (MilliporeSigma, catalog number: Z722634-100EA)
Hard-Shell® 96-well PCR plates (Bio-Rad, catalog number: HSP9601)
Axygen® 0.2 mL Maxymum Recovery® thin-wall PCR tubes (Corning, catalog number: PCR-02-L-C)
DNA LoBind® tubes (Eppendorf, catalog number: 022431021)
QubitTM assay tubes (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: Q32856)
(Optional) x-tracta gel extraction tool (MilliporeSigma, catalog number: Z722390-100EA)
Notes:
Pipette tips used in this protocol should be low-retention, RNase-free, and DNase-free, with an aerosol filter.
PCR tubes and plates used in this protocol should be low-retention, RNase-free, and DNase-free.
Equipment
GILSON® Pipetman (GILSON®, model: D10-D1000)
Freezer (VWR, model: VWR ULT Freezer 528 Eco Premium)
Countess 3 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, model: FL model)
Centrifuge 5418 R (Eppendorf, model: 5418 R)
PCR Cooler (Eppendorf, catalog number: 022510509)
VWR® Mini Centrifuge (VWR, catalog number: 76269-064)
Vortex-Genie® 2 mixer (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: SI-0236)
Vacufuge plus, Centrifuge Concentrator (Eppendorf, model: basic with A-2-VC rotor)
Eppendorf 5810R (Eppendorf, model: 5810R)
ThermoMixer C (Eppendorf, model: 5382)
Bio-Rad C1000 Touch Thermal Cycler (Bio-Rad, model: 1851148)
AirClean Systems 600 PCR workstation (AirClean Systems, model: 600)
Mini-PROTEAN® Tetra Cell (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 1658004)
Mini-PROTEAN® Tetra Cell Casting Module (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 1658021)
UViewTM Mini Transilluminator (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 1660531)
NanoDrop (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: ND-ONE-W)
PowerPacTM Basic Power Supply (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 1645050)
Qubit 4 Fluorometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: Q33238)
2100 Bioanalyzer Instrument (Agilent, model: G2939A)
High-performance computing cluster (NIH, Biowulf, model: NA)
BD FACSAria IIu (BD Bioscience, model: NA)
Magnetic rack (Diagenode, catalog number: B04000001)
Roto mini plus (Benchmark, catalog number: R2020)
Software and datasets
bcl2fastq, v2.20, free: https://support.illumina.com/sequencing/sequencing_software/bcl2fastq-conversion-software.htmL
cutadapt, v 1.15, free: https://cutadapt.readthedocs.io/en/stable/
zUMIs, v.2.9.7, free: https://github.com/sdparekh/zUMIs
The datasets are available at https://github.com/lyuj2022/LAST-seq.
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2024 The Author(s); This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/).
如何引用
Lyu, J. and Chen, C. (2024). Linearly Amplified Single-Stranded RNA-Derived Transcriptome Sequencing (LAST-seq). Bio-protocol 14(11): e4998. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4998.
分类
分子生物学 > RNA > RNA 测序
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link