- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Conditional Depletion of STN1 in Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts
小鼠胚胎成纤维细胞中 STN1 的条件性耗竭
发布: 2024年04月20日第14卷第8期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4977 浏览次数: 4259
评审: Hélène LégerAYŞE NUR PEKTAŞ
Abstract
The CTC1-STN1-TEN1 (CST) complex is a single-strand DNA-binding protein complex that plays an important role in genome maintenance in various model eukaryotes. Dysfunction of CST is the underlying cause of the rare genetic disorder known as Coats plus disease. In addition, down regulation of STN1 promotes colorectal cancer development in mice. While prior studies have utilized RNAi to knock down CST components in mammalian cells, this approach is associated with off-target effects. Attempts to employ CRISPR/Cas9-based knockout of CST components in somatic cell lines have been unsuccessful due to CST's indispensable role in DNA replication and cell proliferation. To address these challenges, we outline a novel approach utilizing a Cre-loxP-based conditional knockout in mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs). This method offers an alternative means to investigate the function and characteristics of the CST complex in mammalian systems, potentially shedding new light on its roles in genome maintenance.
Key features
• Conditional depletion of mammalian STN1 using mouse embryonic fibroblast (MEFs).
• Analysis of oxidative damage sensitivity using STN1-depleted MEFs.
• This protocol requires Stn1flox/flox mice.
Keywords: STN1 (STN1)Graphical overview
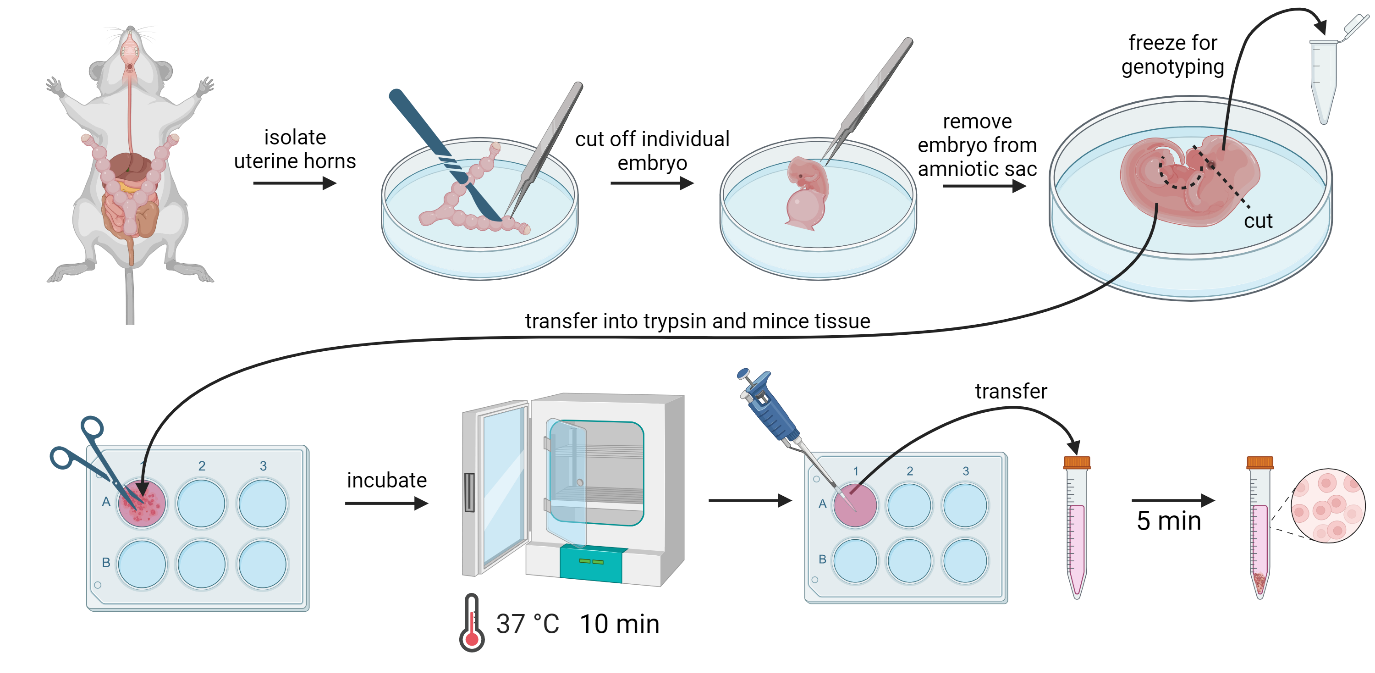
Mouse embryonic fibroblast (MEF) isolation procedure. (Images created using BioRender)
Background
The CTC1-STN1-TEN1 (CST) complex is a single-stranded DNA-binding protein complex essential in several genome maintenance pathways [1–10]. Mutations in CST components, specifically CTC1 (Conserved Telomere Maintenance Component 1) and STN1 (homolog of yeast Stn1, also known as oligonucleotide/oligosaccharide binding fold containing 1 or OBFC1, and alpha accessory factor 44 or AAF44), have been implicated in the pathogenesis of Coats plus syndrome and Dyskeratosis congenita. Coats plus syndrome is a multisystem disorder with manifestations such as retinopathy, stunted growth, and early-onset aging signs [11–13], whereas Dyskeratosis congenita presents with bone marrow failure and notable skin changes [13,14].
Initially identified as co-factors for DNA polymerase α (POLα), CST's interaction with replication machinery, including the MCM helicase complex, signifies its broader regulatory role in DNA replication [15]. Beyond POLα regulation, CST plays a critical role in telomere maintenance by binding to telomeric ssDNA and facilitating C-strand fill-in, thereby preventing telomere over-extension by telomerase and maintaining telomere stability [1,3,5,16–19]. The importance of CST is further highlighted under replication stress conditions, where it protects nascent DNA at stalled replication forks from MRE11 (meiotic recombination 11 homolog A)-mediated degradation [20]. This protection is partly due to CST interaction with RAD51 (DNA repair protein RAD51 homolog 1). CST promotes RAD51 recruitment to replication forks to protect fork stability under stress [8,9,20,21]. Beyond DNA replication, CST is recruited to double-strand breaks by the Shieldin complex, favoring the non-homologous end joining pathway, especially in BRCA1-deficient cells. CST loss in such contexts leads to increased end resection and resistance to PARP inhibitors in BRCA1-deficient cells. Thus, it appears that CST participates in cellular response to PARP inhibitors, especially in BRCA1-deficient tumors [22–25].
Genome-wide association studies have identified that STN1 variants are linked to increased risk of multiple types of cancer [26–31]. Analyses from the TCGA Pan-Cancer project show that decreased CST expression is associated with adverse clinical outcomes [32,33]. In colorectal cancer, CTC1/STN1 expression is markedly reduced, correlating with higher tumor mutation burdens and poorer survival, suggesting their potential as prognostic biomarkers [34].
The crucial role of CST in the development of genetic diseases and cancer underscores the urgency of understanding its functions in genome maintenance pathways. Traditionally, most studies investigating the role of the CST complex in mammalian cells have utilized RNAi to reduce the expression of CST components. However, the effectiveness of RNAi methods may be limited due to unintended off-target effects. Here, we describe an alternative approach using a conditional knockout strategy in mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) to examine the function of Stn1. This method involves the utilization of tamoxifen-inducible Cre recombinase to delete the promoter region and the ATG start codon of the murine Stn1 gene. The tamoxifen-inducible nature of the Cre recombinase enables researchers to grow cells before administering tamoxifen and control the timing of Stn1 deletion. By employing this method, it becomes possible to specifically deplete the mammalian Stn1 protein, leading to the destabilization of the CST complex. Additionally, the study demonstrates that conditional knockout of Stn1 renders cells more susceptible to damage caused by hydrogen peroxide exposure, emphasizing the significance of the CST complex in countering DNA damage during replication stress and oxidative stress.
Materials and reagents
Biological materials
CreERT2 C57BL/6 mice harboring the conditional CreERT2 transgene (Jackson Laboratory, stock 004682)
Homozygous Stn1flox/flox (Stn1F/F) C57BL/6 mice (generated as described in Nguyen et al. [34])
CreERT2; Stn1F/F and control Stn1F/F C57BL/6 mice: generated by crossing with Stn1F/F with CreERT2 C57BL/6 mice to generate progeny heterozygous for Stn1Flox allele and hemizygous for the CreERT2 genotype. These mice were then bred to homozygous Stn1F/F mice to derive Stn1 conditional knockout CreERT2; Stn1F/F and control Stn1F/F genotypes as described previously [34].
DMEM/F-12 (Gibco, catalog number: 11320033)
Fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Biowest, catalog number: S1620)
Antibiotic/antimycotic solution (HyClone, catalog number: SV30079.01)
Trypsin-EDTA 0.05% and 0.025% (Gibco, catalog number: 2530062)
DMSO (Sigma, catalog number: D-5879)
4-Hydroxytamoxifen (4-OHT) (VWR, catalog number: 89152-604)
KOD Hot Start DNA Polymerase kit (Millipore Sigma, catalog number: 710863, solutions provided in the kit)
Oligos:
oIMR5984: 5'-GCTAACCATGTTCATGCCTTC-3' (Cre transgene forward)
oIMR8744: 5'-CAAATGTTGCTTGTCTGGTG-3' (Cre transgene reverse)
oIMR8745: 5'-GTCAGTCGAGTGCATAGTTT-3' (Cre internal positive control forward)
oIMR9074: 5'-AGGCAAATTTTGGTGTACGG-3' (Cre internal positive control reverse)
Stn1loxPShift-F: 5'-TGTAATCCCAGCGCTCAGGAG-3'
Stn1loxPShift-R: 5'-GATCTGACAGAGATCTCCTGGCT-3'
Obfc1 5'wtF2: 5'-GACTCCTTAGCCCCAGATCTCCGTCAT-3'
Obfc1 5'mtR: 5'-CTTCGTATAGCATACATTATACGAAGTTATGGATCCACCGACT-3'
Obfc1 5'mtF: 5'-CCACATAGTCGGTGGATCCATAACTTCGT-3'
Obfc1 5'wtR: 5'-GGGCTAGGGTGTAGCTCAATGGTAGA-3'
Obfc1 3'wtF: 5'-CTCTGGGGAGACTGTCTCAGATGTTCA-3'
Obfc1 3'mtR: 5'-GAGGCTCAGGATCCATAACTTCGT-3'
Obfc1 3'mtF: 5'-GCCAGCCTGGTCTACGTGACAATAACT-3'
Obfc1 3'wtR: 5'-GGTCATATGGCCTCACCCTCTAAGA-3'
Glycerol (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: BP-229-1)
Agarose (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A9539-500G)
DTT (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D0632-5G)
Anti-STN1 antibody (Santa Cruz, catalog number: sc-376450), 1:500 dilution
Anti-β-actin (Sigma, catalog number: A2228) 1:60,000 dilution
Secondary horseradish peroxidase antibody: TrueBlot anti-mouse IgG HRP conjugated (Rockland, catalog number: 18-8817-30) 1:2,000 dilution
SuperSignal West Femto (Thermo Fisher, catalog number: 34095)
Hydrogen peroxide (30%, ACS grade) (Ward’s Science, catalog number: 470301)
Crystal Violet (Sigma, catalog number: C3886)
CHAPS (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: BP571-5)
Ethanol (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 459844-4L)
Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: BP166-500)
Bromophenol Blue (Sigma, catalog number: B-8026)
NaOH (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: S318-500)
NaCl (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: S271-1)
Tris-HCl (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T3253-500G)
Na2HPO4 (VWR, catalog number: 0404-500G)
KH2PO4 (J.T. Baker, catalog number: 3246-01)
KCl (EMD, catalog number: PX1405-1)
Tween-20 (VWR, catalog number: M147-1L)
Non-fat dry milk (Nestle, catalog number: 12428935)
2 mM 4-OHT stock solution (see Recipes)
DNA isolation lysis buffer (see Recipes)
DNA isolation neutralization buffer (see Recipes)
Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), pH 7.4 (see Recipes)
CHAPS lysis buffer (see Recipes)
Loading buffer (see Recipes)
Crystal violet staining solution (see Recipes)
1% SDS in 70% Ethanol
PBS-Tween (PBST)
DMEM/F-12 culture medium (see Recipes)
Recipes
All solutions are prepared with either autoclaved Milli-Q water or DMSO.
2 mM 4-OHT stock solution
Reagent Final concentration Quantity or Volume 4-OHT 2 mM 7.75 mg DMSO n/a 10 mL Total n/a 10 mL Store at -20 °C. Protect from light. For long-term storage, store the solution at -80 °C.
DNA isolation lysis buffer
Reagent Final concentration Quantity or Volume NaOH 25 mM 20 mg EDTA 0.2 mM 1.17 mg H2O n/a 20 mL Total n/a 20 mL Store at room temperature (RT).
DNA isolation neutralization buffer (pH 5.5)
Reagent Final concentration Quantity or Volume Tris-HCl 40 mM 69.9 mg H2O n/a 20 mL Total n/a 20 mL Store at RT.
PBS
Reagent Final concentration Quantity or Volume NaCl 137 mM 8 g KCl 2.7 mM 0.2 g Na2HPO4 10 mM 1.44 g KH2PO4 1.8 mM 0.24 g H2O n/a 1,000 mL Total n/a 1,000 mL Store at RT.
CHAPS lysis buffer
Reagent Final concentration Quantity or Volume CHAPS 10% 1% 10 mL Tris-HCl pH 7.4 30 mM 363.4 mg NaCl 150 mM 876.6 mg DTT 200 mM 3 g H2O n/a 90 mL Total n/a 100 mL Store at -20 °C.
Loading buffer
Reagent Final concentration Quantity or Volume SDS 20% 4% 20 mL Tris-HCl pH 6.8 100 mM 1.21 g Bromophenol Blue 0.2% 0.2 g Glycerol 20% 20 mL H2O n/a 60 mL Total n/a 100 mL Store at RT.
Crystal violet staining solution
Reagent Final concentration Quantity or Volume Crystal Violet 0.5% 2.5 g Ethanol n/a 500 mL Total n/a 500 mL Store at RT.
1% SDS in 70% Ethanol
Reagent Final concentration Quantity or Volume SDS 20% 1% 50 mL Ethanol 70% 700 mL H2O n/a 250 mL Total n/a 1,000 mL Store at RT.
PBST
Reagent Final concentration Quantity or Volume NaCl 137 mM 8 g KCl 2.7 mM 0.2 g Na2HPO4 10 mM 1.44 g KH2PO4 1.8 mM 0.24 g Tween-20 50% 0.05% 1 mL H2O n/a 999 mL Total n/a 1,000 mL Store at RT.
DMEM/F-12 culture medium
Reagent Final concentration Quantity or Volume DMEM/F-12 n/a 500 mL FBS
100× antibiotic/antimycotic
13%
1×
75 mL
5 mL
Total n/a 580 mL
Laboratory supplies
96-well plates (Genesee Scientific, catalog number: 25-109)
6-well plates (VWR, catalog number: 10062-892)
10 cm tissue culture dishes (Nest Biotechnology, catalog number: 704201)
PVDF membrane (MilliporeSigma, catalog number: ISEQ00010)
Forceps (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 08-880)
Dissecting scissors (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 08-940)
Scalpel (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 12-000-164 and 12-000-161)
Equipment
Inverted microscope (Fisherbrand, model: 03000013)
SDS-PAGE and western blot transfer apparatus (Bio-Rad, model: Mini-PROTEAN Tetra System)
Thermocycler (Bio-Rad, model: T100 Thermal Cycler)
iBright imaging system (Thermo Fisher, model: CL1000)
Plate reader (BioTek, model: Synergy H1)
Software and datasets
GraphPad Prism v9.3 (GraphPad, 11/15/2021)
ENSEMBL Mouse genome browser 110 (https://useast.ensembl.org/Mus_musculus/Info/Index)
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2024 The Author(s); This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/).
如何引用
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Knowles, S. and Chai, W. (2024). Conditional Depletion of STN1 in Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts. Bio-protocol 14(8): e4977. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4977.
- Nguyen, D. D., Kim, E., Le, N. T., Ding, X., Jaiswal, R. K., Kostlan, R. J., Nguyen, T. N. T., Shiva, O., Le, M. T. and Chai, W. (2023). Deficiency in mammalian STN1 promotes colon cancer development via inhibiting DNA repair.Sci. Adv. 9(19): eadd8023. https://doi.org/doi:10.1126/sciadv.add8023
分类
癌症生物学 > 基因组不稳定性及突变 > 遗传学
癌症生物学 > 基因组不稳定性及突变 > 动物模型
生物科学 > 生物技术 > CRISPR/Cas9
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link