- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Immunofluorescent Staining Assay of 3D Cell Culture of Colonoids Isolated from Mice Colon
来自小鼠结肠的结肠体在3D细胞培养中的免疫荧光染色分析
发布: 2024年03月05日第14卷第5期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4950 浏览次数: 2480
评审: Samantha HallerAbhijnya KanugoviAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
Here, we describe immunofluorescent (IF) staining assay of 3D cell culture colonoids isolated from mice colon as described previously. Primary cultures developed from isolated colonic stem cells are called colonoids. Immunofluorescence can be used to analyze the distribution of proteins, glycans, and small molecules—both biological and non-biological ones. Four-day-old colonoid cell cultures grown on Lab-Tek 8-well plate are fixed by paraformaldehyde. Fixed colonoids are then subjected to antigen retrieval and blocking followed by incubation with primary antibody. A corresponding secondary antibody tagged with desired fluorescence is used to visualize primary antibody–marked protein. Counter staining to stain actin filaments and nucleus to assess cell structure and DNA in nucleus is performed by choosing the other two contrasting fluorescences. IF staining of colonoids can be utilized to visualize molecular markers of cell behavior. This technique can be used for translation research by isolating colonoids from colitis patients’ colons, monitoring the biomarkers, and customizing their treatments.
Key features
• Analysis of molecular markers of cell behavior.
Protocol to visualize proteins in 3D cell culture.
• This protocol requires colonoids isolated from mice colon grown on matrigel support.
• Protocol requires at least eight days to complete.
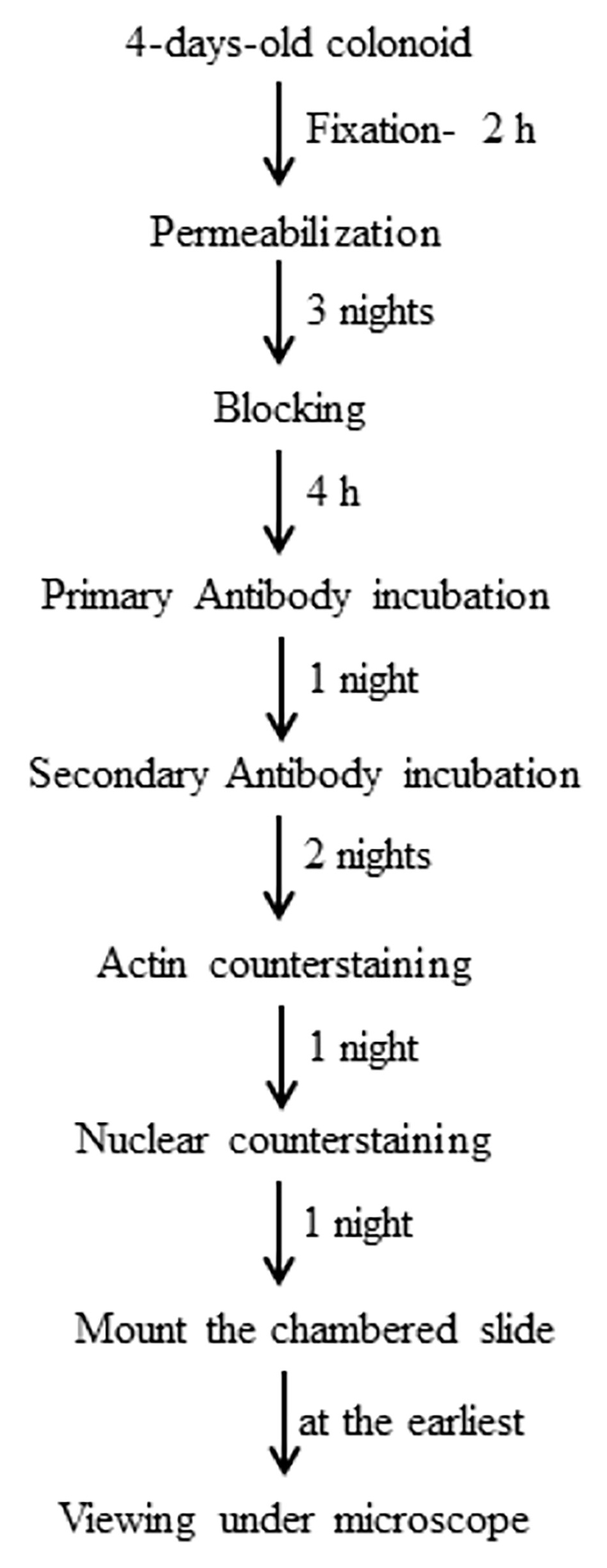
Graphical overview
Background
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) represents a chronic intestinal inflammation with unknown etiology, which has been linked to genetic and environmental factors. Dysregulation of epithelial-mucosal homeostasis is a key feature of IBD pathogenesis. Epithelial-mucosal lining acts as a defensive barrier against harmful luminal microenvironment. In the past, to understand the progression of IBD, immunofluorescent staining was used to assess the key markers of cell differentiation and proliferation. Staining has been used mostly either for fixed intestinal tissues (as an in vivo model) or for traditional 2D cultures of immortal cell lines (as an in vitro model), which lack the spatial 3D orientation of the cells. There are other staining techniques such as in situ hybridization, immunohistochemistry, and Alcian blue staining utilizing colonoids [1]. Here, we describe the use of immunofluorescent staining of colonoids to mimic the intestinal physiological and pathophysiological relevance. This is an assay that shows the expression of a protein as well as its subcellular location in a realistic way, providing significant benefits to translational research by screening potential therapeutic drugs and their effects on cell differentiation and proliferation for IBD patients.
Materials and reagents
Biological materials
4–6-weeks-old C57BL/6Jmice (Jackson Laboratories, strain number: 000664)
Reagents
Pipette tip: 1,000 µL, 20–200 µL, 1–10 µL (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog numbers: P1126, P1179, and P1060, respectively)
Matrigel phenol-red free (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: CB-40234C)
Gibco DMEM/F-12 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 11320033)
Penicillin-Streptomycin (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 15140122)
L-Glutamine solution (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G7513-100ML)
Fetal bovine serum (FBS), heat inactivated (Corning, catalog number: 35-011-CV)
GlutaMAX supplement (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 35050079)
HEPES buffer solution (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 83264-100ML-F)
N-2 supplement (100×) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 17502048)
B27 supplement (50×), serum free (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 17504044)
Epidermal growth factor (EGF) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: E1257-0.1MG)
ROCK inhibitor (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 688001-500UG)
1× phosphate buffered saline (PBS) (without calcium and magnesium) (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: MT21040CM)
Paraformaldehyde 16% (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 043368-9M)
FocusClear solution (CelExplorer, catalog number: FC-101)
Triton X-100 solution (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: P185111)
Tween 20 solution (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: P185113)
Sodium azide (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S2002-5G)
Vector Laboratories goat serum (Cole-Parmer, catalog number: S-1000)
ProLong Gold Antifade Mountant with DNA blue fluorescence stain DAPI (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: P36931)
Ted Pella Inc clear nail polish (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: NC 1849418)
Solutions
Minigut medium (see Recipes)
4% paraformaldehyde solution (see Recipes)
Immunofluorescence (IF) buffer (see Recipes)
Permeabilization solution (see Recipes)
Blocking buffer (see Recipes)
Dilution buffer (see Recipes)
Recipes
Minigut medium
Conditioned medium (1 volume of L-cell medium and 1 volume of DMEM F12 containing 1:100 vol/vol penicillin-streptomycin, 1:100 vol/vol glutamine, and 20% vol/vol FBS) [2]
GlutaMAX 1:100 vol/vol
10 mM HEPES buffer
Penicillin-streptomycin 1:100 vol/vol
N-2 supplement 1:100 vol/vol
B27 supplement 1:50 vol/vol
EGF 50 ng/mL (final concentration)
ROCK inhibitor 10 µM (final concentration)
4% paraformaldehyde solution
1:4 vol/vol 16% paraformaldehyde and 1× PBS
Immunofluorescence (IF) buffer
Triton X-100 0.2% (vol/vol), Tween 20 0.05% (vol/vol), 1× PBS 99.75% (vol/vol)
Permeabilization solution
Triton X-100 2% (vol/vol) and 1× PBS 98% (vol/vol)
Blocking buffer
Goat serum 10% (vol/vol), Triton X-100 2% (vol/vol), sodium azide 0.02% (wt/vol), 1× PBS 88% (vol/vol)
Dilution buffer
Triton X-100 0.25% (vol/vol), goat serum 1% (vol/vol), sodium azide 0.02% (wt/vol), 1× PBS 98.75% (vol/vol)
Equipment
Costar 24-well clear TC-treated multiple well plates individually wrapped, sterile (Corning, catalog number: 3524)
Pipetman—PK1000, PK200, PK20 (Gilson, catalog numbers: F144059M, F144058M, and F144056M, respectively)
Lab-Tek chamber slide 8-well glass slide (Nunc, catalog number: 154941)
Laminar flow hood (LabGard Class II type A2 Biological Safety cabinet) (Nuaire, model: NU-540)
3110 CO2 water jacketed cell incubator (Thermo Fischer Scientific, model: 4120)
Digital water bath (VWR, catalog number: 89501-460)
Sorvall ST 16R centrifuge (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 75-004-240)
All-in-One fluorescence microscope (Keyence BZ-X series, model: BZ-X810) (Figure 1)
Rectangular ice pan (ice tray/bucket) (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 07-210-107)
Micro cover glass (VWR, catalog number: 48393252)
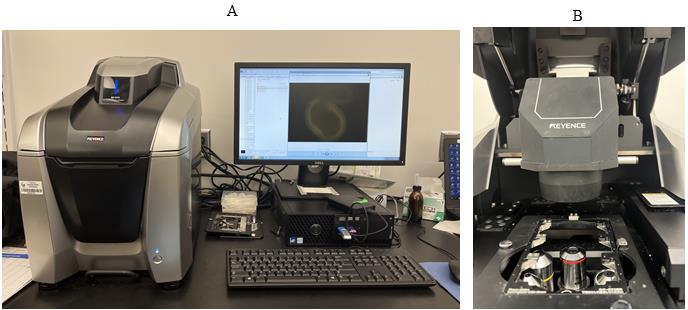
Figure 1. Keyance microscope. A. Keyence microscope with software showing the immunofluorescent staining of a colonoid. B. Keyance microscope showing the holder to be used for 8-well Lab-Tek chamber slide.
Software and datasets
BZ-X analyzer (https://www.keyence.com/bz-x810)
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2024 The Author(s); This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/).
如何引用
Mehrotra, T., Shi, X. and Merlin, D. (2024). Immunofluorescent Staining Assay of 3D Cell Culture of Colonoids Isolated from Mice Colon. Bio-protocol 14(5): e4950. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4950.
分类
干细胞 > 类器官培养
细胞生物学 > 细胞分离和培养 > 3D细胞培养
细胞生物学 > 细胞染色 > 蛋白质
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link