- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Isolation and Culture of Neural Stem/Progenitor Cells from the Hippocampal Dentate Gyrus of Young Adult and Aged Rats
青年和老年大鼠海马齿状回神经干/祖细胞的分离和培养
发布: 2023年10月05日第13卷第19期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4843 浏览次数: 2267
评审: Vivien J. Coulson-ThomasMunenori IshibashiAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
Adult neural stem/progenitor cells (NSPCs) in two neurogenic areas of the brain, the dentate gyrus and the subventricular zone, are major players in adult neurogenesis. Addressing specific questions regarding NSPCs outside of their niche entails in vitro studies through isolation and culture of these cells. As there is heterogeneity in their morphology, proliferation, and differentiation capacity between these two neurogenic areas, NSPCs should be isolated from each area through specific procedures and media. Identifying region-specific NPSCs provides an accurate pathway for assessing the effects of extrinsic factors and drugs on these cells and investigating the mechanisms of neurogenesis in both healthy and pathologic conditions. A great number of isolation and expansion techniques for NSPCs have been reported. The growth and expansion of NSPCs obtained from the dentate gyrus of aged rats are generally difficult. There are relatively limited data and protocols about NSPCs isolation and their culture from aged rats. Our approach is an efficient and reliable strategy to isolate and expand NSPCs obtained from young adult and aged rats. NSPCs isolated by this method maintain their self-renewal and multipotency.
Key features
• NSPCs isolated from the hippocampal dentate gyrus of young adult and aged rats, based on Kempermann et al. (2014) and Aligholi et al. (2014).
• Maintenance of NSPCs isolated from the dentate gyrus of aged rats (20–24 months) in our culture condition is feasible.
• According to our protocol, maximum growth of primary neurospheres obtained from isolated NSPCs of young and aged rats took 15 and 35 days, respectively.
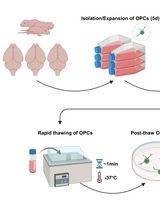
Graphical overview

Isolation and expansion of neural stem/progenitor cells
Background
Neural stem/progenitor cells (NSPCs) in neurogenic areas of the adult mammalian brain, i.e., the subventricular zone (SVZ) of the lateral ventricle and the subgranular zone of the hippocampal dentate gyrus (DG), divide symmetrically and asymmetrically to preserve their lineage (Walker and Kempermann, 2014; Gage, 2019). In a symmetric division, the number of progenitor cells increases, as two identical daughter cells originate from a progenitor cell or stem cell. The asymmetric division of progenitor cells produces two distinct types of cells. For example, one radial-glial cell gives rise to one radial-glial cell and one neuron (Zhao and Moore, 2018). Neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus contributes to learning, memory, and mood regulation, which decline during aging. Isolation of NSPCs from rat dentate gyrus provides valuable adult-cell-based models for identifying cellular and molecular mechanisms of neurogenesis in the hippocampus and to assess the effects of extrinsic factors and drugs on their functions outside their niches. There are different intrinsic regulatory mechanisms for NSPCs in the DG and SVZ (Takei, 2019). With increasing age, a repertoire of intrinsic and extrinsic factors drives most of the NSPCs to enter the senescent stage, limiting their proliferative capacity, and leading to subsequent dysfunctions (Obernier and Alvarez-Buylla, 2019). Slow proliferation and declining differentiation capacity are features of NSPCs in aging, which make finding strategies for improvement of neurogenesis during aging important (Kase et al., 2020).
The study of NSPCs function and their responses to aging, regeneration purposes, and molecular and cellular mechanisms of neurogenesis in various cell-culture-based models of different neurological disorders, including neurodegenerative and neurovascular diseases, requires isolation and culture of NSPCs from adult neurogenic niches (Akers et al., 2014; Christian et al., 2014; Bond et al., 2015). Among various approaches, neurosphere culture provides a 3D environment-like niche of neural stem cells, increases cell division, and offers conditions permissible for more passage numbers (Azari et al., 2010; Guo et al., 2012; Aligholi et al., 2014). However, recognition of cell morphology is difficult in the neurosphere culture system. Cells in the center of neurospheres may differentiate slowly with low survival and yield (Sun et al., 2011). In monolayer cell culture, cells have easy access to nutrients and their morphology could be easily detected. However, cells in this method might differentiate spontaneously, and self-renewal ability declined after more passages (Reynolds and Rietze, 2005; Ray and Gage, 2006).
As the proliferation and differentiation potential of the hippocampal DG differs from the SVZ, developing a complete protocol to obtain high-yield NSPCs from rat DG is needed. There is controversy regarding hippocampus-derived stem cells from adult rats and whether they have unlimited self-renewal or limited proliferative and differentiating potential (Gobbel et al., 2003; Chen et al., 2007). In this method, the expansion of isolated cells from aged rats has been introduced and discussed.
Using this isolation and culture method, we produced a robust and reproducible number of DG neurospheres from young adult and aged rats after 14–18 days and 25–30 days, respectively. In our method, 1.5 × 105 neural progenitor cells yield 120 spheres of 200–250 µm for young adult rats, and 7 × 104 neural progenitor cells yield 90 spheres of 100 µm for aged rats on average. An appropriate approach providing optimal regional-specific NSPCs could improve utilizing cells in a clinical setting for the treatment of neurological disorders as well as boost experimental aging research.
Materials and reagents
Animals
Animal housing was performed in accordance with the Guidelines of the Shefa Neuroscience Research Center, Tehran, Iran. Young adult male Wistar rats between 2 and 3 months of age (180–230 g) and aged rats between 20 and 24 months (400–450 g) were used.
General materials
Ketamine (alfasan, catalog number: 36408/3000)
Xylazine (alfasan, catalog number: 36408/3007)
Glass Petri dish (Nest Biotechnology, catalog number: 704001)
Phosphate buffer saline (PBS) (tablet) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 18912014)
0.2, 0.5, and 1.5 mL Eppendorf tubes (Nest Biotechnology, catalog number: 613111)
6, 12, 24, 48, and 96 adherent well plates (treated) (JetBiofil, catalog number: TCP011096, TCP011012, TCP011048)
Non-adherent well plates: 6 wells (Falcon, catalog number: 353046) and 12 wells (Falcon, catalog number: 351143)
Adherent T-25 flask (JetBiofil, catalog number: TCF012050)
Non-adherent T-25 flask (JetBiofil, catalog number: TCF012600)
0.2 μm filter (PES membrane) (BioFil, catalog number: FMC 2011018)
Parafilm (Sigma, catalog number: P7793)
96% ethanol (Merck, catalog number: 100971)
70 μm cell strainer (BD Falcon, catalog number: 352340)
Petri dish culture (JetBiofil, Germany, MCD000035)
15 and 50 mL Falcon tubes (JetBiofil, catalog number: CFT011500)
Pipette tips blue 1,000 μL (Universal, catalog number: 2451-1K0), yellow 100 μL (Universal, catalog number: 200-B-YL), and 10 μL (Labcon Eclipse, catalog number: 490007-952)
Reagents
0.05% Trypsin/EDTA (Biowest, catalog number: L0931-100)
Digestive enzymes and materials:
Papain (Roche, catalog number: 108014)
Dispase (Gibco, catalog number: 17105-041)
DNase (Roche, catalog number: 11284932001)
Accutase (Sigma, catalog number: A6964)
L-Cysteine (Sigma, catalog number: 52904)
EDTA (Sigma, catalog number: 17892)
Hanks’ balanced salt solution (HBSS) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 24020117)
Fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 10270106)
Trypan blue solution 0.4% (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T8154)
4% Paraformaldehyde (powder) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P6148)
Triton X-100 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T8787)
Bovine serum albumin (BSA) (powder) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A2058)
Normal goat serum (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 50197Z)
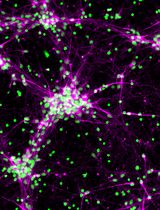
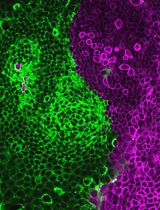
Mouse anti-Nestin (Merck Millipore, catalog number: MAB 353)
Rabbit anti-Sox2 (Santa Cruz, catalog number: SC20088)
Mouse anti-GFAP (Sigma, catalog number: G3893)
Goat anti-rabbit IgG (Abcam, catalog number: ab9717)
Goat anti-mouse (Abcam, catalog number: ab6785)
4’,6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 62248)
Laminin (Sigma, catalog number: L2020)
Poly-L-ornithine solution (Sigma, catalog number: P4957)
Culture medium (see Recipes)
Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM)/F12 (Gibco, catalog number: 11320033)
N2 supplement (Gibco, catalog number: 17501), used for serum-free culture condition of neuroblastoma and primary cells of the central nervous systems. It is composed of vitamins, hormones, insulin, and transferrin. These components maintain neural stem cells in an undifferentiated state and support the proliferation of cells in a serum-free culture
B27 supplement (Gibco, catalog number: 12513-010), a supplement as a cocktail of antioxidants, vitamins, and proteins to reduce reactive oxygen damage and for the long-term survival of neural stem cells. It is a widely used supplement for serum-free culture conditions. Therefore, this supplement contains defined components necessary for maintaining the health of the culture and reducing variability
Heparin (Sigma, catalog number: H3149)
Penicillin/Streptomycin (Pen/Strep) (Sigma, catalog number: P4333)
Amphotericin B (Biowest, catalog number: L0009-050)
Glutamax (Gibco, catalog number: 35050-061)
Basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) (Sigma, catalog number: F0291)
Epidermal growth factor (EGF) (Sigma, catalog number: E4127)
Solutions
70% ethanol (see Recipes)
Digestive solution (sterile, 0.2 μm filtered) (see Recipes)
Blocking solution (see Recipes)
Antibody solution (see Recipes)
Growth medium (culture medium) (see Recipes)
Coating solution (sterile, 0.2 μm filtered) (see Recipes)
Dissection solution (see Recipes)
Ketamine (80 mg/mL) and xylazine (10 mg/mL) working solutions (see Recipes)
PBS (1×) (see Recipes)
Recipes
70% ethanol
Dilute 365 mL of 96% ethanol with 135 mL of distilled water to make up a volume of 500 mL of 70% ethanol.
Digestive solution (sterile, 0.2 μm filtered)
Dissolve 40 μL of Dispase (2 mg/mL), 80 μL of DNase (0.2 mg/mL), 100 μL of Papain (0.5 mg/mL), 1 mg of L-cysteine, and 100 μL of EDTA in 2 mL of DMEM/F12. This volume of solution is appropriate for one rat.
Preparation of papain (0.5 mg/mL): add 100 μL of papain stock solution (10 mg/mL) to 1.95 mL of DMEM/F12 basic medium to prepare 2 mL of 0.5 mg/mL papain working solution.
Preparation of Dispase (2 mg/mL): add 100 μL of Dispase stock solution (10 mg/mL) to 1.9 mL of DMEM/F12 basic medium to prepare 2 mL of 2 mg/mL Dispase working solution.
Preparation of DNase (0.2 mg/mL): add 80 μL of DNase stock solution (5 mg/mL) to 1.96 mL of PBS (1×) to prepare 2 mL of 0.2 mg/mL DNase working solution.
Add 1 mg of L-cysteine and 100 μL of EDTA to the solution.
Blocking solution
Dissolve 10% normal goat serum, 1% BSA, and 0.01% Tween in PBS (1×). To prepare 500 µL of blocking solution, add 50 µL of normal goat serum, 5 µL of BSA, and 0.5 µL of Tween to 444.5 µL of PBS (1×).
Antibody solution
Dilute primary antibodies in blocking solution:
To prepare 350 μL of 1:200 Anti-Nestin solution, add 1.75 μL of Nestin antibody to 348 μL of blocking solution. Prepare before use.
To prepare 350 μL of 1:100 Sox2 solution, add 3.5 μL of Sox2 antibody to 346.5 μL of blocking solution. Prepare before use.
To prepare 250 μL of 1:250 GFAP solution, add 1 μL of GFAP antibody to 249 μL of blocking solution. Prepare the solution before use.
Antibody Stock concentration Dilution range Final concentration (dilution used for staining) Sox2 200 μg/0.1 mL 1:50–1:500 1:100 Nestin 1.25 μg/mL 1:20–1:200 1:200 GFAP 2.5–5 μg/mL Not available for immunocytochemistry 1:250
Growth medium (culture medium)
DMEM/F12
2% B27 supplement
1% N2 supplement
20 ng/mL bFGF
20 ng/mL EGF
2 μg/mL heparin
1% Penicillin/streptomycin
1% Glutamax
Coating solution (sterile, 0.2 μm filtered)
PLO working solution (20 μg/mL):
Dissolve 2 mL of PLO stock solution (0.1 mg/mL) in 8 mL of PBS (1×) to prepare 10 mL of PLO with the final concentration of 20 μg/mL (store at 4 °C).
Laminin working solution (5 μg/mL)
Dissolve 250 μL of stock solution (1 mg/mL) in 49.75 mL of PBS (1×) to get 50 mL of laminin solution with a final concentration of 5 μg/mL.
Dissection solution
To prepare PBS or HBSS or DMEM/F12 containing 3% Pen/Strep and 1% Amphotericin B: add 0.3 mL of Pen/Strep and 0.1 mL of Amphotericin B to 9.7 mL of PBS (1×).
Ketamine (80 mg/mL) and xylazine (10 mg/mL) working solutions
To prepare 3 mL (concentration of 80 mg/mL) of ketamine working solution:
Add 2.4 mL of ketamine stock solution (100 mg/mL) to 0.6 mL of PBS (1×).
To prepare 3 mL (concentration of 10 mg/mL) of xylazine working solution:
Add 1.5 mL of xylazine stock solution (20 mg/mL) to 1.5 mL of PBS (1×).
PBS (1×)
One tablet of PBS in 500 mL of distilled water used to produce PBS (1×) solution. Then the solution is autoclaved.
Equipment
Laminar hood (Jal Tajhiz, catalog number: 1229)
37 °C incubator shaker (IKA, model: KS 4000i Control)
Centrifuge machine (Hettich Lab Technology, model: Universal 320R)
Hemocytometer (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: Z359629)
CO2 cell culture incubator (Memmert, model: INC108 T2T3)
Inverted fluorescence microscope (Optika, model: XDS-2FL)
Small forceps surgical tools (Fine Science Tools, catalog number: 11050-10)
Stereomicroscope (Olympus, catalog number: 7L19549)
Dissection tools
Large scissors (Fishersci, catalog number: 10633652)
Small scissors (Fishersci, catalog number: 15207266)
Forceps (Fishersci, catalog number: 10098140)
Curved forceps (Fishersci, catalog number:10213941)
Angled forceps (Fishersci, catalog number: 22-079-762)
Spatula (Fishersci, catalog number: 11750229)
Autoclave (Kavoosh, catalog number: 2589224)
Oven (Memert, catalog number: 1-100-800)
Rodent guillotine (DCAP, Germany)
Rongerus (Fine Science Tools, catalog number: 16004-16)
Software
Infinity software (version 4.6)
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2023 The Author(s); This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/).
如何引用
Afhami, M., Behnam-Rassouli, M., Gorji, A., Karima, S. and Shahpasand, K. (2023). Isolation and Culture of Neural Stem/Progenitor Cells from the Hippocampal Dentate Gyrus of Young Adult and Aged Rats. Bio-protocol 13(19): e4843. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4843.
分类
神经科学 > 细胞机理 > 细胞分离和培养
细胞生物学 > 细胞分离和培养 > 单层培养
干细胞 > 成体干细胞 > 神经干细胞
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link